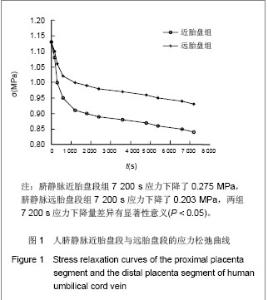
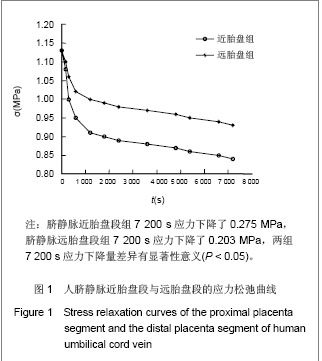
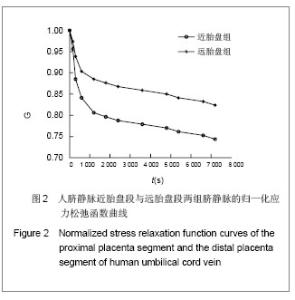
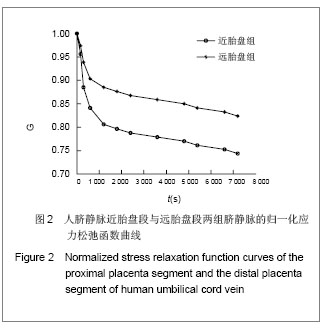
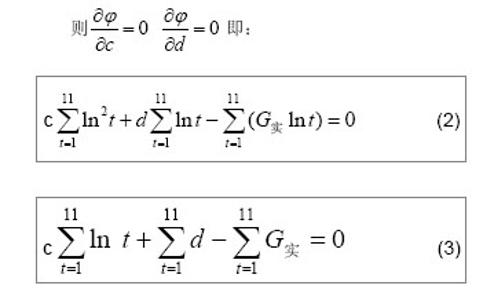
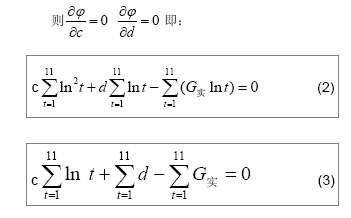| [1]Jeschke MG,Hermanutz V,Wolf SE,et al.Polyurethane vascular prostheses decreases neointimal formation compared with expanded polytetrafluoroethylene. J Vasc Surg.1999;29(1): 168-176.[2]Zhang QQ,Zhang LH,Ma DR,et al.Jichu Yixue yu Linchuang. 2001;21(6): 482-487.张其清,张立海,马东瑞,等. 组织工程及其支架研究进展和面临的问题及展望[J].基础医学与临床,2001,21(6): 482-487.[3]Wang Y,Wang BH,Chen LD,et al. Jichu Yixue yu Linchuang. 2004;24(1):60-64.王韵,汪炳华,陈丽达,等.花生四烯酸诱导人脐静脉内皮细胞氧化损伤和凋亡[J]. 基础医学与临床,2004,24(1):60-64.[4]Dardik I,Darkik H.Vascular hetergraft:human umbilical cord vein as an aortic substitute in baboon.A porliminary report. J Med Primatal.1973;2(5): 269-274.[5]Seye CI,Kong Q,Yu N,et al. P2 receptors in atherosclerosis and postangioplasty restenosis Purinergic Signal.2007;3 (1-2): 153-162.[6]Amisten S,Melander O,Wihlborg AK,et al. Increased risk of acute myocardial infarction and elevated levels of C-reactive protein in carriers of the Thr-87 variant of the ATP receptor P2Y11.Eur Heart J.2007;28 (1): 13-18.[7]Zhang WJ,Wei H,Hagen T,et al.α-Lipoic acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory responses by activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway.PNAS.2007; 3 (10): 4077-4082.[8]Weisman G,Yu N,Agca C,et al.The P2Y2 Nucleotide Receptor Contributes To Intimal Lesion Growth And Regulates Lymphotoxin- {alpha} Secretion. Circulation.2008;118: S571.[9]Stokes L,Surprenant A. Purinergic P2Y2 receptors induce increased MCP-1/CCL2 synthesis and release from rat alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol.2007;179(6): 16-23.[10]Li WC,Zhang YF,Wang J,et al. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2005;9(26):270-272.李文春,张一飞,王军,等.增龄变化对血管移植材料脐带静脉顺应性的影响[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(26):270-272.[11]Xiao ZL,Yang M,Chen MF,et al.Zhongguo Dongmai Yinghua Zazhi. 2010;18(7):532-538.肖智林,杨梅,陈美芳,等.ATP对人脐静脉内皮细胞增殖的抑制作用及其可能机制[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2010,18(7):532-538.[12]Li WC,Zhang HM,Yu MH,et al. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2005;8(23):4880-4885.李文春,张红梅,余明华,等.血管移植中不同段脐带静脉的生物力学特性研究[J].中国临床康复,2005,8(23):4880-4885.[13]Sun WQ,Li WC,Wang HQ.Yiyong Shengwu Lixue. 2001;16(4): 222-230.孙万群,李文春,王汉琴.胎儿脐带静脉生物力学特性的研究[J].医用生物力学,2001,16(4):222-230.[14]Yu B,Feng TJ,Ma HS.Yixue Yanjiu. 2010;39(7):88-90.于波,冯铁键,马洪顺.实验大鼠动脉粥样硬化模型升主动脉力学特性研究[J].医学研究,2010,39(7):88-90.[15]Ma HS,Lu Y,Wang XC.Zhongguo Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng Xuebao. 2003;22(4):364-369.马洪顺,陆有,王晓晨.骨质疏松对骨生物力学性质影响实验研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2003,22(4):364-369.[16]He XJ,Zhang XH,Wang PJ,et al.Zhongguo Linchuang Jiepouxue Zazhi. 2007;25(1):74-76.贺细菊,张兴华,王配军,等. 门静脉高压症猪门静脉的生物力学特性及其临床意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2007,25(1):74-76.[17]Camopbell GR,Campbell JH,Manderson JA,et al. Arterial smooth muscle. A multifunctional mesenchymal cell.Arch Pathol Lab Med.1988;112(10): 977-986.[18]Victor H,Frankel Margareta Nordin.肌肉骨骼系统基础生物力学[M].戴克戎,王以进,周健男,等译,上海:学林出版社,1985:89.[19]Li WC,Wang J,Tang J,et al. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2005;9(30):216-218.李文春,王军,唐杰,等.脐带静脉组织结构的定量分析评估其替代小动脉移植材料的可行性[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(30): 216-218.[20]Li WC,Zhang XH,Zhou XH,et al.Jichu Yixue yu Linchuang. 2004;24(6):637-640.李文春,张兴华,周新华,等.人脐静脉组织构筑及其临床应用价值[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2004,24(6):637-640.[21]Wang PJ,Li WC,Tang J,et al.Yiyong Shengwu Lixue. 2003;18 (4):218-221.王配军, 李文春, 唐杰,等.猪肝门静脉生物力学特性的增龄性变化[J]. 医用生物力学,2003,18 (4):218-221.[22]Chu HJ,Teng ZZ,Ji GY,et al.Lixue Jikan. 2006;27(1):60-68.褚红军,滕忠照,纪广玉,等.外支架对移植静脉力学特性的影响[J].力学季刊, 2006,27(1):60-68. |