Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (21): 3382-3389.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3871
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research and application of biological three-dimensional printing technology in the field of precision medicine: analysis of Chinese and English literature
Pan Xuan1, Zhao Meng2, Zhang Xiumei2, 3, Zhao Jie4, Zhai Yunkai5
- 1Institutes of Science and Development, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China; 2Wanfang Data Co., Ltd., Beijing 100036, China; 3Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China, Beijing 100036, China; 4The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China; 5School of Management Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2020-10-14Revised:2020-10-15Accepted:2020-11-21Online:2021-07-28Published:2021-01-23 -
Contact:Zhang Xiumei, MD, Researcher, Wanfang Data Co., Ltd., Beijing 100036, China; Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China, Beijing 100036, China -
About author:Pan Xuan, PhD, Assistant researcher, Institutes of Science and Development, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China -
Supported by:the Key Special Project of National Key Research and Development Program “Precision Medicine Research”, No. 2017YFC0909900 (to ZJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Pan Xuan, Zhao Meng, Zhang Xiumei, Zhao Jie, Zhai Yunkai. Research and application of biological three-dimensional printing technology in the field of precision medicine: analysis of Chinese and English literature[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3382-3389.
share this article
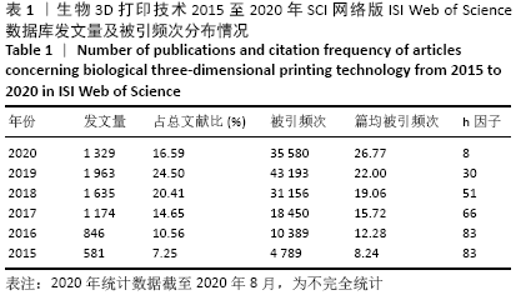
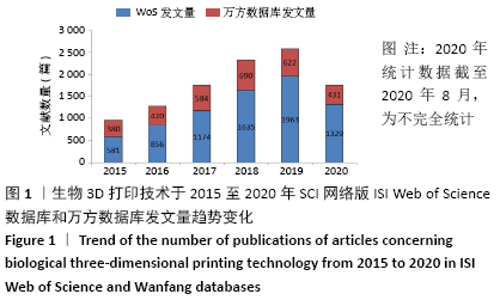
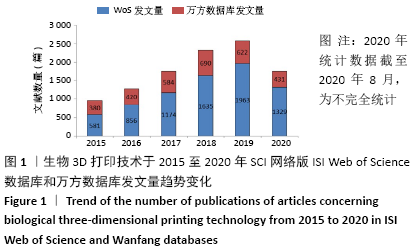
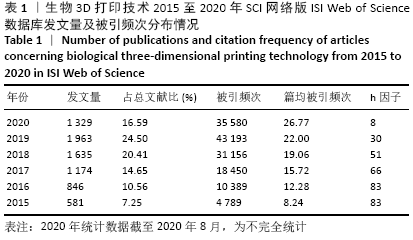
2.1 检索结果 最终万方数据库检索到3 111篇中文文献,ISI Web of Science数据库检索到6 941篇英文文献。按照文献类型分类,中文文献分别有期刊论文2 852篇、会议论文259篇,而英文文献分别有期刊论文5 207篇、综述792篇、会议摘要616篇、论文集829篇、观点材料188篇、图书节选152篇,其中,该领域的期刊论文和研究综述占全部英文文献的86.4%。 2.2 文献量发表年份分布及趋势变化 表1可见,相关研究在2016年发文量快速增长至846篇,是2015年的1.5倍,这与《Bioprinting》《International Journal of Bioprinting》等生物3D打印专业学术期刊在这一年陆续出现有关,也意味着该领域的相关研究持续升温且具有广阔的应用前景。此外,发文量的快速增长趋势一直持续(2020年统计数据截至2020年8月,为不完全统计),被引频次和篇均被引频次自2015年以来一直保持较高的增长速率,反映出该领域仍是目前科研热点领域,且存在较多的高质量论文。另外,能较准确反映学术成就的h因子自2015年起保持较高水平,2015年和2016年h因子为83,达到峰值,说明这2年发表的生物3D打印技术相关论文具有较高影响力。"
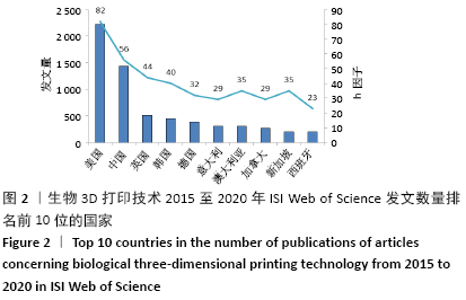
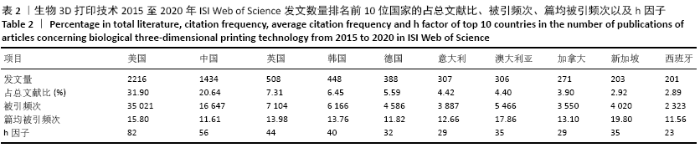
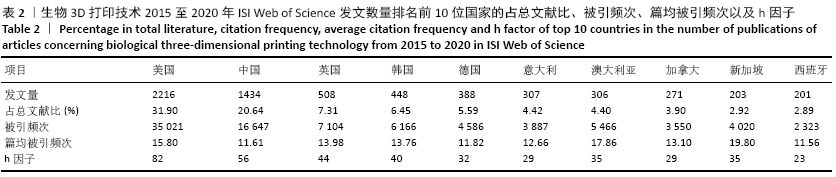
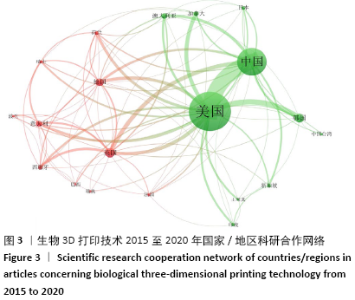
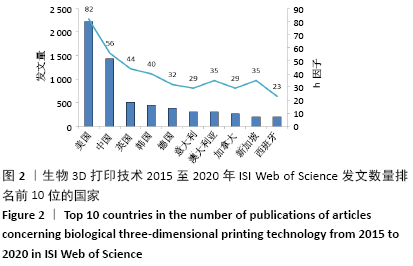
2.3 文献发表国家和地区 由发文量和被引频次分析可知,近5年来生物3D打印技术相关研究出现爆发式增长,对2015至2020年文献发表国家和地区分布进行统计和分析,发现共有53个国家/地区发表了相关论文。其中美国位居全球第1位,发表文献数量为35 021篇;中国以16 647篇的发文量位居第2位,h因子为56也位居第2位,这反映出中国科研人员在这一领域取得了具有一定影响力的学术成就,但篇均被引频次不高仅排名第9位,说明整体研究水平和文章质量还有待提高;英国和韩国分别发文508和448篇,篇均被引频次和h因子也都比较高,说明这2个国家在该领域的科技研究较活跃,学术研究水平较高。尽管澳大利亚和新加坡近5年的文献发表数量排名分别为第7和9名,但其篇均被引频次和h因子都排名靠前,说明这2个国家产出论文的影响力大,科学成就较高,见图2和表2。 "
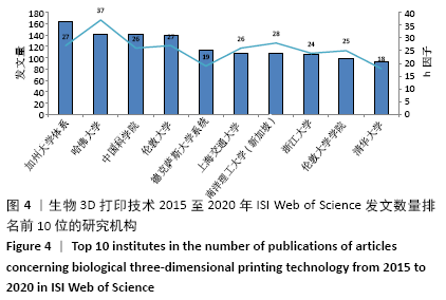
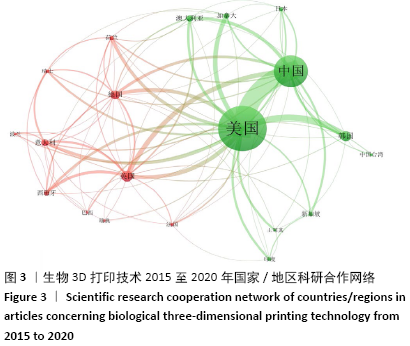
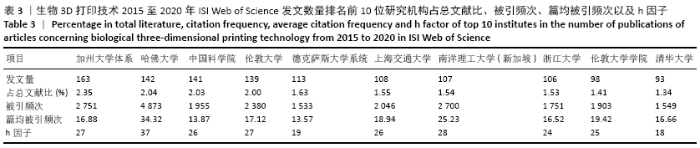
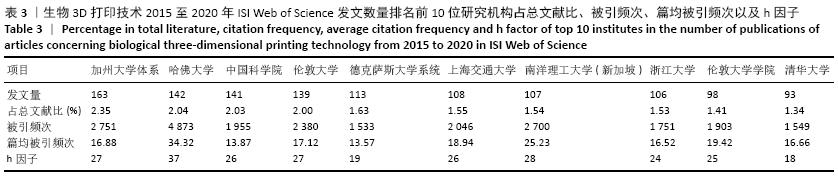
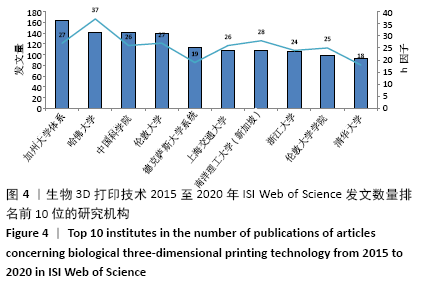
2.4 研究机构 图4和表3可见,近5年全球发表论文最多的研究机构是美国加州大学体系(University of California System),共发表163篇论文;哈佛大学(Harvard University)虽然以发文量142篇位居第2位,但是其被引频次、篇均被引频次、h因子均位居第1位,且具有明显优势,说明其在全球生物3D打印领域中处于引领地位,在相关研究机构中具有最高的研究水平和最大的影响力。中国科学院、上海交通大学、浙江大学和清华大学这4家机构也是发文量居前10名的研究机构,这使得中国成为拥有发文量前10名的研究机构最多的国家,说明近5年来中国科研机构和大学在生物3D打印应用于精准医学领域的研究水平发展较快。新加坡南洋理工大学的发文量虽然排在第7位,但其篇均被引频次和h因子均位居第2位,这反映出其具有较高论文质量和学术成就。根据万方数据库发文量显示,近5年中国发文数量排名前5位的高校/研究机构分别是上海交通大学(96篇)、南方医科大学(42篇)、北京大学第三医院(38篇)、西安交通大学(35篇)、解放军总医院和第四军医大学(均各为30篇)。 基于ISI Web of Science英文文献数据检索结果,利用VOSviewer工具分析得到大学/研究机构在生物3D打印领域的合作网络。图5显示在全球范围,美国加州大学体系(University of California System)展现出最广泛的合作互动,其合作比较紧密大学主要包括伦敦大学学院、哈佛大学、浙江大学、四川大学等;其次,哈佛大学与麻省理工学院以及韩国建国大学也保持着密切的合作;中国科学院、浙江大学、上海交通大学与国内外多所大学和研究机构也保持着广泛而紧密的合作关系。不难发现,近5年来这些在全球范围具有广泛合作性的大学和研究机构其中大多数发文数量也位居前列,可见在生物3D打印领域加强科研人员的国际学术交流与合作有助于提高学术产出。 "

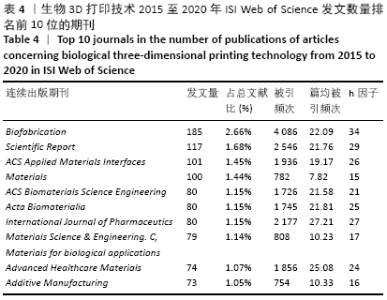
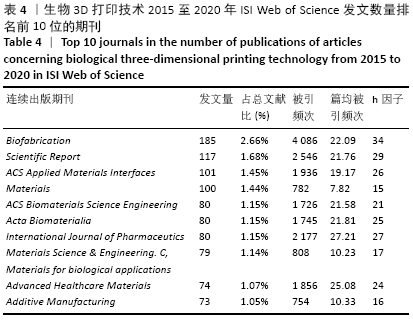
创刊于2016年的《Biofabrication》是发表论文最多的期刊,其发文量达185篇,其被引频次和h因子均位居第1位,仅4年时间就成为相关领域最具影响力的期刊,也反映出近年来生物3D打印技术引起了科技界的高度关注。其中,《International Journal of Pharmaceutics》尽管近5年发文量仅为80篇,但其篇均被引频次位居第1位,被引频次和h因子均位居第3位,说明该期刊的发文质量和影响力具有较高水平,且生物3D打印技术在制药、药剂学方面具有应用前景。 万方数据库检索结果中显示近5年发文数量排名前5位的期刊分别是《中国组织工程研究》132篇、《中华创伤骨科杂志》52篇、《中国骨与关节损伤杂志》46篇、《中国修复重建外科杂志》39篇、《中国矫形外科杂志》33篇。 2.6 高频关键词分布 通过提取ISI Web of Science英文文献检索结果中的关键词,并进行大数据分析和统计后对其中的高频关键词进行可视化展现,可以得出在全球范围生物3D打印技术在精准医学中的研究热点主要包括生物墨水、微流控、矫形外科、组织/器官再生、药物研发等,见图6。 "

| [1] NGO TD, KASHANI A, IMBALZANO G, et al. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos B Eng. 2018;143:172-196. [2] MARTIN JH, YAHATA BD, HUNDLEY JM, et al. 3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys. Nature. 2017;549(7672):365-369. [3] LIGON SC, LISKA R, STAMPFL J, et al. Polymers for 3D Printing and Customized Additive Manufacturing. Chem Rev. 2017;117(15): 10212-10290. [4] ZAREK M, LAYANI M, COOPERSTEIN I, et al. 3D Printing of Shape Memory Polymers for Flexible Electronic Devices. Adv Mater. 2016; 28(22):4449-4454. [5] WAHEED S, CABOT JM, MACDONALD NP, et al. 3D printed microfluidic devices: enablers and barriers. Lab Chip. 2016;16(11):1993-2013. [6] LEE JY, AN J, CHUA CK. Fundamentals and applications of 3D printing for novel materials. Applied Materials Today. 2017;7:120-133. [7] CHIMENE D, LENNOX KK, KAUNAS RR, et al. Advanced Bioinks for 3D Printing: A Materials Science Perspective. Ann Biomed Eng. 2016;44(6): 2090-2102. [8] VADODARIA S, MILLS T. Jetting-based 3D printing of edible materials. Food Hydrocolloids. 2020;106:105857. [9] WELCH JL, XIANG J, MACKIN SR, et al. Inactivation of Severe Acute Respiratory Coronavirus Virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Diverse RNA and DNA Viruses on Three-Dimensionally Printed Surgical Mask Materials. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2020. doi:10.1017/ice.2020.417. [10] KOTZ F, HELMER D, RAPP BE. Emerging Technologies and Materials for High-Resolution 3D Printing of Microfluidic Chips. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2020. doi: 10.1007/10_2020_141. [11] ZHANG Y, ZHANG F, YAN Z, et al. Printing, folding and assembly methods for forming 3D mesostructures in advanced materials. Nat Rev Mater. 2017;2(4):17019. [12] HE R, LIU W, WU Z, et al. Fabrication of complex-shaped zirconia ceramic parts via a DLP- stereolithography-based 3D printing method. Ceram Int. 2018;44(3):3412-3416. [13] BAGHERI SAED A, BEHRAVESH AH, HASANNIA S, et al. Functionalized poly l-lactic acid synthesis and optimization of process parameters for 3D printing of porous scaffolds via digital light processing (DLP) method. J Manuf Process. 2020;56:550-561. [14] 张秀梅,翟运开,丁楠,等.精准医学决策支持知识组织研究[J].医学信息学杂志,2020,41(5):24-29,48. [15] 赵晓宇,刁天喜,高云华,等.美国“精准医学计划”解读与思考[J].军事医学,2015(4):241-244. [16] SAUNDERS RE, DERBY B. Inkjet printing biomaterials for tissue engineering: bioprinting. Inter Mater Rev. 2014;59(8):430-448. [17] HEINRICH MA, LIU W, JIMENEZ A, et al. 3D Bioprinting: from Benches to Translational Applications. Small. 2019;15(23):e1805510. [18] WU C, WANG B, ZHANG C, et al. Bioprinting: an assessment based on manufacturing readiness levels. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2017;37(3): 333-354. [19] JAMRÓZ W, SZAFRANIEC J, KUREK M, et al. 3D Printing in Pharmaceutical and Medical Applications - Recent Achievements and Challenges. Pharm Res. 2018;35(9):176. [20] CUI H, NOWICKI M, FISHER JP, et al. 3D Bioprinting for Organ Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(1):10.1002/adhm.201601118. [21] BIAZAR E, NAJAFI SM, HEIDARI KS, et al. 3D bio-printing technology for body tissues and organs regeneration. J Med Eng Technol. 2018;42(3): 187-202. [22] AIMAR A, PALERMO A, INNOCENTI B. The Role of 3D Printing in Medical Applications: A State of the Art. J Healthc Eng. 2019;2019:5340616. [23] HOSPODIUK M, DEY M, SOSNOSKI D, et al. The bioink: A comprehensive review on bioprintable materials. Biotechnol Adv. 2017;35(2):217-239. [24] HÖLZL K, LIN S, TYTGAT L, et al. Bioink properties before, during and after 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication. 2016;8(3):032002. [25] RASTOGI P, KANDASUBRAMANIAN B. Review of alginate-based hydrogel bioprinting for application in tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2019; 11(4):042001. [26] VALOT L, MARTINEZ J, MEHDI A, et al. Chemical insights into bioinks for 3D printing. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(15):4049-4086. [27] ARRIGONI C, GILARDI M, BERSINI S, et al. Bioprinting and Organ-on-Chip Applications Towards Personalized Medicine for Bone Diseases. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017;13(3):407-417. [28] GOLD K, GAHARWAR AK, JAIN A. Emerging trends in multiscale modeling of vascular pathophysiology: Organ-on-a-chip and 3D printing. Biomaterials. 2019;196:2-17. [29] YU F, CHOUDHURY D. Microfluidic bioprinting for organ-on-a-chip models. Drug Discov Today. 2019;24(6):1248-1257. [30] MI S, DU Z, XU Y, et al. The crossing and integration between microfluidic technology and 3D printing for organ-on-chips. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(39):6191-6206. [31] BHATTACHARJEE N, URRIOS A, KANG S, et al. The upcoming 3D-printing revolution in microfluidics. Lab Chip. 2016;16(10):1720-1742. [32] RADHAKRISHNAN J, VARADARAJ S, DASH SK, et al. Organotypic cancer tissue models for drug screening: 3D constructs, bioprinting and microfluidic chips. Drug Discov Today. 2020;25(5):879-890. [33] RICHARD C, NEILD A, CADARSO VJ. The emerging role of microfluidics in multi-material 3D bioprinting. Lab Chip. 2020;20(12):2044-2056. [34] SANTANA HS, PALMA MSA, LOPES MGM, et al. Microfluidic Devices and 3D Printing for Synthesis and Screening of Drugs and Tissue Engineering. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2020;59(9):3794-3810. [35] SKELLEY NW, HAGERTY MP, STANNARD JT, et al. Sterility of 3D-Printed Orthopedic Implants Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Orthopedics. 2020;43(1):46-51. [36] FRIZZIERO L, LIVERANI A, DONNICI G, et al. New Methodology for Diagnosis of Orthopedic Diseases through Additive Manufacturing Models. Symmetry. 2019;11(4):27. [37] DONG XP, ZHANG YW, PEI YJ, et al. Three-dimensional printing for the accurate orthopedics: clinical cases analysis. Biodes Manuf. 2020;3(2): 122-132. [38] BRUNS N, KRETTEK C. 3D-printing in trauma surgery : Planning, printing and processing. Unfallchirurg. 2019;122(4):270-277. [39] ALLEN B, MOORE C, SEYLER T, et al. Modulating antibiotic release from reservoirs in 3D-printed orthopedic devices to treat periprosthetic joint infection. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(10):2239-2249. [40] HAN C, YAO Y, CHENG X, et al. Electrophoretic Deposition of Gentamicin-Loaded Silk Fibroin Coatings on 3D-Printed Porous Cobalt-Chromium-Molybdenum Bone Substitutes to Prevent Orthopedic Implant Infections. Biomacromolecules. 2017;18(11):3776-3787. [41] VIJAYAVENKATARAMAN S, GOPINATH A, LU WF. A new design of 3D-printed orthopedic bone plates with auxetic structures to mitigate stress shielding and improve intra-operative bending. Biodes Manuf. 2020;3(2):98-108. [42] 朱浩,郑孟杰,李延超,等.3D打印技术在颧上颌复合体骨折治疗中应用[J].创伤与急危重病医学,2020,8(5):335-337. [43] 凌昊楠,李松军.3D打印复合支架修复软骨缺损的研究进展[J].医学综述,2020,26(18):3572-3576,3582. [44] 李焕龙,耿承奎,陈帅,等.3D打印技术在骨盆手术中的应用[J].实用医学杂志,2020,36(17):2329-2333. [45] 唐保明,李钊伟,杨爱荣,等.3D打印技术辅助治疗复杂髋臼骨折的疗效研究[J].中国医学装备,2020,17(9):107-110. [46] 刘婷,杨德雨,刘莉,等.3D打印技术在脑血管病中的应用进展[J].中国卒中杂志,2020,15(8):916-920. [47] CHEN H, HAN Q, WANG C, et al. Porous Scaffold Design for Additive Manufacturing in Orthopedics: A Review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:609. [48] BARTOLOMEU F, DOURADO N, PEREIRA F, et al. Additive manufactured porous biomaterials targeting orthopedic implants: A suitable combination of mechanical, physical and topological properties. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;107:110342. [49] GAO CH, WANG CY, JIN H, et al. Additive manufacturing technique-designed metallic porous implants for clinical application in orthopedics. RSC Adv. 2018;8(44):25210-25227. [50] HAN X, YANG D, YANG C, et al. Carbon Fiber Reinforced PEEK Composites Based on 3D-Printing Technology for Orthopedic and Dental Applications. J Clin Med. 2019;8(2):240. [51] BOSE S, BANERJEE D, SHIVARAM A, et al. Calcium phosphate coated 3D printed porous titanium with nanoscale surface modification for orthopedic and dental applications. Mater Des. 2018;151:102-112. [52] NARITA M, TAKAKI T, SHIBAHARA T, et aI. Utilization of desktop 3D printer-fabricated “Cost-Effective” 3D models in orthognathic surgery. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;42(1):24. [53] LOUVRIER A, MARTY P, BARRABÉ A, et al. How useful is 3D printing in maxillofacial surgery?. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;118(4):206-212. [54] DATTA P, AYAN B, OZBOLAT IT. Bioprinting for vascular and vascularized tissue biofabrication. Acta Biomater. 2017;51:1-20. [55] MONDSCHEIN RJ, KANITKAR A, WILLIAMS CB, et al. Polymer structure-property requirements for stereolithographic 3D printing of soft tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2017;140:170-188. [56] ALI M, P R AK, LEE SJ, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinting for organ bioengineering: promise and pitfalls. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2018;23(6):649-656. [57] WU Y, RAVNIC DJ, OZBOLAT IT. Intraoperative Bioprinting: Repairing Tissues and Organs in a Surgical Setting. Trends Biotechnol. 2020; 38(6):594-605. [58] ESWARAMOORTHY SD, RAMAKRISHNA S, RATH SN. Recent advances in three-dimensional bioprinting of stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(6):908-924. [59] LEI M, WANG X. Biodegradable Polymers and Stem Cells for Bioprinting. Molecules. 2016;21(5):539. [60] AXPE E, OYEN ML. Applications of Alginate-Based Bioinks in 3D Bioprinting. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):1976. [61] SHANJANI Y, KANG Y, ZARNESCU L, et al. Endothelial pattern formation in hybrid constructs of additive manufactured porous rigid scaffolds and cell-laden hydrogels for orthopedic applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;65:356-372. [62] VITHANI K, GOYANES A, JANNIN V, et al. An Overview of 3D Printing Technologies for Soft Materials and Potential Opportunities for Lipid-based Drug Delivery Systems. Pharm Res. 2018;36(1):4. [63] TRENFIELD SJ, AWAD A, MADLA CM, et al. Shaping the future: recent advances of 3D printing in drug delivery and healthcare. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019;16(10):1081-1094. [64] MAZZOCCHI A, SOKER S, SKARDAL A. 3D bioprinting for high-throughput screening: Drug screening, disease modeling, and precision medicine applications. Applied Physics Reviews. 2019;6(1):011302. [65] AFSANA, JAIN V, HAIDER N, et al. 3D Printing in Personalized Drug Delivery. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(42):5062-5071. [66] GOOLE J, AMIGHI K. 3D printing in pharmaceutics: A new tool for designing customized drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm. 2016;499(1-2): 376-394. [67] YAN WC, DAVOODI P, VIJAYAVENKATARAMAN S, et al. 3D bioprinting of skin tissue: From pre-processing to final product evaluation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;132:270-295. [68] MA X, LIU J, ZHU W, et al. 3D bioprinting of functional tissue models for personalized drug screening and in vitro disease modeling. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;132:235-251. [69] 赵莹莹.3D打印技术在药物发展中的应用[J].河南科技,2020,(17): 70-71. [70] 孙冲,刘堂义.3D打印技术在医学中的应用[J].中医学,2019,8(3): 197-202. [71] 陈绍华,徐浩,王拥军,等.3D生物打印药物筛选生理病理模型平台建立的研究进展[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2019,21(9): 1902-1908. [72] 石靖,王增明,郑爱萍.3D打印技术在药物制剂中的应用和挑战[J].药学进展,2019,43(3):164-173. [73] 马薇.3D打印技术在药物制剂中的研究进展[J].今日药学,2018, 28(3):204-206. [74] 陈国宁,舒花,余佩,等.3D打印技术在药学领域研究中的应用[J].中国药学杂志,2016,51(16):1353-1359. [75] 王雪,张灿,平其能.3D打印技术在药物高端制剂中的研究进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2016,47(2):140-147. |
| [1] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [2] | Wang Mengting, Gu Yanping, Ren Wenbo, Qin Qian, Bai Bingyi, Liao Yuanpeng. Research hotspots of blood flow restriction training for dyskinesia based on visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1264-1269. |
| [3] | Xu Junma, Yu Yuechao, Liu Zhi, Liu Yu, Wang Feitong. Application of 3D-printed coplanar template combined with fixed needle technique in percutaneous accurate biopsy of small pulmonary nodules [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 761-764. |
| [4] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Fan Yinuo, Guan Zhiying, Li Weifeng, Chen Lixin, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Research status and development trend of bibliometrics and visualization analysis in the assessment of femoroacetabular impingement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 414-419. |
| [7] | Ren Wenbo, Liao Yuanpeng. Visualization analysis of traumatic osteoarthritis research hotspots and content based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3374-3381. |
| [8] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Buyang Huanwu Decoction in prevention of deep venous thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3267-3274. |
| [9] | Zhang Kai, Zhang Xiaobo, Shi Jintao, Wang Keping, Zhou Haiyu. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: a bibliometric and visualization analysis based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3031-3038. |
| [10] | Zhong Yuanming, Fu Xiaopeng, Xu Wei, Zhao Qingrui, Huang Yong, Ye Weiquan. Nicardipine controlled hypotension applied to perioperative blood loss in orthopedics: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2930-2937. |
| [11] | Huang Na, Liu Jiayue, Huang Yingjie, Wen Junmao, Wang Haibin, Zhang Qingwen, Zhou Chi . Bibliometric and visualized analysis of research on osteonecrosis of the femoral head from the Web of Science in the last 5 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2711-2718. |
| [12] | Xie Jian, Su Jiansheng. Advantages and characteristics of electrospun aligned nanofibers as scaffolds for tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2575-2581. |
| [13] | Bi Haoran, Luo Yaxin, Chen Xiaoxu, Yang Kun. Characteristics and effects of cell-scaffold composite for periodontal soft tissue augmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2582-2588. |
| [14] | Fan Qingtao, Du Yun, Zhou Lei . Analysis of development trends of global three-dimensional bio-printing technology based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1891-1897. |
| [15] | Zhou Chen, Xing Wenhua. Application advantages of three-dimensional printing technology and finite element analysis in scoliosis correction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1898-1903. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||