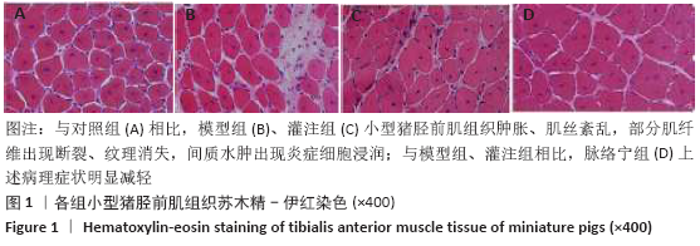
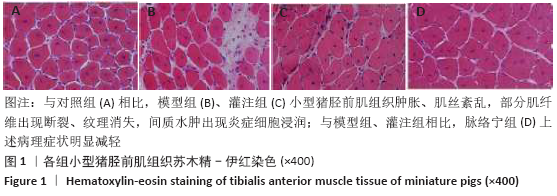
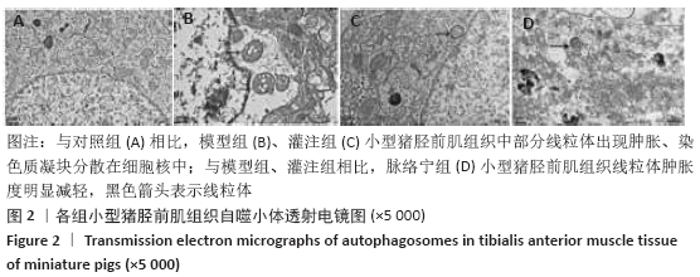
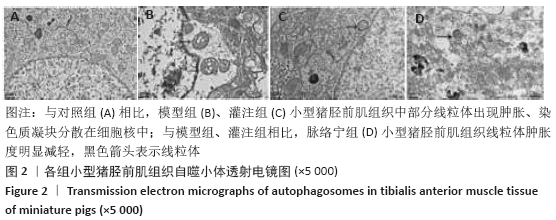
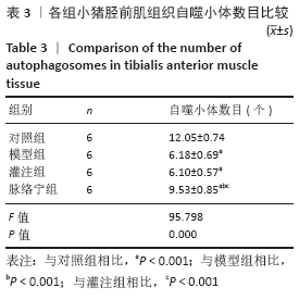
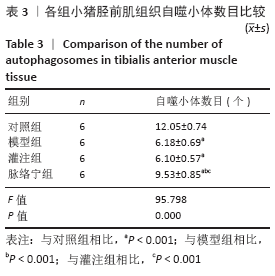
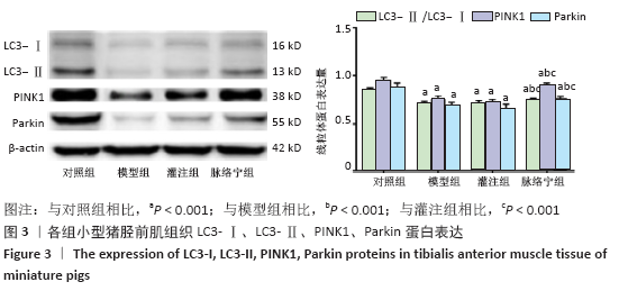
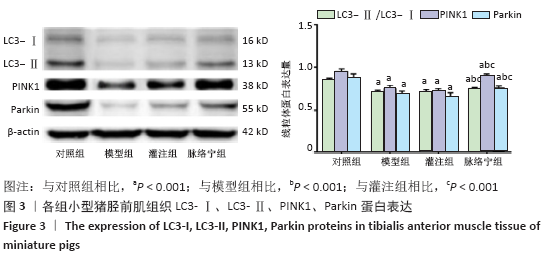
[1] TEKŞEN Y, KADIOĞLU E, KOÇAK C, et al. Effect of Hydrogen Sulfide on Kidney Injury in Rat Model of Crush Syndrome. J Surg Res. 2019;235: 470-478.
[2] ZHOU J, BAI Y, JIANG Y, et al. Immunomodulatory role of recombinant human erythropoietin in acute kidney injury induced by crush syndrome via inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in macrophages. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2020;42(1):37-47.
[3] 孙震,张启福,王涛,等.挤压综合征家兔模型不同挤压时间后心、肾功能与病理观察[J].广东医学,2018,39(1):36-39.
[4] KOBAYASHI J, MURATA I. Nitrite as a pharmacological intervention for the successful treatment of crush syndrome. Physiol Rep. 2018;6(5): e13633.
[5] 任华建,胡琼源,任建安.线粒体DNA损伤在缺血再灌注中的研究进展[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(4):786-789.
[6] 林杰,曾仲.线粒体途径在肝脏缺血再灌注损伤中的作用的研究进展[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2020,26(1):69-72.
[7] 于亮,赵泽铭,赵斌婷,等.BNIP3介导骨骼肌线粒体自噬:不同强度运动的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(5):682-688.
[8] 黄健,林冬静,田洪艳,等. Pink1/Parkin介导线粒体融合发生线粒体自噬的研究进展[J].解剖学杂志,2019,42(1):77-80.
[9] 崔昌胜,庄宝祥,吴洪娟,等.脉络宁注射液对兔肢体缺血/再灌注损伤TNF-α 和NF-κB的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2019, 35(2): 295-296.
[10] 王雷,聂鑫,尹叶锋,等.体外循环灌注系统下应用脉络宁治疗下肢挤压伤-挤压综合征模型猪[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(11): 1723-1729.
[11] 邹圣强,潘鑫,魏超,等.大鼠下肢挤压伤模型不同挤压时间的生化指标观察[J].中华灾害救援医学,2015,3(2):72-75.
[12] STRAUSS MB. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen in crush injuries and skeletal muscle-compartment syndromes. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2012;39(4):847-855.
[13] ACAR D, GÜLPEMBE M, YILDIZ CG, et al. The reno-protective effects of atorvastatin in crush syndrome and rhabdomyolysis:is there a dilemma? Turk J Med Sci. 2017;47(6):1920-1924.
[14] YANG XY, SONG J, HOU SK, et al. Ulinastatin ameliorates acute kidney injury induced by crush syndrome inflammation by modulating Th17/Treg cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;81:106265.
[15] CAI HA, TAO X, ZHENG LJ, et al. Ozone alleviates ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting mitochondrion-mediated apoptosis pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(4):975-984.
[16] WANG Q, XU J, LI X, et al. Sirt3 modulate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through enhancing mitochondrial fusion and activating the ERK-OPA1 signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):23495-23506.
[17] BOWLING JL, SKOLFIELD MC, RILEY WA, et al. Temporal integration of mitochondrial stress signals by the PINK1:Parkin pathway. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(1):33-45.
[18] LIU XW, LU MK, ZHONG HT, et al. Panax Notoginseng Saponins Attenuate Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through the HIF-1α/BNIP3 Pathway of Autophagy. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2019;73(2):92-99.
[19] 梁丹阳,戴汉川.PINK1/Parkin通路在线粒体自噬氧化损伤中的作用[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2018,40(1):116-123.
[20] 郎秀娟,王燕. PIN K1/parkin通路调控线粒体自噬机制的研究进展[J].微生物与感染,2018,13(2):102-106.
[21] 解晓帅,董运茁,潘筱琳,等.脉络宁注射液与复方丹参注射液治疗缺血性脑卒中的成本-效果分析[J].中国药房,2018,29(21): 2962-2965.
[22] 尹文伟,陈思,裴璐,等.脉络宁注射液辅助治疗急性脑梗死的临床观察[J].中国药房,2017,28(20):2834-2837.
[23] 张院军.脉络宁注射液联合前列地尔治疗冠心病合并高血压的疗效及对心功能的影响[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2019, 6(78):36.
[24] 梅高昌,李元海.生脉注射液预先给药对膝关节置换下肢骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤的保护[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(53): 7917-7924.
[25] 庞晓斌,谢欣梅,王海燕,等.脉络宁对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用及其机制研究[J].中国中药杂志,2014,39(4):721-725.
[26] 刘德敏,贾宏宇,柴文静,等.自噬与氧化应激在心血管疾病中的研究进展[J].临床心血管病杂志, 2018,34(4):402-407.
[27] LI Y, CHEN B, YANG X, et al. S100a8/a9 Signaling Causes Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Cardiomyocyte Death in Response to Ischemic/Reperfusion Injury. Circulation. 2019;140(9):751-764.
[28] 温建麟,黄锋,曾志羽.线粒体自噬在心肌缺血再灌注损伤中作用的研究进展[J].山东医药,2018,58(17):84-86.
[29] 尚画雨,张荷,夏志,等. PINK1/Parkin介导的线粒体自噬在运动性骨骼肌损伤中的作用[J].上海体育学院学报,2018,42(3):103-110.
[30] 叶亮,袁淼,肖文峰.脑损伤模型大鼠Pink1/Parkin介导的线粒体自噬作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(11):1695-1700. |