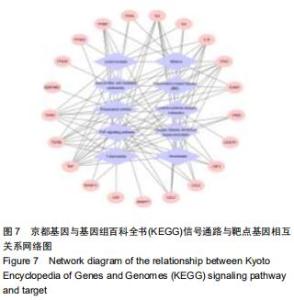
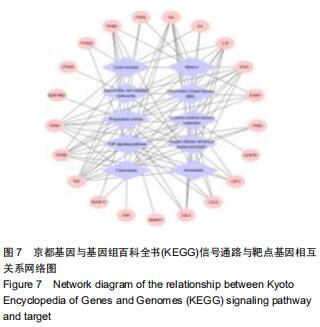
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (36): 5843-5849.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2906
Previous Articles Next Articles
Action mechanism of Wuwei Xiaodu Yin in the treatment of periprosthetic joint infection based on network pharmacology
Zhang Haitao1, Xin Pengfei1, Feng Wenjun2, Cao Houran1, Chen Jinlun2, Deng Peng2, Jie Ke1, Ge Yingjie1, Peng Xinyu1, Li Jie2, Zeng Jianchun2, Zeng Yirong2
- 1First Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Three Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-02-10Revised:2020-02-14Accepted:2020-03-18Online:2020-12-28Published:2020-10-27 -
Contact:Zeng Yirong, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Three Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Haitao, Master candidate, First Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Haitao, Xin Pengfei, Feng Wenjun, Cao Houran, Chen Jinlun, Deng Peng, Jie Ke, Ge Yingjie, Peng Xinyu, Li Jie, Zeng Jianchun, Zeng Yirong. Action mechanism of Wuwei Xiaodu Yin in the treatment of periprosthetic joint infection based on network pharmacology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(36): 5843-5849.
share this article
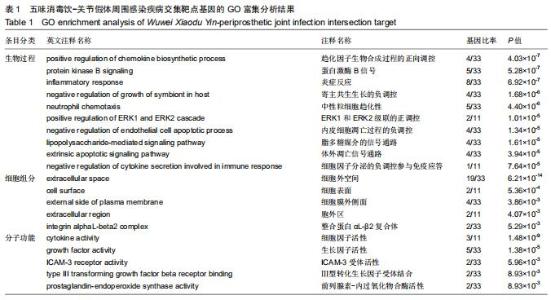
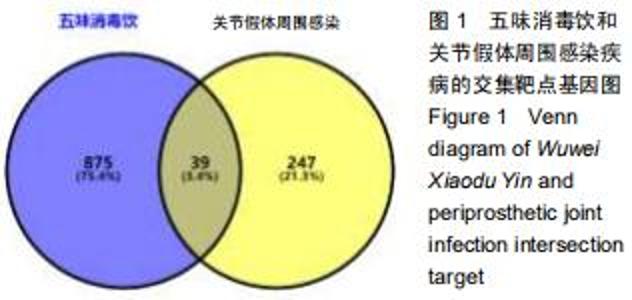
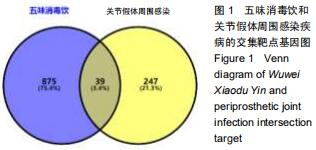
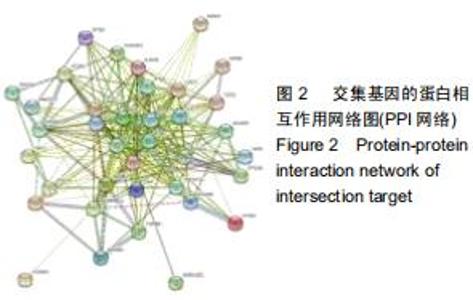
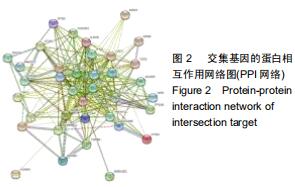
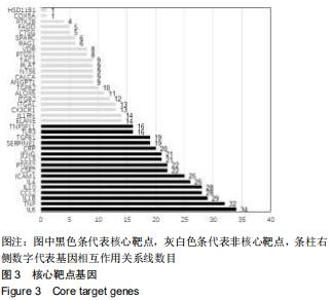
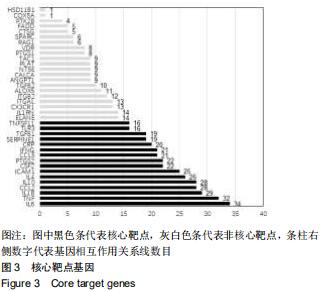
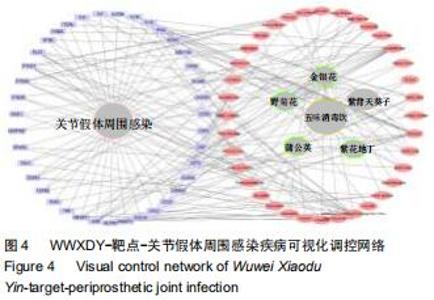
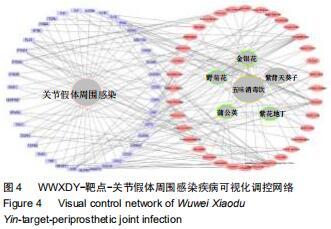
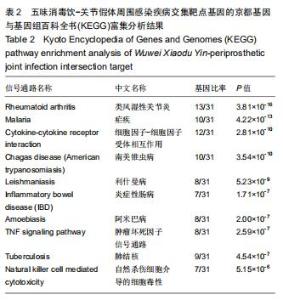
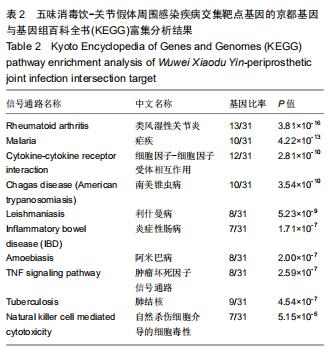
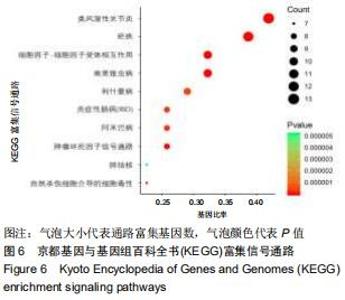
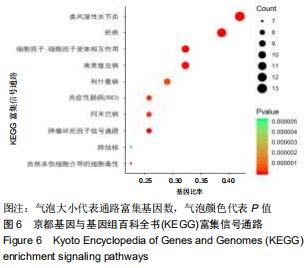
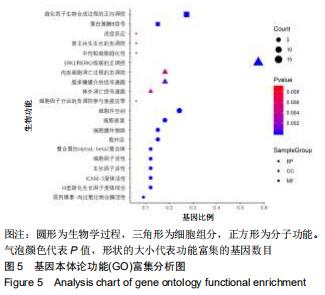
2.4 交集基因的GO富集分析结果 将交集靶点基因输入DAVID在线工具后,获得按P值升序排列的50个功能富集,其中包括生物过程40个,分子功能5个,细胞组分5个。选取排名前10位的生物过程、所有分子功能、所有细胞组分制成表格,见表1,并以气泡图的形式直观展示,见图5。GO富集分析结果显示,WWXDY-PJI疾病交集靶基因的生物过程主要是趋化因子生物合成过程的正向调控、蛋白激酶B信号、炎症反应、寄主共生生长的负调控、中性粒细胞趋化性、ERK1和ERK2级联的正调控、内皮细胞凋亡过程的负调控、脂多糖媒介的信号通路、体外凋亡信号通路、细胞因子分泌的负调控参与免疫应答等;分子功能为细胞因子活性、生长因子活性、ICAM-3受体活性、Ⅲ型转化生长因子受体结合、前列腺素-内过氧化物合酶活性;细胞组分为细胞外空间、细胞表面、细胞膜外侧面、胞外区、整合蛋白αL-β2复合体。 "
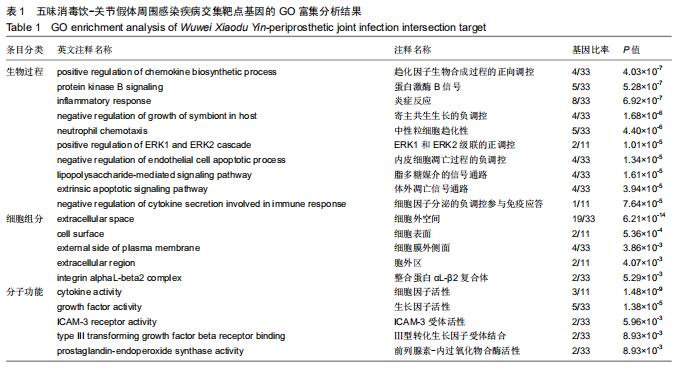
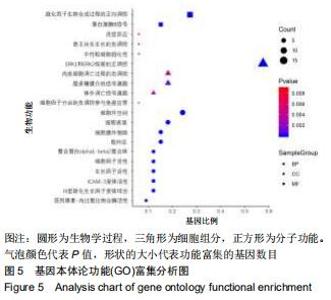
2.4 交集基因的GO富集分析结果 将交集靶点基因输入DAVID在线工具后,获得按P值升序排列的50个功能富集,其中包括生物过程40个,分子功能5个,细胞组分5个。选取排名前10位的生物过程、所有分子功能、所有细胞组分制成表格,见表1,并以气泡图的形式直观展示,见图5。GO富集分析结果显示,WWXDY-PJI疾病交集靶基因的生物过程主要是趋化因子生物合成过程的正向调控、蛋白激酶B信号、炎症反应、寄主共生生长的负调控、中性粒细胞趋化性、ERK1和ERK2级联的正调控、内皮细胞凋亡过程的负调控、脂多糖媒介的信号通路、体外凋亡信号通路、细胞因子分泌的负调控参与免疫应答等;分子功能为细胞因子活性、生长因子活性、ICAM-3受体活性、Ⅲ型转化生长因子受体结合、前列腺素-内过氧化物合酶活性;细胞组分为细胞外空间、细胞表面、细胞膜外侧面、胞外区、整合蛋白αL-β2复合体。 "
|
[1] SPRINGER BD. The diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30: 908-911.
[2] YOON H, CHO S, LEE D, et al. A review of the literature on culture-negative periprosthetic joint infection: epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2017; 29: 155.
[3] AGGARWAL VK, BAKHSHI H, ECKER NU, et al. Organism profile in periprosthetic joint infection: pathogens differ at two arthroplasty infection referral centers in Europe and in the United States. J Knee Surg. 2014; 27: 399-406.
[4] QIU XS, SUN X, CHEN DY, et al. Application of an articulating spacer in two-stage revision for severe infection after total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Surg.2010; 2(4): 299-304.
[5] 黄水仙,田道法.五味消毒饮临床应用研究进展[J].湖南中医药导报,2002, 8(9): 523-525, 529.
[6] 李兆合.五味消毒饮治疗关节置换术后金黄色葡萄球菌感染机理窥探[J].中医学报,2012, 27(5): 613-614.
[7] 赵辉. 五味消毒饮加减预防全髋关节置换术后感染疗效观察[J]. 山东中医杂志,2015,34(3):187,195.
[8] ZIMMERLI W, TRAMPUZ A, OCHSNER PE. Prosthetic-joint infections. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(12):1308.
[9] PARVIZI J, ALIJANIPOUR P, BARBERI EF, et al. Novel developments in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of periprosthetic joint infections. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23 Suppl:S32-43.
[10] 杨晓琴,吴亿晗,白俊毅,等. 五味消毒饮口服液HPLC指纹图谱的建立及6种指标性成分定量测定[J].中草药,2017,48(24): 5151-5157.
[11] 王大忠,孙永强,包伟东. 清创后普朗特液体敷料浸泡联合负压封闭引流和五味消毒饮内服治疗人工髋膝关节置换术后假体周围急性感染[J]. 中医正骨,2016,28(9): 52-54.
[12] LENSKI M, SCHERER MA. Synovial IL-6 as inflammatory marker in periprosthetic joint infections. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29: 1105-1109.
[13] YOKOTA K, SATO K, MIYAZAKI T, et al. Combination of tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin-6 induces mouse osteoclast-like cells with bone resorption activity both in vitro and in vivo. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014; 66: 121-129.
[14] OSAWA R, WILLIAMS KL, SINGH N. The inflammasome regulatory pathway and infections: role in pathophysiology and clinical implications. J Infection. 2011; 62: 119-129.
[15] STAHELOVA A, MRAZEK F, SMIZANSKY M, et al. Variation in the IL1B, TNF and IL6 genes and individual susceptibility to prosthetic joint infection. BMC Immunol. 2012; 13: 25.
[16] RAHMAN MM, MCFADDEN G. Modulation of tumor necrosis factor by microbial pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 2006;2(2):e4.
[17] GUSTAVSSON M. New insights into the structure and function of chemokine receptor:chemokine complexes from an experimental perspective. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. doi: 10.1002/JLB.2MR1219-288R.
[18] BORSIG L, WOLF MJ, ROBLEK M, et al. Inflammatory chemokines and metastasis--tracing the accessory. Oncogene. 2014;33(25): 3217-3224.
[19] ABBOUD D, DAUBEUF F, DO QT, et al. A strategy to discover decoy chemokine ligands with an anti-inflammatory activity. Sci Rep Uk. 2015; 5: 14746.
[20] ANGELINI A, MIYABE Y, NEWSTED D, et al. Directed evolution of broadly crossreactive chemokine-blocking antibodies efficacious in arthritis. Nat Commun. 2018; 9:1461.
[21] LIU Z, GAN L, LIU G, et al. Sirt1 decreased adipose inflammation by interacting with Akt2 and inhibiting mTOR/S6K1 pathway in mice. J Lipid Res. 2016; 57:1373-1381.
[22] CHEN M, CHANG C, HU C, et al. Periprosthetic joint infection caused by gram-positive versus gram-negative bacteria: lipopolysaccharide, but not lipoteichoic acid, exerts adverse osteoclast-mediated effects on the bone. J Clin Med. 2019;8(9). pii: E1289.
[23] GALLO J, SVOBODA M, ZAPLETALOVA J, et al. Serum IL-6 in combination with synovial IL-6/CRP shows excellent diagnostic power to detect hip and knee prosthetic joint infection. PLoS One. 2018;13(6): e0199226.
[24] 顾云,庄重.炎症反射研究新进展[J].中国病理生理杂志,2016,32(12): 2300-2304.
[25] SUGDEN PH, CLERK A. “Stress-responsive” mitogen-activated protein kinases (c-Jun N-terminal kinases and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases) in the myocardium. Circ Res. 1998; 83: 345-352.
[26] HUSSEIN YM, AMAL S, REZK NA, et al. Influence of interleukin-4 gene polymorphisms and interleukin-4 serum level on susceptibility and severity of rheumatoid arthritis in Egyptian population. Cytokine. 2013; 61: 849-855.
[27] CHIN SS, CHORRO L, CHAN J, et al. Splenic Innate B1 B Cell Plasmablasts Produce Sustained Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor and Interleukin-3 Cytokines during Murine Malaria Infections. Infect Immun. 2019;87(12). pii: e00482-19.
[28] COVRE LP, DEVINE O, GARCIA DE MOURA R, et al. Compartmentalized cytotoxic immune response leads to distinct pathogenic roles of natural killer and senescent CD8 T cells in human cutaneous leishmaniasis. Immunology. 2020;159(4):429-440.
[29] VIEIRA CS, MOREIRA OC, BATISTA KKS, et al. The nf-κb inhibitor, imd-0354, affects immune gene expression, bacterial microbiota and infection in midgut. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1189.
[30] SOLAYMANI-MOHAMMADI S, BERZOFSKY JA. Interleukin 21 collaborates with interferon-γ for the optimal expression of interferon-stimulated genes and enhances protection against enteric microbial infection. PLoS Pathog. 2019;15(2):e1007614.
[31] MI-ICHI F, ISHIKAWA T, TAM VK, et al. Characterization of Entamoeba histolytica adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate(APS) kinase; validation as a target and provision of leads for the development of new drugs against amoebiasis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019;13(8):e0007633.
[32] ELLERIN T, RUBIN RH, WEINBLATT ME. Infections and anti–tumor necrosis factor α therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48: 3013-3022.
[33] FONG Y, LOWRY SF. Tumor necrosis factor in the pathophysiology of infection and sepsis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990; 55: 157-170. [34] TAY CH, SZOMOLANYI-TSUDA E, WELSH RM. Control of infections by NK cells. Springer, 1998:193-220. |
| [1] | Zheng Hongrui, Zhang Wenjie, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Shen Yajun, Fan Lei. Femoral neck system combined with platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1390-1395. |
| [2] | Du Xueting, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Yanjun, Wang Mei, Chen Wubiao, Huang Wenhua. Application of compressed sensing technology in two-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1396-1402. |
| [3] | He Yinhao, Li Xiaosheng, Chen Hongwen, Chen Tiezhu. 3D printed porous tantalum metal in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: current status and application prospect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1455-1461. |
| [4] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [5] | Long Guiyue, Li Dongdong, Liao Hongbing. Calcium phosphate cement/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) degradation products promote osteoclast differentiation of mouse monocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1193-1198. |
| [6] | Bi Gengchao, Zhang Yanlong, Li Qiuyue, Hu Longwei, Zhang Yu. Knee joint mechanics and activation characteristics of surrounding muscles during deep jumps at different heights and distances [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1211-1218. |
| [7] | Zhao Lu, Zhao Yifei, Gao Da, Liu Yanfang, Fu Tingting, Xu Jiangyan. Expression of suppressor of Zeste 12 in kidney tissues of rats with diabetic nephropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1179-1186. |
| [8] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [9] | Yuan Hucheng, Ding Yongguo, Ma Xuehua, Ma Wenxin, Sun Jianmin, Wang Zili, Jin Weidong. Sustained releasing of pyrazinamide, capreomycin, moxifloxacin and amikacin loaded bone cement in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1017-1022. |
| [10] | Sun Jiangwei, Wang Junxiang, Baibujiafu·Yellisi, Dai Huijuan, Nijati·Turson. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in different smooth collar implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1004-1011. |
| [11] | Xu Cong, Zhao He, Sun Yan. Regeneration of facial nerve injury repaired by biomaterial nerve conduits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1089-1095. |
| [12] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [13] | Li Wenjie, You Aijia, Zhou Junli, Fang Sujuan, Li Chun. Effects of different dressings in the treatment of burn wounds: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1141-1148. |
| [14] | Li Xinyue, Li Xiheng, Mao Tianjiao, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Three-dimensional culture affects morphology, activity and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [15] | Yuan Wei, Liu Jingdong, Xu Guanghui, Kang Jian, Li Fuping, Wang Yingjie, Zhi Zhongzheng, Li Guanwu. Osteogenic differentiation of human perivascular stem cells and its regulation based on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 866-871. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||