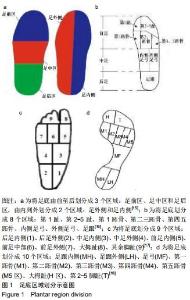
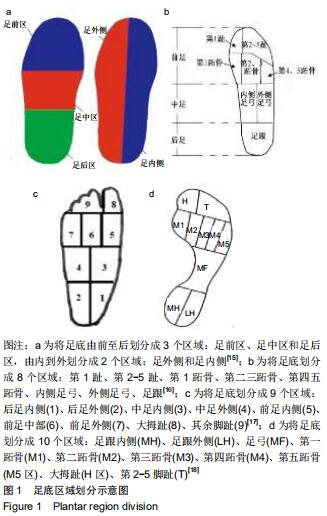
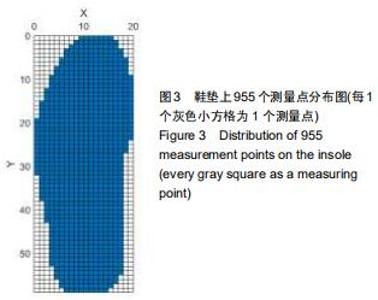
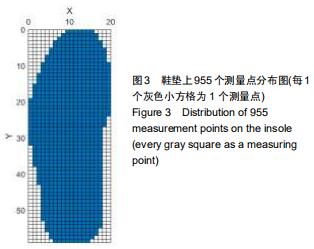
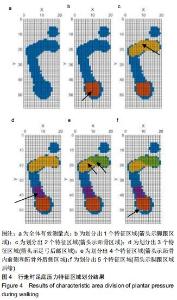
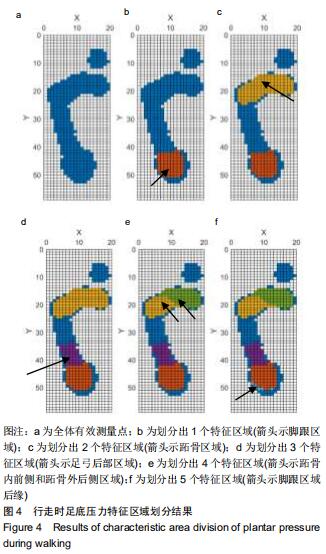
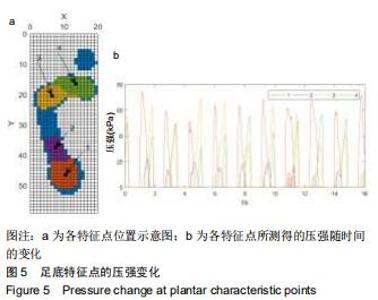
|
[1] 查盼盼,Raju Bista,王椿.足底压力与糖尿病[J].华西医学, 2018, 33(5):593-597.
[2] 贾川,瞿玉兴.糖尿病足步态变化的研究进展[J].医学综述,2018, 24(20):4086-4091.
[3] 夏懿.基于足底压力分布的步行行为感知关键技术研究[D].合肥:中国科学技术大学,2013.
[4] 温爱玲,游永豪,闻剑飞,等.基于数字跑道的青年人正走、倒走步态及足底压力分析[J].南京体育学院学报(自然科学版), 2016, 15(6):53-58.
[5] 张庆来,刘学贞,陈丰才,等.脑力、体力劳动者足底压力参数分布特征及评定[J].体育学刊, 2008(11):100-105.
[6] 叶玲,吴建贤.足底压力测量技术在足外翻脑性瘫痪患儿康复疗效评定中的应用[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2012,27(6):449-451.
[7] 郄淑燕,张庆民,张致媛,等.拇外翻对前足底压力分布的改变[J].医用生物力学,2010,25(3):224-229.
[8] 杨洋,王熙,傅维杰.着鞋和触地方式对慢跑时足部受力特征的影响[J].医用生物力学,2017, 32(2):154-160.
[9] 刘作军,高新智,赵晓东,等.下肢假肢穿戴者跑动步态识别与膝关节控制策略研究[J].仪器仪表学报, 2018,39(7):74-82.
[10] 强家辉,张为公,王东.基于足底压力的人体姿态检测和行为分析方法[J].测控技术,2018, 37(1):1-4,9.
[11] ELFTMAN H.A cinematic study of the distribution of pressure in the human foot.Anat REC.1934;59(4):481-491.
[12] 樊霄燕,周军杰,曹成福,等.基于F-Scan三维动态足底压力分析系统的动静态足底压力分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(50):9406-9409.
[13] PUTTI AB, ARNOLD GP, COCHRANE L, et al. The Pedar® in-shoe system: Repeatability and normal pressure values. Gait Posture.2006;25(3):401-405.
[14] 高敏,张一帆,洪成雨.不同运动状态下人体足底压力分布及分析[J].服装学报,2019,4(4):301-304.
[15] 张峻霞,蔡运红,窦树斐.楼梯行走足底压力与表面肌电参数研究[J].医用生物力学,2018, 33(1):42-47.
[16] 侯宗辰,江东,胡跃林.足底压力分析在慢性踝关节不稳诊疗中的研究进展[J].中国微创外科杂志, 2019,19(2):186-189.
[17] 李韦豪,许胜强,刘奕,等.静态足底压力分布特征在膝关节损伤评估中的应用[J].中国医疗器械杂志,2018,42(6):395-399.
[18] 聂智超,吕杰,丁皓.基于足底压力的步态识别研究进展[J].生物医学工程学进展,2018, 39(3):141-144.
[19] 史文飞,孙珅,赵冬,等.基于智能手机的足底压力监测系统设计[J].医疗卫生装备,2019, 40(12):10-13,21.
[20] 李攀,蒋敏,向超,等.基于多传感器的可穿戴式足底压力测试系统研发及临床应用[J].中国医学装备, 2019,16(3):1-5.
[21] 霍洪峰,王子乾,梁玉,等.基于聚类分析的足横弓承重类型及足底压力特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(7):1251-1254.
[22] 李晓理,黄红拾,王杰,等.前交叉韧带断裂后足底压力特征的聚类分析[J].自动化学报,2017,43(3):418-429.
[23] WANG M, WANG X, FAN Z, et al. Research on feature extraction algorithm for plantar pressure image and gait analysis in stroke patients.J Vis Commun Image Represent. 2019;58:525-531.
[24] SAWACHA Z, SPOLAOR F, GUARNERI G, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of diabetic foot through hierarchical cluster analysis[C]//BioMed Central,2014:A72.
[25] 谢雅婷,唐虹,王芳芳,等.基于足底压力分区优化的鞋垫功能区域设计[J/OL].中国皮革:1-6[2020-03-21]. https://doi.org/10.13536/j.cnki.issn1001-6813.2020-002-007.
|