Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (17): 2735-2741.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2676
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ozone bath in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcer infection
Qin Xinyuan1, Wang Lei2, Wang Jiangning1
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Beijing Shijitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100038, China; 2Emergency Medicine Center, The Second Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2019-12-06Revised:2019-12-12Accepted:2020-01-17Online:2020-06-18Published:2020-03-30 -
Contact:Wang Jiangning, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Beijing Shijitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100038, China -
About author:Qin Xinyuan, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Beijing Shijitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100038, China -
Supported by:the Capital Clinical Characteristic Application Research and Achievement Promotion, No. Z171100001017070
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qin Xinyuan, Wang Lei, Wang Jiangning. Ozone bath in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcer infection[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(17): 2735-2741.
share this article
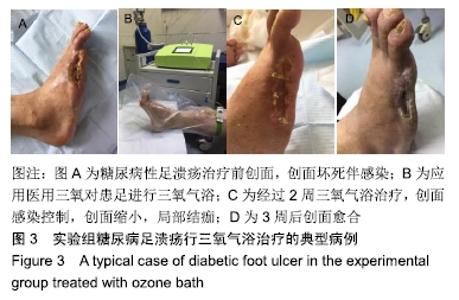
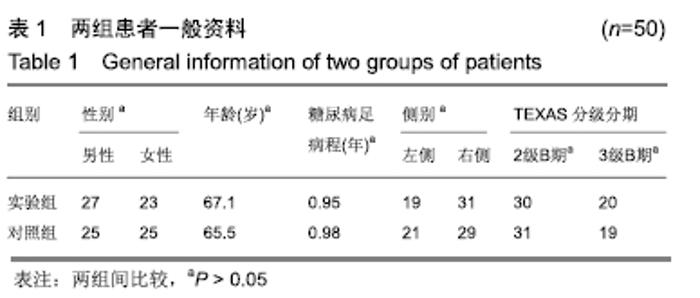
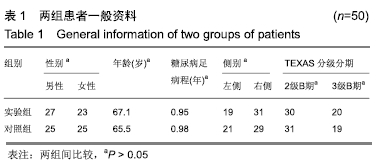
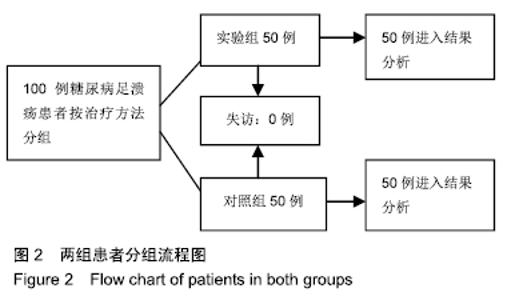
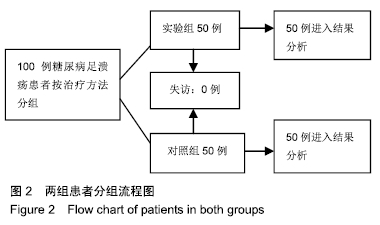
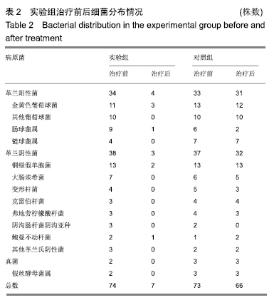
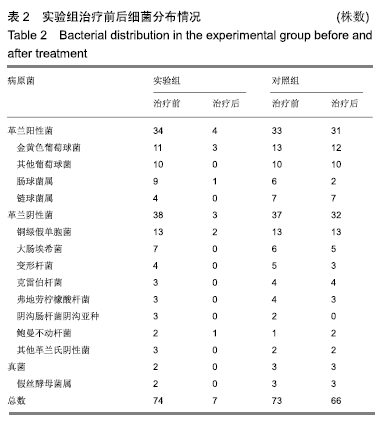
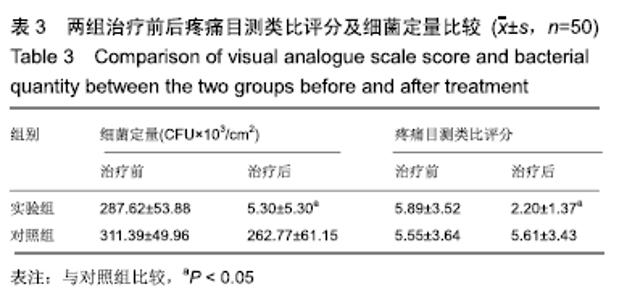
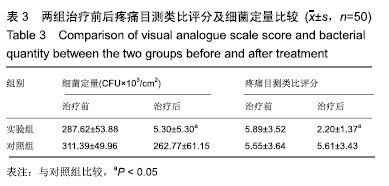
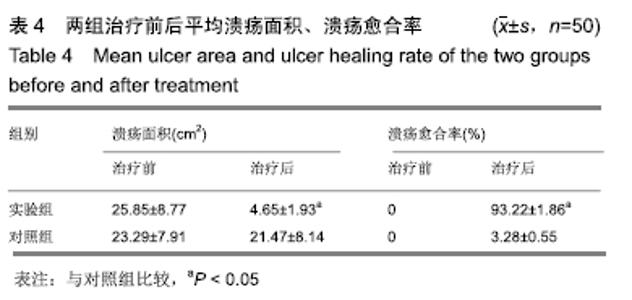
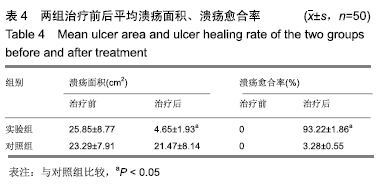
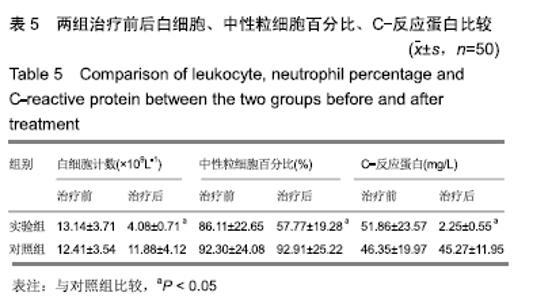
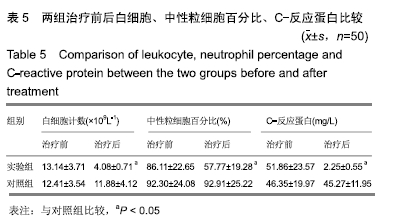
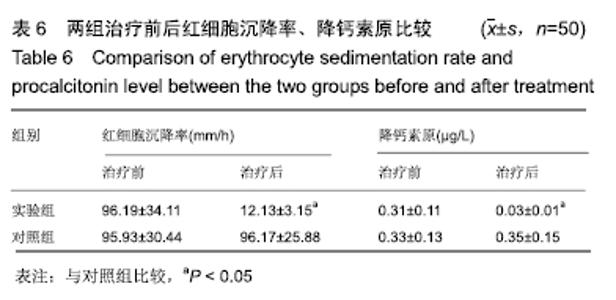
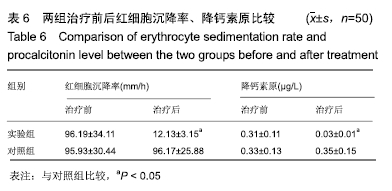
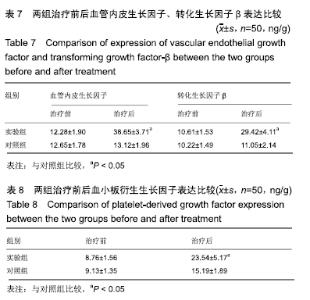
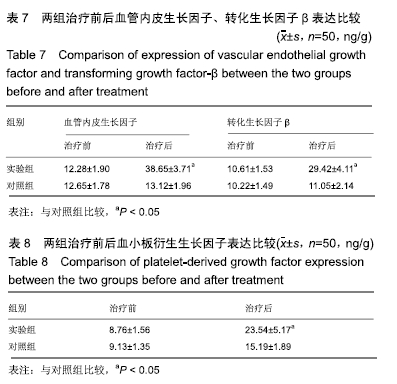
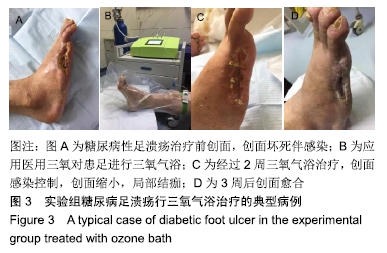
2.6 典型病例 实验组患者,男,51岁。因右足肿胀20 d,足底破溃渗液7 d入院。溃疡面积为16.16 cm2,入院血液化验示:白细胞13.62×109 L-1,中性粒细胞百分比90.3%,C-反应蛋白110.81 mg/L,红细胞沉降率108 mm/h,降钙素原0.39 μg/L,创面分泌物培养为产酸克雷伯菌和金黄色葡萄球菌,细菌定量为253.32×103 CFU/cm2,创面疼痛目测类比评分7分。给予每日创面生理盐水清洁后医用三氧气浴 30 min,连续治疗10 d后创面分泌物培养细菌转阴,治疗 14 d后血液化验示炎症指标趋于正常,白细胞4.42×109 L-1,中性粒细胞百分比54.7%,C-反应蛋白31.4 mg/L,红细胞沉降率61 mm/h,降钙素原0.09 μg/L,创面肉芽新鲜,创面疼痛目测类比评分3分。继续每日三氧气浴至观察期21 d结束后,溃疡完全愈合,炎症指标白细胞4.21×109 L-1,中性粒细胞百分比51.7%,C-反应蛋白1.84 mg/L,红细胞沉降率21 mm/h,降钙素原0.04 μg/L,创面疼痛目测类比评分0分,溃疡愈合率100%。见图3。 "
| [1] HINCHLIFFE R, BROWNRIGG J, APELQVIST J, et al. International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot guidance on the diagnosis, prognosis and management of peripheral artery disease in patients with foot ulcers in diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev.2016; 359:37-44. [2] KARMAKER M, SANYAL SK, SULTANA M, et al. Association of bacteria in diabetic and non-diabetic foot infection-An investigation in patients from Bangladesh. J Infect Public Health. 2016,9(3):267-277. [3] NEVILLE RF, KAYSSI A, BUESCHER T, et al. The diabetic foot. Curr. Probl. Surg. 2016;53(9):408-437. [4] RAMIREZ-ACUÑA JM, CARDENAS-CADENA SA, MARQUEZ-SALAS PA, et al. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Current Advances in Antimicrobial Therapies and Emerging Treatments. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 Oct 24;8(4). [5] 徐俊,王鹏华.2019年国际糖尿病足论坛糖尿病足感染部分介绍[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2019,11(8):565-568. [6] FITZPATRICK E, HOLLAND OJ, VANDERLELIE JJ. Ozone therapy for the treatment of chronic wounds: A systematic review. Int Wound J. 2018;15(4):633-644. [7] IZADI M, KHEIRJOU R, MOHAMMADPOUR R, et al. Efficacy of comprehensive ozone therapy in diabetic foot ulcer healing. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019;13(1):822-825. [8] ALMAZ ME, SONMEZ IS. Ozone therapy in the management and prevention of caries.J Formos Med Assoc.2015;114(1): 3-11. [9] SANTEMA TB, LENSELINK EA, BALM R, et al. Comparing the Meggitt-Wagner and the University of Texas wound classification systems for diabetic foot ulcers: inter-observer analyses. Int Wound J. 2016;13(6):1137-1141. [10] JÜRGEN HARREITER, MICHAEL RODEN. Diabetes mellitus-Definition, Klassifikation, Diagnose, Screening und Pravention (Update 2019). [11] 糖尿病足(肢端坏疽)检查方法及诊断标准(草案)[J].中国糖尿病杂志, 1996,4(2):126-126. [12] ZAHRA M, AHMAD KA, GERALD R, et al. Reduction of Salmonella and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli on alfalfa seeds and sprouts using an ozone generating system. Int J Food Microbiol. 2019;289:57-63. [13] CLINICAL LABORATORY STANDARDS INSTITUTE. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility Testing-Twenty fourth edition: approved standard: M100-S24. Wayne.PA: CLSI. 2014. [14] 李利平,马恩庆. 烧伤创面细菌定量方法及意义[J].中国烧伤创疡杂志,1998,10(4):53-54. [15] REED MD, VAN NOSTRAN W. Assessing pain intensity with the visual analog scale: A plea for uniformity. J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;54(3):241-244. [16] DE LEON JM, DRIVER VR, FYLLING CP, et al. The Clinical Relevance of Treating Chronic Wounds with an Enhanced Near-Physiological Concentration of Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel.Adv Skin Wound Care. 2011;24(8):357-368. [17] WHO. Global report on diabetes. Geneva: WHO.2016. [18] International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 9th edition 2019. http://www.idf.org/. [19] XU Y, WANG L, HE J, et al. Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. 2013;310(9):948-959. [20] DEKKER RG, QIN C, HO BS, et al. The effect of cumulative glycemic burden on the incidence of diabetic foot disease. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):143. [21] HUMPHRIES MD, BRUNSON A, LI CS , et al. Amputation trends for patients with lower extremity ulcers due to diabetes and peripheral artery disease using statewide data. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64(6):1747-1755.e3. [22] AMERICAN DIABETES ASSOCIATION. Erratum. Microvascular complications and foot care. Diabetes Care.2017;40(7):986. [23] ARMSTRONG DG, BOULTON AJM, BUS SA. Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence.N Engl J Med. 2017;376(24): 2367-2375. [24] 王宁,鞠上,杨博华,等.糖尿病足患者大截肢危险因素的Meta分析[J].中华糖尿病杂志, 2018,10(7):465-470. [25] XIAOYING X, YUNWEN B, LIJIA N, et al. Bacterial Profile and Antibiotic Resistance in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcer in Guangzhou, Southern China: Focus on the Differences among Different Wagner’s Grades, IDSA/IWGDF Grades, and Ulcer Types. Int J Endocrinol. 2017;2017:8694903. [26] 武姗,刘洋,朱旅云,等.转化生长因子β及其受体在糖尿病足创面愈合过程中作用机制的研究进展[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2017, 25(6):569-572. [27] 刘洋,杨少玲,武姗,等.血小板源生长因子在糖尿病足创面中的应用[J].临床误诊误治,2017,30(5):110-112. [28] 唐乾利,郭满,吴标良.血管内皮生长因子的研究现状与进展[J].中国烧伤创疡杂志,2017,29(2):77-87. [29] 谭倩,赵鑫,陈贝,等.生长因子在创面愈合中的作用研究进展[J].山东医药,2019,59(4):106-110. [30] SOLOVASTRU LG, STÎNCANU A, DE ASCENTII A, et al. Randomized, controlled study of innovative spray formulation containing ozonated oil and α-bisabolol in the topical treatment of chronic venous leg ulcers. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2015;28(9):406-409. [31] BORRELLI E, BOCCI V. The Use of Ozone in Medicine. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2018;8:117-119 [32] FONTES B, CATTANI HEIMBECKER AM, DE SOUZA BRITO G, et al. Effect of low-dose gaseous ozone on pathogenic bacteria. BMC Infectious Diseases. 2012;12:358. [33] CAMPANATI A, DE BLASIO S, GIULIANO A, et al. Topical ozonated oil versus hyaluronic gel for the treatment of partial- to full-thickness second-degree burns: a prospective, comparative, single-blind, non-randomised, controlled clinical trial. Burns. 2013;39(6):1178-1183. [34] 张雪颖.浅述臭氧的灭菌效能[J].食品安全导刊,2019(6): 141-142. [35] BOCCI V. Oxygen-ozone therapy: a critical evaluation. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.2002:241-324. [36] RESITOGLU B, CELIK Y, KOMUR M, et al. The efficacy of ozone therapy in neonatal rats with hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Bratislavske Lekarske Listy.2018;119(2):81. [37] LUONGO M, BRIGIDA AL, MASCOLO L, et al. Possible Therapeutic Effects of Ozone Mixture on Hypoxia in Tumor Development. Anticancer Res.2017;37(2):425-436. [38] ZHANG J, GUAN M, XIE C, et al. Increased Growth Factors Play a Role in Wound Healing Promoted by Noninvasive Oxygen-Ozone Therapy in Diabetic Patients with Foot Ulcers. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:273475. [39] 王丽萍,王利娴,庞海艳,等.臭氧治疗对糖尿病足局部组织VEGF, TGF-β,PDGF表达的变化影响[J].中国医药导刊, 2017,19(5): 472-473. [40] IZADI M, JONEIDI JAFARI N. Hosseini. Therapeutic effects of ozone in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: review of the literature. Biomedical Res.2017;28(18):7846-7850. [41] 王彦凤,鄢建勤,李平.臭氧在慢性疼痛治疗中的应用研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2019,25(4):298-302. [42] BRAIDY N, IZADI M, SUREDA A, et al. Therapeutic Relevance of Ozone Therapy in degenerative diseases: Focus on Diabetes and Spinal Pain. J Cell Physiol. 2018; 233(4):2705-2714. [43] 安建雄. 三氧自体血疗法专家共识[J].转化医学杂志,2018,7(6): 326-345. [44] COSTA T, LINHARES D, NEVES N, et al. Ozone therapy for low back pain. A systematic review. Acta Reumatol Port. 2018;43(3):172-181. [45] NOORI-ZADEH A, BAKHTIYARI S, KHOOZ R, et al. Intra-articular ozone therapy efficiently attenuates pain in knee osteoarthritic subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Complement Ther Med. 2019;42:240-247. [46] 徐怡珊,文小明,苗国斌,等.臭氧污染及防治对策[J].中国环保产业, 2018(6):35-38. [47] 朱权,王新,严瑾,等.不同浓度医用臭氧对实验大鼠膝关节组织结构安全性评价[J].中国医药,2011,6(13):23-24. [48] 钟远鸣,李嘉琅,李智斐,等.不同浓度臭氧联合射频消融术治疗神经根型颈椎病的疗效对比研究[J].中国全科医学,2019,22(24): 2924-2928. |
| [1] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [2] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [3] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [4] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [5] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [6] | Ma Rui, Wang Jialin, Wu Mengjun, Ge Ying, Wang Wei, Wang Kunzheng. Relationship of pathogenic bacteria distribution with drug resistance and treatment cycle for periprosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 380-385. |
| [7] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [8] | Cheng Chongjie, Yan Yan, Zhang Qidong, Guo Wanshou. Diagnostic value and accuracy of D-dimer in periprosthetic joint infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3921-3928. |
| [9] | Liu Fang, Shan Zhengming, Tang Yulei, Wu Xiaomin, Tian Weiqun. Effects of hemostasis and promoting wound healing of ozone sustained-release hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3445-3449. |
| [10] | Gan Lili, Xiong Na, Liu Yanfei. Hydrogel as drug scaffold in skin wound repair: challenges of clinical application possibilities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3578-3583. |
| [11] | Zhang Haitao, Chen Jinlun, Zhu Xingyang, Zeng Huiliang, Li Jie, Sun Xiaobo, Qi Xinyu, Zeng Jianchun, Zeng Yirong. Effect and molecular mechanism of Honeysuckle-Rhizoma coptidis in the treatment of periprosthetic joint infection based on molecular docking and network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3360-3367. |
| [12] | Tian Lin, Shi Xiaoqing, Duan Zhenglan, Wang Kuan, Zhang Li, Wang Peimin. Efficacy and safety of transverse tibial bone transport technique in the treatment of diabetic foot:a meta-analysis#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3275-3280. |
| [13] | Ren Bingkai, Zheng Yibin, Huang Leiwen, Wu Fanhui, Yang Dong . Value of respiratory tract management and fiberoptic bronchoscopy in traumatic cervical spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2902-2907. |
| [14] | Li Jie, Xu Jianzhen, Hu Ping, Lei Qiqi, Zhang Wenning, Ao Ningjian . Preparation and performance evaluation of carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized glucomannan/Panax notoginseng compound sponge dressing for chronic wound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2528-2534. |
| [15] | Chen Zhenyu, Zhang Xiaoning, Luo Yuxin, Liang Jianwei, Yan Chi. Evaluation of silk fibroin/curcumin composite film for promoting wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2554-2561. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||