[1] Global Observatory Donation and Transplantation [EB/OL]. (2019-03-13). http://www.transplant-observatory.org/.
[2] WHO. Burns[EB/OL].[2018-03-60](2019-03-13). http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs365/en/.
[3] GAIN P, JULLIENNE R, HE Z, et al. Global Survey of Corneal Transplantation and Eye Banking.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016;134(2):167-73.
[4] WHO.10 facts on disability [EB/OL].(2018-05-17). https://www.who.int/features/factfiles/disability/en/.
[5] MENKEN M, MUNSAT TJ.The global burden of disease study: implications for neurology.Arch Neurol. 2000;57(3):418-20.
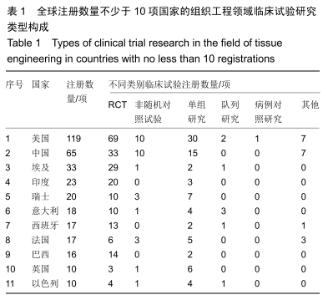
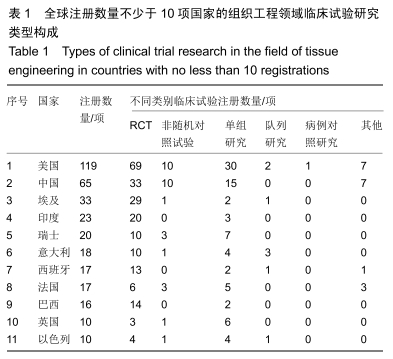
[6] 曹谊林,崔磊,刘伟.中国组织工程研究回顾与发展[J].医学研究杂志,2003, 34(6): 5-6.
[7] WHO.International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP): What is a clinical trial? [EB/OL]. (2018-07-16). https://www.who.int/ictrp/en/.
[8] 中国临床试验注册中心.注册指南[EB/OL].(2018-07-16). http://www.chictr.org.cn/registry.aspx.
[9] International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Clinical Trial Registration [EB/OL]. (2018-07-16). http://www.icmje.org/ recommendations/browse/publishing-and-editorial-issues/ clinical-trial-registration.html.
[10] 李佳,严恺,孔艳婷,等.ClinicalTrials.gov建库以来儿童临床试验注册现况横断面调查[J].中国循证儿科杂志,2016,11(1):3-7.
[11] 庞之楹,尹峰,袁锋.脂肪干细胞治疗膝骨关节炎的相关临床试验项目及注册[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(29):4729-4735.
[12] 叶青松,王晓燕.牙源性干细胞储存和临床应用的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2018,26(1):15-25.
[13] 周晨虹,徐丽丽,郝秀仙,等.外周血CD34~+细胞自体移植促进老年动脉粥样性缺血肢体的血管新生:前瞻性、单中心、开放性、随机对照临床试验方案[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(13):1998-2002.
[14] VIERGEVER RF,LI K.Trends in global clinical trial registration: an analysis of numbers of registered clinical trials in different parts of the world from 2004 to 2013.Bmj Open.2015; 5(9):e008932.
[15] MIKE THELWALL, KAYVAN KOUSHA.Are citations from clinical trials evidence of higher impact research? An analysis of ClinicalTrials.gov.Scientometrics.November 2016;109(2):1341–1351.
[16] 徐潇洁,何琳,邵波.基于科学数据的合作网络研究——以ClinicalTrials.gov临床试验数据为例[J].图书情报工作,2018,62(15):83-91.
[17] ClinicalTrials.gov.What Is ClinicalTrials.gov? [EB/OL].(2018-09-26). https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/about-site/background.
[18] 陈耀龙,李幼平,杜亮,等.医学研究中证据分级和推荐强度的演进[J].中国循证医学杂志,2008,8(2):127-133.
[19] 吴思成.多中心等效性临床试验中区域一致性的统计方法研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2017.
[20] 张晓方,黄丹,王翔宇,等.国际多中心临床试验监管指南研究报告[J].中国新药杂志,2017,26(17):72-78.
[21] 张婷,陈娟,池慧,等.医疗器械临床试验注册特点研究[J].中国医疗设备, 2018,33(10):113-118+131.
[22] 中华人民共和国中央人民政府.国家中长期科学和技术发展规划纲要 (2006-2020年)》[EB/OL]. [2006-02-09](2019-07-14). http://www.gov.cn/jrzg/2006-02/09/content_183787.htm.
[23] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.科技部关于发布国家重点研发计划精准医学研究等重点专项2016年度项目申报指南的通知[EB/OL].[2016-03-07] (2019-07-14). http://www.most.gov.cn/mostinfo/xinxifenlei/fgzc/ gfxwj/gfxwj2016/201603/t20160308_124540.htm.
[24] 曹谊林,刘伟,张文杰,等.组织工程研究进展[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2012,32(9).
[25] 房梦雅,王青华,徐来,等.基于德温特专利数据库近10年组织工程支架、技术、假体领域的专利分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(18):112-117.
[26] 孙晓北.组织工程及其我国发展问题对策研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院, 2009.
|