Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (20): 3275-3280.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3200
Efficacy and safety of transverse tibial bone transport technique in the treatment of diabetic foot:a meta-analysis#br#
Tian Lin, Shi Xiaoqing, Duan Zhenglan, Wang Kuan, Zhang Li, Wang Peimin
- The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2020-05-07Revised:2020-05-09Accepted:2020-06-01Online:2021-07-18Published:2021-01-18 -
Contact:Wang Peimin, Chief physician, MD, Doctoral supervisor, the Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Tian Lin, Master, the Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the leading Talent Preject of Jiansu Province, No. SLJ0207 (to WPM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Lin, Shi Xiaoqing, Duan Zhenglan, Wang Kuan, Zhang Li, Wang Peimin. Efficacy and safety of transverse tibial bone transport technique in the treatment of diabetic foot:a meta-analysis#br#[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3275-3280.
share this article
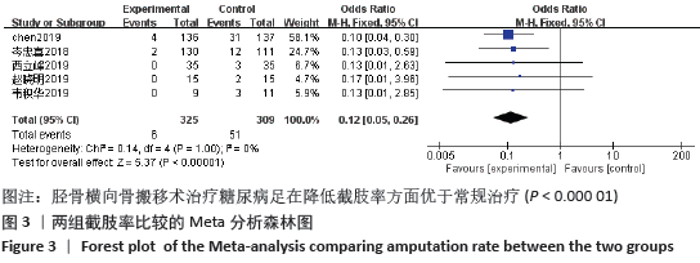
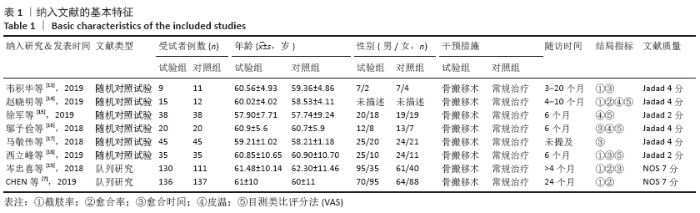
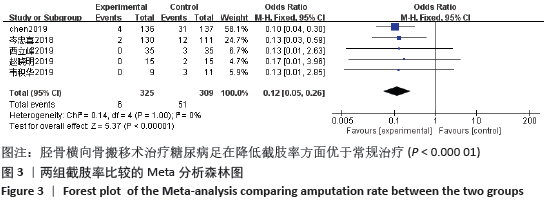
2.3 文献质量评价结果 纳入的研究中有2项研究为队列研究,另外6项研究为随机对照研究,其中4篇文献使用了随机数字表法,有1项研究通过入院顺序产生随机序列,有1项研究使用计算机随机序列。因治疗方式为特殊手术治疗,临床上难以实施盲法,故存在实施偏倚。各研究均未提及分配隐藏。有1项研究提及退出与失访病例,其余研究均未出现退出与失访病例。各研究均数据完整,未涉及其他偏倚。队列研究应用NOS量表进行文献质量评价,2篇均为7分;随机对照研究应用改良后Jadad量表进行文献质量评价,有4篇4分,另外2篇2分,见表1。 2.4 Meta 分析结果 2.4.1 各组截肢率差异 共5篇文献报道了截肢率[7,13-14,18-19],试验组为胫骨横向骨搬移组,对照组为常规治疗组,结果显示数据无异质性(P=1.00,I2=0),故采用固定效应模型计算合并效应量,差异有显著性意义(OR=0.12,95%CI:0.05-0.26,P < 0.000 01)。结果显示胫骨横向骨搬移术治疗糖尿病足在降低截肢率方面优于常规治疗,见图3。 "
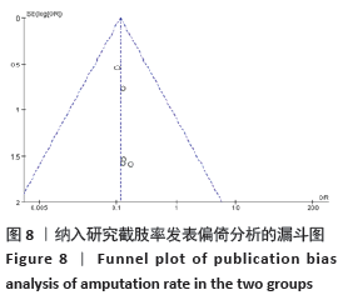
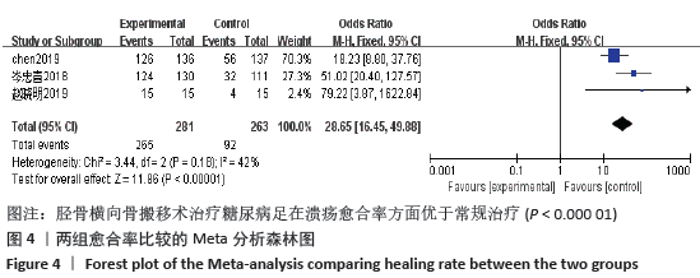
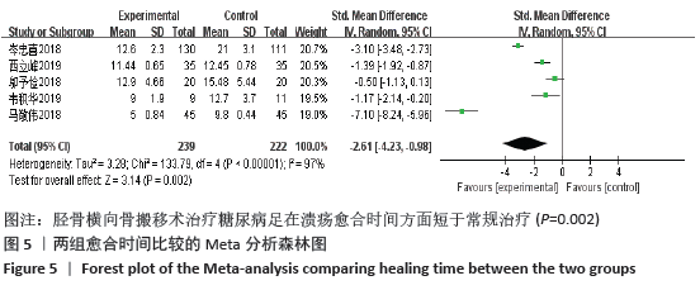
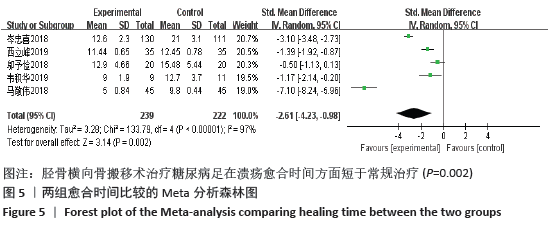
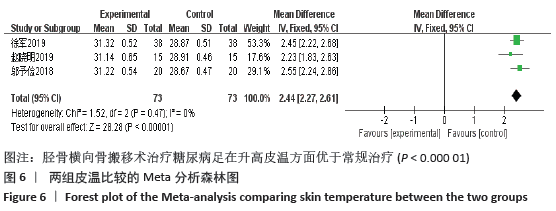
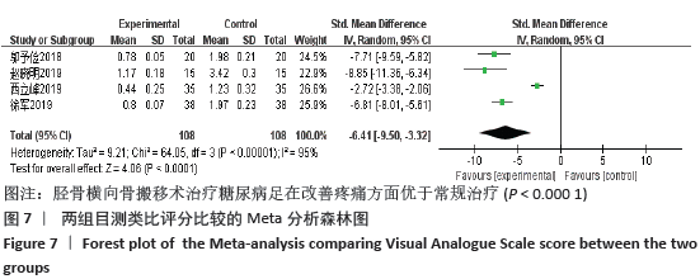
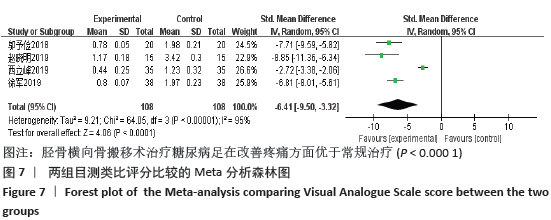
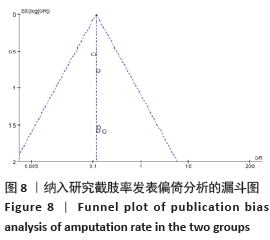
2.4.6 敏感性分析 对于目测类比评分指标,剔除西立峰[18]的研究后,异质性显著降低(P=0.32,I2=12%),说明该项研究为异质性的主要来源,逐一剔除其他各项试验进行Meta分析,结果显示均无显著差异,表明文章稳定性较好。原因可能是该试验对照组干预措施为皮瓣移植,而其他3组均为常规药物治疗,存在临床异质性。 对于愈合时间指标,进行敏感性分析,结果显示马敬伟等[17]和岑忠喜等[19]的研究偏倚较大。文章再次回顾了该2项试验发现,马敬伟等[17]的研究中术后愈合时间较快,明显不同于其他各项研究。而岑忠喜等[19]的研究所纳入样本量明显多于其他研究,且试验组愈合时间显著快于对照组,与其他学者结论差距较大。该2项试验具有统计及临床异质性。在剔除该2项研究后,异质性降低为57%,提示该2项试验为异质性主要来源。 2.4.7 各组不良反应差异 共3项研究提及不良反应的发生[7,13,19],其中共3例患者术后发生胫骨截骨处骨折,均经外固定治疗后愈合;患者6例术后伤口未愈合;患者3例发生针道处感染。 2.4.8 各组复发率差异 仅1项研究提及复发率[7],该研究调查了136例胫骨横向骨搬移术治疗的试验组及137例常规治疗的对照组,在长达2年的随访中,骨搬移组复发率仅为2.9%,远远低于常规治疗组17%的复发率[7]。 2.5 发表偏倚分析 对胫骨横向骨搬移术治疗糖尿病足的截肢率做倒漏斗图进行偏倚分析,见图8,图中散点存在部分不对称,提示可能存在发表偏倚,原因可能是阴性结果的试验未发表,样本量较小等。 "
| [1] MATHERS CD, LONCAR D. Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006;3(11):e442. [2] ZHANG P, LU J, JING Y, et al. Global epidemiology of diabetic foot ulceration: a systematic review and meta-analysis (dagger). Ann Med. 2017;49(2):106-116. [3] IBRAHIM A. IDF Clinical Practice recommendation on the diabetic foot: a guide for healthcare professionals. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;127:285-287. [4] APELQVIST J. Diagnostics and treatment of the diabetic foot. Endocrine. 2012;41(3): 384-397. [5] SUN Y, GAO Y, CHEN J, et al. Evidence mapping of recommendations on diagnosis and therapeutic strategies for diabetes foot: an international review of 22 guidelines. Metabolism. 2019;100:153956. [6] HINCHLIFFE RJ, BROWNRIGG JR, ANDROS G, et al. Effectiveness of revascularization of the ulcerated foot in patients with diabetes and peripheral artery disease: a systematic review. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32 Suppl 1:136-144. [7] CHEN Y, KUANG X, ZHOU J, et al. Proximal tibial cortex transverse distraction facilitating healing and limb salvage in severe and recalcitrant diabetic foot ulcers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478(4):836-851. [8] GUBIN AV, BORZUNOV DY, MARCHENKOVA LO, et al. Ilizarov to bone reconstruction: historical achievements and state of the art. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2016; 11(3):145-152. [9] ARONSON J. Temporal and spatial increases in blood flow during distraction osteogenesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (301):124-131. [10] BEGUN A, MORBACH S, RUMENAPF G, et al. Study of disease progression and relevant risk factors in diabetic foot patients using a multistate continuous-time markov chain model. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e147533. [11] JADAD AR, MOORE RA, CARROLL D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1):1-12. [12] STANG A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9): 603-605. [13] 韦积华,唐乾利,罗群强,等.Ilizarov微循环重建技术对糖尿病足溃疡的临床疗效观察[J]. 右江民族医学院学报,2019, 41(3):239-245. [14] 赵晓明,刘亮,贾中伟,等.胫骨横向搬移技术治疗糖尿病足的临床疗效[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2020,41(2):244-250. [15] 徐军.胫骨横向骨搬移技术在糖尿病足治疗中的临床应用效果探讨[J].糖尿病新世界,2019,22(19):176-177. [16] 邬予俭,何贵,林宝举,等.胫骨横向骨搬移技术治疗糖尿病足的疗效观察及研究[J].双足与保健,2018,27(13):79-80. [17] 马敬伟,赵琳琳,马德春.胫骨横向骨搬移微循环再生技术治疗糖尿病足的临床疗效分析[J]. 黑龙江科学,2018,9(9):6-7. [18] 西立峰.胫骨横向骨搬运技术治疗糖尿病足及下肢血管闭塞症的临床效果[J].中国实用医药,2019,14(15):63-64. [19] 岑忠喜,曾高峰,何基琛,等.改良骨搬移治疗糖尿病足[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(36):5766-5771. [20] ZHIVOV A, PESCHEL S, SCHOBER HC, et al. Diabetic foot syndrome and corneal subbasal nerve plexus changes in congolese patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e119842. [21] POP-BUSUI R, BOULTON AJ, FELDMAN EL, et al. Diabetic neuropathy: a position statement by the american diabetes association. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(1):136-154. [22] LAVERY LA, PETERS EJ, WILLIAMS JR, et al. Reevaluating the way we classify the diabetic foot: restructuring the diabetic foot risk classification system of the International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(1):154-156. [23] DAVIS FM, KIMBALL A, BONIAKOWSKI A, et al. Dysfunctional wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers: new crossroads. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18(1):2. [24] HINCHLIFFE RJ, BROWNRIGG JR, ANDROS G, et al. Effectiveness of revascularization of the ulcerated foot in patients with diabetes and peripheral artery disease: a systematic review. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32 Suppl 1:136-144. [25] BUS SA, ARMSTRONG DG, VAN DEURSEN RW, et al. IWGDF guidance on footwear and offloading interventions to prevent and heal foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32 Suppl 1: 25-36. [26] MUELLER MJ, SINACORE DR, HASTINGS MK, et al. Effect of achilles tendon lengthening on neuropathic plantar ulcers. a randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85(8):1436-1445. [27] ARMSTRONG DG, BOULTON A, BUS SA. Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(24):2367-2375. [28] BUS SA. Priorities in offloading the diabetic foot. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012;28 Suppl 1:54-59. [29] 赵晓明,刘亮,袁启令,等.胫骨横向搬移技术治疗糖尿病足的研究进展[J/OL].中国修复重建外科杂志:1-5[2020-10-26].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1372.R.20200416.1346.016.html. [30] BARKER KL, LAMB SE, SIMPSON AH. Functional recovery in patients with nonunion treated with the Ilizarov technique. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(1): 81-85. [31] GREENMAN RL, PANASYUK S, WANG X, et al. Early changes in the skin microcirculation and muscle metabolism of the diabetic foot. Lancet. 2005;366(9498):1711-1717. [32] ARORA S, POMPOSELLI F, LOGERFO FW, et al. Cutaneous microcirculation in the neuropathic diabetic foot improves significantly but not completely after successful lower extremity revascularization. J Vasc Surg. 2002;35(3):501-505. [33] UCCIOLI L, GANDINI R, GIURATO L, et al. Long-term outcomes of diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia followed in a tertiary referral diabetic foot clinic. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(5):977-982. [34] 镇普祥.横向骨搬移治疗重度糖尿病足疗效与血管再生现象研究[D].桂林:广西医科大学,2019. [35] PATWA JJ, KRISHNAN A. Buerger’s disease (thromboangiitis obliterans)- management by ilizarov’s technique of horizontal distraction. a retrospective study of 60 cases. Indian J Surg. 2011;73(1):40-47. [36] MARWAH V. Management of thromboangiitis obliterans using distraction osteogenesis: a retrospective study. Indian J Orthop. 2012;46(4):490. [37] MARIE PJ, MIRAOUI H, SEVERE N. FGF/FGFR signaling in bone formation: progress and perspectives. Growth Factors. 2012;30(2): 117-123. [38] 任国强,李炳辉,李恭驰,等.糖尿病创面基质金属蛋白酶9对血管内皮生长因子表达的影响[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2017,12(2):123-127. [39] 欧栓机,许长鹏,李贵涛,等.胫骨横向骨搬移对血清血管生成相关因子表达的影响[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2020,34(1):98-101. [40] Gurtner GC, Werner S, Barrandon Y, et al. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008; 453(7193):314-321. [41] 高伟,林震迅,镇普祥,等.胫骨横向骨搬移后巨噬细胞促进重度糖尿病足创面的愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(36):5811-5815. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||