Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (21): 3360-3367.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3870
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect and molecular mechanism of Honeysuckle-Rhizoma coptidis in the treatment of periprosthetic joint infection based on molecular docking and network pharmacology
Zhang Haitao1, Chen Jinlun2, Zhu Xingyang1, Zeng Huiliang3, Li Jie2, Sun Xiaobo1, Qi Xinyu2, Zeng Jianchun2, Zeng Yirong2
- 1First Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 3Foshan Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Foshan 528000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-07-14Revised:2020-07-16Accepted:2020-09-11Online:2021-07-28Published:2021-01-23 -
Contact:Zeng Yirong, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Haitao, Master candidate, First Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Haitao, Chen Jinlun, Zhu Xingyang, Zeng Huiliang, Li Jie, Sun Xiaobo, Qi Xinyu, Zeng Jianchun, Zeng Yirong. Effect and molecular mechanism of Honeysuckle-Rhizoma coptidis in the treatment of periprosthetic joint infection based on molecular docking and network pharmacology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3360-3367.
share this article
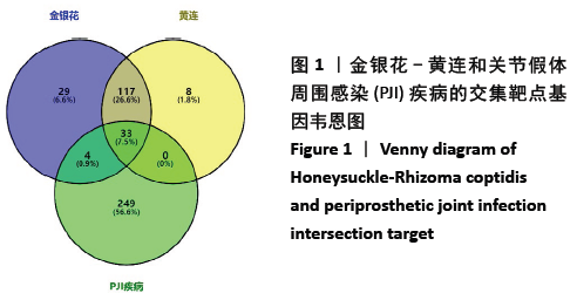
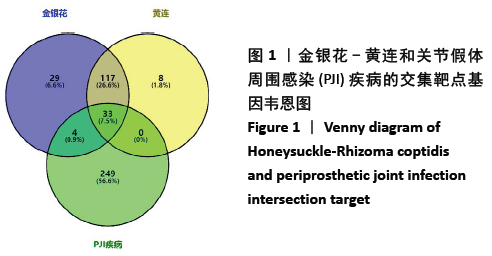
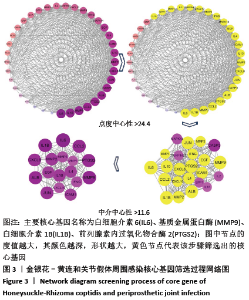
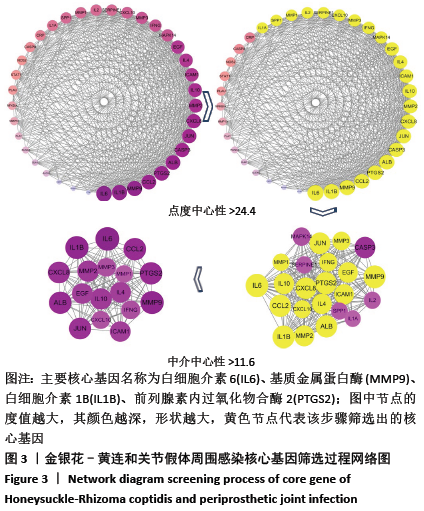
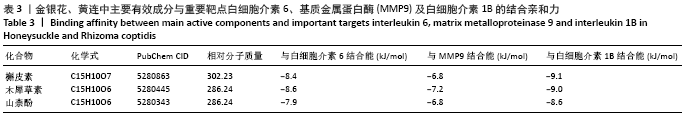
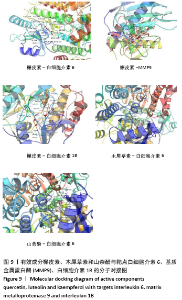
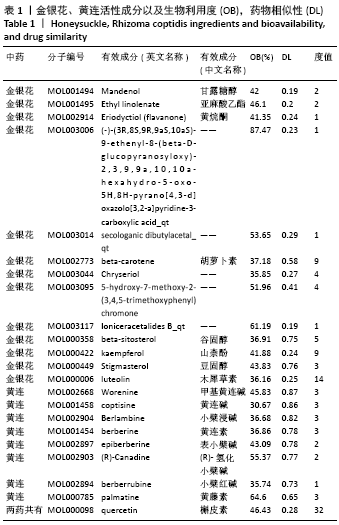
2.1 金银花-黄连有效成分、关节假体周围感染疾病靶点以及交集基因获取结果 通过TCMSP数据库筛选得到金银花治疗关节假体周围感染的有效成分14个,对应靶点183个,黄连治疗关节假体周围感染的有效成分9个,对应靶点158个,两者共同有效成分为槲皮素,共同靶点150个,见表1。通过GeneCards和OMIM数据库共筛选获得关节假体周围感染的疾病靶点共286个。两药对应靶点与关节假体周围感染疾病的靶点取交集后,获得37个交集靶点基因(PTGS1,PTGS2,MMP2,JUN,CASP3,CASP8,MMP1,GJA1,NOS2,STAT1,ICAM1,ALOX5,PLAU,MMP9,白细胞介素10,白细胞介素4,白细胞介素6,白细胞介素2,白细胞介素1B,NFKBIA,IFNG,MMP3,EGF,CCL2,CXCL8,PLAT,SERPINE1,白细胞介素1A,PARP1,CRP,CXCL10,SPP1,RUNX2,CTSD,ALB,MMP10和MAPK14),见图1。 "
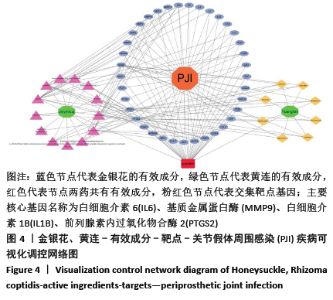
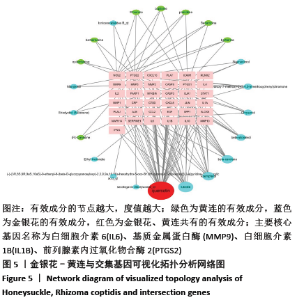
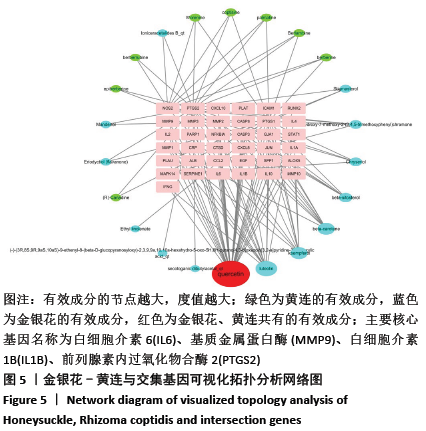
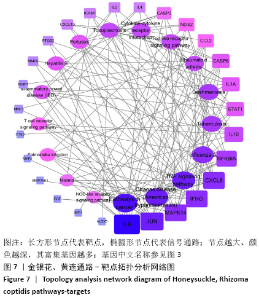
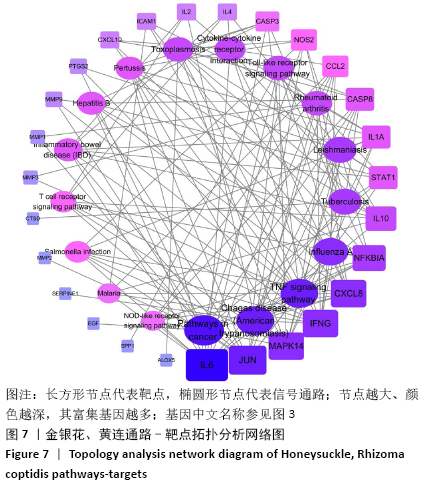
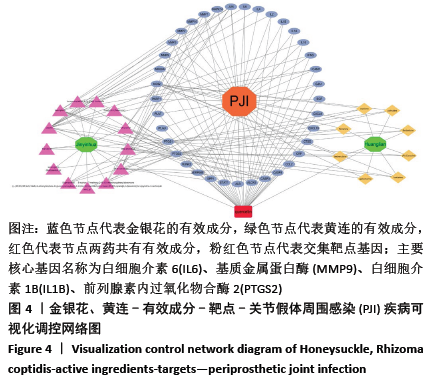
2.3 可视化结构网络的构建 采用Cytoscape 3.7.2软件分别构建了“金银花、黄连-有效成分-交集靶点-关节假体周围感染”可视化调控网络见图4,“有效成分-交集靶点”拓扑分析网络见图5。“金银花、黄连-有效成分-交集靶点-关节假体周围感染”网络中,左侧13个三角形节点为金银花有效成分,右侧8个三角形为黄连有效成分,下方1个长方形红色节点槲皮素为金银花和黄连两药共有成分。图中错综复杂的“边”(连线),体现了金银花和黄连的多种有效成分通过不同的靶点、不同的途径作用于疾病。“有效成分-交集靶点”拓扑分析网络中,蓝色节点代表金银花的有效成分,绿色节点代表黄连的有效成分,红色代表节点两药共有有效成分,粉红色节点代表交集靶点基因,度值大于10以上的有效成分分别是槲皮素为32,木犀草素为14。由此可见,槲皮素在金银花和黄连对治疗关节假体周围感染疾病的作用机制中发挥着举足轻重的作用。 "
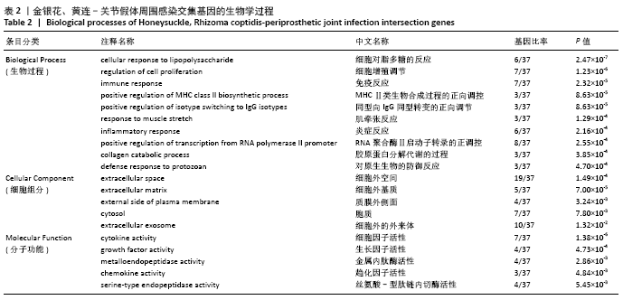
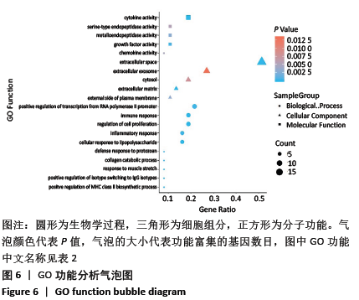
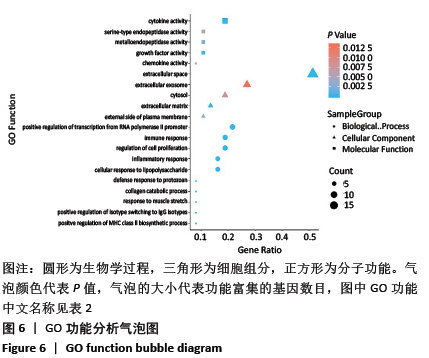
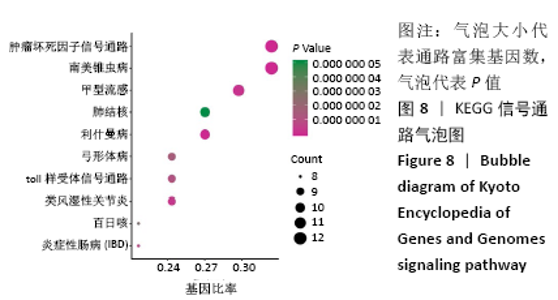
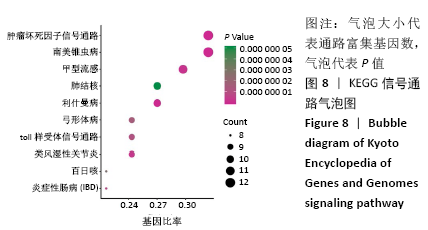
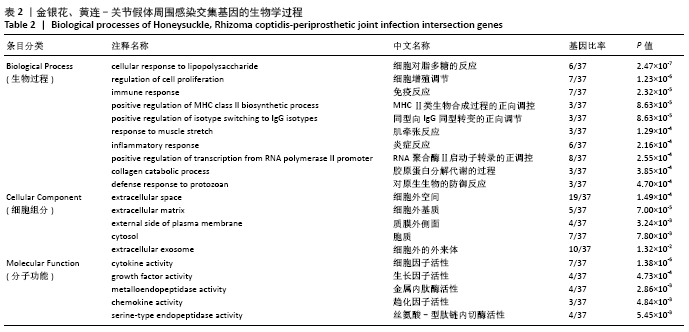
2.4 GO功能富集分析结果 通过DAVID在线工具分析交集靶点基因后,获得按P值升序排列的59个功能富集,其中包括生物过程44个,细胞组分6个,分子功能9个。选取排名前10位的生物过程、排名前5的分子功能、细胞组分制成表格,见表2,并以气泡图的形式直观展示如图6。GO富集分析结果显示,金银花、黄连-关节假体周围感染疾病交集靶基因的生物功能主要包括:细胞对脂多糖的反应、细胞增殖调节、免疫反应、MHC Ⅱ类生物合成过程的正向调控、同型向IgG同型转变的正向调节、肌牵张反应、炎症反应、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ启动子转录的正调控、胶原蛋白分解代谢的过程、对原生生物的防御反应等;细胞组分主要包括:细胞外空间、细胞外基质、质膜外侧面、胞质和细胞外的外来体;分子功能主要为细胞因子活性、生长因子活性、金属内肽酶活性、趋化因子活性及丝氨酸-型肽链内切酶活性等。 "
| [1] KAPADIA BH, BERG RA, DALEY JA, et al. Periprosthetic joint infection. Lancet. 2016;387(10016):386-394. [2] PARVIZI J, ZMISTOWSKI B, ADELI B. Periprosthetic joint infection: treatment options. Orthopedics. 2010;33(9):659. [3] 李兆合.五味消毒饮治疗关节置换术后金黄色葡萄球菌感染机理窥探[J].中医学报,2012,27(5):613-614. [4] 吴娇,王聪,海川.金银花中的化学成分及其药理作用研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(4):225-234. [5] 庄丽,张超,阿里穆斯.金银花的药理作用与临床应用研究进展[J].辽宁中医杂志,2013,40(2):378-380. [6] SI L, LI P, LIU X, et al. Chinese herb medicine against Sortase A catalyzed transformations, a key role in gram-positive bacterial infection progress. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016;31(sup1):184-196. [7] LI X, MOTWANI M, TONG W, et al. Huanglian, a Chinese herbal extract, inhibits cell growth by suppressing the expression of cyclin B1 and inhibiting CDC2 kinase activity in human cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;58(6):1287-1293. [8] 盖晓红,刘素香,任涛.黄连的化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J].中草药,2018,20(49):4919. [9] 王清,朱萱萱,张赤兵,等.金银花提取物抗菌作用的实验研究[J].中国医药导刊,2008,10(9):1428-1430. [10] 张庆莲,黄娟,邵单炫,等.黄连抗菌作用研究进展[J].中医药信息, 2019;36(5):125-127. [11] 徐森楠,庄莉,翟园园,等.基于网络药理学研究二至丸防治骨质疏松症的物质基础与作用机制[J].中国药学杂志,2018,53(22): 1913-1920. [12] RICCIARDI BF, MUTHUKRISHNAN G, MASTERS EA, et al. New developments and future challenges in prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of prosthetic joint infection. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(7): 1423-1435. [13] SONG Z, BORGWARDT L, HØIBY N, et al. Prosthesis infections after orthopedic joint replacement: the possible role of bacterial biofilms. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2013;5(2):65-71. [14] Memariani H, Memariani M, Ghasemian A. An overview on anti-biofilm properties of quercetin against bacterial pathogens. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019;35(9):143. [15] Lv PC, Li HQ, Xue JY, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel luteolin derivatives as antibacterial agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2009;44(2):908-914. [16] Wang Q, Xie M. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of luteolin on Staphylococcus aureus. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2010;50(9):1180-1184. [17] Liu MH, Otsuka N, Noyori K, et al. Synergistic effect of kaempferol glycosides purified from Laurus nobilis and fluoroquinolones on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009; 32(3):489-492. [18] García-Mediavilla V, Crespo I, Collado PS, et al. The anti-inflammatory flavones quercetin and kaempferol cause inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and reactive C-protein, and down-regulation of the nuclear factor kappaB pathway in Chang Liver cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;557(2-3):221-229. [19] Tan J, Wang J, Yang C, et al. Antimicrobial characteristics of Berberine against prosthetic joint infection-related Staphylococcus aureus of different multi-locus sequence types. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19(1):218. [20] Xie Y, Liu X, Zhou P. In vitro antifungal effects of berberine against candida spp. in planktonic and biofilm conditions. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:87-101. [21] Lenski M, Scherer MA. Synovial IL-6 as inflammatory marker in periprosthetic joint infections. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(6):1105-1109. [22] Lee S, Kim B, Choi W, et al. Lack of association between pro-inflammatory genotypes of the interleukin-1 (IL-1B-31 C/+ and IL-1RN* 2/* 2) and gastric cancer/duodenal ulcer in Korean population. Cytokine. 2003;21(4):167-171. [23] Quiney C, Billard C, Mirshahi P, et al. Hyperforin inhibits MMP-9 secretion by B-CLL cells and microtubule formation by endothelial cells. Leukemia. 2006;20(4):583-589. [24] Sharma K, Ivy M, Block DR, et al. Comparative analysis of 23 synovial fluid biomarkers for hip and knee periprosthetic joint infection detection. J Orthop Res. 2020. doi: 10.1002/jor.24766. [25] Ackmann T, Möllenbeck B, Gosheger G, et al. Comparing the diagnostic value of serum D-Dimer to CRP and IL-6 in the diagnosis of chronic prosthetic joint infection. J Clin Med. 2020;9(9):E2917. [26] Rosenfeld Y, Shai Y. Lipopolysaccharide (Endotoxin)-host defense antibacterial peptides interactions: role in bacterial resistance and prevention of sepsis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1758(9):1513-1522. [27] Covre LP, Devine OP, Garcia de Moura R, et al. Compartmentalized cytotoxic immune response leads to distinct pathogenic roles of natural killer and senescent CD8+ T cells in human cutaneous leishmaniasis. Immunology. 2020;159(4):429-440. [28] Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes F, Adib-Conquy M, Cavaillon J. Natural killer (NK) cells in antibacterial innate immunity: angels or devils? Mol Med. 2012;18(2):270-285. [29] Maini RN, Taylor PC. Anti-cytokine therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rev Med. 2000;51(1):207-229. [30] Neurath MF. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(5):329-342. [31] Caradonna L, Amati L, Lella P, et al. Phagocytosis, killing, lymphocyte-mediated antibacterial activity, serum autoantibodies, and plasma endotoxins in inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95(6):1495-1502. [32] Ellerin T, Rubin RH, Weinblatt ME. Infections and anti–tumor necrosis factor α therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(11):3013-3022. [33] Galliera E, Drago L, Vassena C, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 in serum: a potential diagnostic marker of prosthetic joint infection? J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52(2):620-623. [34] Knapp S. Update on the role of Toll-like receptors during bacterial infections and sepsis. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2010;160(5-6):107-111. [35] Koc M, Toprak A, Arikan H, et al. Toll-like receptor expression in monocytes in patients with chronic kidney disease and haemodialysis: relation with inflammation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(3): 955-963. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [6] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [7] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [8] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [9] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [10] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [11] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [12] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [13] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [14] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [15] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||