Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (27): 4294-4299.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.27.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analgesic effect of transcutaneous electrical stimulation at the auricular Shenmen (H 7) point after total knee arthroplasty
Si Jian-luo, Yang Mu-qiang, Sima Liang-jie, Han Xue-chang, Ren Yan-yan
- Department of Anesthesiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Science and Technology & Clinical Medical College of Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471003, Henan Province, China
-
Online:2017-09-28Published:2017-10-24 -
Contact:Si Jian-luo, Department of Anesthesiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Science and Technology & Clinical Medical College of Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471003, Henan Province, China -
About author:Si Jian-luo, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Anesthesiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Science and Technology & Clinical Medical College of Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471003, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Si Jian-luo, Yang Mu-qiang, Sima Liang-jie, Han Xue-chang, Ren Yan-yan. Analgesic effect of transcutaneous electrical stimulation at the auricular Shenmen (H 7) point after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(27): 4294-4299.
share this article
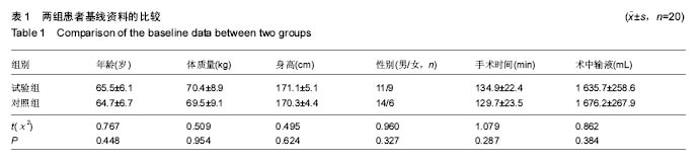
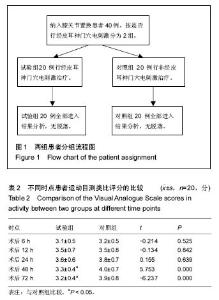
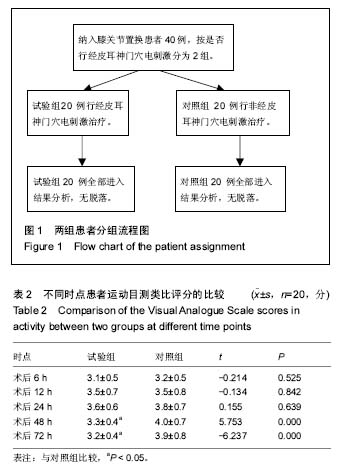
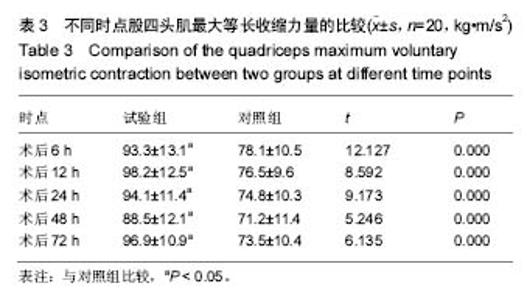
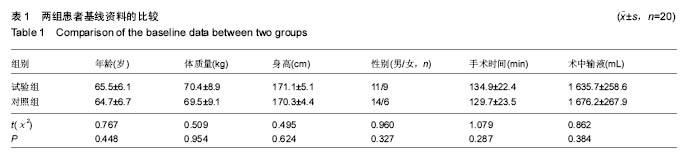
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理,所有纳入的40例患者均顺利完成手术,全部进入结果分析,无脱落。分组流程图见图1。 2.2 基线资料比较 2组患者的基线资料如年龄、体质量、性别构成、手术时间等比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性,见表1。 2.3 两组患者观察指标的比较 与对照组比较,试验组在术后48 h和72 h时运动目测类比评分小于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2。 对照组各时点的股四头肌最大等长收缩的力量均显著低于试验组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表3。 对照组股神经阻滞罗哌卡因的用量(495.7±39.4) mL明显多于试验组(394.5±27.1) mL,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);对照组有7例患者术后注射盐酸曲马多,试验组有1例注射盐酸曲马多,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.4 不良事件 对照组有6例发生恶心呕吐,试验组有1例发生恶心呕吐;对照组有4例头晕,试验组无头晕病例;差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)"
| [1] 王宁华,谢斌,魏星,等. 全膝关节置换术后经皮神经电刺激即刻镇痛的临床对照研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2005,20(3):188-190.[2] 周曙,丁云霞. TEAS对老年全髋置换手术后静脉自控镇痛患者应激反应的影响[J].重庆医学,2015,44(24):3352-3354.[3] Shanthanna H, Huilgol M,ManivackamVK, et al.Comparative study of ultrasound-guided continuous femoral nerve blockade with continuous epidural analgesia for pain relief following total knee replacement.Indian J Anaesth. 2012; 56(3):270-275.[4] 王宇,朱云章,刘刚.高龄患者髋、膝关节置换中罗哌卡因腰椎硬膜外麻醉的镇痛效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(13): 1990-1994.[5] 王怀江,张大志,李世忠.连续股神经阻滞镇痛与静脉镇痛在全膝关节置换术后镇痛效果的比较[J].中华医学杂志,2010,90(33): 2360-2362.[6] 汪涛,何开华.全膝关节置换后连续股神经阻滞镇痛:超声引导下的进针技术与穿刺针选择[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(13): 2005-2010.[7] 蒋嘉,温洪,周权,等.不同镇痛方法对膝关节置换术术后疼痛和功能恢复的影响[J] .临床麻醉学杂志,2014, 30(5):437-440[8] 辛玲,冯艺.收肌管阻滞用于全膝关节置换术后镇痛的研究进展[J] .临床麻醉学杂志,2016,32(6):613-615.[9] 王荣国,齐敦益.膝关节置换后镇痛方案的选择与安全性评价[J] .中国组织工程研究,2015,19(39):6256-6261.[10] 林子洪,王海兴,陈桂浩,等.塞来昔布对膝关节表面置换患者的预防性镇痛[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(48):8307-8312.[11] 刘冰山,李国军,王晓,等.全膝关节置换后的多模式镇痛[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(22):4005-4012.[12] 陆慧红,李贵凤,白浪,等. 全膝关节置换后局部浸润的持续镇痛效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,18(4):529-534.[13] 徐峰,杨玉珍,郝杰.髋膝关节置换后塞来昔布的多模式镇痛[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(44):7065-7070.[14] 孙扬,杨明敏,李亦梅.人工全膝关节置换围术期镇痛方法:多模式方案及最佳疼痛管理[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(44): 7188-7193.[15] Tucker transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)alleviate the pain experienced during bone marrow sampling in addition to standard techniques?a randomised, double-blinded, controlled trial. J Clin Pathol.2015;68(6): 479-483.[16] Huang X,Pan F,Zhao W.Impacts of the transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation on EC50 in the remifentanil inhibition of tracheal intubation response.Zhongguo Zhen Jiu.2015;35(8):812-815.[17] Gao J,Li Y.Multiple functions of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in peri-anesthesia period.Zhongguo Zhen Jiu.2015;35(3):269-273.[18] Yan YN,Li YL,Wang MX.The anesthesiologic value of transcutaneous acupoint electrical stimulation combined with general intravenous anesthesia in endoscopic thyroidectomy patients:a clinical study.Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.2014;34(5):545-548.[19] 周曙,罗富荣,丁云霞.经皮穴位电刺激辅助老年全髋置换手术后自控静脉镇痛临床研究[J].实用中医药杂志,2015,31(5):369-370.[20] 肖欢,汪建胜,孔建强,等.经皮神经电刺激联合硬膜外分娩镇痛的临床研究[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2014,30(8):745-747.[21] 彭文平,黄舜,梁汉生,等.经皮电刺激不同穴位对胸腔镜肺叶切除术患者术中阿片类药物节俭作用的比较[J].中华麻醉学杂志, 2014, 34(1):62-64.[22] Wetzel B, Pavlovic D,Kuse R,et al.The effect of auricular acupuncture on fentanyl requirement during hip arthroplasty :a randomized controlled trial. Clin J Pain. 2011;27(3):262-267.[23] 李井柱,李晓征,王明山,等.经皮电刺激耳神门穴对剖宫产术后恶心呕吐发生率及镇痛效果的影响[J].中华医学杂志, 2012, 92(27):1892-1895.[24] 胡先华,谢亚宁,路志红,等.经皮穴位电刺激镇痛在乳腺癌根治术中的应用[J].中国现代医药杂志,2014,16(8):13-16.[25] Mello LF, Nobrega LF, Lemos A, et al.Transcutaneous electrical stimulation for pain relief during labor:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Bras Fisioter. 2011;15(3): 175-184.[26] Xiang XH , Chen YM, Zhang JM,et al. Low-and high-frequency transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation induces different effects on cerebral μ-opioid receptor availability in rhesus monkeys .J Neurosci Res. 2014; 92(5): 555-563.[27] Chen CC, Johnson MI. An investigation into the hypoalgesic effects of high-and low-frequency transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation(TENS) on experimentally-induced blunt pressure pain in healthy human participants . J Pain. 2010; 11(1):53-61.[28] Han JS.Acupuncture: neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies. Trends Neurosci. 2003;26(1):17-22.[29] King EW, Audette K, Athman GA, et al.Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation activates peripherally located alpha-2A adrenergic receptors. Pain. 2005;115(3):364-373.[30] 张克亮,张东,凌彤,等.经皮电刺激对端侧缝合后神经再生作用的研究[J].中华手外科杂志,2001,17(1):45-47.[31] 宋莉,刘慧,王泉云.经皮神经电刺激(TENS)的研究新进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2006,12(5):300-302.[32] 张磊,罗芳,李欢冬,等.丘脑在经皮穴位电刺激镇痛效果中的作用[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2011,17(11):1039-1043.[33] 耿跃华,徐贵芝,于洪丽,等.磁刺激神门穴脑电信号诱发电位分析及源定位[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(22): 4027-4031.[34] Meng X, Zhang Y, Li A,et al.The effects of opioid receptor antagonists on electroacupuncture-produced anti-allodynia/hyperalgesia in rats with paclitaxel-evoked peripheral neuropathy. Brain Res. 2011;14(14):58-65.[35] 孙瑞卿,王贺春,王韵,等. 不同频率的电针对大鼠神经源性痛的治疗作用[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2002, 18(2):128-130.[36] 丁翔,张屹,邓桢翰,等.经皮神经电刺激治疗膝骨关节炎性疼痛的荟萃分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(11):1798-1804.[37] Leung A,Shukla S,Lee J,et al.Effect of low frequency transcutaneous magnetic stimulation on sensory and motor transmission.Bioelctromagnetics.2015;36(6):410-419.[38] Tanaka K,Ikeuchi M,Izumi M,et al.Effects of two different intensities of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on pain thresholds of contralateral muscles in healthy subjects.J Phys Ther Sci.2015;27(9):2771-2774[39] 章权,章建华,童培建.经皮神经电刺激在全膝关节置换术后多模式镇痛中的应用研究[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(4):283-286.[40] Grech D,Li Z,Morcillo P,et al. Intraoperative low-frequency electroacupuncyure under general anesthesia improves postoperative recovery in a randomized trial.J Acupunct Meridian Stud.2016;9(5):234-241.[41] 赵夏洁,尹金玲,李航兵,等.经皮神经电刺激的镇痛作用机制及最新研究进展[J].实用医学杂志,2015,31(21):3480-3482.[42] 杨博,招伟贤,廖敏,等.静脉全麻中经皮穴位电刺激的镇痛效应测定[J]. 广东医学,2008,29(8):1261-1262.[43] Yu X,Zhang F,Chen B.Effect of transcutaneous electrical acupuncture point stimulation at different frequencies in a rat model of neuropathic pain.Acupunct Med.2017;35(2): 142-147.[44] Sluka KA, Bailey K,Bogush J,et al.Treatment with either high or low frequency TENS reduces the secondary hyperalgesia observed after injection of kaolin and carrageenan into the knee joint.Pain.1998;77(1):97-102.[45] 于晖,何苗,阎学梅,等. 不同时程经皮穴位电刺激对胸腔镜肺叶切除术中患者阿片类药物的节俭作用[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2015, 35(5):571-573.[46] Cherian JJ,Kapadia BH,Bhave A,et al.Use of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation device in early osteoarthritis of the knee.J Knee Surg.2015;28(4):321-327.[47] Jutzeler CR,Curt A,Kramer JL.Effectiveness of high-frequency electrical stimulation following sensitization with capsaicin.J Pain.2015;16(7):595-605.[48] Yokoyama LM,Pires LA,Ferreira EA,et al.Low-and high-frequency transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation have no deleterious or teratogenic effects on pregnant mice. Physiotherapy.2015;101(2):214-218.[49] Sun X,Wei ZR,Xiao Z.Analgesic effect and related mechanism of peripheral acupoints electroacupuncture on superficial partial-thickness burn rats.Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi.2017;33(3):160-165.[50] 袁志民,魏建仝,温景荣,等.全膝关节置换后持续股神经阻滞与持续硬膜外镇痛的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(35): 5728-5734.[51] 朱诗白,翟洁,蒋超,等.膝关节置换围术期的快速康复措施[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(3):456-463.[52] 刘福存,童培建,储小兵,等.快速康复全膝关节置换的临床结果[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(18):1185-1190.[53] Gladwell PW,Badlan K, Cramp F, et al.Direct and indirect benefits reported by users of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for chronic musculoskeletal pain :qualitative exploration using patient interviews. Phys Ther.2015;95(11): 1518-1528.[54] Baki ED,Öz G,Kokulu S,et al.Comparison of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and paravertebral block for postthoracotomy pain relief.Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2015; 63(6):514-518.[55] Sezen CB,Akboga SA,Celik A,et al.Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation effect on postoperative complications.Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann.2017;25(4):276-280. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [3] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [4] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [5] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [6] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [7] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [8] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [9] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [10] | Shao Yangyang, Zhang Junxia, Jiang Meijiao, Liu Zelong, Gao Kun, Yu Shuhan. Kinematics characteristics of lower limb joints of young men running wearing knee pads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 832-837. |
| [11] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [12] | Yuan Jing, Sun Xiaohu, Chen Hui, Qiao Yongjie, Wang Lixin. Digital measurement and analysis of the distal femur in adults with secondary knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 881-885. |
| [13] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [14] | Yang Yang, Li Naxi, Zhang Jian, Wang Mian, Gong Taifang, Gu Liuwei. Effect of tourniquet combined with exsanguination band use on short-term lower extremity venous thrombosis after knee arthroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 898-903. |
| [15] | Yang Kuangyang, Wang Changbing. MRI evaluation of graft maturity and knee function after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with autogenous bone-patellar tendon-bone and quadriceps tendon [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 963-968. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||