Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (24): 3881-3887.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.24.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
A modified rabbit model of gouty knee arthritis
Li Qi, Chen Xu-xu, Li Jian
- Orthopedic Sports Medicine Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Revised:2017-06-01Online:2017-08-28Published:2017-08-30 -
Contact:Li Qi, Orthopedic Sports Medicine Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Li Qi, M.D., Attending physician, Orthopedic Sports Medicine Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Program of Science & Technology Department of Sichuan Province, No. 2013SZ0019
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Qi, Chen Xu-xu, Li Jian. A modified rabbit model of gouty knee arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(24): 3881-3887.
share this article
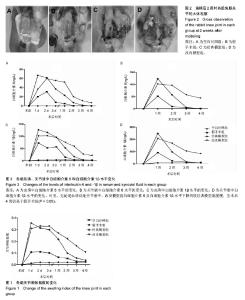
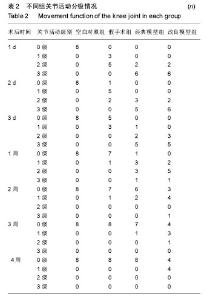
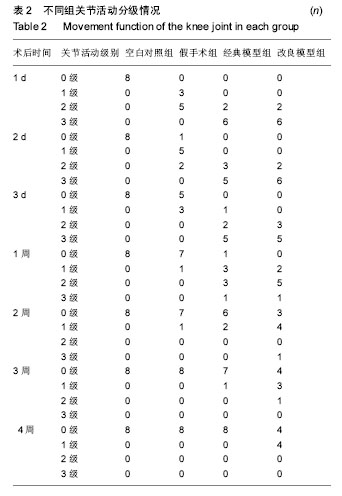
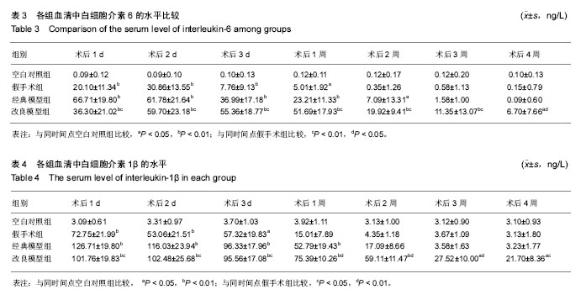
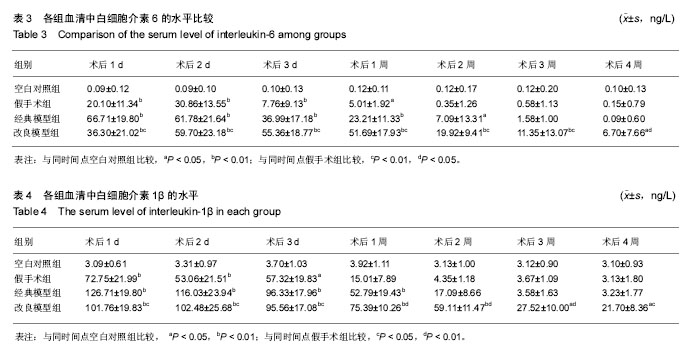
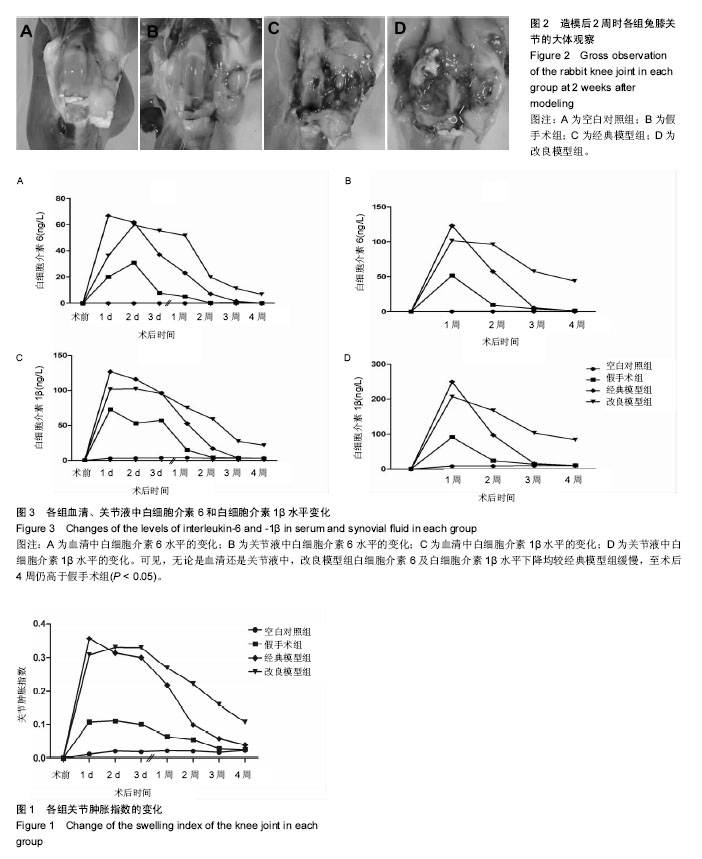
2.3 关节肿胀指数 术后各个组关节肿胀指数的随时间的变化见图1。可以看出,经典模型组和改良模型组术后关节肿胀指数立即增高,在术后第1或2天达到高峰,其后均开始下降,经典模型组下降较迅速,于术后第3周时已趋于正常,与空白对照组相比无明显差异(P=0.371);而改良模型组下降较缓慢,术后第4周时与空白对照组相比存在显著性差异(P=0.017)。与空白对照组相比,经典模型组(P=0.007)和改良模型组(P=0.001)关节肿胀指数的整体变化趋势均有显著性差异。在术后2周内经典模型组的关节肿胀指数均显著性高于空白对照组,而改良模型组在术后4周内均高,且差异有统计学意义。 假手术组,关节肿胀指数在术后1-3 d内亦有轻度的增高,但是到术后1周时基本趋于正常,整体变化趋势与空白对照组相比无显著性差异(P=0.122)。 改良模型组与假手术组相比,关节肿胀指数的整体变化趋势存在显著性差异(P=0.030),在术后4周内改良模型组均显著性高于假手术组。 2.4 大体观察 术后2周时,4组兔膝关节病理学改变大体情况可见图2。改良模型组和经典模型组均呈现出明显的关节炎症改变:滑膜广泛增生,较肥厚,伴充血水肿;关节腔内有较多量关节液形成;周围组织充血水肿;软骨未见明显破坏。此外,改良模型组关节内可见较多量的尿酸盐结晶,被增生的滑膜组织所包裹(图2D);经典模型组关节滑膜内亦可见散在的尿酸盐结晶(图2C),但总量与改良组相比明显较少。 2.5 血清、关节液中白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1β的水平 2.5.1 血清、关节液中白细胞介素6 4组间不同时间点血清中白细胞介素6的水平见表3。图3A显示术后各组血清中白细胞介素6水平随时间的变化。可以看出,经典模型组和改良模型组术后血清白细胞介素6水平立即增高,分别在术后第1和第2天达到高峰,其后均开始下降,经典模型组下降较迅速,于术后第3周时已趋于正常;而改良模型组下降较缓慢,术后第3和4周时与经典模型组相比存在显著性差异(分别为P=0.041和P=0.005)。与空白对照组相比,经典模型组(P=0.013)和改良模型组(P=0.027)血清白细胞介素6水平的整体变化趋势均有显著性差异。在术后4周内改良模型组的白细胞介素6水平均显著性高于空白对照组。假手术组,血清白细胞介素6水平在术后1-3 d内亦有轻度的增高,但是到术后1周时基本趋于正常,整体变化趋势与空白对照组相比无显著性差异(P=0.078)。改良模型组与假手术组相比,血清白细胞介素6水平的整体变化趋势存在显著性差异(P=0.040),在术后4周内各个时间点改良模型组均显著性高于假手术组。 图3B显示术后各个组关节液中白细胞介素6水平随时间的变化。可以看出,经典模型组和改良模型组术后1周时关节液白细胞介素6水平较高,其后均开始下降,经典模型组下降较迅速,于术后第3周时已趋于正常;而改良模型组下降较缓慢,术后第4周时与空白对照组相比亦然存在显著性差异(P=0.010)。在术后4周内改良模型组的白细胞介素6水平均显著性高于空白对照组。假手术组,关节液白细胞介素6水平在术后2周内亦显著性增高,但是到术后3周时基本趋于正常,整体变化趋势与空白对照组相比无显著性差异(P=0.193)。改良模型组与假手术组相比,关节液白细胞介素6水平的整体变化趋势存在显著性差异(P=0.032),在术后4周内各个时间点改良模型组均显著性高于假手术组。 2.5.2 血清、关节液中白细胞介素1β的水平 4组间不同时间点血清中白细胞介素1β水平的情况见表4。图3C显示术后各个组血清中白细胞介素1β水平的随时间的变化。可以看出,经典模型组和改良模型组术后血清白细胞介素1β水平立即增高,分别在术后第1和第2天达到高峰,其后均开始下降,经典模型组下降较迅速,于术后第3周时已趋于正常;而改良模型组下降较缓慢,术后第3和第4周时与经典模型组相比差异存在显著性意义(分别为P=0.037和P=0.027)。与空白对照组相比,经典模型组(P=0.010)和改良模型组(P=0.022)血清白细胞介素1β水平的整体变化趋势均有显著性差异。在术后4周内改良模型组的白细胞介素1β水平均显著性高于空白对照组。假手术组,血清白细胞介素1β水平在术后1-3 d内亦有轻度的增高,但是到术后1周时基本趋于正常。改良模型组与假手术组相比,血清白细胞介素1β水平的整体变化趋势存在显著性差异(P=0.039),在术后4周内各个时间点改良模型组均显著性高于假手术组。 图3D显示术后各个组关节液中白细胞介素1β水平的随时间的变化。可以看出,经典模型组和改良模型组术后1周时关节液白细胞介素1β水平较高,其后均开始下降,经典模型组下降较迅速,于术后第3周时已趋于正常;而改良模型组下降较缓慢,术后第3和第4周时与经典模型组相比存在显著性差异(分别为P=0.043和P=0.016)。在术后4周内改良模型组的白细胞介素1β水平均显著性高于空白对照组。假手术组,关节液白细胞介素1β水平在术后1周内亦显著性增高,但是到术后2周时基本趋于正常,整体变化趋势与空白对照组相比无显著性差异(P=0.087)。改良模型组与假手术组相比,关节液白细胞介素1β水平的整体变化趋势存在显著性差异(P=0.029),在术后4周内各个时间点改良模型组均显著性高于假手术组。"
| [1] Cronstein BN, Sunkureddi P. Mechanistic aspects of inflammation and clinical management of inflammation in acute gouty arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2013; 19(1): 19-29.[2] Chandratre P, Roddy E, Clarson L, et al. Health-related quality of life in gout: a systematic review. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013; 52(11): 2031-2040.[3] 钱伯初,史红,郑晓亮.尿酸钠结晶诱导痛风性关节炎动物模型研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志, 2008,18(6): 65-69.[4] Coderre TJ, Wall PD. Ankle joint urate arthritis (AJUA) in rats: an alternative animal model of arthritis to that produced by Freund's adjuvant. Pain. 1987; 28(3): 379-393.[5] Coderre TJ,Wall PD. Ankle joint urate arthritis in rats provides a useful tool for the evaluation of analgesic and anti-arthritic agents. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1988;29(3):461-466.[6] 秦川.人类疾病动物模型是医药创新研究的前沿[J].中国比较医学杂志,2011,21(10): 13-14.[7] 姚丽,刘树民,于书仪.痛风性关节炎动物模型的改良[J].中国实验动物学报,2009,17(03): 210-212.[8] Wu X, Wakamiya M, Vaishnav S, et al. Hyperuricemia and urate nephropathy in urate oxidase-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994; 91(2): 742–746.[9] 赵璐,孙俊波,魏桂梅.MRP8通过 NF-κB信号通路调控痛风细胞模型中IL-1β的表达[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2015,6:44-47.[10] Miguelez, R, Palacios I, Navarro F, et al., Anti-inflammatory effect of a PAF receptor antagonist and a new molecule with antiproteinase activity in an experimental model of acute urate crystal arthritis. J Lipid Mediat Cell Signal.1996;13(1): 35-49.[11] Ryckman, C, McColl S, Vandal K, et al. Role of S100A8 and S100A9 in neutrophil recruitment in response to monosodium urate monohydrate crystals in the air-pouch model of acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48(8): 2310-2320.[12] Dong J, Han QF, Zhu TY, et al. The associations of uric acid, cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in peritoneal dialysis patients. PLoS One. 2014; 9(1): e82342.[13] Xia X, Zhao C, Peng FF, et al. Serum uric acid predicts cardiovascular mortality in male peritoneal dialysis patients with diabetes. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2016;26(1):20-26.[14] Takahashi M. Inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Nihon Rinsho.2011;69(1):30-33.[15] Terkeltaub R, Sundy JS, Schumacher HR, et al. The interleukin 1 inhibitor rilonacept in treatment of chronic gouty arthritis: results of a placebo-controlled, monosequence crossover, non-randomised, single-blind pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68(10): 1613-1617.[16] Jasvinder A. Singh, MBBS, MPH. Racial and gender disparities in patients with gout. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013; 15(2): 307.[17] Bolzetta F, Veronese N, Manzato E, et al. Chronic gout in the elderly. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2013;25(2):129-137 .[18] 杨玲玲,黄丽贞,邓家刚.痛风性关节炎动物模型研究进展[J].世界中医药,2015 ,10(9) :1461-1467.[19] 李泽,张记恩,荣俊.痛风性关节炎动物模型制备的研究[J].长江大学学报(自科版),2013,10(15):9-12.[20] 谭秋薇,林燕.痛风性关节炎模型研究概况(J).实用中医内科杂志,2008,22(2):79-80.[21] 郭玉星,熊辉,陆小龙,等.改良痛风性关节炎大鼠模型的复制[J].云南中医学院学报,2017,40(2):18-23.[22] Hershfield MS, Ganson NJ, Kelly SJ, et al. Induced and pre-existing anti-polyethylene glycol antibody in a trial of every 3-week dosing of pegloticase for refractory gout, including in organ transplant recipients. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014; 16(2): R63.[23] Christen P, Peacock W C, Christen A E, et al. Urate oxidase in primate phylogenesis. Eur J Biochem. 1970; 12(1): 3-5.[24] Wu XW, Muzny DM, Cheng CL, et al. Two independent mutational events in the loss of urate oxidase during hominoid evolution. J Mol Evol. 1992;34(1): 78-84.[25] Fleischmann R, Kerr B, Yeh LT, et al. Pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic and tolerability evaluation of concomitant administration of lesinurad and febuxostat in gout patients with hyperuricaemia. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53(12): 2167-2174.[26] Lipsky PE, Calabrese LH, Kavanaugh A, et al. Pegloticase immunogenicity: the relationship between efficacy and antibody development in patients treated for refractory chronic gout. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014; 16(2): R60.[27] Singh JA. Emerging therapies for gout. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2012;17 (4): 511-518.[28] Gerwin N, Hops C, Lucke A.Intraarticular drug delivery in osteoarthritis.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006; 58(2): 226-242.[29] 王碧.胶原材料在药物缓释和组织工程中的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2004,18(2): 112-114. |
| [1] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [2] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [3] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [4] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [5] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [6] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [7] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [8] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [9] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [10] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [11] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [12] | Liu Jin, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin, Wang Ze, Zhao Caihong, Lu Wenjing. Ermiao san aqueous extract regulates proliferation, migration, and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synovial cells in collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 688-693. |
| [13] | Zhao Yuwei, Gao Yuting, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin . Mechanism of Ermiao San in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 742-748. |
| [14] | Xu Lei, Han Xiaoqiang, Zhang Jintao, Sun Haibiao. Hyaluronic acid around articular chondrocytes: production, transformation and function characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 768-773. |
| [15] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||