Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (32): 4731-4737.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.32.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Curcumin effect on proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer stem cells via ATK/FoxM1 signaling pathway
He Dong-li
- Department of Gastroenterology, Nanyang Central Hospital, Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2016-06-19Online:2016-08-05Published:2016-08-05 -
About author:He Dong-li, Master, Attending physician, Department of Gastroenterology, Nanyang Central Hospital, Nanyang 473000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Dong-li. Curcumin effect on proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer stem cells via ATK/FoxM1 signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(32): 4731-4737.
share this article
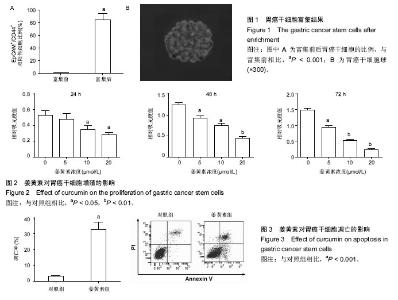
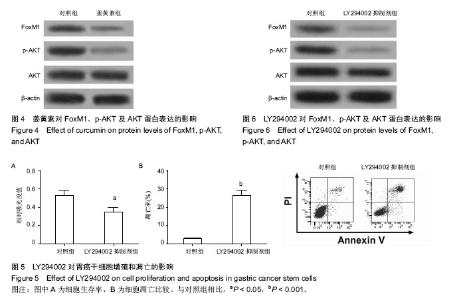
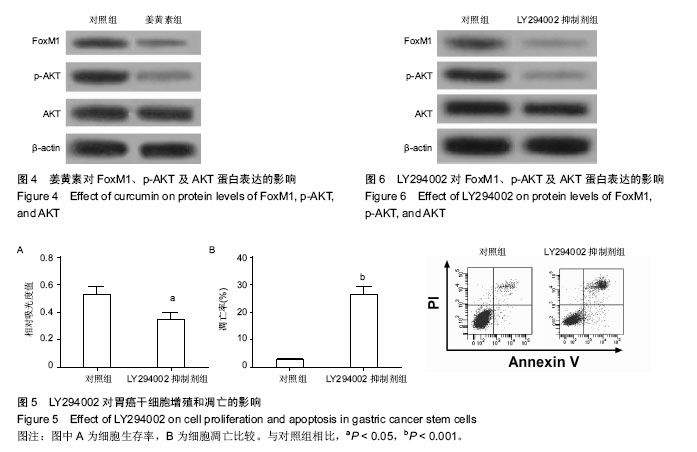
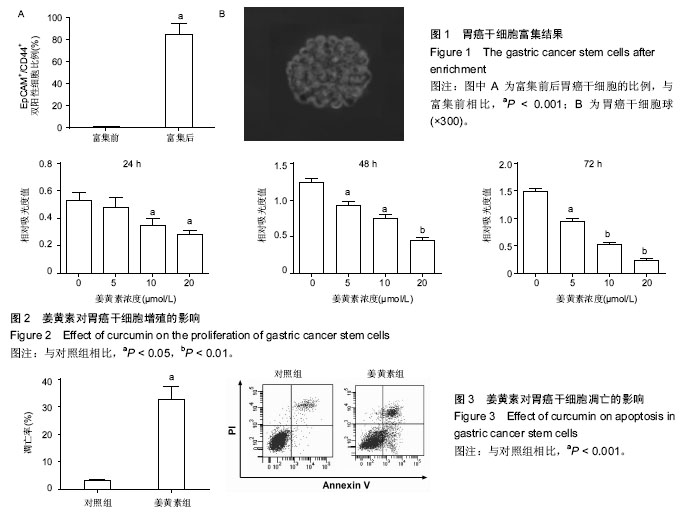
2.1 胃癌SGC7901干细胞富集结果 流式细胞术检测结果显示(图1A),在胃癌干细胞富集培养前SGC7901细胞中表达EpCAM+/CD44+双阳性细胞的比例为0.9%,富集培养后双阳性细胞的比例为85%。图1B展示了分离到的胃癌干细胞球。 2.2 姜黄素对胃癌干细胞增殖的影响 用不同浓度姜黄素(5,10,20 μmol/L)处理胃癌SGC7901干细胞24,48,72 h。MTT实验结果显示,随着药物浓度的增大,其对细胞的抑制作用增强,且随着时间的延长,药物对细胞的抑制作用也呈上升趋势,见图2。可以推测,姜黄素对胃癌干细胞增殖的抑制具有剂量和时间依赖性。 2.3 姜黄素对胃癌干细胞凋亡的影响 使用15 μmol/L姜黄素处理胃癌干细胞48 h后收集细胞,流式细胞仪检测细胞的凋亡情况。结果显示,与对照组相比,15 μmol/L姜黄素组胃癌干细胞凋亡数明显增多,差异有显著性意义(图3)。 2.4 姜黄素对胃癌干细胞中FoxM1、p-AKT及AKT蛋白表达的影响 胃癌干细胞经15 μmol/L姜黄素处理48 h后,Western blot检测细胞内FoxM1、p-AKT及AKT的蛋白表达情况。结果显示,与对照组相比,姜黄素处理组中p-AKT及FoxM1的蛋白表达水平明显降低(图4)。 2.5 LY294002对胃癌干细胞增殖和凋亡的影响 使用AKT信号通路阻断剂LY294002处理胃癌干细胞24 h后,MTT实验检测细胞的增殖和凋亡情况。结果显示,阻断剂处理后,细胞的生存率明显低于对照组(图5A)。细胞凋亡检测结果显示,与对照组相比,阻断剂明显诱导了胃癌干细胞的凋亡(图5B)。2.6 LY294002对FoxM1、p-AKT及AKT蛋白表达的影响 Western blot检测结果显示使用阻断剂处理胃癌干细胞后,与对照组相比,FoxM1及p-AKT的蛋白表达水平明显降低(图6)。可以推测,AKT信号通路的失活降低了FoxM1的蛋白表达水平。"
| [1] 仇长敬,金超,刘焕宝,等.腺病毒介导的基因治疗在胃癌中的研究进展[J].中国现代医药杂志, 2014,16(12): 106-109. [2] Kwee RM, Kwee TC. Role of imaging in predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(7):1650- 1656. [3] Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, et al. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(1):36-46. [4] Hamburger AW, Salmon SE. Primary bioassay of human tumor stem cells. Science. 1977;197(4302): 461-463. [5] Kreso A, Dick JE. Evolution of the cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14(3):275-291. [6] Takaishi S, Okumura T, Wang TC. Gastric cancer stem cells. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(17):2876-2882. [7] Zieker D, Bühler S, Ustündag Z, et al. Induction of tumor stem cell differentiation--novel strategy to overcome therapy resistance in gastric cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2013;398(4):603-608. [8] Boyanapalli SS, Tony Kong AN. "Curcumin, the King of Spices": Epigenetic Regulatory Mechanisms in the Prevention of Cancer, Neurological, and Inflammatory Diseases. Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2015; 1(2):129-139. [9] Prasad S, Gupta SC, Tyagi AK, et al. Curcumin, a component of golden spice: from bedside to bench and back. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32(6):1053-1064. [10] Kuttan R, Bhanumathy P, Nirmala K, et al. Potential anticancer activity of turmeric (Curcuma longa). Cancer Lett. 1985;29(2):197-202. [11] Limtrakul P, Lipigorngoson S, Namwong O, et al. Inhibitory effect of dietary curcumin on skin carcinogenesis in mice. Cancer Lett. 1997;116(2): 197-203. [12] Li Y, Zhang T. Targeting cancer stem cells by curcumin and clinical applications. Cancer Lett. 2014;346(2): 197-205. [13] Ramasamy TS, Ayob AZ, Myint HH, et al. Targeting colorectal cancer stem cells using curcumin and curcumin analogues: insights into the mechanism of the therapeutic efficacy. Cancer Cell Int. 2015;15:96. [14] Mukherjee S, Mazumdar M, Chakraborty S, et al. Curcumin inhibits breast cancer stem cell migration by amplifying the E-cadherin/β-catenin negative feedback loop. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(5):116. [15] Polivka J Jr, Janku F. Molecular targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;142(2):164-175. [16] Guo Y, Du J, Kwiatkowski DJ. Molecular dissection of AKT activation in lung cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer Res. 2013;11(3):282-293. [17] Bergamaschi A,Madakerdogan Z,Lu H,et al. FOXM1-dependent gene expression program controls cancer stem cell and metastasis properties of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2014; 73(3 Supplement): C85. [18] Ning YX, Li QX, Ren KQ, et al. 7-difluoromethoxyl- 5,4'-di-n-octyl genistein inhibits ovarian cancer stem cell characteristics through the downregulation of FOXM1. Oncol Lett. 2014;8(1):295-300. [19] Joshi K, Kim S, Lee J, et al. The MELK/FOXM1 axis is a master regulator of proneural to mesenchymal transition (PMT) in glioma stem cells by controlling EZH2 transcriptional activity. Cancer Res. 2014; 74(19 Supplement):3039. [20] Yung MM, Chan DW, Liu VW, et al. Activation of AMPK inhibits cervical cancer cell growth through AKT/FOXO3a/FOXM1 signaling cascade. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:327. [21] Ho C, Wang C, Mattu S, et al. AKT (v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1) and N-Ras (neuroblastoma ras viral oncogene homolog) coactivation in the mouse liver promotes rapid carcinogenesis by way of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1), FOXM1 (forkhead box M1)/SKP2, and c-Myc pathways. Hepatology. 2012; 55(3):833-845. [22] Wang Z, Li Y, Ahmad A, et al. Down-regulation of Notch-1 is associated with Akt and FoxM1 in inducing cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(1):78-88. [23] Lee AS, Tang C, Rao MS, et al. Tumorigenicity as a clinical hurdle for pluripotent stem cell therapies. Nat Med. 2013;19(8):998-1004. [24] Serakinci N, Fahrioglu U, Christensen R. Mesenchymal stem cells, cancer challenges and new directions. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(8):1522-1530. [25] Tirino V, Desiderio V, Paino F, et al. Cancer stem cells in solid tumors: an overview and new approaches for their isolation and characterization. FASEB J. 2013;27(1):13-24. [26] Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, et al. Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface marker CD44. Stem Cells. 2009;27(5):1006-1020. [27] Xue Z, Yan H, Li J, et al. Identification of cancer stem cells in vincristine preconditioned SGC7901 gastric cancer cell line. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(1):302-312. [28] Gupta SC, Patchva S, Aggarwal BB. Therapeutic roles of curcumin: lessons learned from clinical trials. AAPS J. 2013;15(1):195-218. [29] Park W, Amin AR, Chen ZG, et al. New perspectives of curcumin in cancer prevention. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013;6(5):387-400. [30] Cai XZ, Wang J, Li XD, et al. Curcumin suppresses proliferation and invasion in human gastric cancer cells by downregulation of PAK1 activity and cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009;8(14):1360-1368. [31] Yu LL, Wu JG, Dai N, et al. Curcumin reverses chemoresistance of human gastric cancer cells by downregulating the NF-κB transcription factor. Oncol Rep. 2011;26(5):1197-1203. [32] Norris L, Karmokar A, Howells L, et al. The role of cancer stem cells in the anti-carcinogenicity of curcumin. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013;57(9):1630-1637. [33] 刘尧,刘月平,王小玲,等.PI3K/AKT 通路与肿瘤的研究进展[J].食管外科电子杂志, 2014,2(3): 109-113. [34] Madden J, Chien J. Evidence for modulation of FoxM1 by p21 in ovarian cancer. Cancer Research. 2015; 75 (15 Supplement): 1992. [35] Tan X, Fu Y, Chen L, et al.miR-671-5p promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by downregulating FOXM1 expression in breast cancer. Cancer Research. 2015; 75(15 Supplement): 3062. [36] Li Z, Jia Z, Gao Y, et al. Activation of vitamin D receptor signaling downregulates the expression of nuclear FOXM1 protein and suppresses pancreatic cancer cell stemness. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(4):844-853. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [3] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [6] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [7] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [8] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [9] | Xu Yinqin, Shi Hongmei, Wang Guangyi. Effects of Tongbi prescription hot compress combined with acupuncture on mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, in degenerative intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 713-718. |
| [10] | Zhang Wenwen, Jin Songfeng, Zhao Guoliang, Gong Lihong. Mechanism by which Wenban Decoction reduces homocysteine-induced apoptosis of myocardial microvascular endothelial cells in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 723-728. |
| [11] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [12] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [13] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [14] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [15] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||