Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (32): 4738-4744.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.32.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Gastric cancer stem cells in tumor invasion and metastasis and its influence on angiogenesis ability
Zhang Li-xian1, Zhang Ning2, Yuan Shuang-zhen1, Chen Yu-mei1, Su Xin-ai1, Sun Jian-shun1, Wang Li-hua1, Lin Mei3
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Harrison International Peace Hospital, Hengshui 053000, Hebei Province, China
2Department of Orthopedics, Fourth People’s Hospital of Hengshui, Hengshui 053000, Hebei Province, China
3Department of Gastroenterology, First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 066004, Hebei Province, China
-
Revised:2016-06-12Online:2016-08-05Published:2016-08-05 -
Contact:Lin Mei, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Gastroenterology, First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 066004, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Zhang Li-xian, Master, Department of Gastroenterology, Harrison International Peace Hospital, Hengshui 053000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research and Development Plan Project of Hengshui City, China, in 2012, No. 12012A
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Li-xian, Zhang Ning, Yuan Shuang-zhen, Chen Yu-mei, Su Xin-ai, Sun Jian-shun, Wang Li-hua, Lin Mei. Gastric cancer stem cells in tumor invasion and metastasis and its influence on angiogenesis ability[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(32): 4738-4744.
share this article
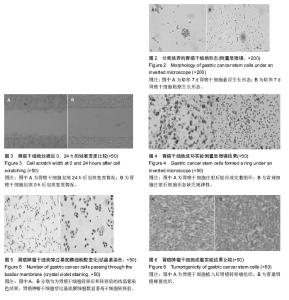
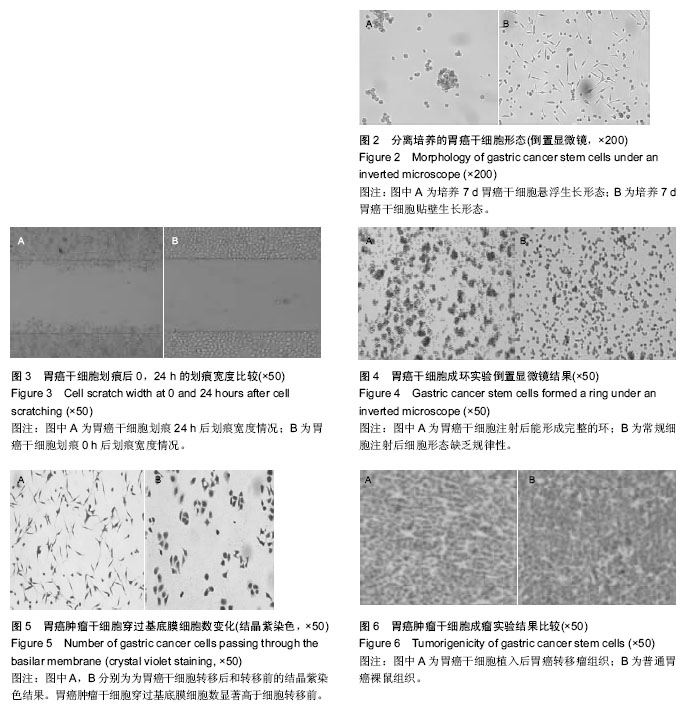
2.1 实验动物数量分析 裸鼠30只全部进入结果分析数量,无脱落。 2.2 胃癌干细胞形态观察 胃癌干细胞分离后进行培养,细胞悬浮生长,培养7 d后贴壁生长,悬浮生长细胞相对较少,多为圆形、椭圆形;贴壁生长细胞相对较多,且缺乏规律性,细胞多为蝌蚪形,见图2。 2.3 细胞划痕实验结果 胃癌干细胞在划痕后0,24 h采用显微镜观察划痕的宽度,结果显示:植入胃癌干细胞前划痕宽度为(0.750±0.023) mm,24 h后划痕宽度为(0.310±0.016) mm,不同时间段划痕宽度差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),倒置显微镜下可见胃癌干细胞位置发生率了明显的变化,见图3。 2.4 胃癌干细胞成环实验结果 调整胃癌干细胞浓度为1×104个接种在96孔板中,培养24 h后观察成环数量,结果显示:胃癌干细胞成环数量为(7.20±1.47)个,通过倒置显微镜观察成环形态,胃癌干细胞注射后能形成完整的环,见图4。 2.5 细胞抑制率实验结果 采用MTS方法检测奥沙利铂以及5-氟尿嘧啶对胃癌干细胞细胞活性的影响。结果显示:奥沙利铂为胃癌干细胞的半抑制浓度为(0.67±0.17) mg/L, 而5-氟尿嘧啶的胃癌干细胞半抑制浓度为(2.23±0.56) mg/L,两者相比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.6 胃癌肿瘤干细胞转移性实验结果 结晶紫染色结果显示,胃癌肿瘤干细胞穿过基底膜细胞数为(172.60±12.28)个,细胞转移前为(85.20±6.57)个,两者比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图5。 2.7 胃癌肿瘤干细胞成瘤实验结果 将1×106个细胞接种在裸鼠背部,在同等条件下喂养4周后麻醉处死裸鼠,测量胃癌组织质量发现,胃癌干细胞植入后胃癌组织质量为(0.624±0.036) g,普通胃癌裸鼠为(0.165± 0.011) g,两者差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),胃癌转移瘤组织变化见图6。"
| [1] Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro- oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9742): 687-697. [2] 张德龙,王伟,张力,等.Wnt/β-catenin 信号途径促进肌源性干细胞向神经细胞分化[J].解放军医学院学报,2014, 3(54):383-387. [3] Xue Z, Yan H, Li J, et al. Identification of cancer stem cells in vincristine preconditioned SGC7901 gastric cancer cell line. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(1): 302-312. [4] Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131(5):861-872. [5] Xi HQ, Cai AZ, Wu XS, et al. Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5 is associated with invasion,metastasis,and could be a potential therapeutic target in human gastric cance. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(8):2011-2020. [6] 赵何伟,王太洪,郑苏文,等.CD90蛋白的研究进展[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2012,19(9):1015-1019. [7] Varon C, Dubus P, Mazurier F, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection recruits bone marrow-derived cells that participate in gastric preneoplasia in mice. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(2):281-291. [8] 谢建伟,黄昌明,郑朝辉,等.肿瘤干细胞表面标记物CD44在胃癌中的表达及其意义[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2013, 16(11):1107-1112. [9] Katsuno Y, Ehata S, Yashiro M, et al. Coordinated expression of REG4 and aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 regulating tumourigenic capacity of diffuse-type gastric carcinoma-initiating cells is inhibited by TGF-beta. J Pathol. 2012;228(3):391-404. [10] 关心,陆智祥,杨同华.肿瘤干细胞的生物学特性及其研究进展[J].生命科学,2014,26(2):194-200. [11] Yoo YA, Kang MH, Lee HJ, et al. Sonic hedgehog pathway promotes metastasis and lymphangiogenesis via activation of Akt, EMT, and MMP-9 pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 2011; 71(22):7061-7070. [12] 林照亮,吴炎,戴少敏,等.肿瘤干细胞及其 Wnt信号通路在胃癌患者中的表达[J].黑龙江医学,2013,37(6): 408-410. [13] Pacheco-Pinedo EC, Durham AC, Stewart KM, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling accelerates mouse lung tumorigenesis by imposing an embryonic distal progenitor phenotype on lung epithelium. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(5):1935-1945. [14] Croker AK, Allan AI. Inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activity reduces chemotherapy and radiation resistance of stem-like ALDHhiCD44? human breast cancer cells. Breast Cencar Res Treat. 2012;133(1):175-187. [15] 赵丽琴,郭伟剑,张晓伟,等.CBX7 在胃癌干细胞样细胞中的表达及其功能研究[J].中国癌症杂志,2013,23(2): 114-119. [16] 郭乐乐,欧阳晓晖,苏秀兰.干细胞与胃癌关系的研究进展[J/CD].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2012,6(20):6461- 6463. [17] 乐雄,杨德同,张洪海.胃癌干细胞对氟尿嘧啶敏感性及化疗药物耐受细胞的生物学机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(19):3022-3026. [18] 周志华,张建东,徐桂芳,等.基于克隆形态分选胃癌干细胞及其对氟尿嘧啶敏感性的检测[J].中华胃肠外科杂志, 2013,16(4):376-380. [19] Lecluse LL, Spuls PI. Photodynamic therapy versus topical imiquimod versus topical fluorouracil for treatment of superficial basal-cell carcinoma: a single blind, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial: a critical appraisal. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172(1):8-10. [20] 朱雯静,杨玥,郝溥辰,等.5-氟尿嘧啶作用人肝癌细胞系SMMC-7721后残存细胞中肿瘤干细胞比例增加[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2012,21(3):224-228. [21] 吴婷,李锦毅,陆士新,等.人胃癌侧群细胞的分离鉴定和生物学特性分析[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2012,34(4):264-268. [22] 王守练,俞继卫,蔡成,等.RNA干扰抑制KATO-Ⅲ CD133阳性胃癌细胞CD133基因表达及对其生物学特性的影响[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2013,16(9):889-894. [23] Yang L, Han S, Sun Y. An IL6-STAT3 loop mediates resistance to PI3K inhibitors by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell expansion in human breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;453(3):582-587. [24] Waki M, Ide Y, Ishizaki I, et al. Single-cell time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry reveals that human breast cancer stem cells have significantly lower content of palmitoleic acid compared to their counterpart non-stem cancer cells. Biochimie. 2014;107 Pt A:73-77. [25] 姜伟,李锦毅,吴婷,等.胃癌侧群细胞的耐药性及致瘤性的初步研究[J].临床肿瘤学杂志,2012,17(8):673-677. [26] 卓志红,张乐鸣,牧启田,等.二十二碳六烯酸联合5-氟尿嘧啶对胃癌细胞生长及bcl-2、bcl 2l12和bax表达的影响[J].中华普通外科杂志,2009,24(1):66-70. [27] Guth AM, Deogracias M, Dow SW. Comparison of cancer stem cell antigen expression by tumor cell lines and by tumor biopsies from dogs with melanoma and osteosarcoma. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2014;161 (3-4): 132-140. [28] 陈军,崔有宏,郝迎学,等.5-氟尿嘧啶及长春新碱对胃癌细胞SGC-7901干细胞相关特性的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2013,35(12):1247-1251. [29] 王欣荣,刘登湘,刘丽华,等.5-FU对小鼠乳腺癌4T1细胞株中肿瘤干细胞样细胞的富集作用[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2012,19(5):478-485. [30] 杨玥,李德龙,朱雯静,等.5-氟尿嘧啶对肝癌细胞系BEL-7402中肿瘤干细胞的富集作用[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2011,19(9):686-691. [31] Kizilbash SH, Ward KC, Liang JJ, et al. Survival outcomes in patients with early stage, resected pancreatic cancer-a comparison of gemcitabine-and 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy and chemoradiation regimens. Int J Clin Pract. 2014; 68(5):578-589. [32] Li SY, Sun R, Wang HX, et al. Combination therapy with epigenetic-targeted and chemotherapeutic drugs delivered by nanoparticles to enhance the chemotherapy response and overcome resistance by breast cancer stem cells. J Control Release. 2015; 205:7-14. [33] 燕丽,史立纲,徐正顺,等.5-氟尿嘧啶对乳腺癌MCF7细胞中干细胞相关基因Oct4、Bmi-1表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(10):1822-1826. [34] 翟荣林,张小明,王继亮,等.O6-甲基鸟嘌呤DNA甲基转移酶在结肠癌干细胞中的表达及其与结肠癌5-氟尿嘧啶获得性耐药的关系[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(2): 248-250. [35] 李德龙,朱雯静,韩旭,等.肝癌干细胞逃避5-氟尿嘧啶单药杀伤可能是造成化疗失败的重要原因[J].实用肝脏病杂志, 2012,15(2):126-129. [36] 吴松洁,贾晓渊,钱其军,等.人胃癌细胞系BGC-823中SP细胞的耐药性研究[J].浙江理工大学学报,2008,25(5): 573-577. [37] Miyoshi N, Ishii H, Nagai K, et al. Defined factors induce reprogramming of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(1):40-45. [38] Goel S, Duda DG, Xu L, et al. Normalization of the vasculature for treatment of cancer and other diseases. Physiol Rev. 2011;91(3):1071-1121. [39] Soda Y, Marumoto T, Friedmann-Morvinski D, et al. Transdifferentiation of glioblastoma cells into vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108(11):4274-4280. [40] 蒋佩佩,胡畅远,武文一,等.microRNA-212在胃癌中的表达及临床意义[J].肿瘤学杂志,2012,18(4):246-249. [41] Abdelfatah E, Kerner Z, Nanda N, et al. Epigenetic therapy in gastrointestinal cancer: the right combination. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. 2016;9(4): 560-579. [42] Lv Y, Song L, Chang L, et al. Inhibitory effects of bevacizumab monoclonal antibodies in combination with chemotherapy in different time sequences on a human gastric carcinoma cell line. Ir J Med Sci. 2016. [43] Khan SA, Khan AM, Karim S, et al. Panacea seed "Nigella": a review focusing on regenerative effects for gastric ailments. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2016;23(4):542-553. [44] Ishido K, Higuchi K, Azuma M, et al. Aprepitant, granisetron, and dexamethasone versus palonosetron and dexamethasone for prophylaxis of cisplatin-induced nausea and vomiting in patients with upper gastrointestinal cancer: a randomized crossover phase II trial (KDOG 1002). Anticancer Drugs. 2016. [45] Omura Y, Lu D, Jones MK, et al. Optimal Dose of Vitamin D3 400 I.U. for Average Adults has A Significant Anti-Cancer Effect, While Widely Used 2000 I.U. or Higher Promotes Cancer: Marked Reduction of Taurine Camp; 1α, 25(OH)2D3 Was Found In Various Cancer Tissues and Oral Intake of Optimal Dose of Taurine 175mg for Average Adults, Rather Than 500mg, Was Found to Be A New Potentially Safe and More Effective Method of Cancer Treatment. Acupunct Electrother Res. 2016;41(1): 39-60. [46] Chen Y, Zheng H, Zhang J, et al. Protective effect and potential mechanisms of Wei-Chang-An pill on high-dose 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. [47] Chen T, Xu XY, Zhou PH. Emerging molecular classifications and therapeutic implications for gastric cancer. Chin J Cancer. 2016;35(1):49. [48] Bano N, Najam R, Qazi F, et al. Clinical Features of Oxaliplatin Induced Hypersensitivity Reactions and Therapeutic Approaches. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016;17(4):1637-1641. [49] Tanaka S, Sanefuji K, Kabashima A, et al. A Case of Virchow's Lymph Node Recurrence of Gastric Cancer Who Had Underwent Gastrectomy, and Treated with S-1 Monotherapy Leading to Complete Response (CR). Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2016 Apr;43(4):455-457. [50] Tsuruda Y, Ishigami S, Uenosono Y, et al. A Case of Recurred Gastric Cancer of the Anastomosis Completely Responding to Docetaxel, Cisplatin, and S-1 Triplet Therapy. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2016; 43(4): 451-453. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [8] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [9] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [10] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [11] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [12] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [13] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [14] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [15] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||