Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (32): 4745-4750.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.32.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Neuron-like differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from children in vitro
Li Ying, Gao Jie, Shang Ya-min, Wang Qi-wei, Wang Hai-lei
- Department of Pediatrics, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475000, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2016-05-30Online:2016-08-05Published:2016-08-05 -
About author:Li Ying, Attending physician, Department of Pediatrics, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Ying, Gao Jie, Shang Ya-min, Wang Qi-wei, Wang Hai-lei. Neuron-like differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from children in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(32): 4745-4750.
share this article
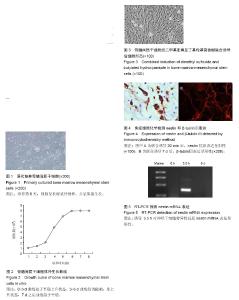
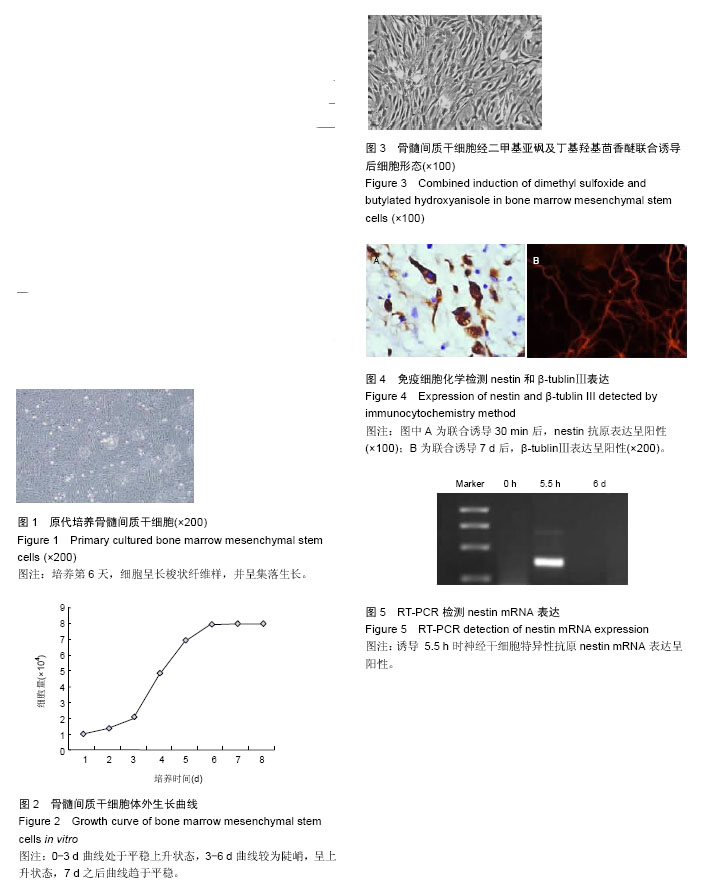
2.1 骨髓间质干细胞形态与表面标记物 原代培养第2天,可见少量单个核细胞发生贴壁,细胞呈短梭形;培养第6天,细胞呈长梭状纤维样,并呈现出集落生长(图1)。 经流式细胞仪检测,第3代骨髓间质干细胞可强表达CD13、CD105,低表达CD34。 2.2 骨髓间质干细胞体外生长曲线 接种后0-3 d为生长潜伏期,曲线处于平稳上升状态,3-6 d处于对数期,曲线较为陡峭,呈上升状态,7 d之后进入平台期,曲线趋于平稳,见图2。 2.3 二甲基亚砜及丁基羟基茴香醚联合诱导后细胞形态 经预诱导,细胞形态未出现明显的改变。经二甲基亚砜及丁基羟基茴香醚联合诱导之后,细胞形态逐渐发生变化,胞体逐渐收缩为锥形和多角形、类圆形,胞体伸出突起并逐渐延长为细丝状。联合诱导至第6天,相邻细胞突起已经相互交织成网状(图3)。 2.4 免疫细胞化学结果 联合诱导30 min后,nestin抗原表达呈阳性(图4A)。联合诱导7 d后,β-tublinⅢ表达呈阳性(图4B),表明二甲基亚砜及丁基羟基茴香醚体外联合诱导骨髓间质干细胞可分化为神经干细胞与神经元细胞。 2.5 RT-PCR检测nestin mRNA表达 联合诱导开始时(0 h)未出现nestin mRNA表达,诱导5.5 h时神经干细胞特异性抗原nestin mRNA表达呈阳性,诱导6 d时不再表达(图5)。"
| [1] 庄琴,朱彦,陆益龙,等.成人骨髓间质干细胞向神经干细胞的诱导分化[J].江苏大学学报:医学版,2011,21(2): 93-96. [2] 彭志强,黄天华,郭杵强,等.补肾益脑胶囊将大鼠骨髓间质干细胞诱导为神经细胞的研究[J].中医临床研究,2014, 4(12):34-36. [3] Lange C, Schroeder J, Stute N, et al. High-potential human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2005; 14(1):70-80. [4] Lee H, Kang JE, Lee JK, et al. Bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote proliferation and neuronal differentiation of Niemann-Pick type C mouse neural stem cells by upregulation and secretion of CCL2. Hum Gene Ther. 2013;24(7): 655-669. [5] Chong PP, Selvaratnam L, Abbas AA, et al. Human peripheral blood derived mesenchymal stem cells demonstrate similar characteristics and chondrogenic differentiation potential to bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(4): 634-642. [6] Karaöz E, Demircan PC, Sa?lam O, et al. Human dental pulp stem cells demonstrate better neural and epithelial stem cell properties than bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Histochem Cell Biol. 2011;136(4):455-473. [7] 叶伟标,邓宇斌,叶美红,等.慢病毒载体介导HIF-1α基因修饰骨髓间质干细胞促进脑缺血大鼠的神经功能恢复[J].中国病理生理杂志,2010,26(2):256-261. [8] Heo JS, Choi SM, Kim HO, et al. Neural transdifferentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on hydrophobic polymer- modified surface and therapeutic effects in an animal model of ischemic stroke. Neuroscience. 2013;238: 305-318. [9] Tang Y, Cui YC, Wang XJ, et al. Neural progenitor cells derived from adult bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote neuronal regeneration. Life Sci. 2012; 91(19-20):951-958. [10] Liu C, Sun J. Potential application of hydrolyzed fish collagen for inducing the multidirectional differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(1):436-443. [11] Habisch HJ, Liebau S, Lenk T, et al. Neuroectodermally converted human mesenchymal stromal cells provide cytoprotective effects on neural stem cells and inhibit their glial differentiation. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(4):491-504. [12] 刘振华,王世军.帕金森病模型大鼠损毁侧纹状体内移植神经干细胞的增殖与分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(36):5843-5847. [13] Wislet-Gendebien S, Laudet E, Neirinckx V, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and neural crest stem cells from adult bone marrow: characterization of their surprising similarities and differences. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012;69(15):2593-2608. [14] Kim SJ, Lee JK, Kim JW, et al. Surface modification of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) induced proliferation and neural-like cells differentiation of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(8):2953-2962. [15] Park JE, Seo YK, Yoon HH, et al. Electromagnetic fields induce neural differentiation of human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells via ROS mediated EGFR activation. Neurochem Int. 2013;62(4): 418-424. [16] 邵景范,黎润光,魏明发,等.牵张应力对儿童骨髓间充质干细胞体外增殖与向成骨分化的影响[J].中华小儿外科杂志, 2007,28(6):305-309. [17] 杨帆.不同年龄组食蟹猴骨髓间质干细胞增殖分化特性研究[D].广州:中山大学,2008. [18] Wexler SA, Donaldson C, Denning-Kendall P, et al. Adult bone marrow is a rich source of human mesenchymal 'stem' cells but umbilical cord and mobilized adult blood are not. Br J Haematol. 2003; 121(2):368-374. [19] 朱灏,许建中,周强,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞体外增殖及成骨分化的增龄变化[J].第三军医大学学报,2005,27(1): 59-62. [20] 姚璎珈,孔亮,教亚男,等.蛇床子素通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进转染APP基因的神经干细胞分化为更多神经元且减少神经元凋亡[J].中国药理学通报,2015,31(11): 1516-1523. [21] 师红,季泽娟,刘福云,等.丁羟茴醚诱导幼儿骨髓间质干细胞分化为神经细胞[J].河南医学研究,2010,19(3): 287-290. [22] 吴中华.脑外源性神经因子基因修饰神经干细胞对脑卒中的神经保护机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(45): 7331-7336. [23] Cho H, Seo YK, Yoon HH, et al. Neural stimulation on human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields. Biotechnol Prog. 2012;28(5):1329-1335. [24] Heng BC, Saxena P, Fussenegger M. Heterogeneity of baseline neural marker expression by undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells may be correlated to donor age. J Biotechnol. 2014;174:29-33. [25] Ayd?n A, Duruksu G, Erman G, et al. Neurogenic differentiation capacity of subacromial bursal tissue- derived stem cells. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(1):151-158. [26] 周君梅,张胜利,陈方,等.利用人胚胎干细胞和人羊水干细胞的神经分化模型建立体外神经毒性测试的实验研究[J].临床儿科杂志,2011,29(2):101-105. [27] Mohanty ST, Cairney CJ, Chantry AD, et al. A small molecule modulator of prion protein increases human mesenchymal stem cell lifespan, ex vivo expansion, and engraftment to bone marrow in NOD/SCID mice. Stem Cells. 2012;30(6):1134-1143. [28] Han F, Wang CY, Yang L, et al. Contribution of murine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to pancreas regeneration after partial pancreatectomy in mice. Cell Biol Int. 2012;36(9):823-831. [29] Wang N, Xu Y, Qin T, et al. Myocardin-related transcription factor-A is a key regulator in retinoic acid-induced neural-like differentiation of adult bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Gene. 2013; 523(2):178-186. [30] 陈树鑫.不同年龄人群脂肪干细胞体外成脂、成骨诱导分化能力的比较[D].广州:中山大学,2009. [31] 李恩琴.儿童急性早幼粒细胞白血病的临床及相关诱导性多能干细胞研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2012. [32] Tao YX, Xu HW, Zheng QY, et al. Noggin induces human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into neural and photoreceptor cells. Indian J Exp Biol. 2010;48(5):444-452. [33] Yan ZJ, Hu YQ, Zhang HT, et al. Comparison of the neural differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells from amniotic fluid and adult bone marrow. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2013;33(4):465-475. [34] 李恩琴,金润铭.儿童白血病诱导性多能干细胞的建立与诱导造血分化[C].上海:中华医学会第十二次全国血液学学术会议论文集,2012:13. [35] 杜喆,张伟国,陶凯,等.β-微管蛋白-Ⅲ在脊髓神经干细胞向神经元定向分化早期的动态变化研究[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2009,3(10):1690-1698. [36] 殷海斌,田新,杨春会,等.间充质干细胞的生物学特性及临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(14):2282-2289. [37] Datta I, Mishra S, Mohanty L, et al. Neuronal plasticity of human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stromal cells to the dopaminergic cell type compared with human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2011; 13(8):918-932. [38] Harris VK, Yan QJ, Vyshkina T, et al. Clinical and pathological effects of intrathecal injection of mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural progenitors in an experimental model of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 2012;313(1-2):167-177. [39] 袁斯明,王修坤,陈荣亮,等.婴幼儿血管瘤来源的间充质干细胞的体外多向分化实验[J].中国美容整形外科杂志, 2012,23(3):144-146. [40] 孙客,王国兵,祖莹,等.不同年龄儿童骨髓间充质干细胞自体血清体外培养及成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(40):7425-7429. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Luo Lin, Song Naiqing, Huang Jin, Zou Xiaodong. Review and prospect of international research on preschool children’s movement development assessment: a CiteSpace-based visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1270-1276. |
| [5] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [6] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [7] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [8] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [9] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [10] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [11] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [12] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [13] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [14] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [15] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||