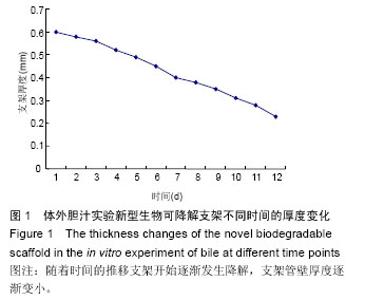
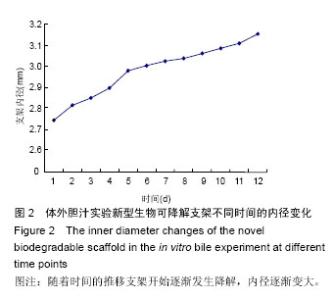
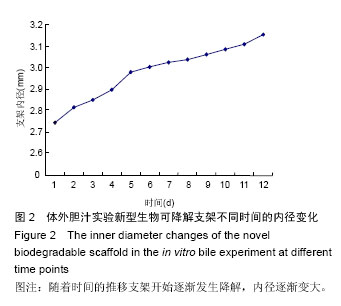
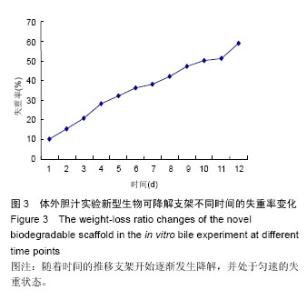
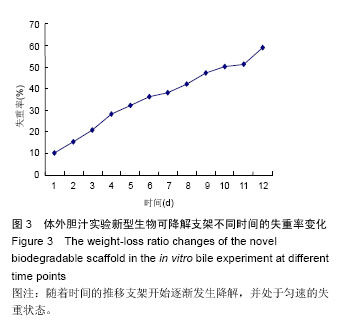
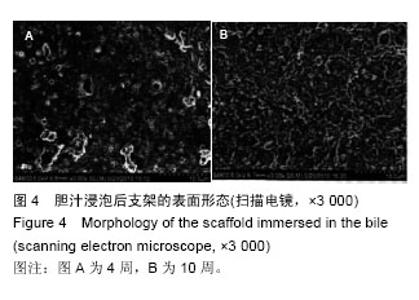
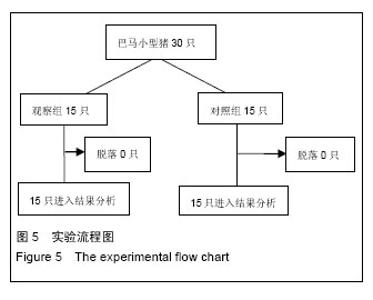
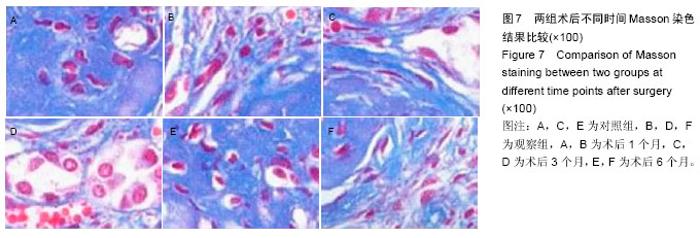
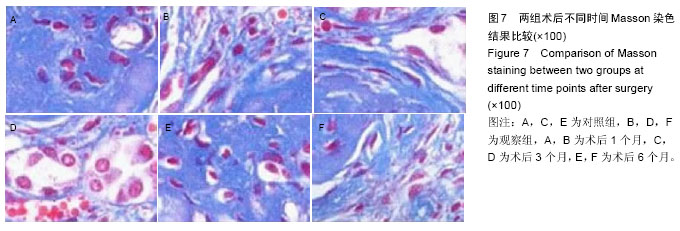
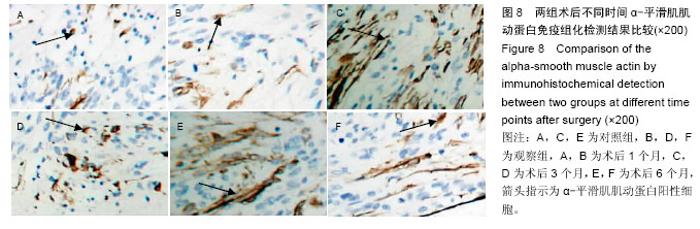
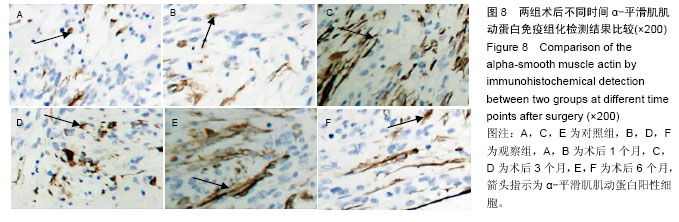
| [1] 白雪巍,孙备,刘杰,等.医源性胆道损伤再手术时机对预后的影响[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2011,17(9):703-706.
[2] 王敬,孟波,周宁新,等.可降解聚乳酸支架在胆管损伤治疗中作用的实验研究[J].中华肝胆外科杂志, 2004,10(12): 841-843.
[3] 丁宗励,施瑞华.生物可降解消化道内支架的研究进展[J].国际消化病杂志,2010,30(3):168-171.
[4] 谭志刚,郭奕彤.胆管支架置入联合锁骨下动脉药盒贯序化疗治疗肝门部胆管癌:不同种类支架选择对治疗效果有影响吗[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13 (52): 10377-10381
[5] Jang SI, Kim JH, You JW, et al. Efficacy of a metallic stent covered with a paclitaxel-incorporated membrane versus a covered metal stent for malignant biliary obstruction: A prospective comparative study. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58(3):865-871.
[6] Glazer ES, Hornbrook MC, Krouse RS, et al. A meta-analysis of randomized trials: Immediate stent placement vs. surgical bypass in the palliative management of malignant biliary obstruction.J Pain Sympt Man. 2014;47(2):307-314.
[7] 黄浩哲,李文涛.生物可降解胆道内支架的研究进展[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2013,19(5):390-393.
[8] 骆乐.NF-κB及其下游抗凋亡因子在胆道损伤愈合过程中的表达的基础研究[D].泸州医学院,2010.
[9] 谢舜峰.人胚血管平滑肌细胞的培养及其与三维可降解乳酸与羟基乙酸共聚物(PLGA)细胞支架的亲和性实验[D].汕头大学,2003.
[10] 高杰,赵文华,崔凯,等.胆道支架的临床应用现状[J].国际外科学杂志,2011,38(5):325-328.
[11] 赵孝君.胆管支架材料及类型对置入效果的影响:改善开通率和延长开通时间[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(16):2991-2994.
[12] Moon JH, Choi HJ, Koo HC, et al. Feasibility of placing a modified fully covered self-expandable metal stent above the papilla to minimize stent-induced bile duct injury in patients with refractory benign biliary strictures (with videos).Gas Endosc. 2012;75(5):1080-1085.
[13] 刘杰,王丹.不同类型肝内及胆管内支架的临床应用及支架内梗阻的预防[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(39):7751-7754.
[14] 常海洋,王永正,王武杰,等.胆道支架置入术联合125I支架内照射治疗恶性梗阻性黄疸效果观察[J].山东医药, 2015, (26):46-47.
[15] Park do H,Song TJ,Eum J, et al. EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy with a fully covered metal stent as the biliary diversion technique for an occluded biliary metal stent after a failed ERCP (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71(2):413-419.
[16] 刘铜军,姜伟,于惠秋,等.CO2激光焊接辅以化学胶Ⅰ期修复犬内置可降解支架胆总管的可行性及安全性[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2007,33(3):449-453.
[17] Kim DU, Kang DH, Kim GH, et al. Bilateral biliary drainage for malignant hilar obstruction using the 'stent-in-stent' method with a Y-stent: Efficacy and complications. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 25(1):99-106.
[18] 邓立春,黄祥忠,于波,等.胆管支架置入联合放疗治疗恶性梗阻性黄疸的疗效[J].中国老年学杂志, 2012,32(2): 257-258.
[19] Mangiavillano B, Luigiano C, Tarantino I, et al. Fully covered, self-expandable metal stents for first-step endoscopic treatment of biliary leaks secondary to hepato-biliary surgery: A retrospective study. Dig Liver Dis. 2013;45(5):430-432.
[20] 刘华,周莹群,徐选福,等.经内镜放置胆管金属支架联合鼻胆管引流治疗恶性胆管梗阻[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2015,(1):64-67.
[21] 姜中华,管敬,范志宁,等.经皮肝穿刺置入胆管支架对胃癌术后复发致胆管梗阻的治疗价值[J].中国微创外科杂志, 2015,15(5):410-413.
[22] Gwon DI, Ko GY, Kim JH, et al. Percutaneous Bilateral Metallic Stent Placement Using a Stent-in-Stent Deployment Technique in Patients With Malignant Hilar Biliary Obstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 200 (4): 909-914.
[23] 蒋雨卉,张俊文.内镜下胆管支架置入术治疗31例恶性胆管梗阻患者的疗效分析[J].重庆医学, 2010,39(23): 3233-3235.
[24] Heistermann HP,Palmes D,Stratmann U,et al.A new tech-nique for reconstruction of the common bile duct by an autolo-gous vein graft and a biodegradable endoluminal stent.J Invest Surg. 2006;19:57-60.
[25] Meng B,Wang J,Zhu N,et al.Study of biodegradable and self-expandable PLLA helical biliary stent in vivo and in vitro.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17:611-617.
[26] Dubravcsik Z, Hritz I, Fejes R, et al. Early ERCP and biliary sphincterotomy with or without small-caliber pancreatic stent insertion in patients with acute biliary pancreatitis: Better overall outcome with adequate pancreatic drainage. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2012; 47(6): 729-736.
[27] 何秀丽.超声引导下肝胆管内支架置入治疗的材料学特征及其生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(16):2987-2990.
[28] Pai M, Valek V, Tomas A, et al. Percutaneous intraductal radiofrequency ablation for clearance of occluded metal stent in malignant biliary obstruction: Feasibility and early results. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2014;37(1):235-240.
[29] 周荣幸,程南生,李富宇,等.脱细胞基质管腔人工仿真胆管的体内重建:动物实验初步报告[J].腹部外科, 2014,27(5): 317-324.
[30] 瞿旭东,颜志平,王建华,等.经皮穿肝胆道引流术(PTCD)辅助支架置放治疗胆管和十二指肠恶性梗阻[J].复旦学报(医学版),2012,39(3):289-292.
[31] Zhu HD,Guo JH, Zhu GY, et al. A novel biliary stent loaded with 125I seeds in patients with malignant biliary obstruction: Preliminary results versus a conventional biliary stent. J Hepatol. 2012;56(5): 1104-1111.
[32] 梁岳龙.新型生物可降解支架材料的生物学特性研究和支架法联合大网膜修复胆道损伤的动物实验研究[D].浙江大学,2012.
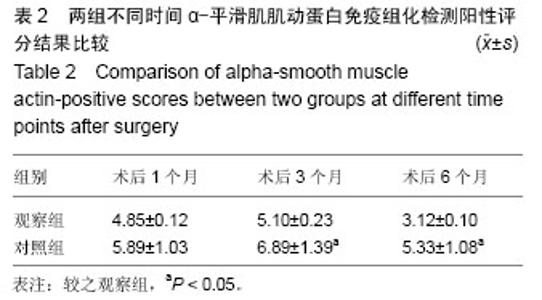
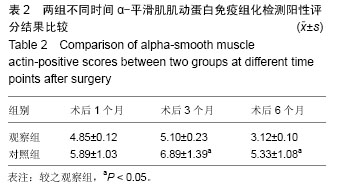
[33] 王得胜,刘莉,李建国,等.丹参对胆道损伤修复过程中α-SMA表达的影响及其意义[J].第三军医大学学报, 2011, 33(15):1657-1659.
[34] 司晓芸,贾汝汉,黄从新,等.宽叶缬草对高脂血症大鼠肾小球α-平滑肌肌动蛋白表达的影响[J].医药导报, 2003, 22(4): 222-224. |