Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 316-322.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0024
Previous Articles Next Articles
3D bioprinting: applications in cells, scaffolds and bone tissue engineering
- 1Grade 2015 of Orthopedics, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; 2Guizhou Orthopedics Hospital, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2017-11-06Online:2018-01-18Published:2018-01-18 -
Contact:Qiu Bing, Professor, Guizhou Orthopedics Hospital, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Hu Chao-ran, Studying for master’s degree, Grade 2015 of Orthopedics, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Funded Project of Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. LS[2012]046
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Chao-ran, Qiu Bing.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
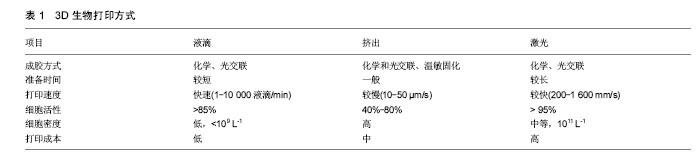
2.1 3D生物打印 2.1.1 原理概述 3D生物打印,是以用户自由设计或医学影像三维重建的计算机三维模型为基础,通过软件分层离散和数控成型的方法,定位装配生物材料或活细胞,制造生物支架、组织器官和个性化医疗器械等生物医学产品的3D打印技术[11],其最终目标是实现打印出的生物体血管化,以构建出具备完整生物学功能的组织和器官,从而精确修复或替代人体病变或衰老的组织和器官[12]。根据它的原理和方法,3D生物打印可以被分为3个过程:首先是对打印前的数据进行收集及软件建模,主要包括3D影像采集、数字化三维设计和打印材料的选择等[13];其次,将选定的材料与细胞制成“生物墨水”(bioink),使用相对应的3D生物打印机,设定相关的打印参数,进行生物打印成型;最后,对生物打印体的仿生结构、机械性能和生物活性等方面进行加工改善等后续培养,最终制造出符合要求的生物体,这也是日后发展为成熟的组织、器官的一个重要步骤[14-15]。 2.1.2 3D生物打印的成型技术 目前的3D生物打印根据其打印方式不同主要分为液滴沉积成型、挤出打印成型和激光固化成型3种介导方式[16-17],通过打印成型可直接获得具有生物活性的打印体。其各自的特性对比见表1。"
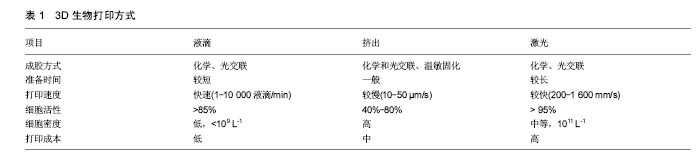
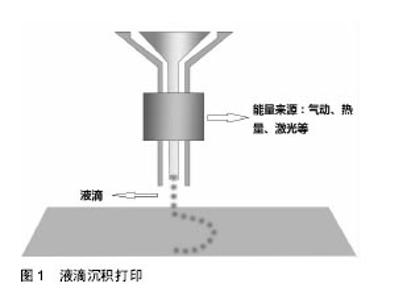
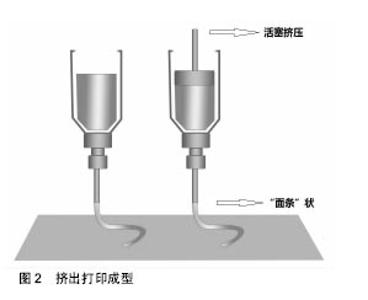
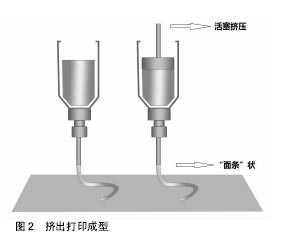
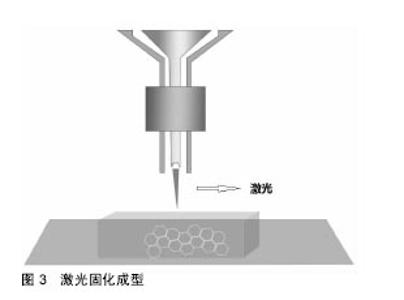
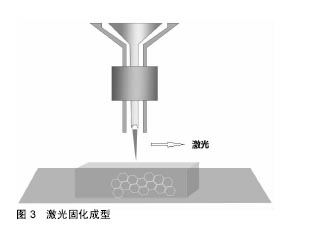
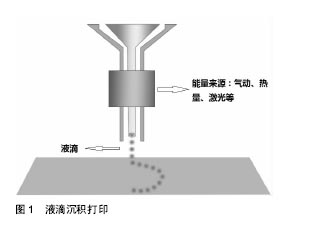
液滴沉积成型技术(Droplet-Based Bioprinting)是一种非接触式图像重构技术, 可以将数字信号通过液滴在移动的底物平台上进行重现,这种技术的优势不仅在于它的简单性和灵活性,同时它能够以一种高通量的方式对微量级液滴进行操作,从而更加精确的控制细胞、生长因子等生物活性物质在预先设定的位置进行沉积,进而提高打印样品的精确性和特异性,如图1。液滴沉积成型技术根据它的能量来源不同又可以分为喷墨型、电流体喷射型、气压辅助型和激光辅助型4种[18-21]。挤出打印成型技术(Extrusion-Based Bioprinting)是3D生物打印技术中最常见的形式,它是以“针头注射器”为基础的细胞沉积系统,将流体点胶系统和机器自动化系统集成于一体[13,22],由前者负责生物墨水的挤出,后者负责生物打印,最终以连续沉积的方式将充满细胞的“细丝”叠加成所需的3D生物结构。不同于液滴沉积技术,挤出型生物打印的打印速度相对较慢[13],但打印体能够获得较好的精确性及结构完整性,如图2。激光固化成型技术(Sterelithography-Based Bioprinting)是由激光介导通过扫描或图像投影模型对细胞悬液或组织悬液进行精确的定位技术,如图3。它对于生物活性物质的沉积具有更高的分辨率及精确性,然而,在这种光固化打印过程中同时会发生一系列光聚合反应,激光的功率、波长、曝光时间、光引发剂等也不可避免的会对细胞活性造成一定的影响[22-23],加上对材料要求的苛刻,设备的昂贵等因素,在一定程度上限制了此种打印方式的应用。 2.2 生物墨水 3D生物打印的材料通常是含有营养成分、基质成分和细胞的流体,又称之为“生物墨水”[24]。生物墨水的成分主要由生物材料和细胞构成,也可包含如生长因子、蛋白质等生物活性物质。 2.2.1 生物材料 3D生物打印中的生物材料通常能够给予细胞力量和保护,保持细胞的水分而不堵喷头,因此必须同时满足以下条件[22,25-28]:①可打印性;②适宜的理化性质;③良好的生物相容性和生物活性;④良好的力学性能;⑤临床可行性。细胞外基质可以给予细胞物理结构的支持与保护,是细胞扩散的联系通道,细胞外基质的改变会影响细胞的生长状态、功能, 甚至会影响细胞的命运[29-30]。对细胞而言,生物材料代替天然组织作为其细胞外基质,其微环境必须要能保证细胞正常的贴附和增殖,并且维持良好的细胞活性。生物材料按其构成可分为天然生物材料和人工合成生物材料两类。 天然生物材料:天然生物材料应用最广泛的为有机凝胶类材料,如海藻酸盐、明胶、透明质酸、胶原等[13]。水凝胶是一类聚合物材料,具有良好的生物相容性和生物可降解性,亲水的性质使它们在三维结构中包含大量水, 因此成为包裹细胞的首选。天然水凝胶由于与组织细胞外基质成分的相似性,目前在生物打印中使用最为广泛[16,26,28]。天然水凝胶在打印后可以通过交联来维持打印出结构的形貌。目前常用的交联方法有物理交联和化学交联,用特定波长光刺激和温度改变引起的交联方法被称为物理交联法;通过特定化合物或离子作用引起的交联称为化学交联法。海藻酸钠是以褐藻或海藻为原料提取分离而成的一种天然多糖[31],海藻酸盐通过与二价阳离子如钙离子的化学交联,能够让它在短时间内从溶胶变为凝胶,这一特性使得海藻酸盐材料在3D组织、器官打印中具有广泛的应用[31-32]。透明质酸是1934年美国哥伦比亚大学眼科教授Meyer等首先从牛眼玻璃体中分离出的一种酸性黏多糖。丙烯酸酯或甲基丙烯酸酯改性的透明质酸可通过光交联形成凝胶。在关节损伤和关节炎的治疗方面,透明质酸以其独特的分子结构和理化性质已经被用于临床治疗数十年[33]。胶原是细胞外基质的主要结构蛋白之一,因其自身的温敏特性,能在生理条件下发生简单的交联反应形成凝胶,这也是它在3D生物打印中的一个重要优势[34-35],然而,较高的成本以及相对较差的机械强度限制了其应用。明胶是由结缔组织中的胶原部分降解而成的薄片或粉粒,明胶里具有丰富的蛋白质能够促进细胞黏附。与胶原类似,明胶同样具有温敏性,其凝胶的转变温度约为30 ℃,故而常用于与其他水凝胶材料混合,使打印过程中具有一定的强度,打印体能够更好的成型。明胶也可以通过甲基丙烯酰胺修饰之后与紫外线进行交联,因此也被广泛用于各种基于光学的生物打印平台[36]。 人工合成生物材料:人工合成聚合物目前已被广泛运用于生物医学领域,它通常能够对原材料进行简单的加工进而改变其原有的理化性质及机械性能,以达到研究人员所需的不同结果[37]。在3D生物打印中,人工聚合物最主要的功能是对打印体的组织结构提供一定的机械强度,因此诸如聚己内酯、聚乳酸-羟基乙酸、聚乙二醇等都已被运用于组织及器官的打印。聚己内酯主要被运用于挤出打印技术中,因为它具有较低的熔融温度(59-64 ℃),故聚己内酯在室温下呈橡胶状且具有一定的流变性,便于印刷加工。同时聚己内酯无毒并具有良好的生物相容性,在3D生物打印的印刷结构中聚己内酯的主要作用是提供一个支持框架以提供具有形状保真度的印刷单元结构[38]。聚乳酸-羟基乙酸是由乳酸和羟基乙酸两种单体随机聚合而成的一种可降解的功能高分子有机化合物,具有良好的热塑性、生物相容性,被广泛应用于制药、医用工程材料和现代化工业领域。3D生物打印中聚乳酸-羟基乙酸常作为细胞堆叠的“生物纸”被应用于激光打印技术中。 聚乙二醇是一种具有亲水性、生物相容性以及获FDA批准的聚合物。聚乙二醇因具有水溶性,因此常被用于制作拥有复杂三维结构体的牺牲材料[39]。对于聚乙二醇作为生物墨水的用途,通常需要对其进行化学修饰,然后加入光引发剂并在紫外光的照射下产生交联并形成凝胶,因此也常被用于激光固化成型技术之中[40]。 2.2.2 细胞 对于生物打印的细胞应该主要考虑以下几个因 素[16,28,41]:①体外能够获得可供生物打印的细胞量;②细胞在支架内的增殖性及分化性;③细胞打印后的活性;④不同细胞类型在结构和功能上的生理差异;⑤组织发育过程中涉及的多细胞间的相互作用及相关生物信号通路。由于宿主免疫反应的原因,自体来源细胞已成为首选,包括胚胎干细胞在内的多能干细胞和诱导多能干细胞是最有前景的细胞类型,这是因为它们虽处于未分化状态,但却具有自我更新的高度增殖潜能,同时能够向多种细胞类型定向诱导分化[13,25],而且人体干细胞来源广泛,具备分化成不同细胞潜能的多能干细胞存在于人体多种组织,如骨髓、脂肪、脐带脐血及皮肤组织等。根据之前的研究表明,高细胞存活性可以通过优化打印参数获得,整个打印过程并不影响干细胞的增殖和分化能力[26]。因此干细胞作为种子细胞来源成为目前生物打印的研究热点。对于复杂组织和器官的再生,不仅需要具有功能性的原代细胞作为支持细胞,也需要具有多向分化能力的干细胞进行进一步的分化[41-43],而干细胞可以通过控制不同的生物活性因子在特定的空间位置中分化成需要的目标细胞类型。因此,干细胞在3D生物打印尤其是对复杂组织和器官的再生提供了一种简单且有效的途径。 2.3 3D生物打印技术在组织工程骨修复中的应用 生物医学材料近年来发展迅猛,3D生物打印则是实现组织工程重建的最重要的手段。如前所述,海藻酸钠作为一种常用的生物墨水,同样被广泛应用于骨组织工程中。有学者将海藻酸钠复合骨形态发生蛋白2进行生物打印,体内试验发现12周后打印体内有明显的骨生成[44];而相较于其他组织,骨组织支架要求较为苛刻,常规的骨组织支架不仅需要具备较高的机械性能[45],同时支架本身也要求一定的孔隙率,以利于细胞的增殖和新生血管的长入[46]。而在生物打印中,因细胞、生长因子等生物活性物质的参与,限制了许多材料的应用。因此,Wüst等[47]研究发现,将明胶、海藻酸钠与羟基磷灰石混合之后发现,8%羟基磷灰石加入到水凝胶中杨氏模量明显增加。北京大学口腔医学院薛世华等[48-49]通过构建人牙髓细胞-海藻酸钠/明胶复合体,发现打印后的3D复合体细胞存活率可达(87±2)%;宋扬等[50-51]对这一体系进行了后续的体内实验,并通过混入少许纳米羟基磷灰石对其进行改良,结果发现打印体内细胞的活性和增殖性并未降低,且打印体的体外成骨分化能力得到了增强。同样,Bendtsen等[52]研究出一种新配方,将聚乙烯醇-羟基磷灰石加入海藻酸钠凝胶体系中,将MC3T3-E1细胞与之混合后进行3D生物打印,结果表明打印体具有一定的机械性能和较高的细胞活性,足以为细胞在体外的培养创造一个适宜的环境。同样有学者将人骨髓干细胞与生物玻璃/纳米羟基磷灰石构建生物打印体,在培养后21 d取材观察,结果表明细胞封装在该混合物中能表现出较高的细胞存活率(86.62±6.02)%和压缩模量(358.91± 48.05)kPa[53]。然而,对于单纯水凝胶体系亦或在其中混入少许无机材料的3D生物打印仍难以满足四肢长骨、大段骨缺损在力学方面的需求,因此必须为支架添加具有一定强度的支撑材料,这也是骨组织生物打印在材料和技术上的一大难点,为了克服这一难题,考虑采取多材料的技术方法,最常见的方法就是利用FDM打印硬热塑性聚合物,如聚己内酯等,同时利用挤压打印含有细胞/生长因子的软性材料,如水凝胶等[54]。Shim等[38]进行了一项研究,该团队发明了一种多喷头式的挤压成型打印机,其中一个喷头加入聚己内酯材料,另外两个喷头分别是用海藻酸钠与成软骨/成骨细胞混合的“生物墨水”。打印开始时,首先打印聚己内酯作为支架的外框架,然后分别将“生物墨水”打入框架之中,最后交联成型,如此通过多喷头的灵活切换,打印体不仅能获得较高的机械强度,同时还可以在特定位置定植特定的细胞,打印后支架中成软骨细胞活性为(93.9±0.3)%,成骨细胞为(95.6±1.8)%。Kang等[55]利用这一方法将脂肪干细胞与聚己内酯/磷酸三钙共打印,并将打印体植入大鼠颅骨缺损处,结果表现出良好的整合和骨修复的证据。因此可以看出,通过对打印技术的改进,有望突破3D生物打印对材料的限制。另外,骨组织工程支架的血管化仍然是现今最具挑战性且需要克服的巨大障碍之一[56],目前已有研究通过生物打印对打印体内特定区域定植相应的生长因子,从而达到促进血管化的目的[57]。 "
| [1]Mouriño V, Boccaccini AR. Bone tissue engineering therapeutics: controlled drug delivery in three-dimensional scaffolds. J R Soc Int. 2010; 7(43):209.[2]Jones AC, Arns CH, Sheppard AP, et al. Assessment of bone ingrowth into porous biomaterials using MICRO-CT. Biomaterials. 2007;28(15):2491-2504.[3]Seitz H, Rieder W, Irsen S, et al. Three-dimensional printing of porous ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005;74B(2):782-788.[4]Behnia H, Khojasteh A, Esmaeelinejad M, et al. Effects of Different Growth Factors on New Bone Formation:, A Systematic Review. J Islam Dent Assoc Iran. 2012.[5]Hassani A, Khojasteh A, Alikhasi M. Anterior Palate of the Maxilla as a Donor Site for Oral and Maxillofacial Reconstructive Procedures. Asian J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;20(3):135-138.[6]Olender E, Brubaker S, Uhrynowskatyszkiewicz I, et al. Autologous osteoblast transplantation, an innovative method of bone defect treatment: role of a tissue and cell bank in the process. Transplant Proc.2014;46(8):2867-2872.[7]Faldini C, Traina F, Perna F, et al. Surgical treatment of aseptic forearm nonunion with plate and opposite bone graft strut. Autograft or allograft? Int Orthop. 2015;39(7): 1343-1349.[8]Amini AR, Laurencin CT, Nukavarapu SP. Bone Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and Challenges. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2012;40(5):363.[9]Derby B. Printing and prototyping of tissues and scaffolds. Science. 2012;338(6109):921-926.[10]Ozbolat IT, Hospodiuk M. Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials. 2016;76(37):321-343.[11]Derby B. Bioprinting: inkjet printing proteins and hybrid cell-containing materials and structures. J Mat Chem. 2008; 18(47):5717-5721.[12]Pati F, Jang J, Ha DH, et al. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink.Nat Commun. 2014;5:3935. [13]Murphy SV, Atala A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(8):773-785.[14][14] Mironov V, Kasyanov V, Markwald RR. Organ printing: From bioprinter to organ biofabrication line. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2011;22(5): 667-673.[15]Pati F, Gantelius J, Svahn HA. 3D Bioprinting of Tissue/Organ Models. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016;55(15):4650-4665. [16]Murphy SV, Atala A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014; 32(8):773-785.[17]Zhang X, Zhang Y. Tissue Engineering Applications of Three-Dimensional Bioprinting. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015; 72(3):777-782.[18]Gasperini L, Maniglio D, Motta A, et al. An Electrohydrodynamic Bioprinter for Alginate Hydrogels Containing Living Cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015; 21(2):123.[19]Mézel C, Souquet A, Hallo L, et al. Bioprinting by laser-induced forward transfer for tissue engineering applications: jet formation modeling. Biofabrication. 2010;2(1): 014103.[20]Nakamura M, Nishiyama Y, Henmi C, et al. Ink jet three-dimensional digital fabrication for biological tissue manufacturing: analysis of alginate microgel beads produced by ink jet droplets for three dimensional tissue fabrication. J Imaging Sci Tech. 2008;52(6):060201–060201-6.[21]Khalil S, Nam J, Sun W. Multi‐nozzle deposition for construction of 3D biopolymer tissue scaffolds. Rapid Prot J. 2005;11(1):9-17(9).[22]Park JH, Jang J, Lee JS, et al. Three-Dimensional Printing of Tissue/Organ Analogues Containing Living Cells. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017;45(1):180.[23]Skoog SA, Goering PL, Narayan RJ. Stereolithography in tissue engineering. J Mat Sci. 2014;25(3):845-56.[24]Fashion’s Biological Future Is Now.www.Biofabricate.Co/[25]Skardal A, Atala A. Biomaterials for Integration with 3-D Bioprinting. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015;43(3):730-746.[26]Ozbolat IT, Hospodiuk M. Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials. 2016;76(37):321.[27]Panwar A, Tan LP. Current Status of Bioinks for Micro- Extrusion-Based 3D Bioprinting. Molecules. 2016;21 (6):685.[28]Lei M, Wang X. Biodegradable Polymers and Stem Cells for Bioprinting. Molecules. 2016;21(5):539.[29]Trappmann B, Chen CS. How cells sense extracellular matrix stiffness: a material's perspective. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013;24(5):948-953.[30]schumperlin DJ, Liu F, Tager AM. Biomechanical regulation of mesenchymal cell function. Curr Opin Rheumatol.2013;25(1): 92-100.[31]Lee KY, Mooney DJ. Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci. 2012;37(1):106-126.[32]Giri TK, Thakur D, Alexander A, et al. Alginate based hydrogel as a potential biopolymeric carrier for drug delivery and cell delivery systems: present status and applications. Curr Drug Deliv. 2012;9(6):539-555.[33]Garg T, Goyal AK. Biomaterial-based scaffolds – current status and future directions. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014; 11(5):767-789.[34]Dong C, Lv Y. Application of Collagen Scaffold in Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and New Perspectives. Polymers. 2016;8(2):42.[35]Aamodt JM, Grainger DW. Extracellular matrix-based biomaterial scaffolds and the host response. Biomaterials. 2016;86:68-82.[36]Klotz BJ, Gawlitta D, Rosenberg AJ, et al. Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Towards Biofabrication-Based Tissue Repair. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34(5):394.[37]Seok J, Warren HS, Cuenca AG, et al. Genomic responses in mouse models poorly mimic human inflammatory diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(9):3507-3512. [38]Shim JH, Lee JS, Kim JY, et al. Bioprinting of a mechanically enhanced three-dimensional dual cell-laden construct for osteochondral tissue engineering using a multi-head tissue/organ building system. J Micromechanics Microengineering. 2012;22(8):85014-85024(11).[39]Duan B, Hockaday LA, Kang KH, et al. 3D Bioprinting of Heterogeneous Aortic Valve Conduits with Alginate/Gelatin Hydrogels. J Biomed Mat Res. 2013;101A(5):1255-1264.[40]Pinar Z, Hyun JJ, Kong H, et al. Stereolithography‐Based Hydrogel Microenvironments to Examine Cellular Interactions. Adv Funct Mat. 2011;21(19):3597-3597.[41]Mandrycky C, Wang Z, Kim K, et al. 3D Bioprinting for Engineering Complex Tissues. Biotechnol Adv. 2016;34(4): 422-434.[42]Mironov V, Visconti R P, Kasyanov V, et al. Organ printing: tissue spheroids as building blocks. Biomaterials. 2009; 30(12):2164.[43]Ozbolat IT. Bioprinting scale-up tissue and organ constructs for transplantation. Trends in Biotechnology. 2015;33(7): 395-400.[44]Poldervaart MT, Wang H, Van d SJ, et al. Sustained release of BMP-2 in bioprinted alginate for osteogenicity in mice and rats. Plos One. 2013;8(8):e72610.[45]Ahn S, Lee H, Lee EJ, et al. A direct cell printing supplemented with low-temperature processing method for obtaining highly porous three-dimensional cell-laden scaffolds. J Mat Chem. 2014;2(18):2773-2782.[46]Bose S, Vahabzadeh S, Bandyopadhyay A. Bone tissue engineering using 3D printing. Mat Today. 2013;16(12): 496-504.[47]Wüst S, Godla ME, Müller R, et al. Tunable hydrogel composite with two-step processing in combination with innovative hardware upgrade for cell-based three-dimensional bioprinting. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(2): 630-640. [48]薛世华,王勇,赵雨,等.人牙髓细胞三维生物打印的初步研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2012,12(17):4103-4107.[49]薛世华,吕培军,王勇,等. 人牙髓细胞共混物三维生物打印技术[J]. 北京大学学报医学版, 2013,45(1):105-108.[50]宋杨,王晓飞,王宇光,等. 人脂肪间充质干细胞与生物材料共混物三维打印体的体内成骨[J]. 北京大学学报医学版, 2016, 48(1):45-50.[51]宋杨,王晓飞,王宇光,等. 纳米羟基磷灰石对人脂肪干细胞共混物三维生物打印影响的初步研究[J]. 北京大学学报医学版, 2016,48(5):894-899.[52]Bendtsen ST, Quinnell SP, Mei W. Development of a novel alginate‐polyvinyl alcohol‐hydroxyapatite hydrogel for 3D bioprinting bone tissue engineered scaffolds. J Biomed Mat Res.2017;105(5):1457.[53]Gao G, Schilling AF, Yonezawa T, et al. Bioactive nanoparticles stimulate bone tissue formation in bioprinted three-dimensional scaffold and human mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechno J. 2014;9(10):1304.[54]Daly AC, Cunniffe GM, Sathy BN, et al. 3D Bioprinting: 3D Bioprinting of Developmentally Inspired Templates for Whole Bone Organ Engineering (Adv. Healthcare Mater. 18/2016). Adv Health Mat. 2016;5(18):2353.[55]Kang HW, Lee SJ, Ko IK, et al. A 3D bioprinting system to produce human-scale tissue constructs with structural integrity]. Nature Biotechnol. 2016;34(3):312.[56]Mercado-Pagán ÁE, Stahl AM, Shanjani Y, et al. Vascularization in Bone Tissue Engineering Constructs. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015;43(3):718-729.[57]Ju YP, Shim JH, Choi SA, et al. 3D printing technology to control BMP-2 and VEGF delivery spatially and temporally to promote large-volume bone regeneration. J Mat Chem. 2015;3(27):5415-5425.[58]Daly AC, Critchley SE, Rencsok EM, et al. A comparison of different bioinks for 3D bioprinting of fibrocartilage and hyaline cartilage. Biofabrication. 2016;8(4):045002. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Liu Zhichao, Zhang Fan, Sun Qi, Kang Xiaole, Yuan Qiaomei, Liu Genzhe, Chen Jiang. Morphology and activity of human nucleus pulposus cells under different hydrostatic pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1172-1176. |
| [5] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [7] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [8] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [9] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [10] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [11] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [12] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [13] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [14] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [15] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||