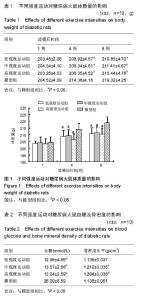
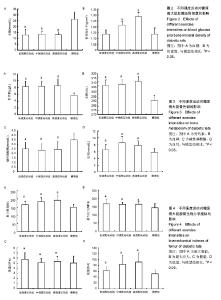
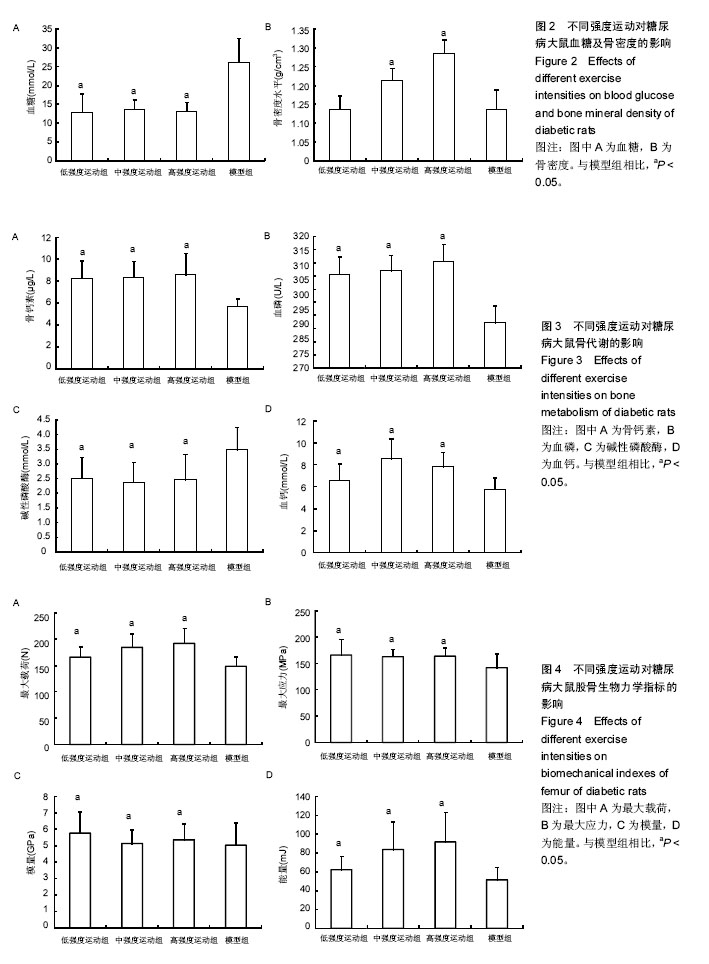
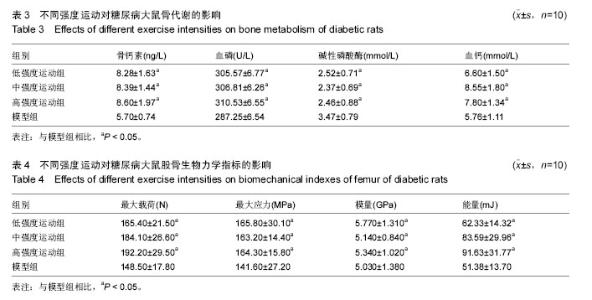
| [1] Hirose A, Tanikawa T, Mori H, et al. Advanced glycation end products increase endothelial permeability through the RAGE/Rho signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 2010;584(1):61-66.
[2] Xu B, Chibber R, Ruggiero D, et al. Impairment of vascular endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity by advanced glycation end products. FASEB J. 2003; 17(10):1289-1291.
[3] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2010年版)[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2012,20(1):S1-37.
[4] Tuttle KR, Anderberg RJ, Cooney SK, et al. Oxidative stress mediates protein kinase C activation and advanced glycation end product formation in a mesangial cell model of diabetes and high protein diet. Am J Nephrol. 2009;29(3):171-180.
[5] 盛正妍,王仲祥,邵安华. 2 型糖尿病遗传学上性别差异的探讨[J].上海预防医学杂志,2000,12(1): 42-44.
[6] Potenza MA, Marasciulo FL, Chieppa DM, et al. Insulin resistance in spontaneously hypertensive rats is associated with endothelial dysfunction characterized by imbalance between NO and ET-1 production. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;289(2):H813-822.
[7] 常柏,甄仲,李修洋,等.长期单独应用开郁清热法治疗肥胖2型糖尿病降糖疗效观察[J].中华中医药杂志, 2009, 24(2): 132-134.
[8] Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, et al. Selective increases of bifidobacteria in gut microflora improve high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice through a mechanism associated with endotoxaemia. Diabetologia. 2007;50(11):2374-2383.
[9] 常柏,刘喜明,甄仲,等.肥胖2型糖尿病的病因病机及证治规律初探[J].北京中医药,2008,27(12):946-948.
[10] 武晓春.健脾益气,养阴清热,活血化瘀治疗2型糖尿病50例临床观察[J].光明中医,2006,21(8):24-25.
[11] 曾艺鹏,黄云胜,胡蕴刚,等.葛根芩连汤配合胰岛素强化治疗湿热证2型糖尿病临床观察[J].中国中西医结合杂志, 2006,26(6):514-520.
[12] 何云娇,冯艺戎,段贤春,等.浅述中药活性成分降血糖机制[J].安徽医药,2013,17(8):1273-1275.
[13] Constantini N, Harman-Boehm I, Dubnov G. Exercise prescription for diabetics: more than a general recommendation. Harefuah. 2005;144(10):717-723, 750.
[14] Shinji S, Shigeru M, Ryusei U, et al. Adherence to a home-based exercise program and incidence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes patients. Int J Sports Med. 2007;28(10):877-879.
[15] 王耀光,吕国枫,任延波.运动疗法对中老年2型糖尿病的疗效[J].中国运动医学杂志.2004,23(6):679-681.
[16] De Angelis K, da Pureza DY, Flores LJ, et al. Physiological effects of exercise training in patients with type 1 diabetes. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2006;50(6):1005-1013.
[17] 王存川,翟贺宁.规范与务实-促进我国肥胖症与代谢病外科的健康发展[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2012,15(11): 1102-1105.
[18] Matsumoto M, Sasaki N, Tsujino T, et al. Iron restriction prevents diabetic nephropathy in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rat. Ren Fail. 2013;35(8):1156-1162.
[19] 曹姣,肖国强.有氧运动和白藜芦醇对II型糖尿病大鼠肝脏氧化应激及NF-κBp65的影响[J].体育学刊,2013,20(6): 138-144.
[20] 丁来标,高怀林,李会玉,等.通络川乌方治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的疗效及对氧化应激状态的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2015,31(1):328-329.
[21] 李雨珂,张木勋.2型糖尿病患者尿白蛋白排泄量与铁代谢指标变化的研究[J].临床内科杂志,2012,29(5):324-326.
[22] To VT, Hüttl TP, Lang R, et al. Changes in body weight, glucose homeostasis, lipid profiles, and metabolic syndrome after restrictive bariatric surgery. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2012;120(9):547-552.
[23] 傅玲玲,吴敏.DPP-4抑制剂治疗2型糖尿病临床前研究到临床应用的转化[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2013,22(31): 3516-3518,3526.
[24] 庞国明,闫镛,朱璞,等.糖尿病周围神经病变中医诊疗规范初稿[J].中华中医药杂志,2010,25(2):260-263.
[25] Perugini RA, Malkani S. Remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus following bariatric surgery: review of mechanisms and presentation of the concept of 'reversibility'. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011;18(2):119-128.
[26] 丁来标,高怀林,李会玉,等.通络川乌方治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的疗效及对氧化应激状态的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2015,31(1):328-329.
[27] 蚁淳,金真,冯细强,等.电针联合温针疗法治疗寒凝血瘀型糖尿病周围神经病变疗效观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2015,24(16):1744-1746.
[28] 吴乃君,刘颖,魏剑芬,等.隔姜灸治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的疗效及对超敏C反应蛋白的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志2015,24(1):24-26.
[29] Kiadaliri AA, Gerdtham UG, Eliasson B, et al. Cost-utility analysis of glucagon-like Peptide-1 agonists compared with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors or neutral protamine hagedorn Basal insulin as add-on to metformin in type 2 diabetes in sweden. Diabetes Ther. 2014;5(2):591-607.
[30] Sripetchwandee J, Pipatpiboon N, Pratchayasakul W, et al. DPP-4 inhibitor and PPARγ agonist restore the loss of CA1 dendritic spines in obese insulin-resistant rats. Arch Med Res. 2014;45(7):547-552.
[31] Anderwald CH, Tura A, Promintzer-Schifferl M, et al. Alterations in gastrointestinal, endocrine, and metabolic processes after bariatric Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(12):2580-2587.
[32] 马宇鹏,杨建华,蔡志敏,等.中医穴位贴敷配合中药足浴治疗糖尿病周围神经病变360例体会[J].实用糖尿病杂志, 2014,10(6):35-36.
[33] 吴英亮,曹志贱,蒋达和,等.作用于钾离子通道蝎毒素的结构特征及活性表面研究进展[J].生物物理学报,2004, 20(2):96-102.
[34] Chen ZY, Hu YT, Yang WS, et al. Hg1, novel peptide inhibitor specific for Kv1.3 channels from first scorpion Kunitz-type potassium channel toxin family. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(17):13813-13821.
[35] 陈宗运,朱国新,谢明红,等.免疫抑制蝎毒活性肽Im169的重组表达和功能鉴定[J].湖北医药学院学报,2014,33(5): 458-463.
[36] Dang B, Kubota T, Mandal K, et al. Native chemical ligation at Asx-Cys, Glx-Cys: chemical synthesis and high-resolution X-ray structure of ShK toxin by racemic protein crystallography. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135(32): 11911-11919. |