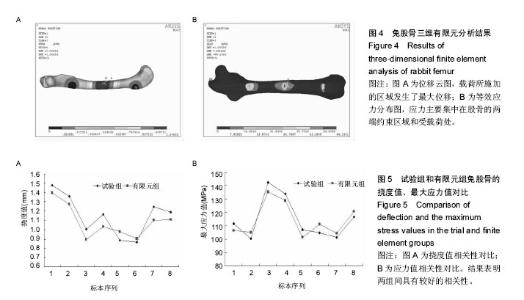
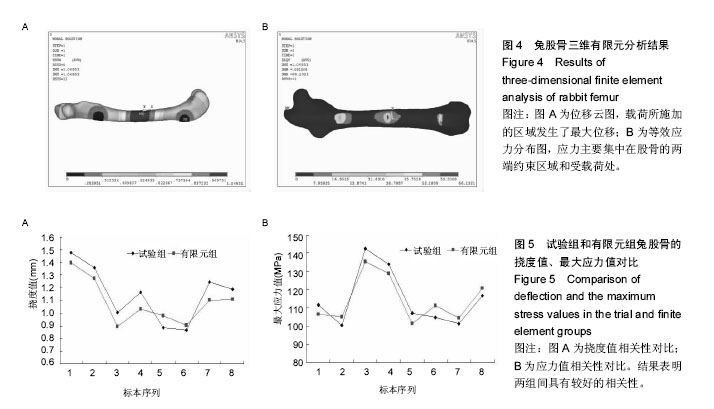
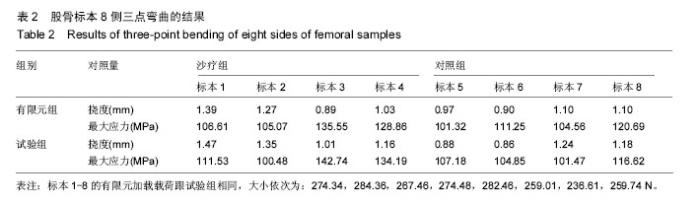
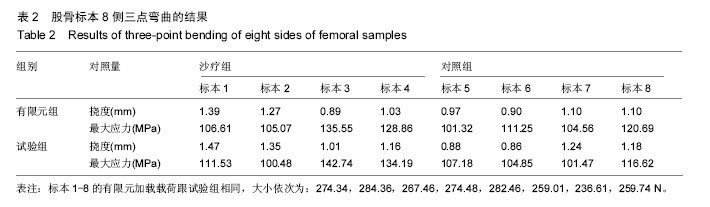
| [1] 卫荣,迪丽娜•马合木提,卡哈尔•库尔班,等.风湿病维吾尔医分型及其沙疗疗效分析[J].中华现代中西医杂志, 2005,3(8):45-47.
[2] 孔春元,迪丽娜尔•马合木提,卫荣.沙疗对关节炎兔股骨力学性能的影响及其有限元分析[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2009,34(1):8-12.
[3] 迪丽娜•热夏提,王春耀等.微量元素及生物传热与维医沙疗[M].乌鲁木齐:新疆人民卫生出版社,2003:16-17.
[4] 崔红新,程方荣,王健智.有限元法及其在生物力学中的应用[J].中医正骨,2005,17(1):53-55.
[5] 李筱贺,李志军,李少华.CT扫描结合逆向工程软件建立下胸椎三维有限元模型半球[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,4(4):594-597.
[6] 王尚城,王冬梅,张宁华.冲击条件下骨盆动脉损伤有限元模型的建立及验证[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(3): 206-212.
[7] 王杰,杨阳,马建雄.PMMA模型股骨与防腐股骨生物力学性能的差异[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(5):502-508.
[8] Lengsfeld M, Schmitt J,Alter P, et al. Comparison of geometry based and CT voxel-based finite element modelling and experimental validation.Med Eng Phys. 1998; 20(7):515-522.
[9] 安梅岩,马爱军.利用内部骨重建理论和有限元法计算骨密度的变化[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2006,23(1):60-65.
[10] Taddei F, Cristofolini L, Martelli S, et al. Subject-specific finite element models of long bones: An in vitro evaluation of the overall accuracy.J Biomech. 2006;39(13):2457-2467.
[11] Zannoni C, Mantovani R, Viceconti M.Material Properties assignment to finite element models of bone struetures:a new method. Med Eng Phys. 1998;20(10): 735-740.Eng Physies.1998;7(20):735-740.
[12] Hvid I,Bentzen SM,IAnde F,X-ray quantitative computed tomosTaphy:the relations to physical properties of proximal tihial trabecular bone specimens. J Biorneeh.1989;22(8/9):837-844.
[13] 尚禹,彭亮,刘加成.均匀材料和基于CT灰度值材料的股骨、胫骨有限元分析[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2008, 27(5):722-727.
[14] Rho JY,Hobath MC,Ashman RB.Relations of mechanical-properties to density and CT numbers in human bone.Med Eng Phys.1995;17(5):347-355.
[15] Wirtz DC,Schiffers N,Pandorf T.Critical evaluation of known bone material properties to realize anisotropic FE-simulation of the proximal femur.J Biomech.2000;33(10):1325-1330.
[16] 张国栋,廖维靖,毛文玉.基于三维重建技术及有限元分析的骨密度测量[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复. 2010, 15(9):1539-1544.
[17] 李伟,居来提•买提肉孜. 兔骨性关节炎模型股骨各骨质层体积与力学性能的关联性分析[J].吉林大学学报:医学版.2013,7(4):680-683.
[18] 居来提•买提肉孜,阿布力米提•买买提.沙疗对骨关节炎兔子股骨骨质影响的对比研究[J]. 新疆大学学报:自然科学版.2013,6(4):396-400.
[19] Fischer KJ, Jacobs CR, Levenston ME,et al. Observation of convergence and uniqueness of node-based bone remodeling simulations. Ann Biomed Eng. 1997;25(2):261-268.
[20] 孟和,顾志华.骨伤科生物力学[M].2版.北京:人民卫生出版社,1998. |