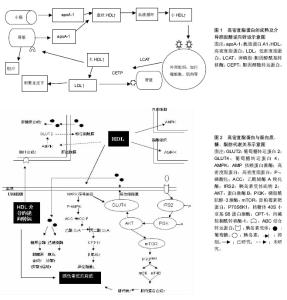
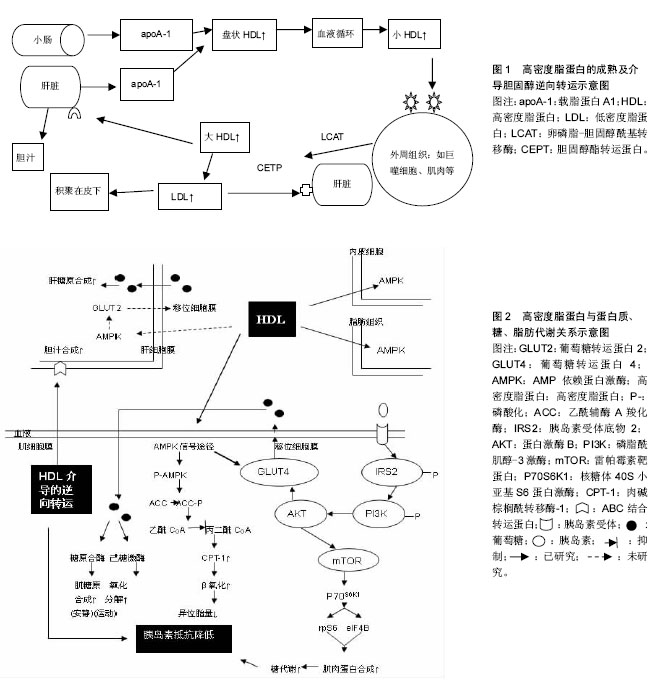
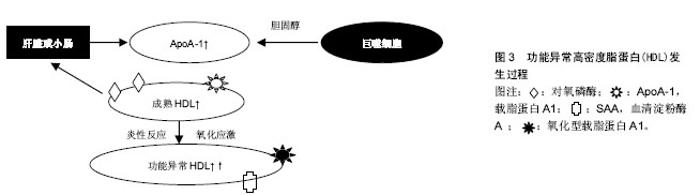
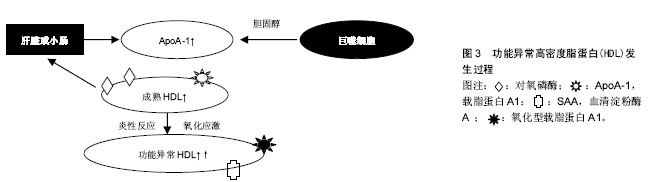
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (37): 6048-6054.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.37.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biological function and exercise regulation of high-density lipoprotein
Su Zhong-jun1, 2, 3, Zhang Su3, Jiang Jun3
- 1School of Sports and Health, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China; 2Institute of Sport Science, General Administration of Sport of China, Beijing 100062, China; 3School of Human Movement Science, Shenyang Sport University, Shenyang 110102, Liaoning Province, China
-
Online:2015-09-10Published:2015-09-10 -
Contact:Su Zhong-jun, School of Sports and Health, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China; Institute of Sport Science, General Administration of Sport of China, Beijing 100062, China; School of Human Movement Science, Shenyang Sport University, Shenyang 110102, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Su Zhong-jun, Studying for doctorate, School of Sports and Health, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China; Institute of Sport Science, General Administration of Sport of China, Beijing 100062, China; School of Human Movement Science, Shenyang Sport University, Shenyang 110102, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Supporting Plan of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, No. 2012BAK23B01; the Fundamental Program of the Institute of Sport Science, General Administration of Sport of China, No. 14-27
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Su Zhong-jun, Zhang Su, Jiang Jun. Biological function and exercise regulation of high-density lipoprotein[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(37): 6048-6054.
share this article
| [1] Remaley AT, Rust S, Rosier M, et al. Human atp-binding cassette transporter 1 (abc1) genomic organization and identification of the genetic defect in the original tangier disease kindred. PNAS. 1999;96:12685-12690. [2] Kennedy MA, Barrera GC, Nakamura K, et al. Abcg1 has a critical role in mediating cholesterol efflux to hdl and preventing cellular lipid accumulation. Cell Metab. 2005;1(2): 121-131. [3] Varma V, Yao-Borengasser A, Rasouli N, et al. Muscle inflammatory response and insulin resistance: synergistic interaction between macrophages and fatty acids leads to impaired insulin action. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 296:E1300-E1310. [4] Hotamisligil GS, Erbay E. Nutrient sensing and inflammation in metabolic diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12):923-934. [5] Montell El, Turini M, Marotta M. Dag accumulation from saturated fatty acids desensitizes insulin stimulation of glucose uptake in muscle cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 280:E229-E237. [6] Samokhvalov VPJB, Jonathan D. Palmitate- and lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages evoke contrasting insulin responses in muscle cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009;296:E37-E46. [7] Drew BG, Duffy SJ, Formosa MF, et al. High-density lipoprotein modulates glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2009;119(15): 2103-2111. [8] Zhang Y, McGillicuddy FC, Hinkle CC, et al. Adipocyte modulation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Circulation. 2010;121(11):1347-1355. [9] Schimmack G, Defronzo RA, Musi N. Amp-activated protein kinase: role in metabolism and therapeutic implications. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006;8(6):591-602. [10] Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, et al. Role of amp-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action.J Clin Invest. 2001; 108(8):1167-1174. [11] Kemp BE, Mitchelhill KI, Stapleton D, et al. Dealing with energy demand the amp-activated protein kinase. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:22-25. [12] Han R, Lai R, Ding Q, et al. Apolipoprotein a-i stimulates amp-activated protein kinase and improves glucose metabolism. Diabetologia. 2007;50(9):1960-1968. [13] Ruan X, Li Z, Zhang Y. et al. Apolipoprotein a-i possesses an anti-obesity effect associated with increase of energy expenditure and up-regulation of ucp1 in brown fat. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(4):763-772. [14] Li J, Murao K, Imachi H, et al. Exendin-4 regulates pancreatic abca1 transcription via camkk/camkiv pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(5):1083-1087. [15] Drew BG, Fidge NH, Gallon-Beaumier G, et al. High-density lipoprotein and apolipoprotein ai increase endothelial no synthase activity by protein association and multisite phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(18): 6999-7004. [16] Adams V, Besler C, Fischer T, et al. Exercise training in patients with chronic heart failure promotes restoration of high-density lipoprotein functional properties. Circ Res. 2013;113(12): 1345-1355. [17] Cockerill GW, Huehns TY, Weerasinghe A, et al. Elevation of plasma high-density lipoprotein concentration reduces interleukin-1-induced expression of e-selectin in an in vivo model of acute inflammation. Circulation. 2001;103(1):108-112. [18] Barter PJ, Baker PW, Rye KA. Effect of high-density lipoproteins on the expression of adhesion molecules in endothelial cells. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2002;13:285-288. [19] Nofer JR, Geigenmüller S, Göpfert C, et al. High density lipoprotein-associated lysosphingolipids reduce e-selectin expression in human endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;310(1):98-103. [20] Barter PJ, Nicholls S, Rye KA, et al. Antiinflammatory properties of hdl. Circ Res. 2004;95(8):764-772. [21] Okura HYS, Ohama T, Saga A, et al. Hdl apolipoprotein a-i binds to macrophage-derived progranulin and suppresses its conversion into proinflammatory granulins. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2010;17(6):568-577. [22] Yamagishi SHA, Matsui T. Decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level is an independent correlate of circulating tumor necrosis factor-alpha in a general population. Clin Cardiol. 2009; 32(9):E29-E32. [23] Ibanez B, Giannarelli C, Cimmino G, et al. Recombinant hdl (milano) exerts greater anti-inflammatory and plaque stabilizing properties than hdl (wild-type). Atherosclerosis. 2012;220(1):72-77. [24] Lowenstein CJ, Cameron SJ.High-density lipoprotein metabolism and endothelial function. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2010;17(2):166-170. [25] Orlov SV, Mogilenko DA, Shavva VS, et al. Effect of tnfalpha on activities of different promoters of human apolipoprotein a-i gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;398(2):224-230. [26] Bursill CA, Castro ML, Beattie DT, et al. High-density lipoproteins suppress chemokines and chemokine receptors in vitro and in vivo. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(9): 1773-1778. [27] Murphy AJ, Woollard KJ, Hoang A, et al. High-density lipoprotein reduces the human monocyte inflammatory response. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28(11): 2071-2077. [28] Bowry VW, Stanley KK, Stocker R. High density lipoprotein is the major carrier of lipid hydroperoxides in human blood plasma from fasting donors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:10316-10320. [29] Navab M, Hama SY, Cooke CJ, et al. Normal high density lipoprotein inhibits three steps in the formation of mildly oxidized low density lipoprotein step 1. J Lipid Res. 2000;41:1481-1494. [30] Valiyaveettil M, Kar N, Ashraf MZ, et al. Oxidized high-density lipoprotein inhibits platelet activation and aggregation via scavenger receptor BI. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2008;111(4): 1962-1971. [31] Benjamin J, Ansell GCF, Alan M. Fogelman.The paradox of dysfunctional high-density lipoprotein.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2007; 18:427-434. [32] Proudfoot JM, Barden AE, Loke WM, et al. Hdl is the major lipoprotein carrier of plasma f2-isoprostanes. J Lipid Res. 2009; 50(4):716-722. [33] Brunham LR, Kruit JK, Pape TD, et al. Beta-cell abca1 influences insulin secretion, glucose homeostasis and response to thiazolidinedione treatment. Nat Med. 2007;13(3):340-347. [34] Fryirs MA, Barter PJ, Appavoo M, et al. Effects of high-density lipoproteins on pancreatic beta-cell insulin secretion. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(8): 1642-1648. [35] Hao M, Head WS, Gunawardana SC, et al. Direct effect of cholesterol on insulin secretion: a novel mechanism for pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Diabetes. 2007;56(9): 2328-2338. [36] Vikman J, Jimenez-Feltstrom J, Nyman P, et al. Insulin secretion is highly sensitive to desorption of plasma membrane cholesterol. FASEB J. 2009;23(1):58-67. [37] Barzegari A, Amouzad Mahdirejei H.. Effects of 8 weeks resistance training on plasma vaspin and lipid profile levels in adult men with type 2 diabetes. Caspian J Intern Med. 2014;5(2): 103-108. [38] Perez-Gomez J, Vicente-Rodriguez G, Ara Royo I, et al. Effect of endurance and resistance training on regional fat mass and lipid profile. Nutr Hosp. 2013;28(2):340-346. [39] Paoli AQ, Moro T, Marcolin G, et al. Effects of high-intensity circuit training, low-intensity circuit training and endurance training on blood pressure and lipoproteins in middle-aged overweight men. Lip Health Dis. 2013;12:131. [40] So WY, Song M, Park YH, et al. Body composition, fitness level, anabolic hormones, and inflammatory cytokines in the elderly: a randomized controlled trial. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2013;25(2): 167-174. [41] Lee MG, Park KS, Kim DU, et al. Effects of high-intensity exercise training on body composition, abdominal fat loss, and cardiorespiratory fitness in middle-aged korean females. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2012;37(6):1019-1027. [42] Sondergaard E, Poulsen MK, Jensen MD, et al. Acute changes in lipoprotein subclasses during exercise. Metabolism. 2014; 63(1):61-68. [43] Casella-Filho A, Chagas AC, Maranhao RC, et al. Effect of exercise training on plasma levels and functional properties of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the metabolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 2011;107(8):1168-1172. [44] Tseng ML1, Ho CC, Chen SC, et al. A simple method for increasing levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol a pilot study of combination aerobic-and resistance-exercise training. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2013;23:271-281. [45] Wellen KE. Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(5):1111-1119. [46] Hardardottie IMA, Memon R. Effects of tnf, il-1, and the combination of both cytokines on cholesterol metabolism in syrian hamsters. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1994;13: 161-166. [47] Blazek A, Rutsky J, Osei K, et al. Exercise-mediated changes in high-density lipoprotein: Impact on form and function. Am Heart J. 2013;166(3):392-400. [48] Kelley GA, aKelley KS. Impact of progressive resistance training on lipids and lipoproteins in adults: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Prev Med. 2009;48(1):9-19. [49] Hornbuckle LM, Liu PY, Ilich JZ, et al. Effects of resistance training and walking on cardiovascular disease risk in african- american women. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(3):525-533. [50] Drew BG, Rye KA, Duffy SJ, et al. The emerging role of hdl in glucose metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8(4):237-245. [51] Tolle M, Huang T, Schuchardt M, et al. High-density lipoprotein loses its anti-inflammatory capacity by accumulation of pro-inflammatory-serum amyloid A. Cardiovasc Res. 2012;94(1):154-162. [52] Terasaka N, Yu S, Yvan-Charvet L, et al. Abcg1 and hdl protect against endothelial dysfunction in mice fed a high-cholesterol diet. J Clin Invest. 2008;118(11):3701-3713. [53] Briand F, Prunet-Marcassus B, Thieblemont Q, et al. Raising hdl with cetp inhibitor torcetrapib improves glucose homeostasis in dyslipidemic and insulin resistant hamsters. Atherosclerosis. 2014;233(2):359-362. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [3] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [6] | Zheng Xiaolong, He Xiaoming, Gong Shuidi, Pang Fengxiang, Yang Fan, He Wei, Liu Shaojun, Wei Qiushi. Bone turnover characteristics in patients with alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 657-661. |
| [7] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [8] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [9] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [10] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [11] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [12] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [13] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [14] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [15] | Zhu Rui, Zeng Qing, Huang Guozhi. Ferroptosis and stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3734-3739. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||