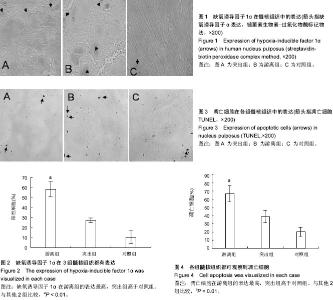
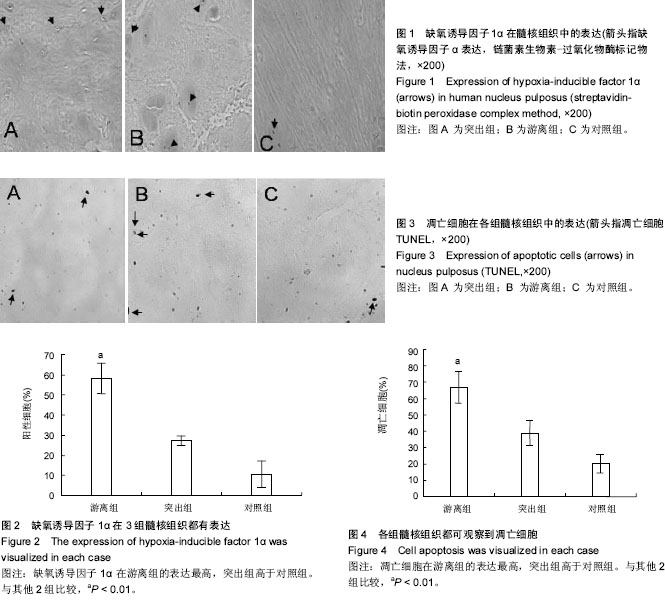
| [1] 胡有谷.腰椎间盘突出症[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2004: 414.
[2] Maigne JY,Rime B,Deligne B.Computed tomographic follow-up study of forty- eight cases of nonoperatively treated lumbar intervertebral disc herniation.spine.1992;17:1071- 1074.
[3] Ahn SH,Ahn MW,Byun WM.Effect of the transligamentous extentsion of lumbar disc herniations on their regression and the clinical outcome of sciation.spine.2005; 25(4):475-480.
[4] Mabjeesh NJ,Amir S.Hypoxia-inducible factor(HIF) in human tumorigenesis. Hi- stol Histopathol.2007;22(5):559-572.
[5] Ratcliffe PJ.HIF-1 and HIF-2:working alone or together in hypoxia?.J Clin Inv- est.2007;117(4):862-865.
[6] Sakamoto T,Seiki M.Mint3 enhances the activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in macrophages by suppressing the activity of factor inhibiting HIF-1.Biol Chen. 2009;9(2): 1-15.
[7] Gassmann M,Chilov D,Wenger RH.Regulation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha. ARNT is not necessary for hypoxic induction of HIF-1 alpha in the nucle-us.Adv Exp Med Biol.2000;475:87-99.
[8] Yang Y,Bai J,Shen R,et al.Polo-like kinase 3 functions as a tumor supperssor and is a negative regulator of hypoxia- inducible factor-1 alpha under hypoxic condit-ions. Cancer Res. 2008;68(11):4077-4085.
[9] Pugh CW,Ratclife PJ.Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia:role of the HIF syst- em. Nat Med.2003;9:677-684.
[10] Mazure NM,Brabimi Horn MC,Pouysscgur J.Protein kinase and the hypoxia–in- ducible factor-1,two switches in angiogenesis Curr Pharm Des.2003;9:531-541.
[11] Kim JY, Ahn HJ,Ryu JH,et al.BH3-only protein Noxa is a mediator of hypoxic c-ell death induced by hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha.J Exp Med.2004;199(1):113-124.
[12] Teplick JG,Haskin ME.Spontaneous regression of herniated nucleus pulposus AJR Am J Roentgenol.1985;145(2): 371-375.
[13] 刘锦涛,姜宏,徐坤林,等.破裂游离型腰椎间盘突出组织重吸收2例报告[J].颈腰痛杂志,2010,31(2):158-160.
[14] 段德宇,杨述华,熊晓芊,等.白细胞介素-6抑制白细胞介素-1B诱导的兔纤维环细胞凋亡的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2006, 23(8): 1005-1007.
[15] 刘杰,陆焱,周跃,等.营养剥夺诱导髓核细胞凋亡与BNIP3蛋白表达上调[J].中华实验外科杂志,2011,28(9):1541-1543.
[16] 黄东生,丁悦,叶伟,等.促炎因子与抗炎因子在突出腰椎间盘组织中的表达及其意义[J].中华实验外科杂志,2006,23(1):86-87.
[17] Zhao CQ, Jiang LS,Dai LY.Programmed cell death in intervertebral disc degener-ation.Apoptosis. 2006;11(12): 2079-2088.
[18] Gruber HE,Hanley EN Jr.Analysis of aging and degeneration of the human inter-vertebral disc.Comparison of surgical specimens with normal controls .Spine. 1998; 23:751-7.
[19] Buckwalter JA.Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disa.Spine. 1995;20:1307-14
[20] Goyeneche AA,Harmon JM,Telleria CM.Cell death induced by serum deprivati-on in luteal cells involves the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis.Reproduction. 2006;131(1):103-111.
[21] Wang H, Liu H, Zheng ZM, et al. Role of death receptor, mitochondrial and endo pasmic reticulum pathways in different stages of degenerative human lumbar dis-c. Apoptosis.2011;16(10): 990-1003.
[22] Zhao CQ, Jiang LS, Dai LY. Programmed cell death in intervertebral disc dege- neration. Apoptosis.2006;11(12): 2079 -2088.
[23] Erwin WM, Islam D, Inman RD, et al. Notochordal cells protect nucleus pul- posus cells from degradation and apoptosis: implica tions for the mechanisms of intervertebral disc degeneration.Arthritis Res Ther.2011;13(6):R215.
[24] Niu CC, Lin SS, Yuan LJ, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment suppress MAPK signaling and mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in degenerated human intervert-ebral disc cells. J Orthop Res.2013;31(2):204 -209. |