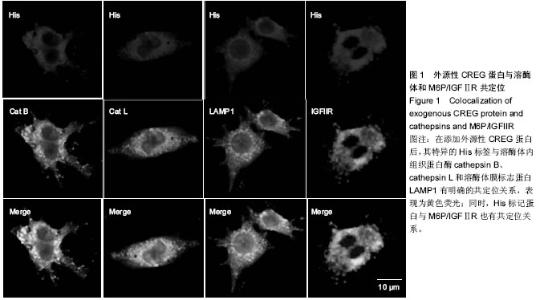
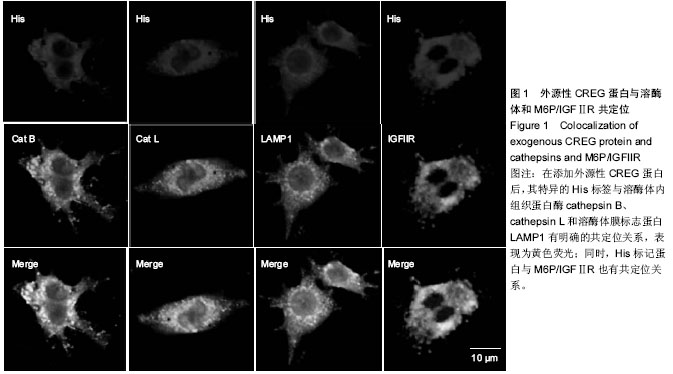
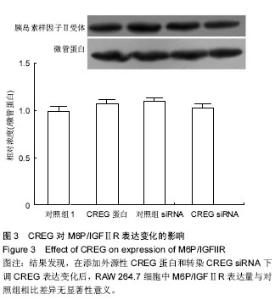
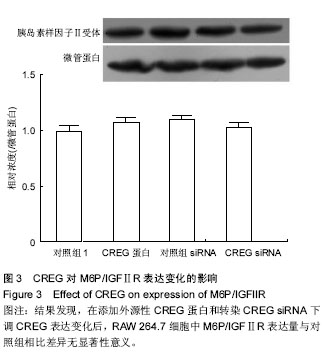
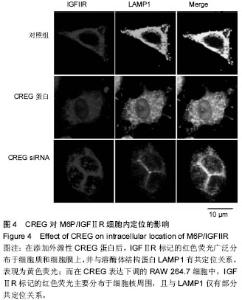
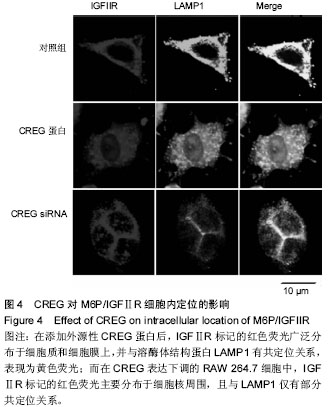
| [1] Galkina E, Ley K.Immune and inflammatory mechanisms of atherosclerosis (*).Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:165-197.
[2] Libby P, Ridker PM,Hansson GK.Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature.2011; 473: 317-325.
[3] Pols TW, Nomura M, Harach T, et al.TGR5 activation inhibits atherosclerosis by reducing macrophage inflammation and lipid loading, Cell metabolism. 2011;14:747-757.
[4] Dupont N, Jiang S, Pilli M, et al.Autophagy-based unconventional secretory pathway for extracellular delivery of IL-1beta. EMBO J. 2011;30:4701-4711.
[5] Levine B, Mizushima N,Virgin HW.Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature. 2011;469:323-335.
[6] Deretic V, Levine B.Autophagy, immunity, and microbial adaptations.Cell Host Microbe.2009;5:527-549.
[7] Munz C.Enhancing immunity through autophagy. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:423-449.
[8] Veal E, Groisman R, Eisenstein M, et al.The secreted glycoprotein CREG enhances differentiation of NTERA-2 human embryonal carcinoma cells.Oncogene. 2000;19: 2120-2128.
[9] Schahs P, Weidinger P, Probst OC, et al.Cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes is a bona fide lysosomal protein which undergoes proteolytic maturation during its biosynthesis. Experimental cell research.2008;314:3036-3047.
[10] Kang JX,Bell J,Leaf A,et al.Retinoic acid alters the intracellular trafficking of the mannose-6-phosphate/ insulin-like growth factor II receptor and lysosomal enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95(23):13687-13691.
[11] Lorenzo K, Ton P, Clark JL, et al.Invasive properties of murine squamous carcinoma cells: secretion of matrix-degrading cathepsins is attributable to a deficiency in the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptor. Cancer Res. 2000;60:4070-4076.
[12] Xie S,Kang JX.Differential expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/ insulin-like growth factor-II receptor in human breast cancer cell lines of different invasive potential.Med Sci Monit. 2002;8:Br293-300.
[13] Di Bacco A,Gill G.The secreted glycoprotein CREG inhibits cell growth dependent on the mannose-6-phosphate/ insulin-like growth factor II receptor. Oncogene.2003;22: 5436-5445.
[14] Kollmann K, Mutenda KE,Balleininger M, et al.Identification of novel lysosomal matrix proteins by proteome analysis. Proteomics. 2005;5:3966-3978. |