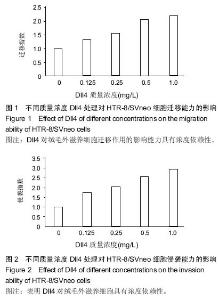
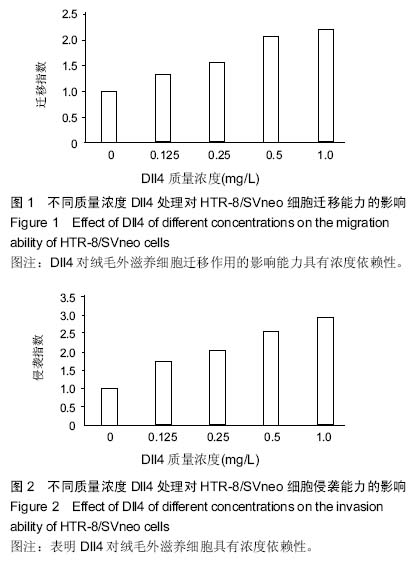
| [1] Muhlhauser J,Crescimanno C,Kaufmann P, et al. Differentiation and proliferation patterns in human trophoblast revealed by c-erbB-2 oncogene product and EGF-R. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993;41(2):165-173.
[2] Ji L, Brkic J, Liu M, et al. Placental trophoblast cell differentiation: physiological regulation and pathological relevance to preeclampsia. Mol Aspects Med. 2013;34(5):981-1023.
[3] Soares MJ, Chakraborty D, Kubota K, et al. Adaptive mechanisms controlling uterine spiral artery remodeling during the establishment of pregnancy. The International journal of developmental biology. 2014;58(2-4):247-259.
[4] Pijnenborg R, Vercruysse L, Hanssens M. The uterine spiral arteries in human pregnancy: facts and controversies. Placenta. 2006;27(9-10):939-958.
[5] Harris LK. Review: Trophoblast-vascular cell interactions in early pregnancy: how to remodel a vessel. Placenta. 2010;31 Suppl:S93-S98.
[6] Pijnenborg R, Vercruysse L, Brosens I. Deep placentation. Best practice & research Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology. 2011;25(3):273-285.
[7] Cross JC, Hemberger M, Lu Y, et al. Trophoblast functions, angiogenesis and remodeling of the maternal vasculature in the placenta. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002;187(1-2):207-212
[8] Knofler M. Critical growth factors and signalling pathways controlling human trophoblast invasion.Int J Dev Biol. 2010; 54(2-3):269-280.
[9] Li JL,Sainson RC,Shi W,et al.Delta-like 4 Notch ligand regulates tumor angiogenesis, improves tumor vascular function, and promotes tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res. 2007;67(23):11244-11253.
[10] De Miguel JR, Quintana R, Gonzalez-Rodilla I, et al. Exaggerated placental site/placental site trophoblastic tumor: an underestimated risk factor for emergency peripartum hysterectomy. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2014;41(6):638-640.
[11] Kuksin CA, Minter LM. The Link between Autoimmunity and Lymphoma: Does NOTCH Signaling Play a Contributing Role? Front Oncol. 2015;5:51.
[12] Milner LA, Bigas A. Notch as a mediator of cell fate determination in hematopoiesis: evidence and speculation. Blood. 1999;93(8):2431-2448.
[13] Parks AL, Klueg KM, Stout JR,et al. Ligand endocytosis drives receptor dissociation and activation in the Notch pathway. Development. 2000;127(7):1373-1385.
[14] Marathe S, Alberi L. Notch in memories: A reasoned updating review. Hippocampus. 2015.
[15] Ridgway J, Zhang G, Wu Y,et al.Inhibition of Dll4 signalling inhibits tumour growth by deregulating angiogenesis. Nature. 2006;444(7122):1083-1087.
[16] Lunghi L, Ferretti ME, Medici S, et al. Control of human trophoblast function. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2007;5:6
[17] Holtan SG, Creedon DJ, Haluska P, et al. Cancer and pregnancy: parallels in growth, invasion, and immune modulation and implications for cancer therapeutic agents. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009;84(11):985-1000.
[18] Zhao WX, Huang TT, Jiang M,et al.Expression of notch family proteins in placentas from patients with early-onset severe preeclampsia.Reproductive sciences. 2014;21(6):716-723.
[19] Fang Y, Yu S, Ma Y,et al. Association of Dll4/notch and HIF-1a -VEGF signaling in the angiogenesis of missed abortion. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e70667.
[20] Graham CH, Hawley TS, Hawley RG, et al. Establishment and characterization of first trimester human trophoblast cells with extended lifespan. Exp Cell Res. 1993;206(2):204-211.
[21] Shutter JR, Scully S, Fan W, et al. Dll4, a novel Notch ligand expressed in arterial endothelium. Genes Dev. 2000;14(11): 1313-1318.
[22] Brzozowa M, Wojnicz R, Kowalczyk-Ziomek G,et al. The Notch ligand Delta-like 4 (DLL4) as a target in angiogenesis-based cancer therapy? Contemporary oncology. 2013;17(3):234-237.
[23] Wang H, Huang X, Zhang J, et al. The expression of VEGF and Dll4/Notch pathway molecules in ovarian cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2014;436:243-248.
[24] Kuramoto T, Goto H, Mitsuhashi A, et al. Dll4-Fc, an inhibitor of Dll4-notch signaling, suppresses liver metastasis of small cell lung cancer cells through the downregulation of the NF-kappaB activity. Mol Cancer Ther.2012;11(12):2578-2587.
[25] Kontomanolis E, Panteliadou M, Giatromanolaki A, et al. Delta-like ligand 4 (DLL4) in the plasma and neoplastic tissues from breast cancer patients: correlation with metastasis. Medical Oncol. 2014;31(5):945.
[26] Ishigami S, Arigami T, Uenosono Y, et al. Clinical implications of DLL4 expression in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013;32:46.
[27] Jubb AM, Turley H, Moeller HC, et al. Expression of delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4) and markers of hypoxia in colon cancer. Br J Cancer.2009;101(10):1749-1757.
[28] Chiorean EG, LoRusso PM, Strother RM, et al. A phase I first-in-human study of enoticumab (REGN421), a fully-human Delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4) monoclonal antibody in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 27. pii: clincanres.2797.2014. [Epub ahead of print].
[29] Holtan SG, Creedon DJ, Haluska P, et al. Cancer and pregnancy: parallels in growth, invasion, and immune modulation and implications for cancer therapeutic agents. Mayo Clin Proc.2009;84(11):985-1000.
[30] Herr F, Schreiner I, Baal N, et al. Expression patterns of Notch receptors and their ligands Jagged and Delta in human placenta. Placenta. 2011;32(8):554-563.
[31] Ball E, Bulmer JN, Ayis S,et al. Late sporadic miscarriage is associated with abnormalities in spiral artery transformation and trophoblast invasion. J Pathol. 2006;208(4):535-542.
[32] Crosley EJ,Elliot MG,Christians JK,et al. Placental invasion, preeclampsia risk and adaptive molecular evolution at the origin of the great apes: evidence from genome-wide analyses. Placenta. 2013;34(2):127-132.
[33] Aminin DL, Menchinskaya ES, Pisliagin EA, et al. Anticancer Activity of Sea Cucumber Triterpene Glycosides. Marine drugs. 2015;13(3):1202-1223.
[34] Cohen M, Bischof P. Factors regulating trophoblast invasion. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2007;64(3):126-130.
[35] Huang QB, Ma X, Li HZ, et al. Endothelial Delta-like 4 (DLL4) promotes renal cell carcinoma hematogenous metastasis. Oncotarget.2014;5(10):3066-3075.
[36] Funahashi Y, Shawber CJ, Sharma A, et al. Notch modulates VEGF action in endothelial cells by inducing Matrix Metalloprotease activity. Vascular cell. 2011;3(1):2.
[37] Li GG, Li L, Li C, et al. Influence of up-regulation of Notch ligand DLL4 on biological behaviors of human gastric cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(28):4486-4494.
[38] El Hindy N, Keyvani K, Pagenstecher A, et al.Implications of Dll4-Notch signaling activation in primary glioblastoma multiforme.Neuro Oncol.2013;15(10):1366-1378.
[39] Hagenbeek TJ, Wu X, Choy L,et al.Murine Pten(-/-) T-ALL requires non-redundant PI3K/mTOR and DLL4/Notch1 signals for maintenance and gammac/TCR signals for thymic exit. Cancer letters. 2014;346(2):237-248.
[40] Cheng JC, Chou CH, Kuo ML et al. Radiation-enhanced hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion with MMP-9 expression through PI3 K /Akt /NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. Oncogene. 2006;25(53 ):7009-7018.
|