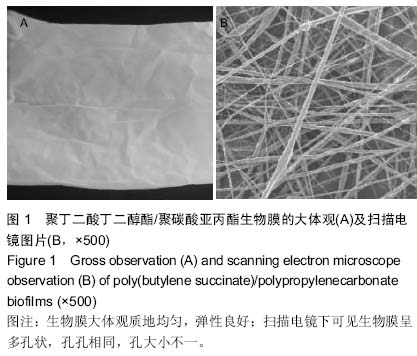
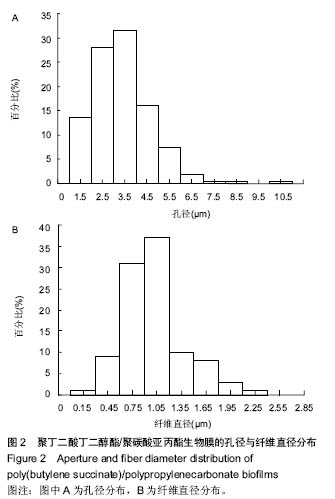
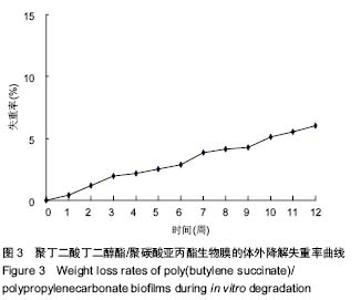
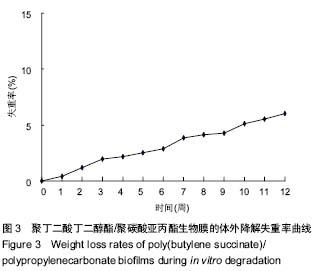
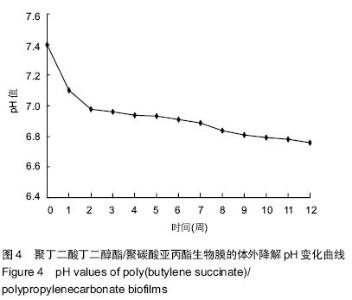
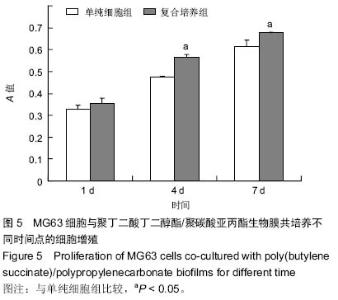
| [1] 王放. 聚碳酸亚丙酯的改性及其医学应用基础研究[D].长春:吉林大学博士学位论文,2008.
[2] 孙淑芬.静电纺PBS纳米纤维膜及缓释血小板内生长因子的PBS纳米纤维膜的制备及生物活性评价[D].长春: 吉林大学博士学位论文,2012.
[3] Dorati R,Colonna C,Genta I,et al.Effect of porogen on the physico-chemical properties and degradation performance of PLGA scaffolds. Polymer Degradation and Stability.2010; 95(4): 694-701.
[4] Nyman S, Gottlow J, KarringT, et al. The regenerative potential of the periodontal ligament:An experimental study in themonkeys.J Clin Periodontal.1982;9(3):257-265.
[5] Buser D,Dula K,Belser U,et al.Localized ridge augmentation using guided bone regeneration. 1. Surgical procedure in the maxilla.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1993;13(1):29-45.
[6] Nyman R,Mangnusson M,Sennerby L, et al. Membrane guided bone regeneration. Segmental radius defects studied in the rabbit.Acta Orthop Scand.1995;66(2):169-173.
[7] Hammerle CH, Schmid J, Lang NP, et al. Temporal dynamics of healing in rabbit cranial defects using guided bone regeneration.J Oral Maxillofac Surg.1995;53(2):167-174.
[8] Kostopoulos L, Karring T. Guided bone regeneration inmandibular defect in rats using a bioresorbable polymer.Clin Oral Implants Res.1994;5(2):66-74.
[9] Cao AM,Okamura T,Ishiguro C,et al.Studies on syntheses and physical characterization of biodegradable aliphatic poly(butylene succinate-co- -caprolactone)s.Polymer. 2002; 43(3):671-679.
[10] 邓利民.PBS及其共聚物的合成与表征[D].成都:四川大学硕士学位论文,2004.
[11] 季君晖.全生物降解塑料的研究与应用[J].塑料,2007,36(2): 37-45.
[12] Li HY,Chang J,Cao AM,et al.In vitro Evaluation of Biodegradable Poly(butylenes succinate) as a Novel Biomaterial.Macromol Biosci.2005;5(5):433-440.
[13] 左秀霞,王晓青,石峰晖,等.聚丁二酸丁二醇酯在生物材料领域的研究进展[J].中国塑料, 2007,21(7):6-9.
[14] 张勇,冯增国,刘凤香,等.聚对苯二甲酸丁二醇酯-co-聚丁二酸丁二醇酯-b-聚乙二醇嵌段共聚物的合成及表征[J].化学学报,2002, 60(12):2225-2231.
[15] Cao AM,Okamura T,Nakayama K,et al. Studies on syntheses and physical properties of biodegradable aliphatic poly(butylene succinate-co-ethylene succinate)s and poly(butylene succinate-co-diethylene glycol succinate)s. Polymer Degradation and Stability.2002;78(1):107-117.
[16] Zhang SP, Yang J, Liu XY, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly (butylene succinate-co-butylene malate). Biomacromolecules.2003;4(2):437-445.
[17] Yang J,Hao QH,Liu XY,et al.Novel Biodegradable Aliphatic Poly(butylenes Succinate-co-cyclic carbonate)s Bearing Functionalizable Carbonate Building Blocks: II.Enzymatic Biodegradation and in Vitro Biocompatibility Assay. Biomacromolecules.2004;5(6):2258-2268.
[18] Takanashi M,Nomura Y,Yoshida Y,et al. Functional polycarbonate by copolymerization of carbon dioxide and epoxide: Synthesis and hydrolysis.Macromol Chem.2003; 183(9):2085-2092.
[19] Hwang Y, Ree M,Kim H,et al.Enzymatic degradation of poly(propylene carbonate) and poly(propylene carbonate-co-epsilon-caprolactone) synthesized via CO2 fixationCatalysis Today.2006;115(1):288-294.
[20] Zhang J,Qi H,Wang H,et al.Engineering of vascular grafts with genetically modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on poly (propylene carbonate) graft. Artif Organs. 2006;30(12): 898-905.
[21] 王海河.改性聚碳酸亚丙酯医用材料生物相容性研究[D].长春:吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2006.
[22] Lekovic V, Camargo P, Weinländer M. Effectiveness of a combination of platelet-rich plasma, bovine porous bone mineral and guided tissue regeneration in the treatment of mandibular grade II molar furcations in humans.J Clin Periodont.2003;30(8):746-751.
[23] Hutmacher D,Hurzeler MB,Schliephake H.A review of material properties of biodegradable and bioresorbable polymers and devices for GTR and GBR applications. Int J OralMax Impl.1996;11(1):667-678.
[24] Crpio L,Loza J,Lynch S,et al.Guide bone regeneration around endosseous implants with anorganic bovine bone mineral.A randomized controlled trial comparing bioresorbable versus non-resorbable barriers.J Periodontol.2000;71(1)∶1743-1749.
[25] Weng B. Development of resorbable membranes for bone regeneration[C]. Symposium on" difficult t reatment option for bone regeneration" April 6 ,1995,Zurich Switzerland.
[26] 周艺群,吴汉江.三种GBR膜材料的比较研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2004, 18(5):418-421.
[27] Hämmerle CH,Jung RE,Yaman D,et al. Ridge augmentation by applying bioresorbable membranes and deproteinized bovine bone mineral: a report of twelve consecutive cases. Clin Oral Implants Res.2008;19(1):19-25.
|