Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (13): 2087-2096.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2192
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and potential of adipose-derived stem cells in cranio-maxillofacial bone regeneration
Chen Jufang, Tian Yulou, Hao Xin
- Second Department of Orthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, China Medical University, Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Shenyang 110002, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2020-04-16Revised:2020-04-29Accepted:2020-06-03Online:2021-05-08Published:2020-12-29 -
Contact:Tian Yulou, MD, Professor, Second Department of Orthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, China Medical University, Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Shenyang 110002, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Chen Jufang, Master candidate, Second Department of Orthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, China Medical University, Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Shenyang 110002, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Research and Development Project in Liaoning Province, No. 2020JH 2/10300069 (to TYL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Jufang, Tian Yulou, Hao Xin. Role and potential of adipose-derived stem cells in cranio-maxillofacial bone regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2087-2096.
share this article

2.1 脂肪干细胞的生物学性能 脂肪干细胞具有多向分化潜能,可以分化为脂肪细胞、成骨细胞、软骨细胞、肌细胞和内皮细胞[6-8]。脂肪干细胞分泌多种生长因子,如转化生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子、血管内皮生长因子和肝细胞生长因子[9],具有血管生成和抗凋亡能力。脂肪干细胞表达CD44、CD73和CD105等经典间充质干细胞标志,但不表达CD14、CD19、CD34、CD45和HLA-DR[10];由于脂肪干细胞低表达MHC,可作为同种异体种子细胞的来源[11],且在动物实验中得到了验证[12-15]。以上提示可以将同种异体脂肪干细胞作为一种成品用于临床,不需要等待自体细胞的扩增,但需要充足的临床前研究。 有研究认为脂肪干细胞的成骨能力与年龄无关[16],也有研究得出与老年人的脂肪干细胞相比,婴儿的脂肪干细胞表现出更强的血管生成和成骨能力[17]。不同采集部位的脂肪干细胞成骨分化能力不同:有学者比较了口腔颊脂垫、腹部、髋部来源的脂肪干细胞性能,结果发现颊脂垫来源的脂肪干细胞增殖率最高,倍增时间最短,并表达CD34和CD146等血管内皮细胞标志物,具有更高的成骨潜能[18];网膜来源的脂肪干细胞比皮下和心包脂肪来源的脂肪干细胞显示出更强的成骨分化能力[19]。以上提示在利用脂肪干细胞进行干细胞治疗或临床前研究时,应将脂肪干细胞的组织来源作为重要考量因素。 2.2 miRNAs(microRNAs)对脂肪干细胞成骨分化的影响 研究发现,小的、非编码的miRNAs(microRNAs)参与了脂肪干细胞成骨分化。miR-140-5p在人脂肪干细胞成脂过程中表达上调,在成骨过程中表达下调,与MEG3呈负相关,推测MEG3通过miR-140-5p来调节人脂肪干细胞成脂和成骨分化的平衡[20],见图2。体外研究表明,miR-145通过直接抑制FoxO1,从而抑制人脂肪干细胞成骨分化[21],见图3。Wnt信号通路是促进脂肪干细胞成骨分化的重要通路:miR-218通过激活Wnt信号通路正向调节人脂肪干细胞成骨分化[22],见图4;LI等[23]通过下调miR-214,激活Wnt通路,上调成骨因子β-catenin/Runx2,下调成脂因子PPAR-γ和C/EBP-α,从而促进骨质疏松大鼠临界大小的骨缺损修复,见图5;miR-145-5P靶向信号素3A抑制脂肪干细胞成骨分化,而抑制miR-145-5p可增强脂肪干细胞成骨潜能,且至少部分是通过调节Wnt信号通路完成[24],见图6。HODGES等[25]研究发现miR-17、miR-23a和miR-31等抑制骨形态发生蛋白2介导的成骨过程,负向调控脂肪干细胞成骨分化,见图7。值得注意的是,包括miR-17和miR-31在内的许多抑制脂肪干细胞成骨分化的miRNAs都受到转化生长因子β1的刺激,这提示降低转化生长因子β1活性可能会提高脂肪干细胞成骨分化潜力。根据基因芯片预测,发现6个miRNAs(miR-143-3p、miR-135a-5p、miR-31-5p、miR-22-3p、miR-193b-3p和let-7i-5p)与脂肪干细胞的成骨密切相关,二氢嘧啶酶样蛋白3被鉴定为该过程中的新的成骨分化关键调控因子,可能成为骨再生相关疾病治疗的潜在靶点[26]。脂肪干细胞成骨是一个复杂的过程,受一系列内源性和环境因素及信号转导途径的调控[27],人们对miRNAs在其中的具体作用机制仍知之甚少。 2.3 提高脂肪干细胞成骨分化潜能的途径 2.3.1 与其他细胞共培养 KIM等[28]发现将脂肪干细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞以0.5∶1的比例共培养时,成骨分化和矿化程度、血管生成能力明显高于单独培养骨髓间充质干细胞。Micro-CT结果表明,脂肪干细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞共同修复小鼠颅骨缺损的效果优于单独使用脂肪干细胞或骨髓间充质干细胞,骨结构恢复较好,其机制可能与共培养后血管内皮生长因子、趋化因子配体1、成骨因子Wnt5a、转化生长因子βR1、Smad3含量增加有关。实验证实了联合使用脂肪干细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞在骨再生方面的有效性。 LIU等[29]分离兔脂肪干细胞和成骨细胞,以1∶1的比例分别在含体积分数为5%和体积分数为10%胎牛血清的培养基中共培养,结果发现共培养2周后,脂肪干细胞呈高度分化,碱性磷酸酶染色、茜素红染色呈阳性,与成熟的成骨细胞相似;两组Ⅰ型胶原和骨钙素mRNA表达均增加,以体积分数为10%胎牛血清组增加最为明显。实验证实兔脂肪干细胞与成骨细胞共培养,在高浓度血清诱导下可分化为成骨细胞。ROZILA等[30]将人脂肪干细胞、人成骨细胞在电纺三维聚[(R)-3-羟基丁酸]-牛源性羟基磷灰石支架上共培养,结果表明不同的人脂肪干细胞/人成骨细胞比例会影响人脂肪干细胞成骨分化程度,1∶1共培养组碱性磷酸酶含量、细胞外矿化及成骨相关转录因子、骨涎蛋白、骨桥蛋白和骨钙素高于其他组。 研究表明,人羊膜间充质干细胞可以促进人脂肪干细胞成骨分化和血管生成,ERK1/2-MAPK信号通路可能参与其 中[31-32]。此外,人羊膜间充质干细胞通过APPL1-ERK1/2信号通路促进脂联素分泌,从而促进人脂肪干细胞成骨分化[33]。 YANG等[34]将人脂肪干细胞诱导为成骨脂肪干细胞和内皮脂肪干细胞,并以不同比例(?2∶1,1∶1,1∶2)共培养。结果表明以1∶1比例共培养成骨脂肪干细胞和内皮脂肪干细胞具有较强的成骨和血管分化能力。 孙仕晨等[35]将人脂肪干细胞成骨诱导7 d后,再将其分别与骨髓间充质干细胞、脐带间充质干细胞和胎盘间充质干细胞共培养,并检测碱性磷酸酶活性、钙化基质形成。结果表明,诱导后的人脂肪干细胞在共培养条件下成骨能力明显提高,且脐带间充质干细胞和胎盘间充质干细胞在矿化阶段诱导人脂肪干细胞成骨的能力要强于骨髓间充质干细胞。 共培养技术能够很好地模拟细胞在体内的生长环境,利用一种辅助细胞去诱导脂肪干细胞成骨分化、增殖及维持细胞活性,便于进一步探究其中机制。不同组织来源的间充质干细胞促进脂肪干细胞成骨分化有不同特点,不同细胞间的最适浓度比例不尽相同,但脂肪干细胞与其他细胞共培养为促进骨再生提供了有效方法。在共培养系统中,细胞间接触机制和旁分泌机制都发挥作用,相关分泌因子的变化、信号转导途径仍有待进一步研究。 2.3.2 与富血小板血浆联合应用 富血小板血浆是通过去除红细胞来富集血浆中的血小板,其含有各种生长因子,如血小板衍生生长因子、表皮生长因子、转化生长因子β1、胰岛素样生长因子、血管内皮生长因子、肝细胞生长因子[36-38]。这些生长因子通过细胞增殖、迁移和分化在组织再生中发挥重要作用,可以促进伤口愈合,修复骨骼缺损。对于脂肪干细胞而言,富血小板血浆是一种良好的成骨诱导剂,它取材于自体血液,微创,制备简单,成本低,有效避免传染性疾病和免疫排斥反应,且可制成凝胶支架,作为干细胞治疗的载体,在再生医学中具有明显的优势[39]。CRUZ等[40]将人脂肪干细胞、犬自体富血小板血浆凝胶支架用于修复比格犬胫骨缺损,与自体骨移植组相比,富血小板血浆与人脂肪干细胞结合组能促进骨缺损中更多的骨形成和成熟。TOBITA等[41]将自体脂肪干细胞和富血小板血浆凝胶植入犬牙周组织缺损区域,2个月后影像学和组织学分析显示形成牙槽骨、牙骨质样、牙周膜样结构,而单纯富血小板血浆组和未植入组虽在部分牙本质组织表面可观察到新形成的牙骨质样结构,但在牙周组织缺损区并未观察到牙周膜样结构,这提示脂肪干细胞和富血小板血浆的联合应用可能是牙周组织工程的一种有效选择。TAJIMA等[38]在大鼠颅骨缺损模型中证明脂肪干细胞和富血小板血浆联合使用对骨再生有显著促进作用,新生骨表面积、三维体积均明显大于其他各组,且5%富血小板血浆可显著促进脂肪干细胞分泌生长因子(胰岛素样生长因子1、转化生长因子β1、肝细胞生长因子、血管内皮生长因子),其诱导成骨分化的作用优于体积分数为10%胎牛血清。 2.3.3 改性的钛金属增强脂肪干细胞成骨分化潜能 钛及钛合金是口腔科、骨科和整形外科手术中常用的金属,钛种植体表面对于骨整合的成功和长期稳定非常重要,钛金属的表面改性及其性能优化在骨组织工程中具有重要意义。提高脂肪干细胞在钛金属表面成骨分化能力,是新的研究热点。 纳米材料是由尺寸在1-100 nm之间的元素构成,表面小颗粒具有良好的比表面积,细胞-纳米形貌的相互作用是一种在骨组织工程中精确控制种子细胞功能和分化的方法。二氧化钛(TiO2)纳米管阵列是一种几何参数可调的高度有序的纳米结构,可以通过简单的阳极氧化策略在植入物或三维支架表面形成,实现二维和三维界面的骨整合,因此具有广阔的临床应用前景。开发具有纳米形貌的钛种植体表面,在口腔科和骨科中成功进行骨再生和骨愈合,是新的发展趋势。MALEC等[42]在含氟离子的丙烷-1,2,3-三醇基电解液中,采用三步阳极氧化法成功制备二氧化钛纳米多孔薄膜,以基础培养基、成骨培养基、未经处理的钛样品作为对照,探讨纳米多孔二氧化钛对人脂肪干细胞生长、活力和成骨分化能力的影响。结果表明,纳米二氧化钛是一种安全无毒的生物材料,可促进人脂肪干细胞成骨分化,推测是二氧化钛纳米形貌模拟了天然骨的多孔结构,为人脂肪干细胞成骨分化创造了更好的条件。Lv等[43]研究表明纳米尺度可影响人脂肪干细胞成骨分化,与50 nm和100 nm的二氧化钛纳米管相比,70 nm的二氧化钛纳米管对人脂肪干细胞成骨分化促进效果最好。二氧化钛纳米管通过上调成骨基因Runx2和骨钙素启动子区域组蛋白H3K4的甲基化水平,抑制去甲基化的视网膜母细胞瘤结合蛋白2,从而促进人脂肪干细胞成骨分化。COWDEN等[44]将人脂肪干细胞接种于二氧化钛纳米管和钛表面增殖7 d,用成骨培养基(培养液中添加10 nmol/L地塞米松、5.4 mmol/L β-甘油磷酸酯和300 μmol/L抗坏血酸)诱导成骨。结果表明,人脂肪干细胞在二氧化钛纳米管表面增殖分化能力强于钛表面,碱性磷酸酶活性和骨钙素含量随二氧化钛纳米管直径的增大而降低。 金纳米颗粒比其他纳米材料具有更好的生物相容性和表面特异性,金纳米颗粒在药物、肽和基因的靶向传递、诊断、生物传感、分子成像和组织工程等领域应用广泛。金纳米颗粒能促进人脂肪干细胞向成骨细胞分化,KO等[45]研究认为金纳米颗粒的浓度固定为1 μmol/L时,相较于15,75, 100 nm的金纳米颗粒,30 nm和50 nm的金纳米颗粒对脂肪干细胞成骨分化的促进作用最强。HEO等[46]用(3-巯丙基)三甲氧基硅烷化学处理制备了硅烷化的钛表面,并通过Au-S键将金纳米颗粒固定在其表面,得到钛-金纳米颗粒。细胞实验表明,钛-金纳米颗粒可显著促进人脂肪干细胞成骨分化,Ⅰ型胶原、Runx2、骨钙素、碱性磷酸酶、钙沉积增加。动物实验表明,植入兔股骨内3周后,钛-金纳米颗粒组表面的骨密度较纯钛组明显增加,钛-金纳米颗粒组骨体积、骨体积分数、骨表面密度等均显著增加。由此证明钛-金纳米颗粒可作为诱导骨整合的牙种植体,也可用于修复骨组织缺损。 2.3.4 基因技术增强脂肪干细胞成骨分化潜能 (1)基因编辑技术:基因编辑技术指能够让人类对目标基因进行定点“编辑”,实现对特定DNA片段的修饰,通过对特定片段的删除、插入等,人为改造遗传物质。 Twist是一种高度保守的发育蛋白,在间充质细胞系的转录调控中发挥关键作用。QUARTO等[47]研究表明敲除Twist1基因,可促进人脂肪干细胞的体内外成骨分化,这是通过激活BMP-ERK/FGF信号和上调TAZ完成的。敲除基因泛素特异性蛋白酶7(ubiquitin specific protease 7,USP7),人脂肪干细胞体外成骨明显受到抑制,过表达USP7则增强人脂肪干细胞的成骨分化能力。将敲除USP7的人脂肪干细胞植入裸鼠皮下,CT分析显示新骨形成面积明显小于对照组,表明USP7对人脂肪干细胞体内成骨分化是必不可少的[48]。CHIARELLA等[49]发现锌指蛋白521(Zinc finger protein 521,ZNF521)过表达显著降低了人脂肪干细胞成骨分化,导致Ⅰ型胶原、碱性磷酸酶、骨甾醇、骨桥蛋白和钙沉积的水平降低。敲除ZNF521显著促进了人脂肪干细胞成骨分化,早期成骨细胞相关标志物和晚期矿化骨结节的积累明显增加。 基因编辑以其能够高效、精确地进行定点基因组编辑,从DNA水平改变基因表达,在基因研究、基因治疗、遗传改良等方面展示出了巨大的潜力。利用基因编辑技术对脂肪干细胞进行修饰,可敲除抑制成骨的基因,这是骨组织工程发展的新方向。但基因网络庞杂,相关基因需要进一步挖掘与探索,在应用于临床之前仍有很长一段路要走,且可能面临伦理学的质疑。 (2)细胞转染技术:细胞转染是指将外源分子(如DNA、RNA等)导入(真核)细胞的实验技术之一,主要包括电击法、磷酸钙法、脂质体介导法和病毒感染法。随着分子生物学和细胞生物学研究的不断发展,转染已经成为研究和控制真核细胞基因功能的常规工具。通过转染,可持续高效表达促进脂肪干细胞成骨的基因,从而增强脂肪干细胞成骨分化潜能。 LIM矿化蛋白1(LIM mineralization protein-1,LMP-1)是BMP通路上游的正性调节因子,在促进骨再生的基因层面比BMP更具优势[50]。缺氧诱导因子1α(hypoxia-inducible factor -1α,HIF-1α)可以协调血管生成从而促进骨折修复[51]。PAN等[52]研究发现,与单独转染LMP-1或HIF-1α相比,LMP-1和HIF-1α基因同时转染促进了脂肪干细胞的体外成骨、裸鼠皮下异位成骨,血管生成数量明显增多。基质细胞衍生因子1(stromal derived factor-1,SDF-1)是一种能够触发干细胞迁移的趋化因子,能增强骨形态发生蛋白2(bone morphogenetic protein-2,BMP-2)诱导的骨形成。LO等[53]使用Cre/LoxP系统杆状病毒感染脂肪干细胞,使BMP-2/SDF-1强劲而持续的表达,协同激活Smad和ERK1/2通路,并制备脂肪干细胞/多孔明胶支架材料,修复大鼠临界大小(6 mm)颅骨缺损,12周后micro-CT显示BMP-2/SDF-1共表达组骨修复效果优于BMP-2或SDF-1单独表达组。 2.3.5 增强脂肪干细胞成骨分化潜能的其他处理 相较于难度较大的基因技术,使用细胞因子、药物等处理脂肪干细胞,增强成骨基因表达,从而促进其成骨分化,是一种可供替代的选择。 YANAI等[54]研究表明,在添加rhBMP-2的培养基中,人脂肪干细胞钙沉积增加,Runx2、Osterix、碱性磷酸酶、骨联素、骨涎蛋白和骨钙素的蛋白表达增加,促进了人脂肪干细胞成骨分化。此外,升高细胞外钙浓度,可以激活钙敏感受体,升高细胞内钙浓度、Ca2+/钙调蛋白依赖性NFAT信号通路来增强BMP-2的表达,从而促进人脂肪干细胞成骨分化。人脂肪干细胞体外扩增过程中,经成纤维细胞生长因子2预处理后,第7代细胞数量增加约为对照组的44倍,成骨标志物Cbfa1、Runx2和碱性磷酸酶表达增加;成纤维细胞生长因子2预处理的人脂肪干细胞在小鼠皮下产生丰富的类骨/ 骨基质,而对照组几乎无骨基质形成[55]。川续断皂苷Ⅵ又称木通皂苷D,是一种从川续断根茎中分离出的三萜皂苷,常用于止血、促进骨损伤愈合。DING等[56]研究表明,川续断皂苷Ⅵ对脂肪干细胞增殖无明显影响,但可增强碱性磷酸酶活性和钙沉积,上调骨钙素、Runx2和Smad2/3磷酸化水平,增强脂肪干细胞成骨分化能力。ELISA结果显示,川续断皂苷Ⅵ可抑制脂肪干细胞释放肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1β,提示川续断皂苷Ⅵ对脂肪干细胞具有抗炎作用。转录共激活因子TAZ是Hippo信号通路下游的重要效应分子,参与细胞增殖、分化。体外研究发现,TAZ过表达可增强脂肪干细胞成骨分化和骨再生,削弱成脂分化。将TAZ的化学激活剂TM-25659预处理的脂肪干细胞植入裸鼠皮下,增强了脂肪干细胞体内成骨,提示TAZ在脂肪干细胞中的药理激活可能是促进骨再生和修复的有效途径[57]。W9是一种肽,通过阻断核因子κB配体(RANKL)-RANK信号而抑制破骨细胞分化从而激活骨形成。OTSUKI等[58]研究表明W9肽可增强人脂肪干细胞成骨分化,经W9处理的人脂肪干细胞可诱导成骨相关基因Runx2和Ⅰ型胶原A1表达,钙沉积明显高于经BMP-2处理的人脂肪干细胞,这主要是通过磷酸化成骨信号通路中的p38、JNK、Erk和Akt来实现的。骨化三醇在细胞增殖和分化的局部调节中起自分泌或旁分泌作用。骨化三醇预处理人脂肪干细胞30 min不仅能增强细胞在双相磷酸钙支架上的黏附,且比连续处理更能促进人脂肪干细胞的增殖和成骨分化[59]。ZHANG等[60]将仿生磷酸钙颗粒内部掺入辛伐他汀,并与人脂肪干细胞结合,制成新型组织工程骨,体外实验表明仿生磷酸钙释放的辛伐他汀能显著促进人脂肪干细胞增殖,提高碱性磷酸酶活性、矿化结节形成和成骨基因表达,且该材料能够在裸鼠皮下形成新骨。 细胞因子、化学制剂、药物等外源性因子对脂肪干细胞成骨分化都有一定促进作用,已经引起了学者们的关注,但其具体机制仍需要更深入的研究,在正式应用于临床前仍有很长的路需要走。 "

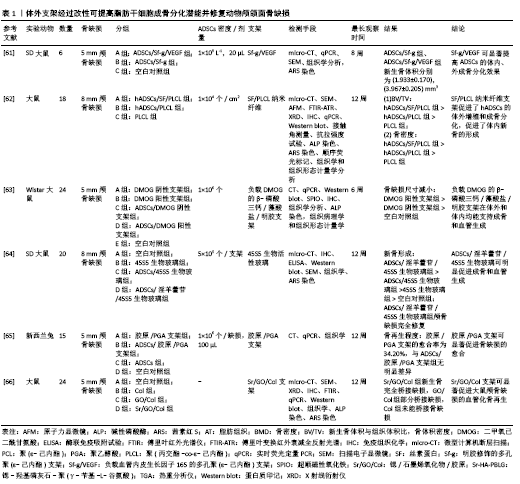
2.4 脂肪干细胞复合可注射性支架在颅颌面骨再生中的应用 支架一直是骨组织工程的研究重点之一。理想的支架应该具有良好的生物相容性及生物安全性,有合适的孔隙以促进新生血管的形成,为干细胞的黏附和增殖提供良好的微环境。体外支架经过改性可提高脂肪干细胞成骨分化潜能,修复动物颅颌面骨缺损,见表1[61-66],但常规体外支架修复颅颌面骨缺损需要开放手术,不适合修复不规则形状的骨缺损和骨不连。可注射性支架具有保持细胞分化表型和修复不规则骨缺损的能力,使用针头注射器操作,手术时间短[67],在颅颌面骨再生的应用中具有更大的潜力。 水凝胶是一种在体内模拟细胞外基质的材料,含有与人体环境相似的水,且水凝胶中包含的药物、蛋白质、生长因子等物质可以缓慢释放,为细胞生存提供良好的环境[68-69]。 可注射性水凝胶在植入缺损部位发生交联反应,可以与周围结构紧密接触。OLIVEIRA等[70]发现甲基丙烯酸酯结冷胶(Methacrylated gellan-gum,GG-MA)具有良好的细胞黏附性,在无任何成骨或骨传导因子的情况下,能够诱导人脂肪干细胞成骨分化,成骨过程依赖于肌动蛋白-肌球蛋白收缩通路的机械转导而完成。LEE等[71]在明胶骨架(gelatin,Gel)上合成了酪胺(tyramine,Ty),将N-乙酰基半胱氨酸(N-acetyl cysteine,NAC)连接到GNPs表面,得到含有G-NAC的Gel-Ty 水凝胶(Gel-Ty/G-NAC)。Gel-Ty/G-NAC具有良好的机械强度和生物相容性,包含在Gel-Ty中的G-NAC可以促进人脂肪干细胞成骨分化。LIAO等[72]将生物相容性热凝胶透明质酸-壳聚糖-聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺[hyaluronic acid-g-chitosan-g-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide),HA-CPN]作为三维有机凝胶基质包埋兔脂肪干细胞,将双相磷酸钙(BCP)陶瓷微粒作为矿化骨基质嵌入凝胶基质中,并用富血小板血浆进一步强化其诱导成骨的作用。从基因表达、扫描电镜/能量色散X射线扫描、钙含量分析来看,PRP/BCP促进HA-CPN凝胶基质中脂肪干细胞成骨分化和细胞外基质矿化。CT分析证实同种异体兔脂肪干细胞应用于HA-CPN/PRP/BCP复合支架可以有效修复兔临界大小颅骨缺损。水凝胶易于获得,成本低,能够诱导脂肪干细胞成骨分化,作为可注射生物支架材料具有很高的潜力,在非负重骨、不规则骨缺损再生方面具有广阔的应用前景。 微球是一种生物物理靶向载药制剂,常见的多孔微球细胞微载体是由高分子材料制备而成。HUANG等[73]制备γ-苄基-L-谷氨酸[poly (γ-benzyl-L-glutamate),PBLG]多孔可注射性微球,将成骨分化的脂肪干细胞种植于微球内,实验显示脂肪干细胞可以在PBLG微球表面黏附,并能够保持其成骨表型,碱性磷酸酶含量、钙沉积量增加。Micro-CT显示ADSCs/PBLG复合材料可修复小鼠股骨不连,证明PBLG微球具有良好的生物相容性和细胞相容性,可注射性微球对颅颌面骨缺损的修复具有重要意义。 2.5 脂肪干细胞在颅颌面骨再生中的临床前研究 小鼠、大鼠等小型动物常被用来制作颅骨、四肢骨骨缺损模型,裸鼠常用来进行皮下异位成骨实验,而上下颌骨缺损、牵张成骨、种植后骨结合、牙周组织缺损等实验,还需要选用大型动物,如兔、犬、猪等。 POUREBRAHIM等[74]建立犬上颌牙槽裂模型,分别用负载脂肪干细胞的羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙支架、自体骨进行修复。术后15 d和60 d时,自体移植侧的骨形成高于干细胞侧,自体侧分别为45%和96%,干细胞侧分别为5%和70%。MEHRABANI等[75]利用荷兰兔制造双侧下颌骨缺损动物模型,分别用纤维蛋白胶、脂肪干细胞联合纤维蛋白胶、自体骨移植进行治疗,并设立空白对照组。冠状位CT显示在术后28 d和56 d脂肪干细胞联合纤维蛋白胶治疗组皮质骨显著重建。脂肪干细胞联合纤维蛋白胶组与纤维蛋白胶组的新皮质骨厚度存在显著差异,脂肪干细胞联合纤维蛋白胶组与自体骨移植组之间没有发现显著差异。使用脂肪干细胞联合纤维蛋白胶支架时,愈合过程加快,新生骨皮质厚度显著增加,这提示脂肪干细胞组织工程骨可以提供一个可接受的替代方案,特别是在自体骨移植有效性有限或供区并发症的情况下。 3D打印系统能够在微米级精确控制和快速生产所需的3D形状结构,3D打印支架具有机械性能、孔径和孔隙率可控的优点。LEE等[76]使用3D打印技术制造了聚己内酯/磷酸三钙复合支架,将脂肪干细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞分别种植于支架中,并植入比格犬上颌骨缺损处,两组均显示出良好的促进成骨作用。3D-CT显示,在8周和12周时,脂肪干细胞组比骨髓间充质干细胞组观察到更明显的骨化;组织学分析显示,与骨髓间充质干细胞组相比,脂肪干细胞组骨化程度更高,这提示脂肪干细胞与3D打印聚己内酯/磷酸三钙支架联合使用,可作为骨髓间充质干细胞的良好替代品,以改善骨移植中的骨整合和骨缺损的再生。 Osterix(OSX)是一种含有由SP7基因编码的锌指转录因子,也是成骨细胞分化所必需的转录因子。LAI等[77]实验证明转染pEGFP-OSX的脂肪干细胞可以有效促进兔下颌骨牵张成骨区新骨形成,牵张区新生骨小梁厚度、新生骨皮质体积和松质骨体积高于脂肪干细胞组与生理盐水组。单纯将脂肪干细胞植入牵张间隙没有任何效果,这表明未经成骨诱导的脂肪干细胞在动物骨组织中迁移和分化的能力较低,可能是因为牵张区的微环境并没有促进脂肪干细胞存活或分化。 BRESSAN等[78]在拔出下颌前磨牙与第一磨牙的犬模型中植入种植体,并用负载了人脂肪干细胞的羟基磷灰石支架填充种植体边缘。组织学分析显示,相较于单纯羟基磷灰石支架组,负载人脂肪干细胞的羟基磷灰石支架组可显著促进骨再生,观察到新生血管、成骨细胞和新生骨基质,且无炎性细胞,从而论证在即刻种植牙的情况下,脂肪干细胞可用于加速种植体周围缺损的骨愈合。 2.6 脂肪干细胞在颅颌面骨再生中的临床应用 2004年,LENDECKEL等[79]使用自体脂肪干细胞、髂骨、纤维蛋白胶成功修复了7岁女孩的大面积颅骨缺损。3个月后3D-CT扫描显示有新骨形成,颅骨连续性良好,这是脂肪干细胞用于骨缺损的最早期临床报道之一,对后来的临床应用具有重要的借鉴和指导意义。 2009年,MESIM?KI等[80]使用自体脂肪干细胞与重组人骨形态发生蛋白2和β-磷酸三钙颗粒在微血管皮瓣内进行异位成骨,并应用于成人大面积复发性角化囊肿切除后上颌骨缺损的修复。上颌骨缺损重建4个月后,在新生牙槽骨中植入4颗种植体,具有良好的骨整合和稳定性,这是首例在微血管重建手术中使用自体脂肪干细胞异位骨的临床病例。 2014年,Sándor等[81]使用人脂肪干细胞结合生物活性玻璃、β-磷酸三钙颗粒、重组人骨形态发生蛋白2修复颅颌面部硬组织缺损13例(额窦3例、颅骨5例、下颌骨3例、鼻中隔2例),在12-52个月的随访中,13例中有10例支架与周围骨骼成功结合。此外,Sándor团队联合应用人脂肪干细胞与重组人骨形态发生蛋白2和β-磷酸三钙成功修复下颌骨缺损[82]、颅颌面骨缺损[83],为颅颌面骨缺损的修复提供了新的思路。 基质血管成分是脂肪组织经胶原酶消化、过滤、离心除去成熟脂肪细胞后得到的,含有丰富的脂肪干细胞[84]。2016年,PRINS等[85]将基质血管成分接种于β-磷酸三钙或双相磷酸钙支架,并用于上颌窦底提升手术,术后6个月在种植牙的同时取新生骨组织进行micro-CT、组织学检测。在活检的10例患者中,观察到7例骨形成活跃,证明了基质血管成分用于骨再生的可行性、安全性和巨大潜力。 2017年,CASTILLO-CARDIEL等[86]对下颌角骨折患者进行单盲对照临床试验,研究组骨折复位并应用自体脂肪干细胞,对照组单纯骨折复位,在12周的随访中,CT扫描显示研究组的骨化率更高。研究结果表明应用人脂肪干细胞治疗下颌骨骨折可以有效促进骨再生。 2019年,KHOJASTEH等[87]选用14例下颌牙槽嵴萎缩患者作为研究对象,分别用50%无机牛骨矿物质与颊脂垫源性脂肪干细胞混合、50%无机牛骨矿物质与颗粒状自体骨混合修复牙槽骨萎缩,锥形束CT显示颊脂垫源性脂肪干细胞和自体颗粒骨结合无机牛骨矿物质在骨体积形成方面没有差异。颊脂垫可以在拔除第三磨牙的过程中获取,且颊脂垫源性脂肪干细胞成骨分化能力较强,在脂肪干细胞中具有一定的优势,可能为牙槽嵴缺损修复提供一种替代自体骨的方法,但需要大规模临床试验证实。 "
| [1] 邵高海,李德霞,余雨,等.骨质疏松治疗仪对骨折愈合影响的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(1):31-34. [2] SVEDBOM A, HERNLUND E, IVERGÅRD M, et al. Osteoporosis in the European Union: a compendium of country-specific reports. Arch Osteoporos. 2013;8:137. [3] DUFRANE D. Impact of Age on Human Adipose Stem Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering. Cell Transplantation. 2017;26(9):1496-1504. [4] BURROW KL, HOYLAND JA. Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Exhibit Enhanced Proliferative Capacity and Retain Multipotency Longer than Donor-Matched Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells during Expansion In Vitro. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:1-15. [5] SCHNEIDER S, UNGER M, VAN GRIENSVEN M. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from liposuction and resected fat are feasible sources for regenerative medicine. Eur J Med Res. 2017;22:17. [6] TRUJILLO NA, POPAT KC. Increased Adipogenic and Decreased Chondrogenic Differentiation of Adipose Derived Stem Cells on Nanowire Surfaces. Materials (Basel). 2014;7(4):2605-2630. [7] LOTFY A, SALAMA M, ZAHRAN F, et al. Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells derived from rat bone marrow and adipose tissue:a comparative study. Int J Stem Cells. 2014;7:135-142. [8] SAÇAK B, CERTEL F, AKDENIZ ZD, et al. Repair of critical size defects using bioactive glass seeded with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105:1002-1008. [9] TAJIMA S, TOBITA M, MIZUNO H. Bone Regeneration with a Combination of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Platelet-Rich Plasma. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1773:261-272. [10] DI BATTISTA JA, SHEBABY W, KIZILAY O, et al. Proliferation and differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ASCs) into osteoblastic lineage are passage dependent. Inflamm Res. 2014;63(11):907-917. [11] GU H, XIONG Z, YIN X, et al. Bone regeneration in a rabbit ulna defect model: use of allogeneic adipose-derivedstem cells with low immunogenicity. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;358:453-464. [12] NOMURA I, WATANABE K, MATSUBARA H, et al. Uncultured autogenous adipose-derived regenerative cells promote bone formation during distraction osteogenesis in rats. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(12): 3798-3806. [13] WAGNER JM, CONZE N, LEWIK G, et al. Bone allografts combined with adipose-derived stem cells in an optimized cell/volume ratio showed enhanced osteogenesis and angiogenesis in a murine femur defect model. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97:1439-1450. [14] 沈凌,王锡友,陈萍,等.同种异体脂肪干细胞复合纳米级胶原基骨材料修复尺骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(32): 5162-5166. [15] 杨函,康建平,丁裕名,等.同种异体脂肪干细胞复合脱钙骨支架材料修复尺骨缺损:CT扫描及组织学检测[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(28):4520-4525. [16] DING DC, CHOU HL, HUNG WT, et al. Human adipose-derived stem cells cultured in keratinocyte serum free medium:Donor’s age does not affect the proliferation and differentiation capacities. J Biomed Sci. 2013;20(1):59. [17] WU W, NIKLASON L, STEINBACHER DM. The effect of age on human adipose-derived stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131:27-37. [18] REZAI RAD M, BOHLOLI M, AKHAVAN RAHNAMA M, et al. Impact of Tissue Harvesting Sites on the Cellular Behaviors of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Implication for Bone Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:2156478. [19] RUSSO V, YU C, BELLIVEAU P, et al. Comparison of human adipose-derived stem cells isolated from subcutaneous, omental, and intrathoracic adipose tissue depots for regenerative applications. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(2):206-217. [20] LI Z, JIN C, CHEN S, et al. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits adipogenesis and promotes osteogenesis of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via miR-140-5p. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017;433: 51-60. [21] HAO W, LIU H, ZHOU L, et al. MiR-145 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells through targeting FoxO1. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018;243:386-393. [22] ZHANG WB, ZHONG WJ, WANG L. A signal-amplification circuit between miR-218 and Wnt/β-catenin signal promotes human adipose tissue-derived stem cells osteogenic differentiation. Bone. 2014;58:59-66. [23] LI KC, CHANG YH, HSU MN, et al. Baculovirus-Mediated miR-214 Knockdown Shifts Osteoporotic ASCs Differentiation and Improves Osteoporotic Bone Defects Repair. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16225. [24] LIU X, ZHU W, WANG L, et al. miR-145-5p suppresses osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells by targeting semaphorin 3A. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019;55:189-202. [25] HODGES WM, O’BRIEN F, FULZELE S. Function of microRNAs in the Osteogenic Differentiation and Therapeutic Application of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ASCs). Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(12):2597. [26] JIA B, ZHANG Z, QIU X, et al. Analysis of the miRNA and mRNA involved in osteogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16:1111-1120. [27] CALABRESE G, GIUFFRIDA R, FORTE S, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded into a collagen-hydroxyapatite scaffold promote bone augmentation after implantation in the mouse. Sci Rep. 2017;7:7110. [28] KIM KI, PARK S. Osteogenic differentiation and angiogenesis with cocultured adipose-derived stromal cells and bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials. 2014;35:4792-4804. [29] LIU DC, YANG XN, HUANG CZ, et al. Experimental study on co-culturing adipose-derived stem cells with osteoblasts under different conditions. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016;20:3535-3543. [30] ROZILA I, AZARI P, MUNIRAH S, et al. Differential osteogenic potential of human adipose-derived stem cells co-cultured with human osteoblasts on polymeric microfiber scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104:377-387. [31] WANG Y, CHEN X, YIN Y. Human amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells induced osteogenesis and angiogenesis in human adipose-derived stem cells via ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathway. BMB Rep. 2018;51: 194-199. [32] ZHANG C, YU L, LIU S. Human amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote osteogenic and angiogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0186253. [33] WANG Y, DU Y, YUAN H, et al. Human amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance the osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by promoting adiponectin excretion via the APPL1-ERK1/2 signaling pathway. IUBMB Life. 2020;72:296-304. [34] YANG H, HONG N, LIU H, et al. Differentiated adipose-derived stem cell cocultures for bone regeneration in RADA16-I in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:9458-9472. [35] 孙仕晨,董腾哲,黄昕,等.Transwell共培养条件下诱导脂肪干细胞成骨能力的改变[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(28):4155-4161. [36] BUSILACCHI A, GIGANTE A, MATTIOLI-BELMONTE M, et al. Chitosan stabilizes platelet growth factors and modulates stem cell differentiation toward tissue regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2013; 98(1):665-676. [37] AMABLE PR, CARIAS RB, TEIXEIRA MV, et al. Platelet-rich plasma preparation for regenerative medicine: optimization and quantification of cytokines and growth factors. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(3):67. [38] TAJIMA S, TOBITA M, ORBAY H, et al. Direct and indirect effects of a combination of adipose-derived stem cells and platelet-rich plasma on bone regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21:895-905. [39] 吴雪莲,杨春.富血小板血浆在颞下颌关节骨关节炎的作用机制及应用研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2018,11(2):122-126. [40] CRUZ AC, CAON T, MENIN Á, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells incorporated into platelet-rich plasma improved bone regeneration and maturation in vivo. Dent Traumatol. 2015;31(1):42-48. [41] TOBITA M, UYSAL CA, GUO X, et al. Periodontal tissue regeneration by combined implantation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells and platelet-rich plasma in a canine model. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(12): 1517-1526. [42] MALEC K, GÓRALSKA J, HUBALEWSKA-MAZGAJ M, et al. Effects of nanoporous anodic titanium oxide on human adipose derived stem cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:5349-5360. [43] LV L, LIU Y, ZHANG P, et al. The nanoscale geometry of TiO2 nanotubes influences the osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by modulating H3K4 trimethylation. Biomaterials. 2015;39: 193-205. [44] COWDEN K, DIAS-NETIPANYJ MF, POPAT KC. Effects of titania nanotube surfaces on osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Nanomedicine. 2019;17:380-390. [45] KO WK, HEO DN, MOON HJ, et al. The effect of gold nanoparticle size on osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2015;438:68-76. [46] HEO DN, KO WK, LEE HR, et al. Titanium dental implants surface-immobilized with gold nanoparticles as osteoinductive agents for rapid osseointegration. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016;469:129-137. [47] QUARTO N, SENARATH-YAPA K, RENDA A. TWIST1 silencing enhances in vitro and in vivo osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by triggering activation of BMP-ERK/FGF signaling and TAZ upregulation. Stem Cells. 2015;33(3):833-847. [48] TANG Y, LV L, LI W, et al. Protein deubiquitinase USP7 is required for osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):186. [49] CHIARELLA E, ALOISIO A, SCICCHITANO S, et al. ZNF521 Represses Osteoblastic Differentiation in Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(12):4095. [50] STROHBACH CA, RUNDLE CH, WERGEDAL JE, et al. LMP-1 retroviral gene therapy influences osteoblast differentiation and fracture repair: a preliminary study. Calcif Tissue Int. 2008;83(3):202-211. [51] ZOU D, ZHANG Z, YE D, et al. Repair of critical-sized rat calvarial defects using genetically engineered bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Stem Cells. 2011;29: 1380-1390. [52] PAN WM, CAO Z, JIA SJ, et al. Synergistic enhancement of bone regeneration by LMP-1 and HIF-1α delivered by adipose derived stem cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2016;38:377-384. [53] LO SC, LI KC, CHANG YH, et al. Enhanced critical-size calvarial bone healing by ASCs engineered with Cre/loxP-based hybrid baculovirus. Biomaterials. 2017;124:1-11. [54] YANAI R, TETSUO F, ITO S, et al. Extracellular calcium stimulates osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by enhancing bone morphogenetic protein-2 expression. Cell Calcium. 2019;83:102058. [55] LIM S, CHO H, LEE E, et al. Osteogenic stimulation of human adipose-derived stem cells by pre-treatment with fibroblast growth factor 2. Cell Tissue Res. 2016;364:137-147. [56] DING XP, LI WY, CHEN DS, et al. Asperosaponin VI stimulates osteogenic differentiation of rat adipose-derived stem cells. Regenerative therapy. 2019;11:17-24. [57] ZHU Y, WU Y, CHENG J, et al. Pharmacological activation of TAZ enhances osteogenic differentiation and bone formation of adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):53. [58] OTSUKI Y, II M, MORIWAKI K, et al. W9 peptide enhanced osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495:904-910. [59] MOKHTARI-JAFARI F, AMOABEDINY G, DEHGHAN MM, et al. Short Pretreatment with Calcitriol Is Far Superior to Continuous Treatment in Stimulating Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose Stem Cells. Cell J. 2020;22:293-301. [60] ZHANG X, JIANG W, LIU YS, et al. Human adipose-derived stem cells and simvastatin-functionalized biomimetic calcium phosphate to construct a novel tissue-engineered bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018; 495:1264-1270. [61] 徐万林,卢浩,叶金海,等.载VEGF165多孔聚己内酯支架促进脂肪来源干细胞体内外成骨分化的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(3):270-275. [62] WANG Z, LIN M, XIE Q, et al. Electrospun silk fibroin/poly(lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) nanofibrous scaffolds for bone regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:1483-1500. [63] JAHANGIR S, HOSSEINI S, MOSTAFAEI F, et al. 3D-poroβ-tricalcium phosphate-alginate-gelatin scaffold with DMOG delivery promotes angiogenesis and bone formation in rat calvarial defects. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018;30(1):1-14. [64] JING X, YIN W, TIAN H, et al. Icariin doped bioactive glasses seeded with rat adipose-derived stem cells to promote bone repair viaenhanced osteogenic and angiogenic activities. Life Sci. 2018;202:52-60. [65] TOOSI S, NADERI-MESHKIN H, KALALINIA F, et al. Bone defect healing is induced by collagen sponge/polyglycolic acid. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(3):1-10. [66] CHEN Y, ZHENG Z, ZHOU R, et al. Developing a Strontium-Releasing Graphene Oxide-/Collagen-Based Organic-Inorganic Nanobiocomposite for Large Bone Defect Regeneration via MAPK Signaling Pathway. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(17):15986-15997. [67] KIM SE, YUN YP, SHIM KS, et al. Effect of lactoferrin-impregnated porous poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) microspheres on osteogenic differentiation of rabbit adipose-derived stem cells (rADSCs). Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;122:457-464. [68] PARK SH, KWON JS, LEE BS, et al. BMP2-modified injectable hydrogel for osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7:6603. [69] MI L, LIU H, GAO Y, et al. Injectable nanoparticles/hydrogels composite as sustained release system with stromal cell-derived factor-1α for calvarial bone regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;101:341-347. [70] OLIVEIRA MB, CUSTÓDIO CA, GASPERINI L, et al. Autonomous osteogenic differentiation of hASCs encapsulated in methacrylated gellan-gum hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2016;41:119-132. [71] LEE D, HEO DN, NAH HR, et al. Injectable hydrogel composite containing modified gold nanoparticles: implication in bone tissue regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:7019-7031. [72] LIAO HT, TSAI MJ, BRAHMAYYA M, et al. Bone Regeneration Using Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in Injectable Thermo-Gelling Hydrogel Scaffold Containing Platelet-Rich Plasma and Biphasic Calcium Phosphate. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(9):2537. [73] HUANG Z, GU H, YIN X, et al. Bone regeneration using injectable poly (γ-benzyl-L-glutamate) microspheres loaded with adipose-derived stem cells in a mouse femoral non-union model. Am J Transl Res. 2019; 11(5):2641-2656. [74] POUREBRAHIM N, HASHEMIBENI B, SHAHNASERI S, et al. A comparison of tissue-engineered bone from adipose-derived stem cell with autogenous bone repair in maxillary alveolar cleft model in dogs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;42(5):562-568. [75] MEHRABANI D, KHODAKARAM-TAFTI A, SHATERZADEH-YAZDI H, et al. Comparison of the regenerative effect of adipose-derived stem cells,fibrin glue scaffold,and autologous bone graft in experimental mandibular defect in rabbit. Dent Traumatol. 2018;34(6):413-420. [76] LEE JW, CHU SG, KIM HT, et al. Osteogenesis of Adipose-Derived and Bone Marrow Stem Cells with Polycaprolactone/Tricalcium Phosphate and Three-Dimensional Printing Technology in a Dog Model of Maxillary Bone Defects. Polymers (Basel). 2017;9(12):450. [77] LAI QG, SUN SL, ZHOU XH, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells transfected with pEGFP-OSX enhance bone formation during distraction osteogenesis. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2014;15(5):482-490. [78] BRESSAN E, BOTTICELLI D, SIVOLELLA S, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as a Tool for Dental Implant Osseointegration: an Experimental Study in the Dog. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2015;4:197-208. [79] LENDECKEL S, JÖDICKE A, CHRISTOPHIS P, et al. Autologous stem cells (adipose) and fibrin glue used to treat widespread traumatic calvarial defects: case report. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2004;32(6):370-373. [80] MESIMÄKI K, LINDROOS B, TÖRNWALL J, et al. Novel maxillary reconstruction with ectopic bone formation by GMP adipose stem cells. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 38(3): 201-209. [81] SÁNDOR GK, NUMMINEN J, WOLFF J, et al. Adipose stem cells used to reconstruct 13 cases with cranio-maxillofacial hard-tissue defects. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(4):530-540. [82] SÁNDOR GK, TUOVINEN VJ, WOLFF J, et al. Adipose stem cell tissue-engineered construct used to treat large anterior mandibular defect: a case report and review of the clinical application of good manufacturing practice-level adipose stem cells for bone regeneration. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(5):938-950. [83] SÁNDOR GK. Tissue engineering of bone:Clinical observations with adipose-derived stem cells, resorbable scaffolds, and growth factors. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2012;2(1):8-11. [84] 张蕾,孟芝竹,张斌.人脂肪组织来源血管周干细胞成骨、成脂、成软骨分化能力研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2018,11(7):420-425. [85] PRINS HJ, SCHULTEN EA, TEN BRUGGENKATE CM, et al. Bone Regeneration Using the Freshly Isolated Autologous Stromal Vascular Fraction of Adipose Tissue in Combination With Calcium Phosphate Ceramics. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(10):1362-1374. [86] CASTILLO-CARDIEL G, LÓPEZ-ECHAURY AC, SAUCEDO-ORTIZ JA, et al. Bone regeneration in mandibular fractures after the application of autologous mesenchymal stem cells, a randomized clinical trial. Dent Traumatol. 2017;33(1):38-44. [87] KHOJASTEH A, HOSSEINPOUR S, REZAI RAD M, et al. Buccal fat pad-derived stem cells with anorganic bovine bone mineral scaffold for augmentation of atrophic posterior mandible:An exploratory prospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21: 292-300. [88] IM GI, SHIN YW. Do adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells have the same osteogenic and chondrogenic potential as bone marrow-derived cells? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(10):845-853. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [4] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [6] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [7] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [8] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [9] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [10] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [11] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [12] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [13] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [14] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [15] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||