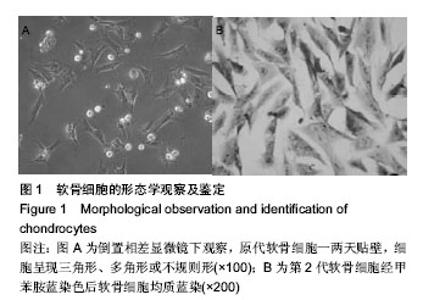
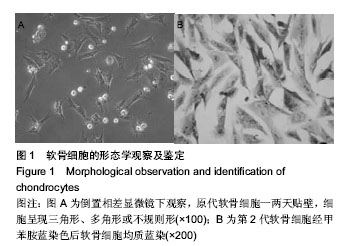
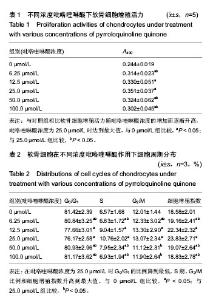
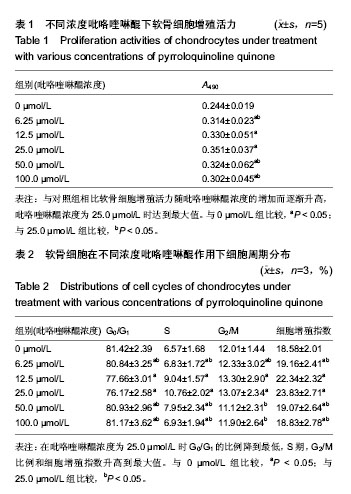
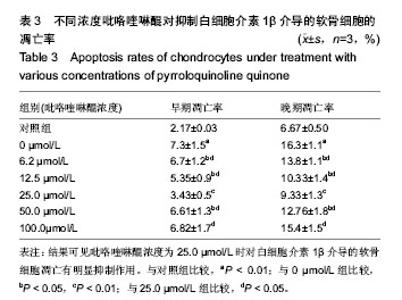
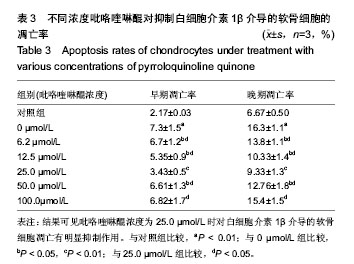
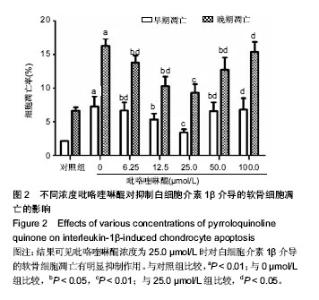
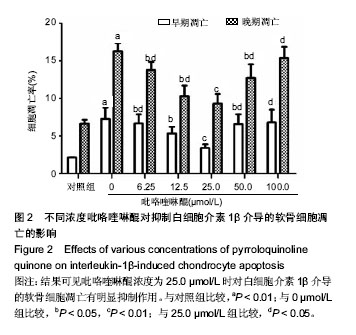
| [1] KIm HA, Blanco FJ.Cell death and apoptpsis in osteoarthrifis cartilage. Current Drug Targets. 2007;8(2):333-345.
[2] Kasahara T, Kat o T .Nutritional biochemistry:A new redox-cofactor vitamin for mammals.Nature. 2003;422( 6934): 832.
[3] Steinberg F,Stites TE, Anderson P,et al.Pyrroloquinoline quinone improves growth and reproductive performance in mice fed chemically defined diets[J]. Exp Biol Med.2003; 228:160-166 .
[4] Andrea C R, Antonio R, Augusto R,et al. Modeling novel quinocofactors: An overview.Bioorganic Chemistry. 1999; 27(4): 253-288.
[5] Heurteaux C, Gandin C, Borsotto M.et al. Neuroprotective and neuroproliferative activities of NeuroAid (MLC601, MLC901), a Chinese medicine, in vitro and in vivo. Neuropharmacology.2010;58:987-1001.
[6] He K, Nukada H, Urakami T,et al. Antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties of pyrroloquinoline quinone(PQQ): implications for its function in biological systems. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2003;65 (1):67-74.
[7] 熊顺华,王君,龚坚,等.吡咯喹啉醌对培养的鼠海马神经元的促生长作用[J].陕西医学杂志,2007,35(5):527-572.
[8] Zhang Q, Shen M, Ding M, et al.The neuroprotective action of pyrroloquinoline quinone against glutamate-induced apoptosis in hippocampal neurons is mediated through the activation of PI3K Akt pathway.Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology.2001;252(1):62-72.
[9] 贺斌,刘世淸,李浩恒.PI3K/Akt信号通路在吡咯喹啉醌促雪旺细胞增殖中的作用[J].中华整形外科杂志,2010,26(1):53-56.
[10] Rochard P, Rodier A, Casas F,et al. Mitochondrial activity is involved in the regulation of myoblast differentiation through myogenin expression and activity of myogenic factors.J Biol Chem.2000;275(4):2733-2744.
[11] Schauen M, Spitkovsky D, Schubert J,et al. Respiratory chain deficiency slows down cell-cycle progression via reduced ROS generation and is associated with a reduction of p21CIP1/WAF1.J Cell Physiol.2006;209(1):103-112.
[12] Stites T, Storms D, Bauerly K,et al.Pyrroloquinoline quinone modulates mitochondrial quantity and function in mice.J Nutr. 2006;136(2):390-396.
[13] Naito Y,Kumazawa T, Kino I, et al .Effects of pyrroloquinoline quinone(PQQ)and PQQ-oxazole on DNA synthesis of cultured human fibroblasts.Life Sci.1993; 52(24):1909-1915.
[14] Rajpurohit YS,Gopalakrishnan R,Misra HS.Involvement of a protein kinase activity inducer in DNA double strand break repair and radioresistance of Deinococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol.2008;190(11):3948-3954.
[15] Khaimar NP, Kamble VA, Mangoli SH, et al. Involvement of a periplasmie protein kinase in DNA strand break repair and homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 2007;65(2):294-304.
[16] Tao R, Karliner JS, Simonis U, et al. Pyrroloquinoline quinone preserves mitochondrial function and prevents oxidative injury in adult rat cardiac myocytes. Biochem Binphys Res Commun. 2007;363(2):257-262.
[17] Misra HS, Khairnar NP,Barik A,et al.Pyrroloquinoline quinone a reactive oxygen species scavenger in bacteria.FEBS Lett. 2004;578(1-2):26-30.
[18] Zhu BQ, Simonis U, Cecchini G, et al. Comparison of pyrroloquinoline quinone and/or metoprolol on myocardial infarct size and mitochondrial damage in a rat model of ischemia/reperfusion injury.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2006;11(2):119-128.
[19] Zhang Y, Feustel PJ,Kimelberg HK.Neuroprotection by pyrroloquinoline quinone(PQQ)in reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in the adult rat.Brain Res. 2006;1094(1): 200-206.
[20] Zhang JJ, Zhang RF,Meng XK.Protective effect of pyrroloquinoline quinone against Abeta-induced neurotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.Neurosci Lett. 2009; 464(3):165-169. |