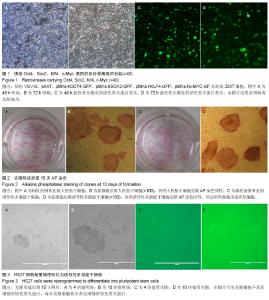
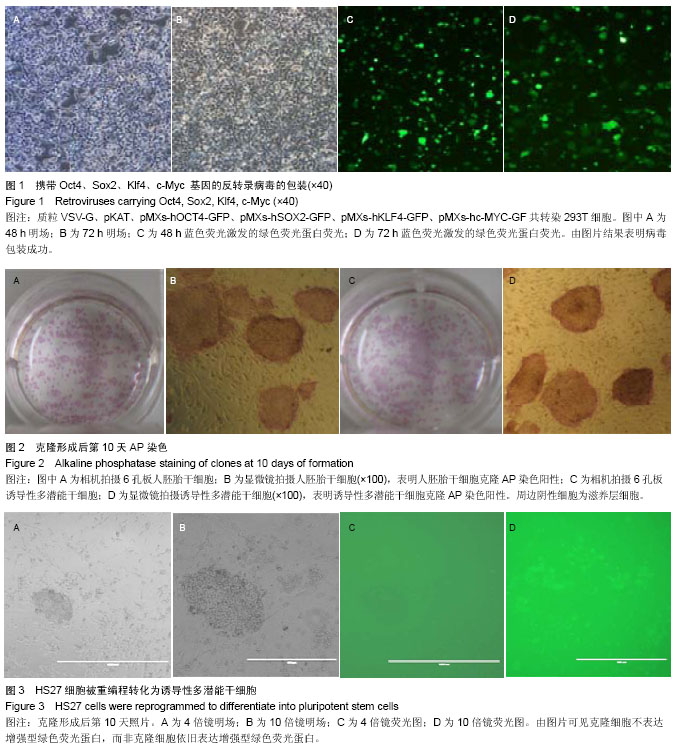
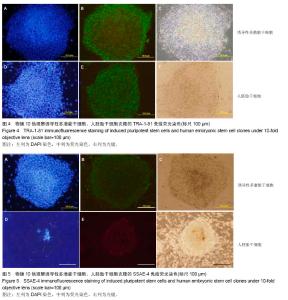
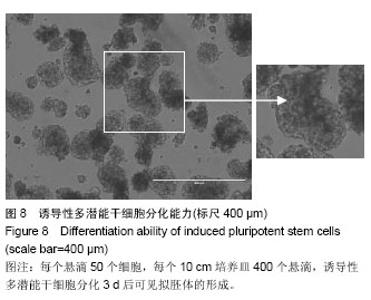
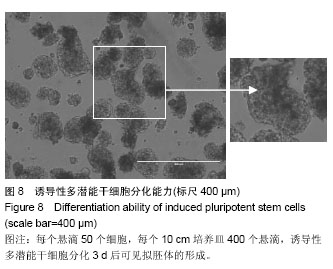
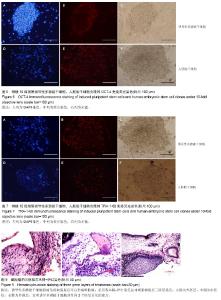
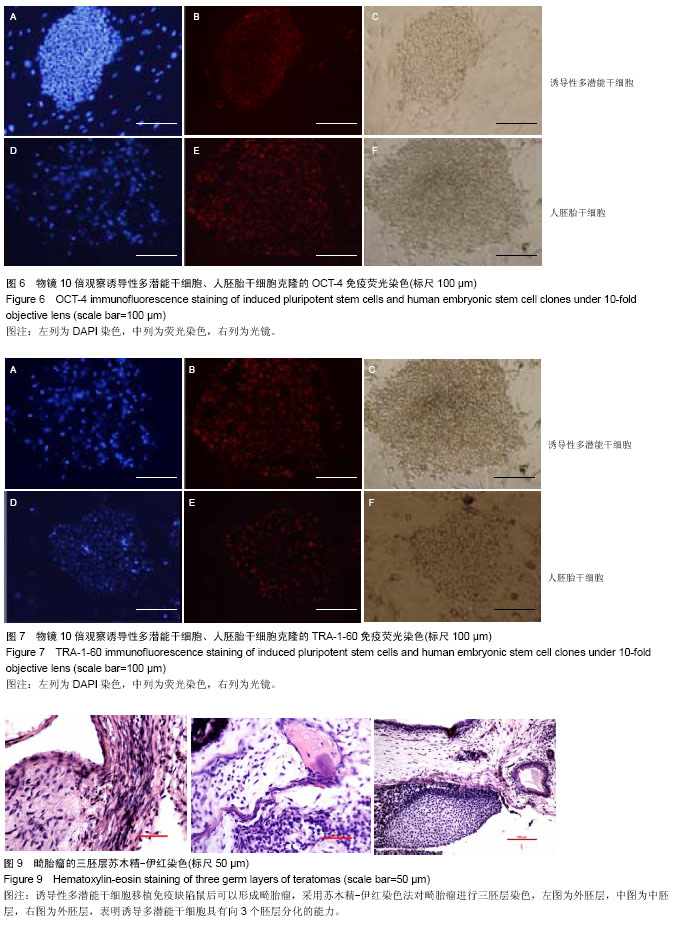
| [1] Takahashi K, Yamanaka S.Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors.Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676.
[2] Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M,et al.Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors.Cell. 2007;131(5):861-872.
[3] Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K,et al.Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells.Science. 2007;318(5858):1917-1920.
[4] Geurts AM, Cost GJ, Freyvert Y,et al.Knockout rats via embryo microinjection of zinc-finger nucleases.Science. 2009; 325(5939):433.
[5] Liu H, Zhu F, Yong J,et al.Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from adult rhesus monkey fibroblasts.Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(6):587-590.
[6] Wu Z, Chen J, Ren J,et al.Generation of pig induced pluripotent stem cells with a drug-inducible system.J Mol Cell Biol. 2009;1(1):46-54.
[7] Huangfu D, Maehr R, Guo W,et al.Induction of pluripotent stem cells by defined factors is greatly improved by small-molecule compounds.Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(7): 795-797.
[8] Rhee YH, Ko JY, Chang MY,et al.Protein-based human iPS cells efficiently generate functional dopamine neurons and can treat a rat model of Parkinson disease.J Clin Invest. 2011;121(6):2326-2335.
[9] Jia F, Wilson KD, Sun N,et al.A nonviral minicircle vector for deriving human iPS cells.Nat Methods. 2010;7(3):197-199.
[10] Fukushima S, Ihn H, Nishimura Y,et al.Cancer immunotherapy by utilizing dedritic cells derived from pluripotent stem cells.Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2011;34(3):113-120.
[11] Hou P, Li Y, Zhang X, et al.Pluripotent stem cells induced from mouse somatic cells by small-molecule compounds.Science. 2013;341(6146):651-654.
[12] Kohandel M, Haselwandter CA, Kardar M,et al. Quantitative model for efficient temporal targeting of tumor cells and neovasculature.Comput Math Methods Med. 2011;2011: 790721.
[13] Allegrucci C, Rushton MD, Dixon JE,et al.Epigenetic reprogramming of breast cancer cells with oocyte extracts. Mol Cancer. 2011;10(1):7.
[14] Shah M, Allegrucci C.Stem cell plasticity in development and cancer: epigenetic origin of cancer stem cells.Subcell Biochem. 2013;61:545-565.
[15] Takahashi K, Okita K, Nakagawa M,et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from fibroblast cultures.Nat Protoc. 2007;2(12):3081-3089.
[16] Kutner RH, Zhang XY, Reiser J.Production, concentration and titration of pseudotyped HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors.Nat Protoc. 2009;4(4):495-505.
[17] Tiscornia G, Singer O, Verma IM.Production and purification of lentiviral vectors.Nat Protoc. 2006;1(1):241-245.
[18] Takahashi K, Yamanaka S.Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors.Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676.
[19] Shu J, Wu C, Wu Y, et al.Induction of pluripotency in mouse somatic cells with lineage specifiers.Cell. 2013;153(5): 963-975.
[20] Hanna JH, Saha K, Jaenisch R.Pluripotency and cellular reprogramming: facts, hypotheses, unresolved issues.Cell. 2010;143(4):508-525.
[21] Warren L, Manos PD, Ahfeldt T,et al.Highly efficient reprogramming to pluripotency and directed differentiation of human cells with synthetic modified mRNA.Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(5):618-630.
[22] Gurdon JB, Melton DA.Nuclear reprogramming in cells. Science. 2008;322(5909):1811-1815.
[23] Costa FF, Seftor EA, Bischof JM,et al.Epigenetically reprogramming metastatic tumor cells with an embryonic microenvironment.Epigenomics. 2009;1(2):387-398.
[24] Allegrucci C, Rushton MD, Dixon JE,et al.Epigenetic reprogramming of breast cancer cells with oocyte extracts. Mol Cancer. 2011;10(1):7.
[25] Lin SL, Chang DC, Chang-Lin S,et al.Mir-302 reprograms human skin cancer cells into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state.RNA. 2008;14(10):2115-2124.
[26] Utikal J, Maherali N, Kulalert W,et al.Sox2 is dispensable for the reprogramming of melanocytes and melanoma cells into induced pluripotent stem cells.J Cell Sci. 2009;122(Pt 19): 3502-3510.
[27] Carette JE, Pruszak J, Varadarajan M,et al.Generation of iPSCs from cultured human malignant cells.Blood. 2010; 115(20):4039-4042. |