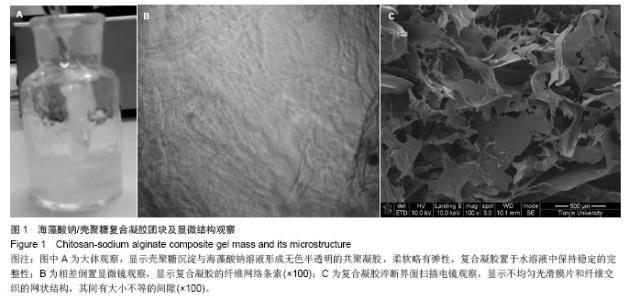
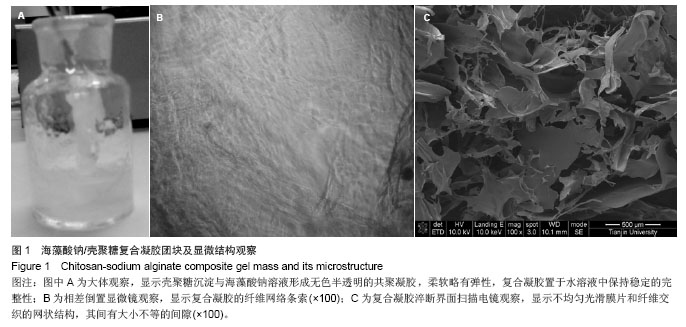
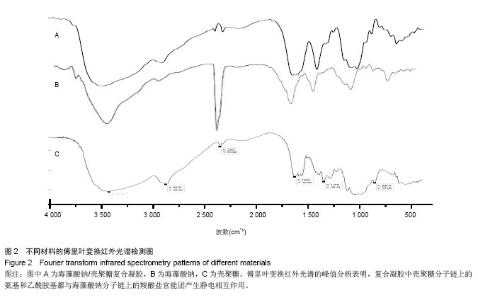
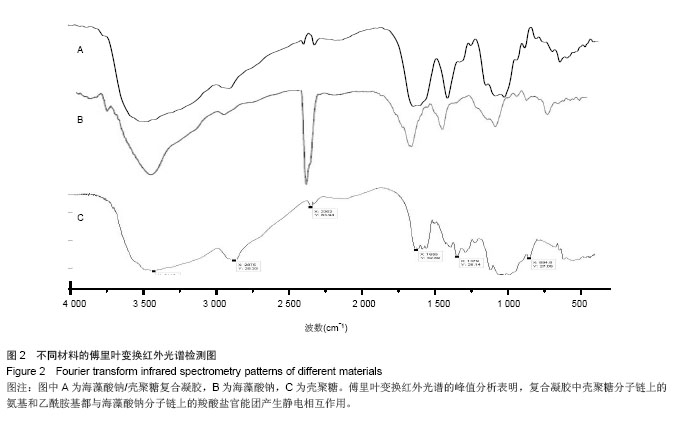
| [1]黄若昆.可注射性骨组织工程载体研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(9):681-683.
[2]李志宏,黄姝杰,关静,等.可注射骨修复材料研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009,23(11):1382-1387.
[3]顾其胜,朱彬.海藻酸盐基生物医用材料[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(26):5194-5198.
[4]谭荣伟.海藻酸基可注射骨修复材料的研究[D].北京:清华大学, 2011:6-14.
[5]谈伟强,刘友山,徐靖宏,等.注射型藻酸钙/BMP复合材料的制备及成骨性能研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2008,27(3): 457-461.
[6]顾其胜,陶伟栋,蒋丽霞.壳聚糖基复合材料类新型生物医用材料[J].上海生物医学工程,2007,28(1):31-35.
[7]吴清华,邱林,李明勇,等.壳聚糖支架上骨髓间充质干细胞的浓度及黏附生长[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(8): 1369-1372.
[8]刘昊,张永刚,郭全义,等.新型脱细胞骨基质-壳聚糖骨组织工程支架的制备及性能评价[J].军医进修学院学报,2011,32(6): 616-619.
[9]袁江.两种壳聚糖基复合水凝胶的比较研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2012.
[10]Ebrahim A,Alireza N,Ismaeil H,et al.Release profile and stability evaluation of optimized chitosan/alginate nanoparticles as EGFR antisense vector.In J Nanomedicine. 2010;5:455-461.
[11]谭红梅.可注射壳聚糖/海藻酸钠复合水凝胶的制备研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2010.
[12]Wang Q,Jamal S,Michael S,et al. PLGA-chitosan/ PLGA-alginate nanoparticle blends as biodegradable colloidal gels for seeding human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.J Biomed Mater Res A.2011;96(3):520-527.
[13]李琳,刘宝林,韩宝三,等.海藻酸钠/壳聚糖微载体的制备及生物活性评价[J].应用化工, 2013,42(2):233-238.
[14]王华明,曹阳,徐龙,等.可注射型海藻酸钙-壳聚糖复合材料的凝胶性能研究[J].材料导报,2009,23(3):51-53.
[15]鲁路,桑守山,周长忍,等.可注射型海藻酸/磷酸化壳聚糖复合水凝胶的制备及其生物相容性[J].暨南大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 29(1):81-84.
[16]李沁华,王迪.冻干法制备的海藻酸钙-壳聚糖组织工程复合材料支架[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(29):5441-5444.
[17]刘映薇,于炜婷,刘袖洞,等.海藻酸钠-壳聚糖-海藻酸钠(ACA}微胶囊的蛋白质通透性研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2006, 25(3):370-373.
[18]刘袖洞,于炜婷,王为,等.海藻酸钠和壳聚糖聚电解质微胶囊及其生物医学应用[J].化学进展,2008,20(1):126-139.
[19]侯红萍,王家东.壳聚糖-海藻酸钠共混凝胶制备及其包埋固定糖化酶的研究[J].中国食品学报,2009,9(3):50-57.
[20]林成真,郑豪,朱克龙.替硝唑-壳聚糖-海藻酸钠生物复合膜的缓释性能研究[J].浙江大学学报:理学版,2006,33(4):444-446,480.
[21]郎轶咏,李峥,张晓莉,等.海藻酸钠-壳聚糖固定化凝血酶微球的制备及稳定性研究[J]. 解放军药学学报,2012,28(4):311-314.
[22]田丰.壳聚糖-海藻酸钠聚电解质膜的制备及性能调控研究[D].天津:军事医学科学院卫生装备研究所,2010.
[23]Park DJ,Choi BH,Zhu SJ,et al.Injectable bone using chitosan-alginate gel/mesenchymal stem cells/BMP-2 composites.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2005;33(1):50-54.
[24]彭博,臧圣奇,刘敏杰,等.两种消毒方法对壳聚糖温敏凝胶物理性能及生物学特性影响的研究[J].牙体牙髓牙周病杂志, 2012, 22(4): 203-207.
[25]何东保,石毅,梁红波,等.壳聚糖一海藻酸钠协同相互作用及其凝胶化的研究[J].武汉大学学报:理学版,2002,48(2):193-196.
[26]陆轶业,刘黎,张亚琼,等.壳聚糖一海藻酸盐复合物的表征及其吸湿性和崩解性研究[J].上海交通大学学报,2007,4(10): 1683-1687.
[27]樊李红,潘晓然,周月,等.羟丙基壳聚糖/氧化海藻酸钠水凝胶的制备及表征[J].武汉大学学报:理学版,2010,56(5):501-506.
[28]吴敏,倪才华.大茴香醛改性海藻酸钠凝胶的制备及释药性能[J].化学研究与应用, 2012,24(3):400-403.
[29]吴年强,潘春跃,张报进,等.一种氧化海藻酸钠基温敏凝胶的制备与性能[J].高分子学报,2007,6(6):497-502.
[30]IS0 1 0993—1:2003,Biological evaluation of medical devices—Part 1:Evaluation and testing.
[31]IS0 10993—5:1999,Biological evaluation of medical devices—Part 5:Tests for in vitro cytotoxicity.
[32]郝和平.医疗器械生物学评价标准实施指南[M].北京:中国标准出版社,2000:100-101.
[33]李瑞,王青山,王云,等.四甲基偶氮唑盐法评价牙体修复性纳米羟基磷灰石复合材料的体外细胞毒性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(34):6321-6325.
[34]黄桂娟,景红霞,夏栋林,等.纳米银猪脱细胞真皮敷料的细胞毒性评估[J].中国组织工程研究,2010,14(25):4607-4610.
[35]张玉石,李汉忠,张锐强.组织工程用猪膀胱无细胞基质的体外细胞毒性检测[J].基础医学与临床,2007,27(7):826-827.
[36]Naghavi N,Ghoddusi J,Hamid R,et al.Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium enriched mixture cements on L929 mouse fibroblast cells. Dent Mater J. 2014;33(1):64-69.
[37]Doostmohammadia A,Monshia A,Salehi R,et al.Cytotoxicity evaluation of 63s bioactive glass and bone-derived hydroxyapatite particles using human bone-marrow stem cells. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2011;155(4):323-326.
[38]Atay A,Bozok Cetintas V,Cal E,et al.Cytotoxicity of hard and soft denture lining materials. Dent Mater J. 2012;31(6): 1082-1086. |