Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (34): 5428-5433.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2325
Previous Articles Next Articles
Sustained-release effect and clinical application of thermosensitive gels
Chen Yongjia, Li Yanlin, Liu Dejian, He Yinghong, Yang Xiao
Department of Sports Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2019-09-26Revised:2019-09-28Accepted:2019-11-15Online:2020-11-08Published:2020-09-11 -
Contact:Li Yanlin, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Sports Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Chen Yongjia, Master candidate, Department of Sports Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760403 and 81960409; the Natural Science Foundation of Yunnan Province (Key Program), No. 2017FE467(-007)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Yongjia, Li Yanlin, Liu Dejian, He Yinghong, Yang Xiao. Sustained-release effect and clinical application of thermosensitive gels[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5428-5433.
share this article
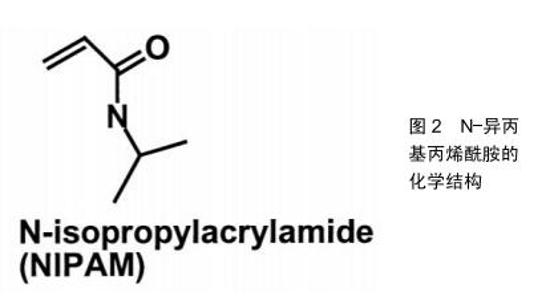
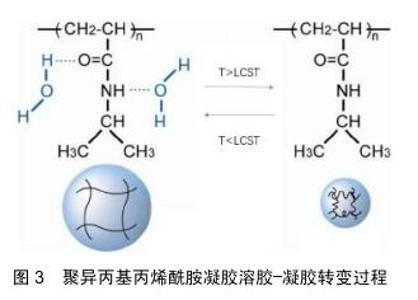
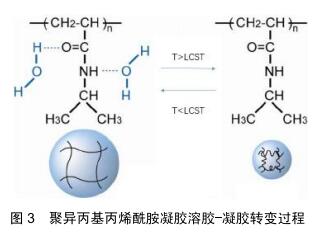
2.1 温敏型凝胶的释药模式 随着温敏型凝胶研究发展不断深入,用于制备温敏型凝胶的高分子材料也在不断发现,有天然的壳聚糖、胶原和明胶到合成的聚丙烯酸类、聚丙烯酰胺类、聚肽类等[15]。而目前研究最多的温敏型凝胶是丙烯酰胺类,如N-异丙基丙烯酰胺,其化学结构如图2[16],其有亲水的酰胺基同时也具有疏水的异丙基,经研究发现在特定的环境温度下,这两种基团的亲疏水性在聚异丙基丙烯酰胺凝胶的溶胶-凝胶转变过程中起着关键的作用。当外界温度低于32 ℃时,分子内的酰胺基占主导地位,聚合物网络中的酰胺基通过氢键与水分子结合,聚异丙基丙烯酰胺凝胶发生溶胀;当温度高于32 ℃时,分子内的异丙基占主导地位,酰胺基和水分子间的氢键被破坏,聚异丙基丙烯酰胺凝胶失水发生收缩,如图3[17-18]。此外,科学家们发现在N-异丙基丙烯酰胺凝胶的溶胶-凝胶转变过程中,其聚合浓度的改变、添加额外的物质等行为都可能对相转变产生影响,通过这些因素来调控温敏型凝胶的低临界溶解温度可以调节微凝胶的溶胀行为,在生物医学工程中有很好的发展潜力,例如作为具有可调渗透性的膜材料[19-20]。 2.2 温敏型凝胶的给药途径 2.2.1 注射给药 用于关节腔内给药的药物中,由于单纯药物溶剂注射给药后将从关节腔快速代谢而难以维持常规注射的效果,而温敏型凝胶制剂在注射部位于一定温度下可凝成半固体状,其控释特性可有效提高关节腔内的局部药物浓度,并降低药物全身毒副作用,目前已被广泛研究应用[21]。NODA等[22]制备了含有吲哚菁绿作为荧光标记物的凝胶,将其注入大鼠膝关节腔后,通过体内成像系统发现吲哚菁绿作为水溶液在短时间内从关节腔内逐渐消失,并在1 d内排出体外。另一方面,温敏型凝胶中的吲哚菁绿由于在大鼠膝关节腔内温度下迅速成胶,因此保留时间更长并能在关节中缓释1周。制备了含有透明质酸凝胶基质的缓释制剂,给药后观察大鼠行走距离发现,凝胶制剂可以在关节腔内持续释放药物并缓解疼痛,与透明质酸凝胶的组合可有效改善急性疼痛期模型大鼠的活动性。SARDANA等[23]制备了含有酮洛芬的传递体凝胶,并与口服塞来昔布的安全性和有效性作对比,结果证明含酮洛芬的传递体凝胶是治疗膝关节骨性关节炎症状的有效手段,优于口服塞来昔布,并且不良反应小,在体温下即可成胶,停留患处时间更长,可减少用药次数,对于那些不能服用口服非类固醇抗炎药的人来说是一种理想的治疗药物。目前注射型凝胶常用于关节腔内注射,但是临床使用时其配制过程须严格控制在无菌条件下,适宜灭菌方式的选择也极其重要,而且注射过程中也需注意感染风险,这也增大了该类制剂的制作难度[24]。 2.2.2 口腔给药 目前在牙周炎治疗上,全身和局部抗菌药物都被作为辅助药物。但是全身给药会使得药物在到达作用部位之前就被多次稀释,从而需要使用更高剂量,此外还有细菌耐药的风险。而凝胶制剂的因其在口腔内温度下即可成胶,使药物在口腔保留更长的时间并维持药物有效浓度,减少了给药频率和患者的不依从 性[25]。CARVALHO等[26]研制了阿仑膦酸钠凝胶,其可有效抑制破骨过程,稳定骨结构,在牙周手术期间用1%阿仑膦酸钠凝胶或空白凝胶随机治疗,术后3,6个月全口牙周检查显示患者牙周出血减少,对牙周的修复有着积极作用,说明局部应用1%阿仑膦酸钠可能是治疗牙周外科骨缺损的一种有前景和有益的辅助手段。TRAN等[27]以菌落形成单位来评估胶体银凝胶对变形链球菌、血链球菌和唾液链球菌活力的影响,结果显示胶体银凝胶在37 ℃下形成半固体凝胶,可有效抑制细菌生长,比同类其他非凝胶制剂药物的效果更好,可加入牙膏中有效防止蛀牙和口腔菌斑的形成。但是目前如何将此新型凝胶制剂更安全的用于人体,并且使其附着在病灶时间更长仍是需要解决的问题。另外市面上所售的口腔给药剂型往往只包含分散在凝胶基质的药物,效果往往一般,需要再继续研究添加组织愈合特性较好的添加剂,促进血管生成等,从而提高药效[28]。 2.2.3 鼻腔给药 为提高鼻腔给药的生物利用度并解决常规鼻腔给药剂型在病灶停留时间较短的问题,可将药物装入温敏性材料中制备温敏型凝胶制剂,以液体形式滴入鼻腔后,使其凝成半固体黏附在鼻黏膜上[29]。KUMAR等[30]研制含有氯苯那敏马来酸盐负载纳米颗粒的温敏型凝胶,将优化的制剂纳米粒子配制成热可逆性原位凝胶,可以加强鼻黏膜与药物之间的接触,增加并促进药物吸收,提高其生物利用度。基于凝胶化能力和黏膜黏附强度选择免疫球蛋白G4制剂作为优化制剂,结果显示没有出现组织损伤,氯苯那敏马来酸盐负载纳米颗粒的原位凝胶是安全的,在治疗过敏性鼻炎上具有很好的发展前景。GHOLIZADEH等[31]采用壳聚糖和氨甲环酸开发了一种促进鼻上皮伤口愈合的温敏型凝胶制剂,研究结果发现该制剂在32 ℃下约5 min内凝胶化,该温度恰好在人鼻腔温度范围内,其凝胶化还可有效防止药物从鼻腔中流失,并且不会使药物沉积在肺部,另外对鼻上皮无刺激性,并且伤口愈合速度是单纯使用氨甲环酸溶液对照组的6倍,为治疗鼻腔上皮损伤药物研究提供了新的方向。此外,鼻用凝胶的不足目前来说由于鼻纤毛的清除作用,使其在患处停留时间缩短,生物利用度降低。另外,还需要严格要求对鼻黏膜无不良反应,以免使鼻腔生物屏障无法正常发挥作用。 2.2.4 眼内给药 眼科治疗药物的生物利用度低主要因为存在生理屏障,其阻止了外源性药物的进入,因此也降低了局部给药的生物利用度,需要反复多次给药[32]。传统的液体性眼用制剂由于频繁眨眼及眨眼反射等保护作用,会使入眼内的药液迅速从角膜消除,使其难以长时间发挥药效[33]。而温敏型凝胶有利于药物长时间地停留而发挥药效,同时可增加载药量,患者更容易接受。OZEN等[34]将发病3 d内的腺病毒眼部感染患者分成2组:第1组100例患者使用人工泪液治疗,第2组100例患者使用更昔洛韦眼用凝胶加人工泪液,所有患者在治疗后第1,5,10,15天接受同一眼科医生的眼科检查,研究显示第2组更昔洛韦眼用凝胶在体温下成胶后在眼中停留时间更长,并使症状改善速度更快,角膜和结膜受累更少,对侧眼睛和周围环境的传播更少。SCHAEFER等[35]研制五嵌段共聚物凝胶作为眼用药物缓释注射制剂,将该制剂注入兔的前房内并做相关测试,结果显示五嵌段共聚物凝胶在兔前房内温度下迅速成胶,并且释放药物能达28 d,耐受性良好,聚合物随着药物释放而降解,这些结果证明了前房内五嵌段共聚物凝胶制剂对于眼前段中持续缓释药物的生物疗法的潜力。另外在眼科手术中也有应用。SHIROMA等[36]在同等条件下比较使用5%和2%利多卡因2种不同麻醉凝胶的止痛的功效及安全性,结果显示5%和2%利多卡因凝胶在滴注后 5 min内有类似的止痛效果,但5%利多卡因凝胶更有效、作用时间更长,在两种浓度下均未发现角膜毒性。可见利多卡因凝胶制剂对人体有着不错的止痛效果,在一定范围内提高载药浓度提高效果的同时安全性也较好。目前眼用凝胶也有诸多缺点,例如载药药量较少,无法完全消除对眼的刺激性,某些种类凝胶在眼部形成较硬块状较难被眼泪溶蚀,有着较强的异物感,需要继续改善材料的使用。 2.2.5 耳内给药 传统滴耳液给药后药液容易流失,须多次给药,而且由于血-内耳屏障的存在,治疗耳疾也需要较大的剂量,使得用药风险明显增加。耳用温敏凝胶不仅可以使药物在耳道内的滞留时间延长,还能达到缓、控释效果,提高生物利用度,减少给药次数、克服滴耳液需频繁给药的不足,成为一种新型耳用凝胶制 剂[37]。目前通过鼓室内给药被越来越多地用于临床和研究,但是其最大缺点就是药物在中耳因为各种原因会迅速流失。对此,SALT等[38]研制了含有地塞米松的泊洛沙姆水凝胶制剂,通过豚鼠鼓膜注射50 μL的地塞米松溶液或含有地塞米松的凝胶,给药后凝胶在豚鼠耳道内温度下形成半固体凝胶,经过检测耳蜗淋巴液药物浓度后发现,基于泊洛沙姆水凝胶的地塞米松制剂延长了药物在耳内停留的有效时间,可较长时间的缓释药物,使药物在内耳中分布更加均匀,获得更好的治疗效果。LI等[39]使用泊洛沙姆407制备左氧氟沙星温敏凝胶,测定 3 g/L含左氧氟沙星16%,17%,18%,19%和20%泊洛沙姆407或泊洛沙姆407溶液的相转化温度,并选择能在34 ℃左右作为成胶的最佳浓度。然后建立SD大鼠化脓性中耳炎模型并注射相应药物,结果显示17%为泊洛沙姆407的最佳浓度,而左氧氟沙星热敏凝胶和左氧氟沙星滴剂能在前3 d缓解局部炎症,但左氧氟沙星滴剂不能抑制化脓性中耳炎复发,而左氧氟沙星凝胶可以长时间缓释药物使得炎症不复发。可见左氧氟沙星凝胶相较其传统剂型能够在炎症部位作用更长时间,药效更好,在对化脓性中耳炎治疗上有很大的潜力。此外,耳用凝胶制剂目前也在逐渐改善由耳道狭窄性带来的不便给药和不易深入的问题[40]。 2.2.6 经皮给药 温敏凝胶经皮给药能使药物在经过皮肤扩散、渗透吸收,进入血液循环后较长时间保持有效血药浓度,这提高了药物的生物利用度并便于给药,涂抹于皮肤表面对皮肤无刺激性,患者依从性较好[41]。刺激性接触性皮炎是一种慢性和复发性皮肤病,具有严重的湿疹病变。尽管其患病率不断增加,但治疗方法仍然有限。SHROTRIYA等[42]考虑到局部白藜芦醇虽然对刺激性接触性皮炎有效,但由于溶解度低和生物利用度差,于是制备了皮肤靶向的局部白藜芦醇负载固体脂质纳米粒子,将局部白藜芦醇负载固体脂质纳米粒子掺入卡波普凝胶中并研究其体外皮肤渗透作用,研究药物在皮肤的沉积和刺激性。结果表明局部白藜芦醇负载固体脂质纳米粒子负载凝胶的体外药物释放长达24 h;另外,体外药物沉积研究显示皮肤靶向的可能性,而且没有皮肤刺激。因此,局部白藜芦醇负载固体脂质纳米粒子凝胶将是用于治疗刺激性接触性皮炎安全且有效的替代物。由于芬戈莫德严重的全身不良反应,TAMAKUWALA等[43]研制了羟丙基纤维素(2%)芬戈莫德凝胶,希望能用于治疗多发性硬化症。此外还使用了胶体燕麦,结果证明含有6%Aveeno?胶体燕麦片的0.50%芬戈莫德凝胶具有非常不错的渗透特性,可将芬戈莫德靶向输送到皮肤,还避免了其严重的全身不良反应,能够较长时间作用于患处。但经皮给药凝胶包含的药物往往经皮渗透效果并不是很好,需额外加入促进剂,另外如果材料使用增加,凝胶的黏度增大,会降低药物的扩散作用,降低药效,这也是需要解决的问题。 2.2.7 直肠给药 常规口服给药通常难以作用于直肠,仅作用于升结肠和横结肠。而直肠给药途径是一种有效的、无创替代给药途径,能避免药物严重的全身反应,直肠为药物输送提供了相对稳定的环境,使血药浓度保持稳定,并部分避免胃肠吸收困难和肝脏首过代谢[44-45]。然而,常规的固体栓剂通常伴有不适,可能导致患者依从性差。此外,如果缺乏黏膜黏附性,传统的栓剂可能会到达结肠末端,掺入的药物还会由于首过代谢导致生物利用率降低[46]。CHEN等[47]针对咪达唑仑口服生物利用度较低和注射制剂具有较低的患者依从性原因研制了咪达唑仑直肠凝胶,结果显示在相同剂量下,咪达唑仑凝胶给药后在直肠内温度下成胶并黏附在肠壁,而且咪达唑仑的峰浓度和药-时曲线下面积比口服溶液高8-10倍。直肠刺激试验表明,频繁使用咪达唑仑直肠凝胶并不会引起直肠黏膜损伤,说明其可以减轻患者在使用过程中的不适感,可能是一种特别适用于婴儿和儿童的镇静药物剂型。MOAWAD等[48]将盐酸替扎尼定(一种用于治疗痉挛的肌张力松解剂)用羟丙基甲基纤维素作为黏附性聚合物加入到泊洛沙姆凝胶中,结果与口服溶液相比,载药凝胶组提高了盐酸替扎尼定的生物利用度约2.18倍,并将t1/2增加至约10 h,说明加入凝胶后可以达成延长盐酸替扎尼定释放和增强生物利用度的双重目的,因此可以被认为是用于治疗痉挛有前景的方式。直肠给药凝胶制剂目前还未出现上市品种,由于凝胶制剂黏度较大和直肠给药的特殊性使其使用不方便,另外制作时还需加入增溶剂、pH调节剂、防腐剂等使得药物分析测试难度加大,因此还需要研究出更容易给药、易制备、疗效更好的凝胶制剂。 "
|
[1] CAO M, WANG Y, HU XZ, et al. Reversible Thermoresponsive Peptide-PNIPAM Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery. Biomacromolecules.2019;20:3601-3610.
[2] 任彦荣,霍丹群,侯长军.温敏性聚合物聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺及其应用[J].材料导报, 2004,18(11):54-56.
[3] GONG J, HOSAKA E, SAKAI K, et al. Processing and thermal response of temperature-sensitive-gel (TSG)/polymer composites. Polymers.2018;10(5):486.
[4] BARSE RK, TAGALPALLEWAR AA, KOKARE CR, et al. Formulation and ex vivo–in vivo evaluation of pH-triggered brimonidine tartrate in situ gel for the glaucoma treatment using application of 32 factorial design.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018;44(5):800-807.
[5] ZHAO TT, PENG ZW, YUAN D, et al. Metal-organic gel enhanced fluorescence anisotropy for sensitive detection of prostate specific antigen.Spectrochim Acta Part A.2018;192: 328-332.
[6] HISHIKAWA Y, KAKINO Y, TSUKAMOTO H, et al. Control of Drug Diffusion Behavior of Xanthan and Locust Bean Gum Gel by Agar Gel. Chem Pharm Bull.2016;64(10):1450-1457.
[7] EL-SHERIDY NA, RAMADAN AA, EID AA, et al. Itraconazole lipid nanocapsules gel for dermatological applications: In vitro characteristics and treatment of induced cutaneous candidiasis. Colloids Surf B.2019;181:623-631.
[8] ZHENG L, LI C, HUANG X, et al. Thermosensitive hydrogels for sustained-release of sorafenib and selenium nanoparticles for localized synergistic chemoradiotherapy. Biomaterials. 2019;216:119220.
[9] MORIN KT, TRANQUILLO RT. In vitro models of angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in fibrin gel. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(16):2409-2417.
[10] ALIDADI S, ORYAN A, BIGHAM-SADEGH A, et al. Role of platelet gel embedded within gelatin scaffold on healing of experimentally induced critical-sized radial bone defects in rats.Int Orthop.2017;41(4):805-812.
[11] FENG L, ZHANG S, LIU Z. Graphene based gene transfection. Nanoscale.2011;3(3):1252-1257.
[12] MATSUMOTO K, SAKIKAWA N, MIYATA T. Thermo-responsive gels that absorb moisture and ooze water. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):2315.
[13] FU TS, WEI YH, CHENG PY, et al. A Novel Biodegradable and Thermosensitive Poly(Ester-Amide) Hydrogel for Cartilage Tissue Engineering.Biomed Res Int.2018;2018: 2710892.
[14] FEDORCZYK M, KRZYWICKA A, CIECIORSKI P, et al. A Novel Strategy for the Synthesis of Amphiphilic and Thermoresponsive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-b- Polystyrene Block Copolymers via ATRP. Polymers(Basel). 2019;11(9):1484.
[15] 姜玲海,冯怡,沈岚,等.温敏凝胶释药模式及机制研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2008,33(1):105-107.
[16] PELTON R. Temperature-sensitive aqueous microgels.Adv Colloid Interface Sci.2000; 85(1): 1-33.
[17] PODEWITZ M, WANG Y, QUOIKA PK, et al. Coil-Globule Transition Thermodynamics of Poly(-isopropylacrylamide).J Phys Chem B.2019;123:8838-8847.
[18] 成瑾瑾温度敏感性水凝胶的制备及其在铜离子吸附中的应用[D].杭州:浙江大学,2017.
[19] 吴宇航.基于 NIPAM 的水凝胶与有机凝胶的流变学性能研究[D].深圳:深圳大学,2017.
[20] BRANDEL T, DIRKSEN M, HELLWEG T. Tuning the Swelling Properties of Smart Multiresponsive Core-Shell Microgels by Copolymerization.Polymers (Basel).2019;11(8):1269.
[21] 李杰.注射用温度敏感型壳聚糖原位凝胶给药系统的研究[D].沈阳:沈阳药科大学,2008.
[22] NODA T, OKUDA T, BAN K, et al. Development of Intra-knee Joint Sustained-release Gel Formulation and Evaluation of its Pharmacological Efficiency in Rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017; 40(6):830-836.
[23] SARDANA V, BURZYNSKI J, ZALZAL P. Safety and efficacy of topical ketoprofen in transfersome gel in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Musculoskeletal Care. 2017;15(2): 114-121.
[24] 季可非.关节腔注射用甲氨蝶呤温敏凝胶的研究[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学,2016.
[25] SHESHALA R, QUAH SY, TAN GC, et al. Investigation on solution-to-gel characteristic of thermosensitive and mucoadhesive biopolymers for the development of moxifloxacin-loaded sustained release periodontal in situ gels. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019;9:434-443.
[26] CARVALHO BD, OLIVEIRA A, OLIVEIRA PAD, et al. Effects of topical application of 1% sodium alendronate gel in the surgical treatment of periodontal intrabony defects: a 6-month randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol.2019; 90(10): 1079-1087.
[27] TRAN PL, LUTH K, WANG J, et al. Efficacy of a silver colloidal gel against selected oral bacteria in vitro. F1000 Res. 2019;8:267.
[28] 郑云龙.唇裂术后上唇部瘢痕组织中血管密度与生成模式的研究[D].青岛:青岛大学,2015.
[29] WANG Q, ZUO Z, CHEUNG CKC, et al. Updates on thermosensitive hydrogel for nasal, ocular and cutaneous delivery.Int J Pharm. 2019;559:86-101.
[30] KUMAR M, UPADHAYAY P, SHANKAR R, et al. Chlorpheniramine maleate containing chitosan-based nanoparticle-loaded thermosensitive in situ gel for management in allergic rhinitis.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019;9(6):1017-1026.
[31] GHOLIZADEH H, MESSEROTTI E, POZZOLI M, et al. Application of a Thermosensitive In Situ Gel of Chitosan-Based Nasal Spray Loaded with Tranexamic Acid for Localised Treatment of Nasal Wounds.AAPS Pharm Sci Tech.2019;20:299.
[32] SAPINO S, CHIRIO D, PEIRA E, et al. Ocular Drug Delivery: A Special Focus on the Thermosensitive Approach. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019;9(6):pii: E884.
[33] 陈桂添,吴艳婷,时军,等.温敏凝胶的研究进展[J].广东药科大学学报,2017,33(4):556-560.
[34] OZEN S, OZER MA. Ganciclovir ophthalmic gel treatment shortens the recovery time and prevents complications in the adenoviral eye infection. Int Ophthalmol. 2017;37(1): 245-249. [35] SCHAEFER E,SMITH SM,SALMON J,et al. Evaluation of Intracameral Pentablock Copolymer Thermosensitive Gel for Sustained Drug Delivery to the Anterior Chamber of the Eye. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2017;33(5):353-360.
[36] SHIROMA HF, SHIMONO KE, FARAH ME, et al. Comparative Study Between Lidocaine Gel 2% and 5% for Ophthalmic Procedures.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther.2016;32(4):192-195.
[37] 戴娟.复方多组分内耳给药新模式:纳米粒及纳米粒—温敏凝胶双相释药系统的研究[D].广州:广东药科大学,2017.
[38] SALT AN, HARTSOCK J, PLONTKE S, et al. Distribution of Dexamethasone and Preservation of Inner Ear Function following Intratympanic Delivery of a Gel-Based Formulation. Audiol Neurootol. 2011;16(5):323-335.
[39] LI C, GU J, MAO X,et al. Preparation of levofloxacin thermo-sensitive gel and clinical application in the treatment of suppurative otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol. 2014;134(5): 468-474.
[40] 曾佩.丹参酮ⅡA/纳米银复合物凝胶的制备及其用于中耳炎的治疗[D].广州:广东药科大学,2017.
[41] GRILLO R, DIAS FV, QUEROBINO SM, et al. Influence of hybrid polymeric nanoparticle/thermosensitive hydrogels systems on formulation tracking and in vitro artificial membrane permeation: A promising system for skin drug-delivery.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;174:56-62.
[42] SHROTRIYA SN, RANPISE NS, VIDHATE BV. Skin targeting of resveratrol utilizing solid lipid nanoparticle-engrossed gel for chemically induced irritant contact dermatitis. Drug Deliv Transl Res.2017;7(1):37-52.
[43] TAMAKUWALA M, STAGNI G. Fingolimod Hydrochloride Gel for Dermatological Applications: Optimization of Formulation Strength and Effect of Colloidal Oatmeal (Aveeno?) as Penetration Enhancer. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2016;17(4): 907-914.
[44] AKL MA, ISMAEL HR, ABD AFI, et al. Tolmetin sodium-loaded thermosensitive mucoadhesive liquid suppositories for rectal delivery; strategy to overcome oral delivery drawbacks. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019;45:252-264.
[45] EL-LEITHY ES, SHAKER DS, GHORAB MK, et al. Evaluation of mucoadhesive hydrogels loaded with diclofenac sodium–chitosan microspheres for rectal administration. Aaps Pharmscitech. 2010;11(4):1695-1702.
[46] ÖZGÜNEY I, KARDHIQI A, YıLDıZ G, et al. In vitro–in vivo evaluation of in situ gelling and thermosensitive ketoprofen liquid suppositories.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2014; 39(4): 283-291.
[47] CHEN X, LI W, LI Y, et al. Preparation and Evaluation of Midazolam Rectal Gel in vitro and in vivo. Drug Res. 2018; 68(10):560-566.
[48] MOAWAD FA, ALI AA, SALEM HF. Nanotransfersomes- loaded thermosensitive in situ gel as a rectal delivery system of tizanidine HCl: preparation, in vitro and in vivo performance. Drug Deliv. 2017;24(1):252-260.
[49] 徐杉,吴敬波,傅少志.水凝胶在抗肿瘤药物中的研究进展[J].中国现代应用药学, 2016,33(5):676-682. |
| [1] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [2] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [3] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [5] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [6] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [7] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [8] | Zhang Guomei, Zhu Jun, Hu Yang, Jiao Hongwei. Stress of three-dimensional finite element models of E-MAX porcelain inlay [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 537-541. |
| [9] | Cheng Jun, Tan Jun, Zhao Yun, Cheng Fangdong, Shi Guojia. Effect of thrombin concentration on the prevention of postoperative cerebrospinal leakage by fibrin glue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 570-575. |
| [10] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [11] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [12] | Ye Haimin, Ding Linghua, Kong Weihao, Huang Zutai, Xiong Long. Role and mechanism of hierarchical microchanneled bone scaffolds in promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 621-625. |
| [13] | Yu Langbo, Qing Mingsong, Zhao Chuntao, Peng Jiachen. Hot issues in clinical application of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in orthopedics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 449-455. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Wang Xinting, Xu Dandi, Zhang Junxia, Su Hailong Wang Qi. Stability of load-bearing cross barrier of different arch structures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3838-3843. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||