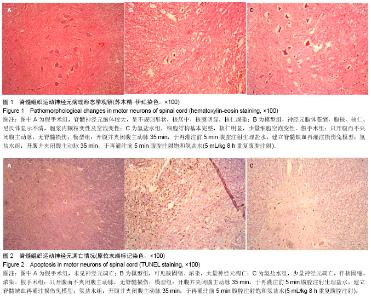
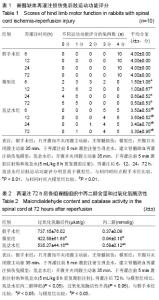
| [1] Wyndaele M, Wyndaele JJ. Incidence, prevalence and epidemiology of spinal cord injury: what learns a worldwide literature survey? Spinal Cord. 2006;44(9):523-529.
[2] Allen AR. Surgery of experimental lesion of spinal cord equivalent to crush injury of fracture dislocation of spinal column:A preliminary report. JAMA. 1911;57(8):878-880.
[3] Crawford ES, Rubia PA. Reappraisal of adjuncts to avoid ischemia in the treatment of aneurysms of descending thoracic aorta. J Thorac Cardiovacs Surg. 1973;66(5):693-704.
[4] 孙延卿,陈雄生.脊髓缺血再灌注损伤的研究进展[J].脊柱外科杂志,2010,8(5):311-315.
[5] Cuzzocrea S, Riley DP, CaputiAP, et al. Antioxidant therapy: a new pharmacological approach in shock, inflammation, and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Rev. 2001;53(1): 135-159.
[6] Tator CH, Koyanagi I. Vascular mechanisms in the pathophysiology of human spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg. 1997;86(3):483-492.
[7] Mody I, MacDonald JF. NMDA receptor-dependent excitotoxicity: the role of intracellular Ca2+ release. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995;16(10):356-359.
[8] Beattie MS, Hermann GE, Rogers RC, et al. Cell death in models of spinal cord injury. Prog Brain Res. 2002;137:37-47.
[9] Wu D, Miyamoto O, Shibuya S, et al. Different expression of macrophages and microglia in rat spinal cord contusion injury model at morphological and regional levels. Acta Med Okayama. 2005;59(4):121-127.
[10] Qiang S, Zhimin K, Jianmei C et al. Hydrogen-rich saline protects myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Exp Bio Med (Maywood). 2009;234(10):1212-1219.
[11] JianMei C, ZhiMin K, Kan L, et al. Neuroprotective effects of hydrogen saline in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model. Brain Res. 2008;2056:129-137.
[12] Zivin JA, Saito HT. Reduction of neurological by a peptide segment of the amyloid beta/A4 protein precursor in a rabbit spinal cord ischemia model. Exp Neurol. 1994;129(2):112-119.
[13] Tarlov IM. Acute spinal cord compression paralysis. J Neurosurg. 1972;36(1):10-20.
[14] Ding Q, Wang Q, Deng J, et al. Sevoflurane preconditioning induces rapid ischemic tolerance against spinal cord ischemia/ reperfusion through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in rabbits. Anesth Analg. 2009;109:1263-1272.
[15] Dong H, Xiong L, Zhu, Z, et al.Preconditioning with hyperbaric oxygen and hyperoxia induces tolerance against spinal cord ischemia in rabbits. Anesthesiology. 2002;96(4):907-912.
[16] 姚俊岩,翁浩,张兰,等.脊髓缺血再灌注损伤模型的改进及脊髓耐受缺血时限的研究[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2007,38(3): 497-500.
[17] 刘碧波,刘淼,马巍,等.脊髓缺血再灌注损伤时间窗及其行为学的实验研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2004,12(33):1080-1082.
[18] Moore WM Jr, Hollier LH. The influence of severity of spinal cord ischemia in the etiology of delayed-onset paraplegia. Ann Surg. 1991;213:427-432.
[19] Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, et al. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 2007;13(6):688-694.
[20] JianMei C, ZhiMin K, WenWu L, et al. Hydrogen therapy reduces apoptosis in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model. Neurosci Lett. 2008;441(2):167-172.
[21] Fukuda K, Asoh S, Ishikawa M, et al. Inhalation of hydrogen gas suppresses hepatic injury caused by ischemia/reperfusion through reducing oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;361(3):670-674.
[22] George JF, Agarwal A. Hydrogen: another gas with therapeutic potential. Kidney int. 2010;77:85-87.
[23] Hayashida K, Sano M, Ohsawa I, et al. Inhalation of hydrogen gas reduces infarct size in the rat model of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;373(1):30-35.
[24] Ohta S. Hydrogen gas and hydrogen water act as a therapeutic and preventive antioxidant with a novel concept. Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 2008;45(4):355-362.
[25] Xie K, Yu Y, Hou L, et al. Protective effects of hydrogen gas on murine polymicrobial spesis via reducing oxidative stree and HMGB1 release. Shock. 2010;34(1):90-97.
[26] Xie K, Yu Y, Zhang Z, et al. Hydrogen gas improves survival rate and organ damage in zymosan-induce generalized inflammation model. Shock. 2010;34(5):495-501.
[27] Mao YF, Zheng XF, Cai JM, et al. Hydrogen-rich saline reduces lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;381(4):602- 605.
[28] Sato Y, Kajiya ma S, Amano A, et al. Hydrogen-rich pure water prevents superoxide formation in brain slices of vitamin C-depleted SMP30/GNL knockout mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;375:346-350.
[29] Zheng X, Mao Y, Cai J, et al. Hydrogen-rich saline protects against intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Free Radic. Res. 2009;43(5):478-484.
[30] Ji X, Liu W, K Qu, et al. Beneficial effects of hydrogen gas in a rat model of traumatic brain injury via reducing oxidative stress. Brain Res. 2010;1354:262-272.
[31] Chen C, Chen Q, Mao Y, et al. Hydrogen-rich saline protects against spinal cord injury in rats. Neurochem Res. 2010; 35(7):1111-1118.
[32] Beattie MS, Farooqui AA, Bresnahan JC. Review of current evidence for apoptosis after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2000;17(10):915-925.
[33] Hayashi T, Sakurai M, Abe K, et al. Apoptosis of motor neurons with induction of caspases in the spinal cord after ischemia. Stroke. 1998;29(5):1007-1013.
[34] Elmore S. Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 2007;35(4):495-516.
[35] Perry SW, Epstein LG, Gelbard HA. Simultaneous in situ detection of apoptosis and necrosis in monolayer cultures by TUNEL and trypan blue staining. Biotechniques. 1997;22(6): 1102-1106.
[36] Kumar A, Panigrahi I, Basu S, et al. Urinary malondialdehyde levels in newborns following delivery room resuscitation. Neonatology. 2008;94(2):96-99.
[37] Basu S, Hellberg A, Ulus AT, et al. Biomarkers of free radical injury during spinal cord ischemia. FEBS Lett. 2001; 508(1): 36-38.
[38] Sakamoto M, Takaki E, Yamashita K, et al. Nonenzymatic derived lipid peroxide, 8-iso-PGF2 alpha, participates in the pathogenesis of delayed cerebral vasospasm in a canine SAH model. Neurol Res. 2002;24(3):301-306.
[39] Hall ED. Inhibition of lipid penxidation in CNS trauma. J Neurotrauma. 1991;8:31-40.
[40] Loew Oscar. A new enzyme of general occurrence in organisms. Science. 1900;11(279):701-702.
[41] Satpute RM, Kashyap RS, Deopujari JY, et al. Protection of PC12 cells from chemical ischemia induce doxidtive stress by Fagonia arabica. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009;47(11):2689- 2695.
[42] 林山,练克俭,陈长青.脊髓缺血再灌注损伤与细胞凋亡相关基因研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2007,28(1):53-55 |