Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (12): 1907-1913.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.12.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application and characteristics of self-assembling peptide nanofiber hydrogel in three-dimensional cell culture systems
Liu Xi1, 2, Wang Xiu-mei2
- 1National Engineering Laboratory for Modern Silk, College of Textile and Clothing Engineering, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China
2Institute for Regenerative Medicine and Biomimetic Materials, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Revised:2014-01-18Online:2014-03-19Published:2014-03-19 -
Contact:Wang Xiu-mei, Professor, Institute for Regenerative Medicine and Biomimetic Materials, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China -
About author:Liu Xi, Ph.D., Assistant professor, National Engineering Laboratory for Modern Silk, College of Textile and Clothing Engineering, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China; Institute for Regenerative Medicine and Biomimetic Materials, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of the Higher Education Institutions of Jiangsu Province, No. 13KJB430019; China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2013M541724; Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program, No. 20121087982
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Xi, Wang Xiu-mei. Application and characteristics of self-assembling peptide nanofiber hydrogel in three-dimensional cell culture systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(12): 1907-1913.
share this article
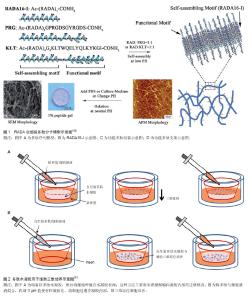
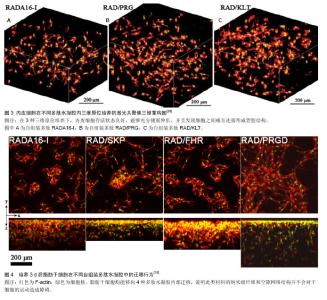
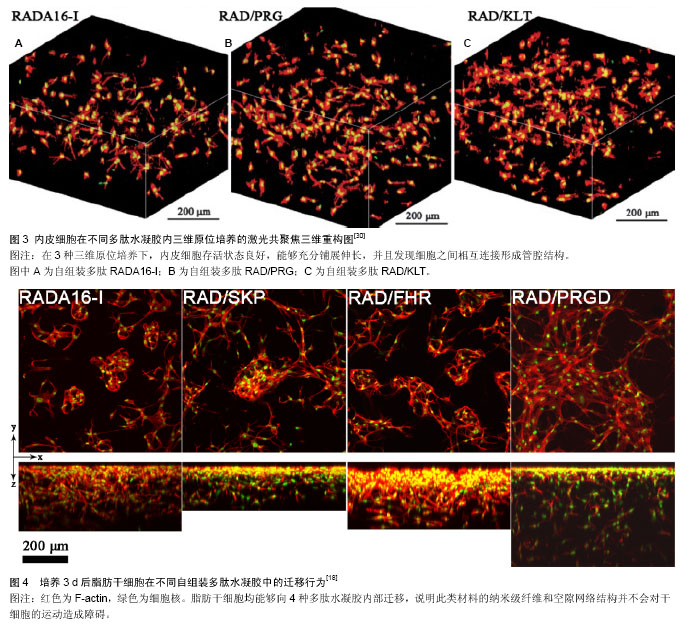
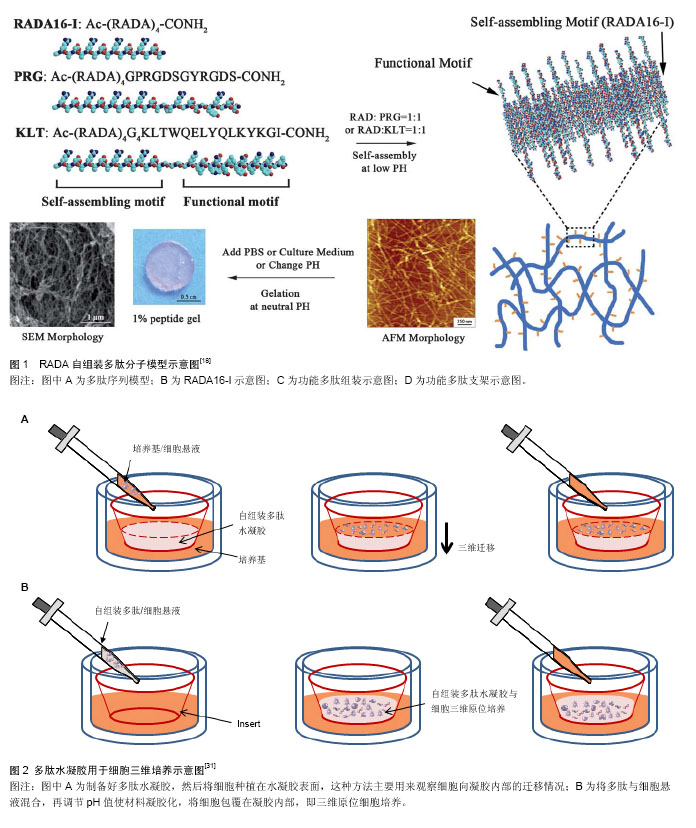
2.1 自组装多肽的发现 第1个自组装多肽EAK16-II (AEAEAKAKAEAEAKAK)的发现源于对酵母遗传学和结构蛋白学的研究,它由丙氨酸(alanine,A)、谷氨酸(glutamate,E)和赖氨酸(lysine,K)交替排列而成,并在水中能够形成稳定的β折叠结构[10-11]。由于该β折叠结构一侧是非极性疏水端,另一侧是由带有正负电氨基酸组成的亲水端,这类多肽分子又被称为“离子互补型自组装多肽分子”。在水溶液中,多肽分子发生自组装,通过分子间的疏水作用力,肽链的疏水端聚集在内侧,而外侧亲水端的氨基酸通过互补的离子相互作用横向交替排列,使自组装的多肽分子延长并形成稳定的直径约10 nm的纳米纤维。在改变多肽溶液pH值或加入碱性阳离子的情况下,自组装多肽分子开始凝胶化,形成含水量99%(5-10 g/L)以上的水凝胶。 基于这一发现,多种具有类似特征的多肽序列越来越受到人们的关注与研究,尽管设计方案和组装形态不尽相同,但在组织工程领域都取得了令人欣喜的结果。其中,Zhang等[12-17]设计的RADA16-I (AcN- RADARADARADARADA-CNH2)与RADA16-II (AcN-RARADADARARADADA-CNH2)研究和应用最为广泛,RADA16-I已被商品化(PuraMatrixTM,BD Biosciences)。这里由精氨酸(arginine,R)和天门冬氨酸(aspartate,D)分别代替赖氨酸K和谷氨酸E。除RADA外,自组装多肽分子家族仍在不断增加。在自组装多肽分子的设计中,疏水性和多肽序列长度是影响多肽自组装特性的重要因素。疏水性越高、多肽序列越长,自组装过程越容易发生。 2.2 功能化RADA自组装多肽水凝胶 以短肽为基本组成单元,不仅使得这类多肽材料具有更好的生物相容性、可降解性,更为突出的优点是其具有可设计性,可根据需求不同复合不同的生物活性分子,赋予该类材料“生物智能”的特性。在RADA自组装多肽的基础上,可以复合具有细胞特异性的功能短肽片段,显著提高材料的生物功能和特异性[3-5]。复合功能片段主要是在多肽固相合成过程中,通过延长C末端将自组装多肽和功能多肽通过几个甘氨酸连接起来(图1)。 其中,甘氨酸的作用是为了增加功能片段的灵活性,避免功能片段影响自组装多肽的自组装过程。一般将接枝有功能短肽的多肽与RADA多肽1∶1混合使用,实验表明功能片段并未影响自组装多肽的自组装过程,并且能够显著提高自组装多肽的生物功能。下面简要介绍一些常见的功能片段:"
| [1] Lutolf MP,Gilbert PM,Blau HM.Designing materials to direct stem-cell fate.Nature.2009;462(7272):433-441. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Liu Zhichao, Zhang Fan, Sun Qi, Kang Xiaole, Yuan Qiaomei, Liu Genzhe, Chen Jiang. Morphology and activity of human nucleus pulposus cells under different hydrostatic pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1172-1176. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [8] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [9] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [10] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [11] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [12] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [13] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [14] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [15] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 397
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 362
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||