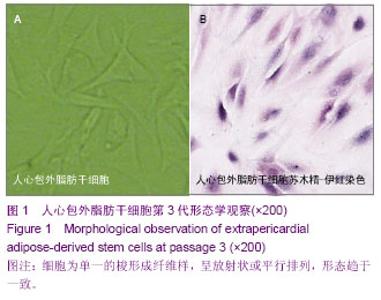
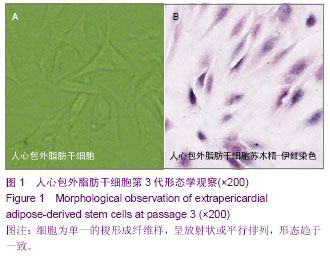
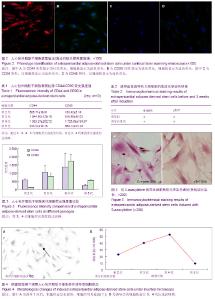
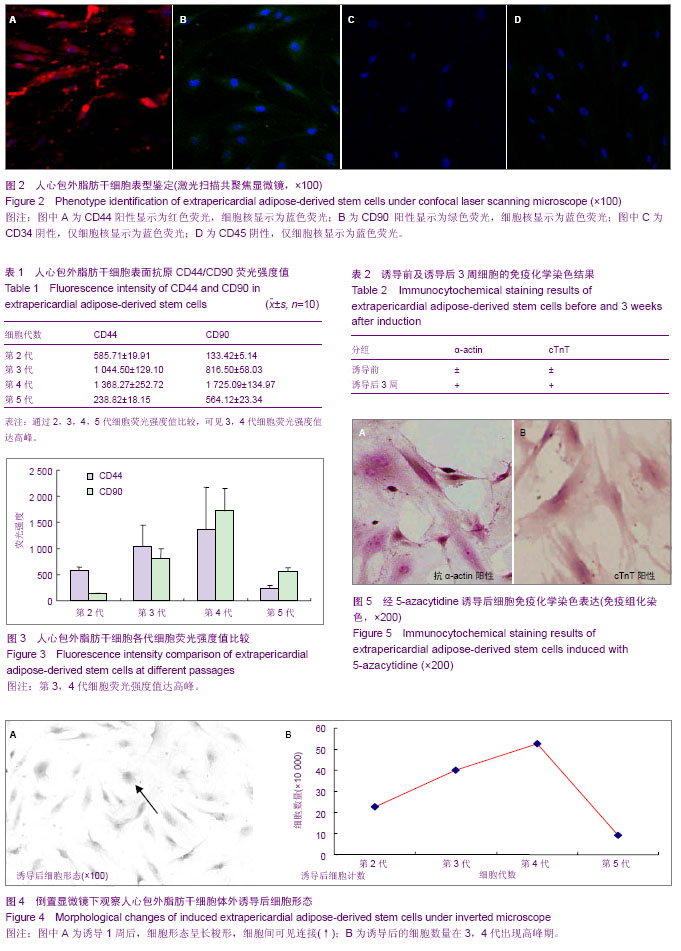
| [1] 张超,龚跃昆.脂肪干细胞的研究新进展[J].昆明医学院学报, 2008,29(1):167-171.[2] Witkowska-Zimny M, Walenko K. Stem cells from adipose tissue. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2011;16(2):236-257.[3] 雷华,李青峰.脂肪干细胞的研究进展[J].中华整形外科杂志, 2003,19(6):465-466.[4] Simões IN, Boura JS, dos Santos F, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells from the umbilical cord matrix: successful isolation and ex vivo expansion using serum-/xeno-free culture media. Biotechnol J. 2013;8(4):448-458. [5] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228. [6] Salem SA, Hwie AN, Saim A, et al. Human adipose tissue derived stem cells as a source of smooth muscle cells in the regeneration of muscular layer of urinary bladder wall. Malays J Med Sci. 2013;20(4):80-87. [7] Beresford JN, Bennett JH, Devlin C, et al. Evidence for an inverse relationship between the differentiation of adipocytic and osteogenic cells in rat marrow stromal cell cultures. J Cell Sci. 1992;102(Pt 2):341-351. [8] Coleman CM, Vaughan EE, Browe DC, et al. Growth differentiation factor-5 enhances in vitro mesenchymal stromal cell chondrogenesis and hypertrophy. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(13):1968-1976. [9] Schagemann JC, Paul S, Casper ME, et al. ogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells via biomimetic and bioactive poly-ε-caprolactone scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(6):1620-1628. [10] Grigoriadis AE, Heersche JN, Aubin JE. Differentiation of muscle, fat, cartilage, and bone from progenitor cells present in a bone-derived clonal cell population: effect of dexamethasone. J Cell Biol. 1988;106(6):2139-2151.[11] Prins HJ, Braat AK, Gawlitta D, et al. In vitro induction of alkaline phosphatase levels predicts in vivo bone forming capacity of human bone marrow stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. 2013;12(2):428-440.[12] Granéli C, Thorfve A, Ruetschi U, et al. Novel markers of osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells identified using a quantitative proteomics approach. Stem Cell Res. 2013;12(1):153-165.[13] Wu C, Han P, Liu X, et al. Mussel-inspired bioceramics with self-assembled Ca-P/polydopamine composite nanolayer: Preparation, formation mechanism, improved cellular bioactivity and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(1):428-438. [14] Dennis JE, Merriam A, Awadallah A, et al. A quadripotential mesenchymal progenitor cell isolated from the marrow of an adult mouse. J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14(5):700-709. [15] Jin P, Zhang X, Wu Y, et al. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat-derived bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells have impaired abilities in proliferation, paracrine, antiapoptosis, and myogenic differentiation. Transplant Proc. 2010;42(7): 2745-2752. [16] Luth ES, Jun SJ, Wessen MK, et al. Bone marrow side population cells are enriched for progenitors capable of myogenic differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2008;121(Pt 9):1426- 1434. [17] Xynos A, Corbella P, Belmonte N, et al. Bone marrow-derived hematopoietic cells undergo myogenic differentiation following a Pax-7 independent pathway. Stem Cells. 2010; 28(5):965-973. [18] Russo V, Yu C, Belliveau P, et al. Comparison of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Isolated from Subcutaneous, Omental, and Intrathoracic Adipose Tissue Depots for Regenerative Applications. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013.[19] Jun HS, Choi W, Kim JY, et al. Electrical impedance characterization of adipose tissue-derived stem cells cultured on indium tin oxide electrodes. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2013; 9(4):699-702.[20] Buehrer BM, Cheatham B. Isolation and characterization of human adipose-derived stem cells for use in tissue engineering. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1001:1-11. [21] Li D, Yang C,Qu R,et al. Cognitive improvement following transvenous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Neural Regeneration Research. 2011;6(10):129-134.[22] Ou Y, Yuan X, Cai Y,et al. A novel ethanol-based method to induce differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells into astrocytes. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(10):231-237.[23] Caspar-Bauguil S, Cousin B, Galinier A, et al. Adipose tissues as an ancestral immune organ: site-specific change in obesity. FEBS Lett. 2005;579(17):3487-3492. [24] Tapp H, Hanley EN Jr, Patt JC, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells: characterization and current application in orthopaedic tissue repair. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2009; 234(1):1-9. [25] Prunet-Marcassus B, Cousin B, Caton D, et al. From heterogeneity to plasticity in adipose tissues: site-specific differences. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(6):727-736. [26] Zuk PA. The adipose-derived stem cell: looking back and looking ahead. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21(11):1783-1787. [27] Park E, Patel AN. Changes in the expression pattern of mesenchymal and pluripotent markers in human adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Biol Int. 2010;34(10): 979-984. [28] Rodríguez-Serrano F, Alvarez P, Caba O, et al. Promotion of human adipose-derived stem cell proliferation mediated by exogenous nucleosides. Cell Biol Int. 2010;34(9): 917-924.[29] Wan Safwani WK, Makpol S, Sathapan S, et al. 5-Azacytidine is insufficient for cardiogenesis in human adipose-derived stem cells. J Negat Results Biomed. 2012;11:3. [30] Wan Safwani WK, Makpol S, Sathapan S, et al. 5-Azacytidine is insufficient for cardiogenesis in human adipose-derived stem cells. J Negat Results Biomed. 2012;11:3. |