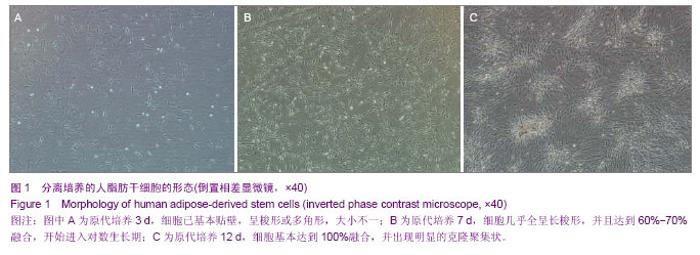
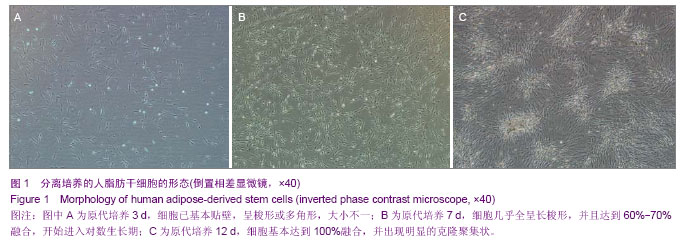
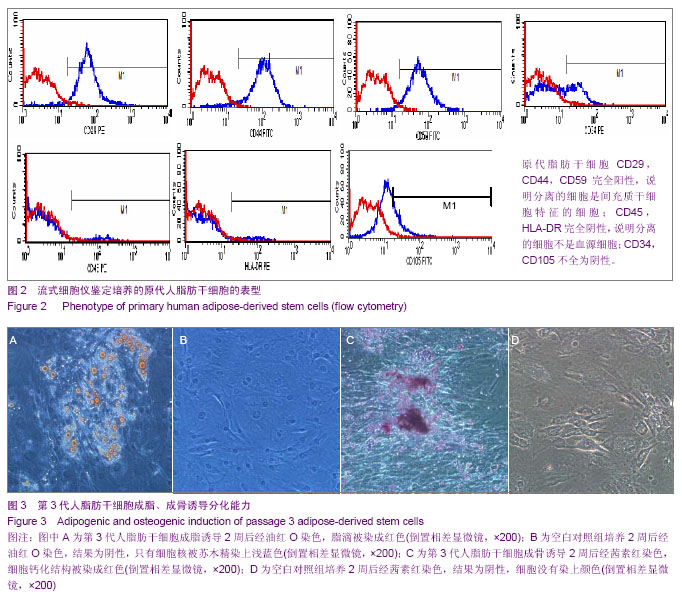
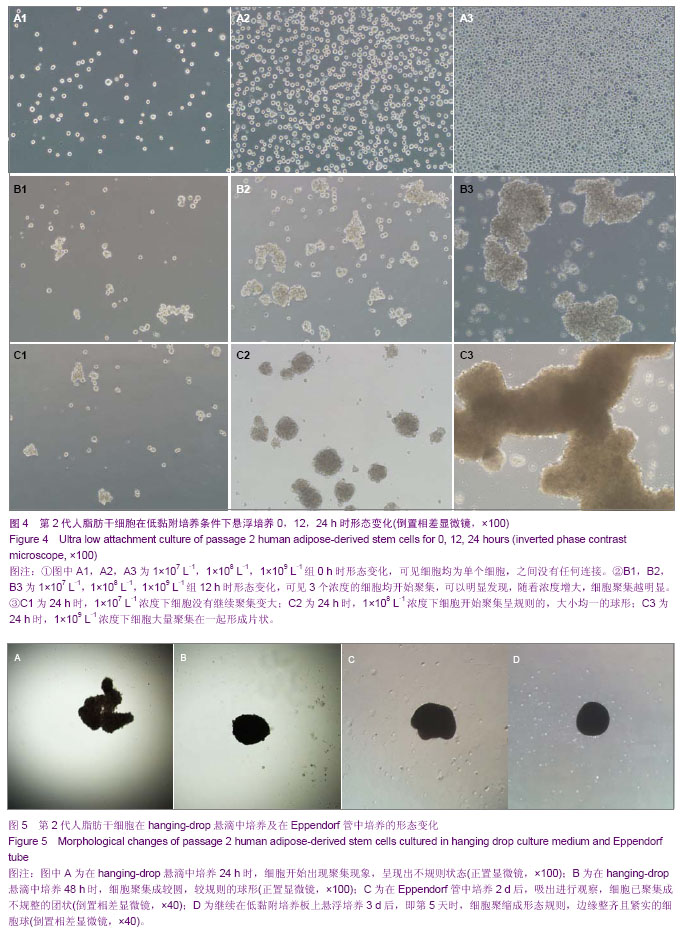
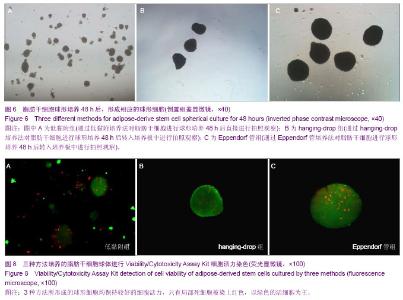
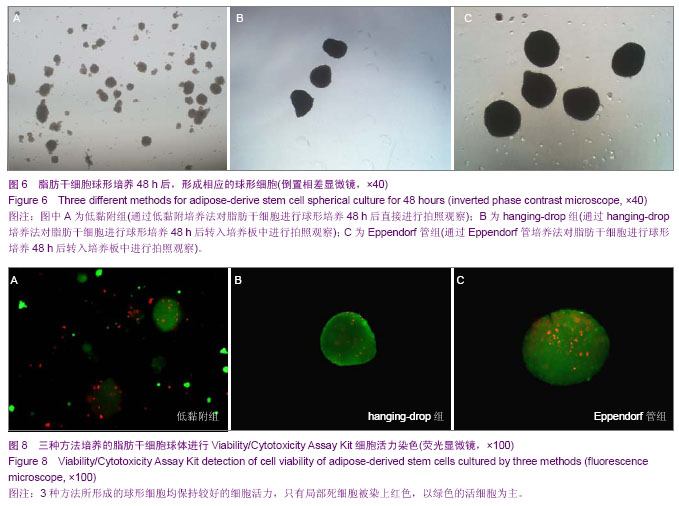
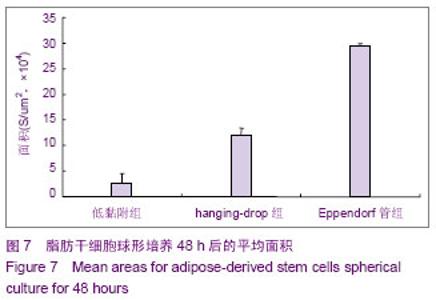
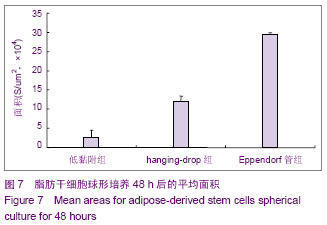
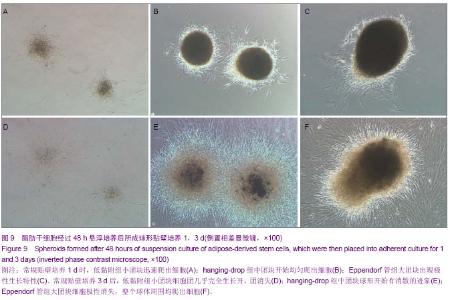
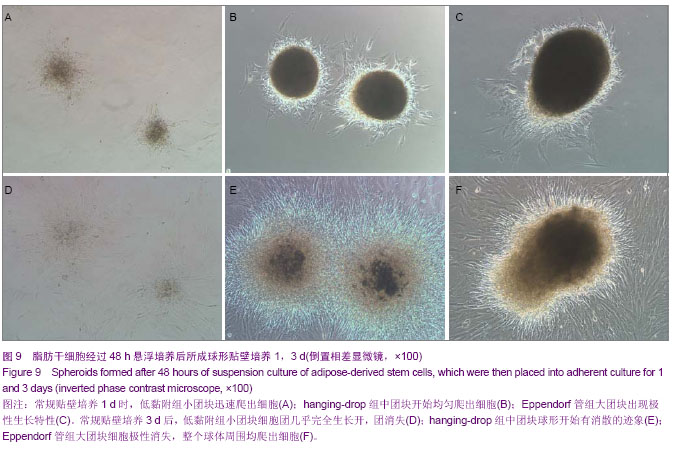
| [1] 王刚,曹卫刚.具有多向分化潜能的脂肪干细胞研究的新进展[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志,2009,5(3):173-176.
[2] Lin RZ, Chang HY. Recent advances in three-dimensional multicellular spheroid culture for biomedical research. Biotechnol J. 2008;3(9-10):1172-1184.
[3] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H,et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.
[4] Scott SG, Jun AS, Chakravarti S.Sphere formation from corneal keratocytes and phenotype specific markers. Exp Eye Res. 2011;93(6):898-905.
[5] Rajanahalli P, Meyer K, Zhu L,et al. Conversion of mouse fibroblasts to sphere cells induced by AlbuMAXI-containing medium. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012;4:1813-1822.
[6] Kapur SK, Wang X, Shang H,et al. Human adipose stem cells maintain proliferative, synthetic and multipotential properties when suspension cultured as self-assembling spheroids. Biofabrication. 2012;4(2):025004.
[7] Funderburgh ML, Mann MM, Funderburgh JL. Keratocyte phenotype is enhanced in the absence of attachment to the substratum. Mol Vis. 2008;14:308-317.
[8] Page H, Flood P, Reynaud EG.Three-dimensional tissue cultures: current trends and beyond. Cell Tissue Res. 2013; 352(1):123-131.
[9] Wang W, Itaka K, Ohba S,et al. 3D spheroid culture system on micropatterned substrates for improved differentiation efficiency of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2009;30(14):2705-2715.
[10] Yokoo S, Yamagami S, Yanagi Y,et al. Human corneal endothelial cell precursors isolated by sphere-forming assay. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46(5):1626-1631.
[11] Mimura T, Yamagami S, Yokoo S,et al. Sphere therapy for corneal endothelium deficiency in a rabbit model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46(9):3128-3135.
[12] Dromard C, Bourin P, André M,et al. Human adipose derived stroma/stem cells grow in serum-free medium as floating spheres. Exp Cell Res. 2011 ;317(6):770-780.
[13] Yoshida S, Shimmura S, Shimazaki J,et al. Serum-free spheroid culture of mouse corneal keratocytes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46(5):1653-1658.
[14] Zhang Q, Nguyen AL, Shi S,et al. Three-dimensional spheroid culture of human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhances mitigation of chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(6):937-947.
[15] Napolitano AP, Dean DM, Man AJ,et al. Scaffold-free three- dimensional cell culture utilizing micromolded nonadhesive hydrogels. Biotechniques. 2007;43(4):494, 496-500.
[16] Mi S, Chen B, Wright B,et al. Ex vivo construction of an artificial ocular surface by combination of corneal limbal epithelial cells and a compressed collagen scaffold containing keratocytes.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(6):2091-2100.
[17] Ong SY, Dai H, Leong KW. Inducing hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in pellet culture. Biomaterials. 2006;27(22):4087-4097.
[18] Lee JI, Sato M, Kim HW,et al. Transplantatation of scaffold-free spheroids composed of synovium-derived cells and chondrocytes for the treatment of cartilage defects of the knee. Eur Cell Mater. 2011;22:275-290.
[19] Bae KS, Park JB, Kim HS,et al. Neuron-like differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Yonsei Med J. 2011;52(3):401-412.
[20] Chen YH, Wang IJ, Young TH. Formation of keratocyte spheroids on chitosan-coated surface can maintain keratocyte phenotypes.Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(8):2001-2013.
[21] Lei XH, Ning LN, Cao YJ,et al. NASA-approved rotary bioreactor enhances proliferation of human epidermal stem cells and supports formation of 3D epidermis-like structure. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e26603.
[22] Sakai Y, Yoshiura Y, Nakazawa K. Embryoid body culture of mouse embryonic stem cells using microwell and micropatterned chips. J Biosci Bioeng. 2011;111(1):85-91.
[23] Yang MJ, Chen CH, Lin PJ,et al. Novel method of forming human embryoid bodies in a polystyrene dish surface-coated with a temperature-responsive methylcellulose hydrogel. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8(9):2746-2752.
[24] Kim C, Lee IH, Lee K,et al. Multi-well chip for forming a uniform embryoid body in a tiny droplet with mouse embryonic stem cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2007;71(12):2985-2991.
[25] 管利东,王韫芳,刘大庆,等.人脂肪来源干细胞在模拟微重力环境中的生长特性[J]. 自然科学进展, 2007,1(1):22-28.
[26] Skardal A, Sarker SF, Crabbé A,et al. The generation of 3-D tissue models based on hyaluronan hydrogel-coated microcarriers within a rotating wall vessel bioreactor. Biomaterials. 2010;31(32):8426-8435.
[27] Muhitch JW, O'Connor KC, Blake DA,et al. Characterization of aggregation and protein expression of bovine corneal endothelial cells as microcarrier cultures in a rotating-wall vessel. Cytotechnology. 2000;32(3):253-263.
[28] 徐巧瑜.人脂肪干细胞(ADSCs)体外培养的研究及应用进展[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(7):1265-1267.
[29] Radtke C, Schmitz B, Spies M,et al. Peripheral glial cell differentiation from neurospheres derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2009;27(8): 817-823.
[30] Huang GS, Dai LG, Yen BL,et al. Spheroid formation of mesenchymal stem cells on chitosan and chitosan- hyaluronan membranes.Biomaterials. 2011;32(29):6929-6945.
[31] Ferro F, Spelat R, Falini G,et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cell in vitro differentiation in a three-dimensional dental bud structure.Am J Pathol. 2011;178(5):2299-2310. |