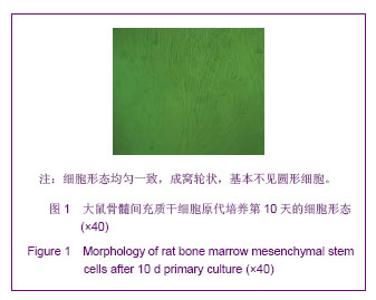
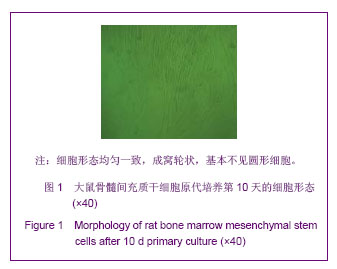
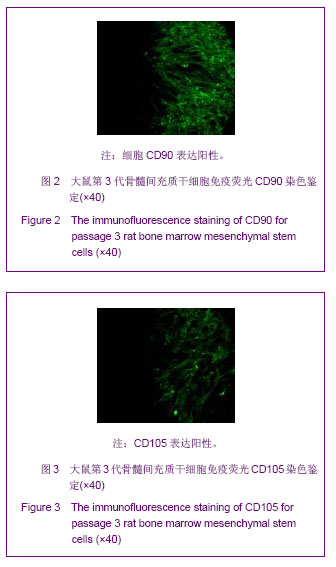
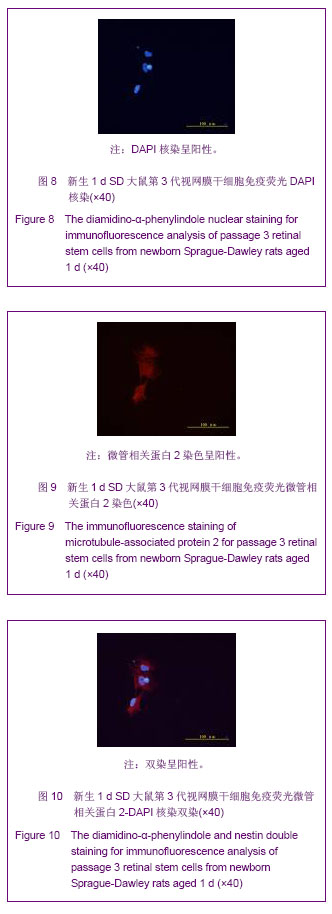
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (40): 7027-7027.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.40.001
Retinal stem cell culture supernatant induces differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Wang Zhuo, Wang Dan, Hao Dong-hai, Li Bo
- He’s University, Shenyang 110163, Liaoning Province, China
-
Online:2013-10-01Published:2013-10-31 -
Contact:Li Bo, M.D., Associate professor, He’s University, Shenyang 110163, Liaoning Province, China peterlibo@gmail.com -
About author:Wang Zhuo, Lecturer, He’s University, Shenyang 110163, Liaoning Province, China luckzhuo1982@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zhuo, Wang Dan, Hao Dong-hai, Li Bo. Retinal stem cell culture supernatant induces differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(40): 7027-7027.
share this article
| [1]Piertdomenico L,Bonsi L,Calvitti M,et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells with immunosuppressive activity can be easily isolated from dental pulp. Tranephmtation. 2005; 80(6):836-842. [2]Delorme B, Chateauvieux S, Charbord P. The concept of mesenchymal stem cells. Regen Med. 2006;1(4):497-509. [3]Jacobs SA, Roobrouck VD, Verfaillie CM, et al. Immunological characteristics of human mesenchymal stem cells and multipotent adult progenitor cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013;91(1):32-39. [4]Mareschi K, Biasin E, Piacibello W, et al. Isolation of human mesenchymal stem cells: bone marrow versus umbilical cord blood. Haematologica. 2001;86(10):1099-1100. [5]Chamberlain G, Fox J, Ashton B, et al. Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing. Stem Cells. 2007;25(11):2739-2749. [6]Tolar J, Le Blanc K, Keating A, et al. Concise review: hitting the right spot with mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells. 2010;28(8):1446-1455. [7]韩小改,李建斌,马建军,等.成人骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞的诱导分化:最佳诱导剂与诱导时间[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(32):6332-6337. [8]Adolphe M, Parodi AL. Ethical issues in animal experimentation. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2009;193(8): 1803-1804. [9]Kumar S, Wan C, Ramaswamy G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells expressing osteogenic and angiogenic factors synergistically enhance bone formation in a mouse model of segmental bone defect. Mol Ther. 2010;18(5):1026-1034. [10]Tormin A, Li O, Brune JC, et al. CD146 expression on primary nonhematopoietic bone marrow stem cells is correlated with in situ localization. Blood. 2011;117(19):5067-5077. [11]石芊,彭秀军.干细胞移植治疗视网膜疾病的研究现状[J].国际眼科杂志,2008,8(5):994-996. [12]Noth U, Rackwitz L, Heymer A, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in collagen type I hydrogels. J Biomed. 2007;83(3):626-635. [13]Briggs T, Treiser MD, Holmes PF, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on poly(ethyleneglycol)-variant biomaterials. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;91(4):975-984. [14]Lin W, Chen X, Wang X, et al. Adult rat bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into Schwann cell-like cells in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008;44(1-2):31-40. [15]Kassem M, Kristiansen M, Abdallsh BM. Mesenchymal stem cells: cell biology and potential use in therapy. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;95(5):209-241. [16]Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derive dfrom adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):412-449. [17]Wang XS, Li HF, Zhao Y, et al. Radix Astragali-induced differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2009;4(7):497-502. [18]Goolsby J, Marty MC, Heletz DC, et al. Hematopoietic progenitors express neuralgenes. ProcNatl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100(25):14926-14931. [19]Li Q, Geng YJ, Lu L, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin-induced bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblast-like cells and neural cells. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(31):2419-2423. [20]Yin YQ, Chen B, Ke JL, et al. Xuefuzhuyu injection induces neuronal differentiation of rat bone morrow mesenchymal stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(3):177-182. [21]Lund RD,Wang S, Lu B,et al. Ceils isolated from umbilical cord tissue rescue photoreceptors and visual functions in a rodent model of retinal disease. Stem Cells. 2007;25(3): 602-611. [22]Tomita M,Adachi Y,Yamada H,et al.Bone marrow-derived stem cells can differentiate into retinal cells in injured rat retina. Stem Cells. 2002;20(4):279-283. [23]De Bari C, Dell’Accio F, Vandenabeele F,et al. Skeletal muscle repair by adult human mesenchymal stem cells from synovial membrane. J Cell Biol. 2003;160(6):909-918. [24]Zomorodian E, Baghaban Eslaminejad M. Mesenchymal stem cells as a potent cell source for bone regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2012;2012:980353. [25]Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49. [26]Haasters F, Prall WC, Anz D, et al.Morphological and immunocytochemical characteristics indicate the yield of early progenitors and represent a quality control for human mesenchymal stem cell culturing. J Anat. 2009;214(5): 759-767. [27]Colter DC, Class R, DiGirolamo CM, et al. Rapid expansion of recycling stem cells in cultures of plastic-adherent cells from human bone marrow. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97(7): 213-3219. [28]Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317. [29]Matsuda Y, Hagio M, Ishiwata T. Nestin: a novel angiogenesis marker and possible target for tumor angiogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(1):42-48. [30]Alfaro-Cervello C, Soriano-Navarro M, Mirzadeh Z, et al. Biciliated ependymal cell proliferation contributes to spinal cord growth. J Comp Neurol. 2012;520(15):3528-3552. [31]Méndez-Ferrer S, Michurina TV, Ferraro F, et al. Mesenchymal and haematopoietic stem cells form a unique bone marrow niche. Nature. 2010;466(7308):829-834. [32]Fischer AJ, McGuire CR, Dierks BD, et al. Insulin and fibroblast growth factor 2 activate a neurogenic program in Müller glia of the chicken retina. J Neurosci. 2002;22(21): 9387-9398. [33]Gritti A, Vescovi AL, Galli R. Adult neural stem cells: plasticity and developmental potential. J Physiol Paris. 2002;96(1-2): 81-90. [34]Qin Z, Kidd AR 3rd, Thomas JL, et al. FGF signaling regulates rod photoreceptor cell maintenance and regeneration in zebrafish. Exp Eye Res. 2011;93(5):726-734. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [4] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [5] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [7] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [8] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [9] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [10] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [11] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [12] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [13] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [14] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [15] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||