Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Root canal filling material added with tea polyphenols inhibits the generation of Candida albicans biofilm
Xu Ying1, Lü Qing1, Kang Liang2, Zhang Hui-ming3
- 1 Second Department of Endodontics, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China
2 First Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China
3 Experimental Center of Life Sciences, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2012-12-18Revised:2013-03-27Online:2013-05-21Published:2013-05-21 -
Contact:Lü Qing, Master, Second Department of Endodontics, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China lq861229@126.com -
About author:Xu Ying, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Second Department of Endodontics, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China xuyingjiayi@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Ying, Lü Qing, Kang Liang, Zhang Hui-ming. Root canal filling material added with tea polyphenols inhibits the generation of Candida albicans biofilm[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.21.025.
share this article
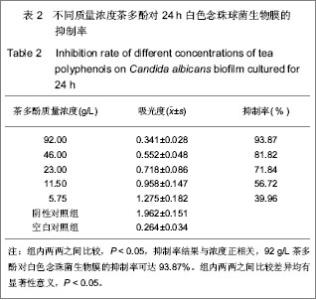
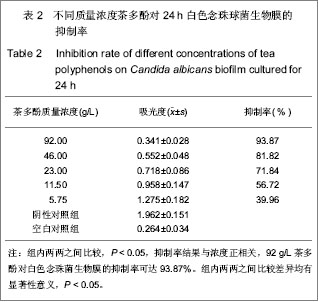
1.3 结果 1.3.1 茶多酚的质量检测 茶多酚质量浓度与吸光度值的线性回归为y=0.244 8c-7.07×10-4,线性范围4×10-6-36×10-5 g/mL,重现性=1.3%符合分析要求。经检测茶多酚有效含量达到对照品含量的90%以上,符合国家有关中药原药材提取物质量标准的相关规定。 1.3.2 茶多酚的抑菌效果 纸片扩散法显示2种根管冲洗液均有明显的抑菌圈,其中52.5 g/L次氯酸钠液抑菌圈较大,茶多酚较小,作为空白对照的生理盐水组没有出现抑菌圈。根据微孔板滴定法测得茶多酚对白色念珠菌生物膜最小抑菌浓度为11.5 g/L,最小杀菌浓度为 23 g/L。四甲基偶氮唑盐微量酶反应比色法测定不同浓度茶多酚对24 h白色念珠菌生物膜的吸光值,计算其抑制率,见表2。"
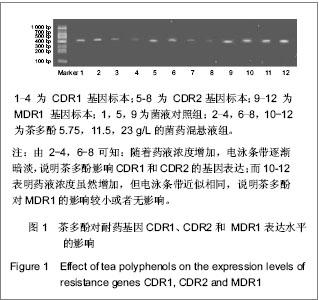
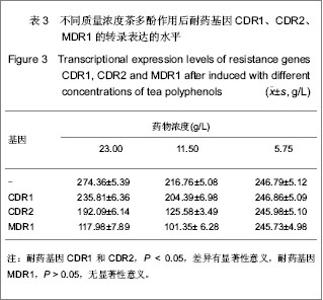
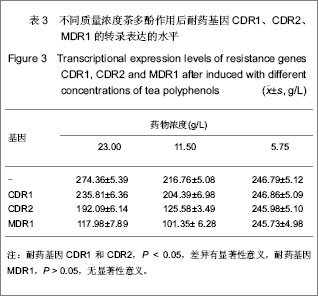
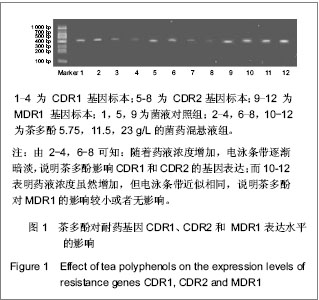
1.3.3 茶多酚对耐药基因CDR1、CDR2和 MDR1表达水平的影响 如图1所示,选取作用24 h后阳性对照组及药物终浓度分别为 5.75,11.5,23 g/L的菌药混悬液测定耐药基因CDR1、CDR2和MDR1的表达水平。①阳性对照组及药物终浓度为5.75 g/L时聚合酶链式反应扩增的耐药基因CDR1、CDR2和MDR1电泳条带较清晰;药物终浓度11.5 g/L时CDR1、CDR2的聚合酶链式反应扩增基因的电泳条带亮度变淡,耐药基因MDR1电泳条带仍较清晰;药物终浓度为23.0 g/L时,耐药基因CDR1、CDR2特异性条带亮度更加暗淡,耐药基因MDR1电泳条带依然较清晰。②4组平行组同等条件下多次重复实验操作,凝胶成像系统软件对图像进行电泳条带吸光度值测定。"
| [1] Mah TF,O'Toole GA.Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents.Trends Microbiol.2001;9(1):34-39.[2] Chandra J,Kuhn DM,Mukherjee PK,et al.Biofilm formation by the fungal pathogen Candida albicans: development, architecture, and drug resistance.J Bacteriol.2001;183(18): 5385-5394.[3] Sun Z,Liu H. Yi Xue Yan Jiu Za Zhi. 2012;41(6):182-184.孙智,刘泓.新型根管充填材料的回顾研究[J].医学研究杂志, 2012, 41(6):182-184.[4] Liu M,Li Z,Gao WX. Zhong Guo Lao Nian Xue Za Zhi. 2009; 29(9):1144-1145.刘明,李泽,高文信.两种根管充填材料的封闭性能比较[J].中国老年学杂志,2009,29(9):1144-1145.[5] Wang P,Liang HY,Wu J,et al. Zhong Guo Zu Zhi Gong Cheng Yan Jiu Yu Lin Chuang Kang Fu. 2010;14(12):2179-2182.王萍,梁焕友,吴坚,等.两种根管充填材料的封闭性能比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(12):2179-2182. [6] Qin H,Gong YQ,Xu ZH. Zhongguo Zughi Gongcheng Yanjiu Yu Linchuang Kangfu.2011;15(2): 232-235.秦晗,龚永庆,徐宏志.根管充填体外模型构建中X射线牙片的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(2): 232-235.[7] Gu LS,Ling JQ. Guoji Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi.2006;33(5): 349-351.古丽莎,凌均棨.根管生物膜及其临床控制的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2006,33(5):349-351.[8] Qi FF,Wang S,Guo J.Xiandai Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi.2011; 25 (5): 359-362.齐芳芳,王山,郭洁.茶多酚、厚朴酚抑制早期人工根面龋作用的实验研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2011,25(5):359-362.[9] Luo YN,Yu XY,Liu LQ.Hua Xue Shi Jie.2011;52(9):526-533.罗亚楠,于晓洋,刘立群.茶叶中茶多酚的提取及分析检测[J].化学世界,2011,52(9):526-533.[10] Liao XL,Lang HY,Xu WF,et al.Fenxi Shiyanshi.2003;22(5): 70-72.廖晓玲,郎惠云,徐文峰,等.钼酸铵分光光度法测定绿茶中的茶多酚[J].分析试验室,2003,22(5):70-72.[11] Tong Z,Dong L,Zhou L,et al.Nisin inhibits dental caries-associated microorganism in vitro.Peptides.2010;31 (11): 2003-2008.[12] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2012-08-10. https://www.cnki.net[13] SCI数据库.Web of Sciencevia ISI Web of Knowledge[DB/OL]. 2012-08-10.http://ip-science.thomsonreuters.com/mjl[14] Soustre J,Rodier MH,Imbert-Bouyer S,et al.Caspofungin modulates in vitro adherence of Candida albicans to plastic coated with extracellular matrix proteins.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004;53(3):522-525. [15] Bachmann SP,VandeWalle K,Ramage G,et al.In vitro activity of caspofungin against Candida albicans biofilms.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2002;46(11):3591-3596.[16] Alem MA,Douglas LJ.Effects of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on biofilms and planktonic cells of Candida albicans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2004; 48(1): 41-47.[17] Chandra J,Kuhn DM,Mukherjee PK,et al.Biofilm formation by the fungal pathogen Candida albicans: development, architecture, and drug resistance.J Bacteriol.2001;183(18): 5385-5394.[18] Hazan Z,Zumeris J,Jacob H,et al.Effective prevention of microbial biofilm formation on medical devices by low-energy surface acoustic waves.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2006; 50(12):4144-4152.[19] Kuhn DM,Chandra J,Mukherjee PK,et al.Comparison of biofilms formed by Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis on bioprosthetic surfaces.Infect Immun.2002; 70(2):878-888.[20] Chandra J,Patel JD,Li J,et al.Modification of surface properties of biomaterials influences the ability of Candida albicans to form biofilms.Appl Environ Microbiol.2005; 71(12):8795-8801.[21] Andes D,Nett J,Oschel P,et al.Development and characterization of an in vivo central venous catheter Candida albicans biofilm model.Infect Immun.2004;72(10): 6023-86031.[22] Tsang CS,Ng H,McMillan AS.Antifungal susceptibility of Candida albicans biofilms on titanium discs with different surface roughness.Clin Oral Investig.2007;11(4):361-368.[23] LaFleur MD,Kumamoto CA,Lewis K.Candida albicans biofilms produce antifungal-tolerant persister cells.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2006;50(11):3839-3846.[24] Szomolay B,Klapper I,Dockery J,et al.Adaptive responses to antimicrobial agents in biofilms.Environ Microbiol.2005;7(8): 1186-1191.[25] Chang GJ,Wang AL.Shan Dong Yi Yao.2007;47(5):81-82.常桂娇,王艾琳.细菌生物膜及其与细菌耐药性关系的研究进展[J].山东医药,2007,47(5):81-82.[26] Alem MA,Oteef MD,Flowers TH,et al.Production of tyrosol by Candida albicans biofilms and its role in quorum sensing and biofilm development.Eukaryot Cell.2006;5(10):1770-1779.[27] Zhang L,Huang YC,Xi TF.Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Yu Lin Chuang.2006;10(3):194-196.张良,黄云超,奚廷斐.表皮葡萄球菌生物膜形成与生物材料感染[J].生物医学工程与临床,2006,10(3):194-196.[28] Thurnheer T,Gmür R,Shapiro S,et al.Mass transport of macromolecules within an in vitro model of supragingival plaque.Appl Environ Microbiol.2003;69(3):1702-1709.[29] Melchior MB,Fink-Gremmels J,Gaastra W.Comparative assessment of the antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bovine mastitis in biofilm versus planktonic culture.J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health.2006;53(7):326-332.[30] Baillie GS,Douglas LJ.Iron-limited biofilms of Candida albicans and their susceptibility to amphotericin B.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.1998;42(8):2146-2149.[31] Shi Q,Wang HN,Liu L.Wei Sheng Wu Xue Tong Bao.2008; 35(10):1633-1637.史巧,王红宁,刘立.细菌生物膜与耐药性相关性研究进展[J].微生物学通报.2008;35(10):1633-1637.[32] Borriello G,Werner E,Roe F,et al.Oxygen limitation contributes to antibiotic tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in biofilms.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2004;48(7): 2659-2664.[33] Wang YX,Li HL,Li PY.Zhonghua Weishengwuxue He Mianyi Xue Zazhi.2003;23(6):428-431.王勇翔,李华林,李平洋.表皮葡萄球菌生物膜形成与ica操纵子的相关性研究[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志,2003,23(6): 428-431.[34] Mukherjee PK,Chandra J,Kuhn DM,et al.Mechanism of fluconazole resistance in Candida albicans biofilms: phase-specific role of efflux pumps and membrane sterols. Infect Immun.2003;71(8):4333-4340.[35] Chen H,Fujita M,Feng Q,et al.Tyrosol is a quorum-sensing molecule in Candida albicans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2004; 101(14):5048-5052.[36] Kohli A,Smriti,Mukhopadhyay K,et al.In vitro low-level resistance to azoles in Candida albicans is associated with changes in membrane lipid fluidity and asymmetry.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2002;46(4):1046-1052.[37] Khot PD,Suci PA,Miller RL,et al. small subpopulation of blastospores in candida albicans biofilms exhibit resistance to amphotericin B associated with differential regulation of ergosterol and beta-1,6-glucan pathway genes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2006;50(11):3708-3716.[38] Nickerson KW,Atkin AL,Hornby JM. Quorum sensing in dimorphic fungi: farnesol and beyond.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72(6):3805-3813.[39] Xue P,Liu DC.Zhong Guo Yi Yao Dao Bao.2008;5(23):21-22.徐芃,刘东成.临茶多酚抗氧化和抑菌机制的研究[J].中国医药导报,2008,5(23):21-22.[40] Cao YB,Xu Z,Zhang JD,et al.Zhongguo Xinyao Zazhi.2004; 13(2):102-105.曹永兵,徐铮,张军东,等.白色念珠菌耐药性产生的分子机制[J].中国新药杂志,2004,13(2):102-105.[41] Morschhäuser J.The genetic basis of fluconazole resistance development in Candida albicans.Biochim Biophys Acta.2002;1587(2-3):240-248. |
| [1] | Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Zhao Qiao, Chen Shuo, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and properties of copper-loaded antibacterial functional film on titanium surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| [2] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [3] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [4] | Ma Rui, Wang Jialin, Wu Mengjun, Ge Ying, Wang Wei, Wang Kunzheng. Relationship of pathogenic bacteria distribution with drug resistance and treatment cycle for periprosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 380-385. |
| [5] | Zhou Anqi, Tang Yufei, Wu Bingfeng, Xiang Lin. Designing of periosteum tissue engineering: combination of generality and individuality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [6] | Lang Limin, He Sheng, Jiang Zengyu, Hu Yiyi, Zhang Zhixing, Liang Minqian. Application progress of conductive composite materials in the field of tissue engineering treatment of myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [7] | Li Wenhui, Liu Guobin. Knowledge mapping analysis on the international research of diabetic foot: a visual analysis based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3178-3184. |
| [8] | Wang Liang, Guo Yuxing, Wu Xun, Huang Hua, Yuan Guangyin, Zhang Lei. Antibacterial properties of Jiao Da Bio-Magnesium scaffolds in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2506-2513. |
| [9] | Chen Zhenyu, Zhang Xiaoning, Luo Yuxin, Liang Jianwei, Yan Chi. Evaluation of silk fibroin/curcumin composite film for promoting wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2554-2561. |
| [10] | Xie Jian, Su Jiansheng. Advantages and characteristics of electrospun aligned nanofibers as scaffolds for tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2575-2581. |
| [11] | Ji Qi, Yu Zhengwen, Zhang Jian. Problems and trends of technique and clinical application of metallic biomaterials prepared by three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2597-2604. |
| [12] | Qian Nannan, Zhang Qian, Yang Rui, Ao Jun, Zhang Tao. Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury: cell therapy and combination of new drugs and biomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2114-2120. |
| [13] | Gao Ziqing, Ruan Sibei, Li Li, Ling Feng, Tang Xiaoqin, Kang Qingmei, Luo Siyi, Luo Jing, Tang Yaping, Tang Mingxi . Identification and survival analysis of tTA/tetO-CCKR-2 double transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1682-1687. |
| [14] | Jia Wei, Zhang Mandong, Chen Weiyi, Wang Chenyan, Guo Yuan. Effects of femoral prosthetic materials on artificial knee arthroplasty performance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1477-1481. |
| [15] | Wang Qian, Li Lu, Shu Jingyuan, Dong Zhiheng, Jin Youshi, Wang Qingshan. Micro-morphology and phase of zirconia-based nano-hydroxyapatite functional gradient biomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1517-1521. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||