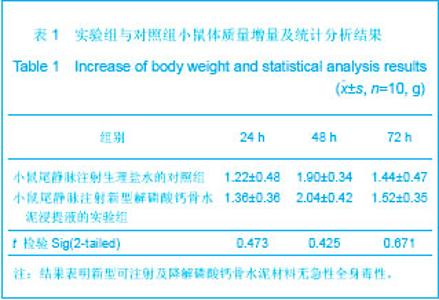
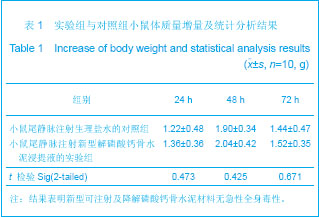
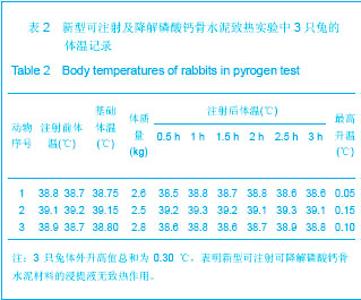
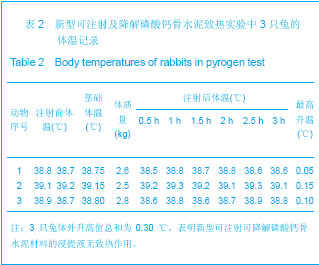
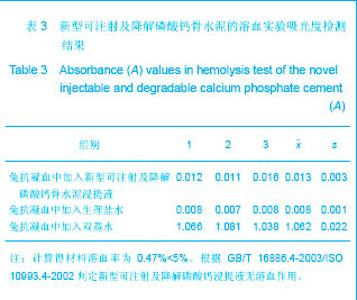
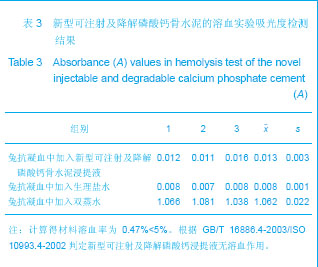
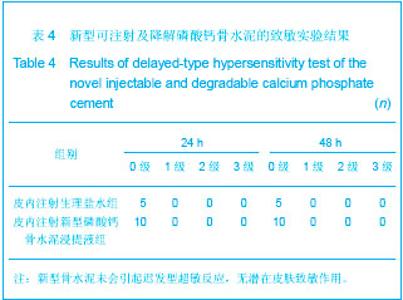
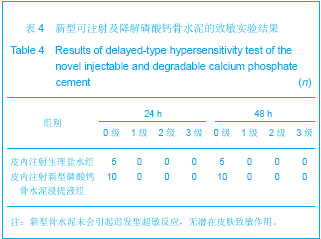
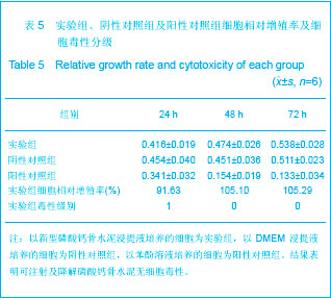
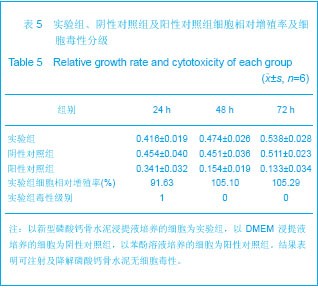
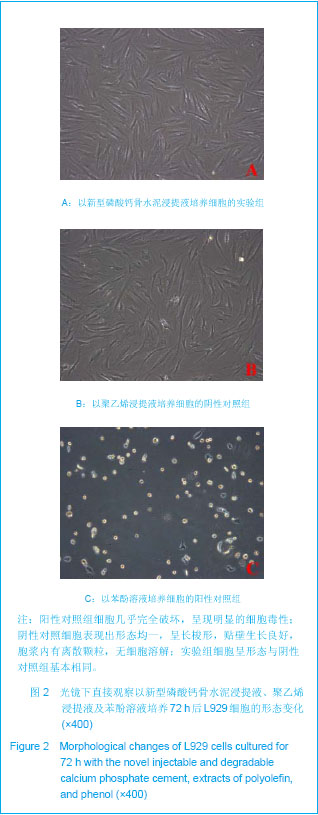
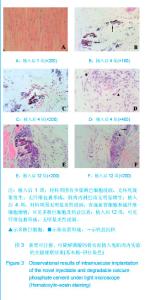
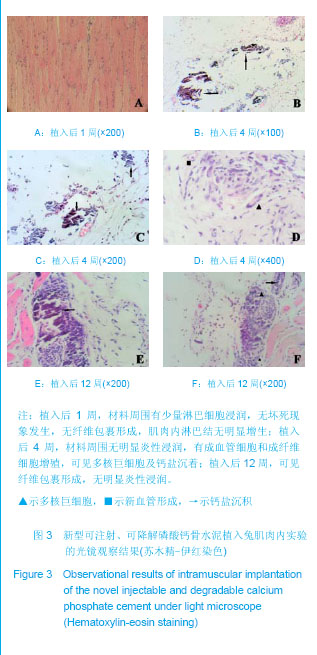
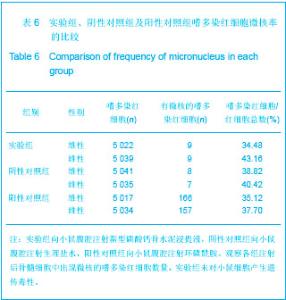
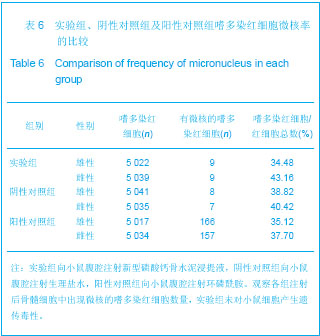
| [1] Smiler D,Soltan M,Lee JW.A Histomorphogenic Analysis of BoneGrafts Augmented With Adult Stem Cells. Implant Dent. 2007;16(1):42-53.[2] Schreurs BW,Bolder SB,Gardeniers JW,et al.Acetabular revision with impacted morsellised cancellous bone grafting and a cemented cup. A 15-to-20-year follow-up.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2004;86(4):492-497.[3] Schreurs BW,Busch VJ,Welten ML,et al.Acetabular reconstruction with impaction bone-grafting and a cemented cup in patients younger than fifty years old. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2004;86(11):2385-2392.[4] Liu CS,Wang W,Shen W,et al.Evaluation of the biocompatibility of a nonceramic hydroxyapatite.J Endon. 1997;23(8): 490-493.[5] Kelly CM,Wilkins RM. Treatment of benign bone lesions with an injectable calcium sulfate-based bone graft substitute.Orthopedics.2004;27(1 Suppl):s131-s135.[6] Theiss F,Apelt D,Brand B,et al.Biocompatibility and resorption of a brushite calcium phosphate cement.Biomaterials.2005; 26(21):4383-4394.[7] Qi X,Ye J,Wang Y.Improved injectability and in vitro degradation of a calcium phosphate cement containing poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. Acta Biomater. 2008; 4(6):1837-1845.[8] ISO TC WG.ISO 10993-5.Biological evaluation of medical devices part 5: Tests for in vitro cytotoxicity: Multiple.American National Standards Institute,2007. [9] Camilleri J.The biocompatibility of modified experimental Portland cements with potential for use in dentistry. Int Endod J. 2008;41(12):1107-1114.[10] van Dijkhuizen-Radersma R,Hesseling SC,Kaim PE,et al. Biocompatibility and degradation of poly(ether-ester) microspheres: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Biomaterials. 2002;23(24):4719-4729.[11] Wang X,Ye JD,Wang Y.Hydration mechanism of a novel PCCP + DCPA cement system. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008; 19(2):813-816.[12] Athanasiou KA,Niederauer GG,Agrawal CM.Sterilization, toxicity, biocompatibility and clinical applications of polylactic acid/polyglycolic acid copolymers. Biomaterials.1996;17(2): 93-102.[13] Ishaug-Riley SL,Crane-Kruger GM,Yaszemski MJ,et al.Three-dimensional culture of rat calvarial osteoblasts in porous biodegradable polymers. Biomaterials.1998; 19(15): 1405-1412.[14] Ruh PQ,Hedberg EL,Padron NT,et al.Biocompatibility and degradation of poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid)/calcium phosphate cement composites. J Biomed Mater Res A.2005; 74(4):533-544.[15] Simon CG Jr,Khatri CA,Wight SA,et al.Preliminary report on the biocompatibility of a moldable, resorbable, composite bone graft consisting of calcium phosphate cement and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(3):473-482.[16] Habraken WJ,Wolke JG,Mikos AG,et al. Porcine gelatin microsphere/calcium phosphate cement composites: an in vitro degradation study. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2009;91(2):555-561. [17] Zhao J,Ohba S,Komiyama Y,et al.Icariin: a potential osteoinductive compound for bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A.2010;16(1): 233-243.[18] You SH.Zhongguo Yiliao Qixie Xinxi. 2005;11 (1):15-19.由少华.解读GB/T 16886《医疗器械生物学评价》系列标准[J].中国医疗器械信息,2005,11 (1):15-19.[19] Zambuzzi WF,Oliveira RC,Pereira FL,et al. Rat subcutaneous tissue response to macrogranular porous anorganic bovine bone graft. Braz Dent J.2006;17(4):274-278.[20] Jordan DR,Brownstein S,Dorey M,et al. Fibrovascularization of porous polyethylene (Medpor) orbital implant in a rabbit model. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg.2004;20(2):136-143.[21] Qiu CH,Qu HF,Jiang H,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007:11(18);3532-3535.邱长虹,翟弘峰,姜华,等. 胶原-壳聚糖复合材料的制备及生物安全性检测[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(18):3532-3535.[22] Guo H,Su J,Wei J,et al. Biocompatibility and osteogenicity of degradable Ca-deficient hydroxyapatite scaffolds from calcium phosphate cement for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater.2009;5(1):268-278.[23] Link DP,van den Dolder J,Wolke JG,et al. The cytocompatibility and early osteogenic characteristics of an injectable calcium phosphate cement. Tissue Eng.2007;13(3):493-500. |