Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (5): 859-865.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.05.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment of a mouse-rat cervical cardiac xenotransplantation model by cuff technique
Li Chuan, Qi Feng, Liu Tong, Li Fu-xin, Wang Peng-zhi
- Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300052, China
-
Received:2012-08-22Revised:2012-09-16Online:2013-01-29Published:2013-01-29 -
Contact:Qi Feng, Doctor, Professor, Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300052, China qf@medmail.com.cn -
About author:Li Chuan☆, Studying for doctorate, Attending physician, Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300052, China lichuan1980@gmail.com -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.30940066
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Chuan, Qi Feng, Liu Tong, Li Fu-xin, Wang Peng-zhi. Establishment of a mouse-rat cervical cardiac xenotransplantation model by cuff technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(5): 859-865.
share this article
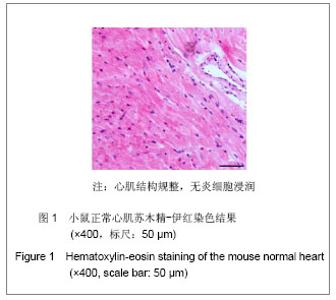
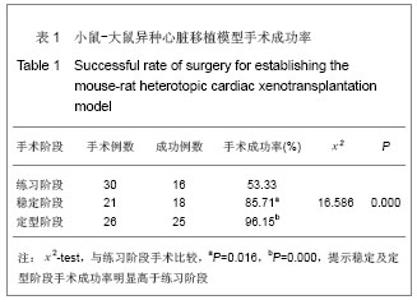
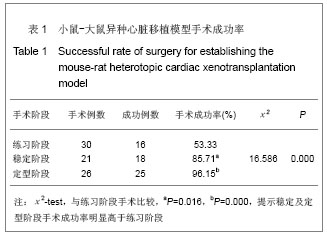
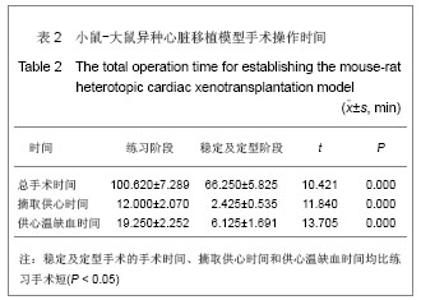
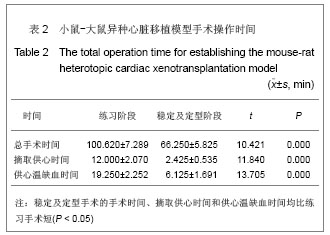
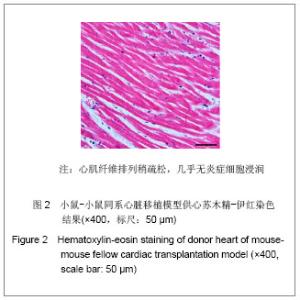
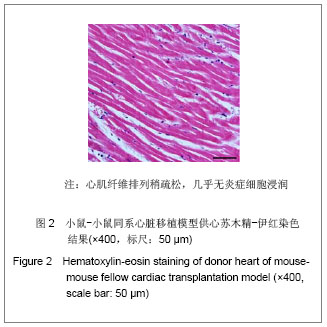
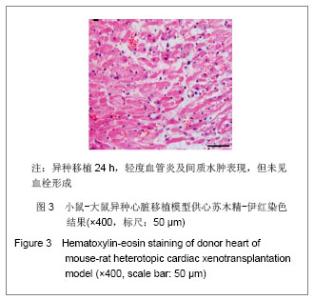
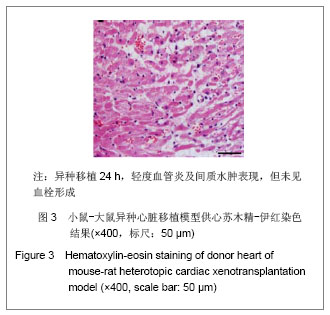
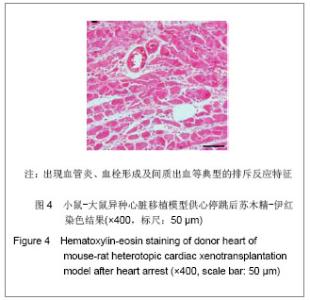
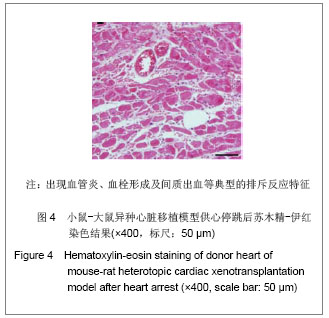
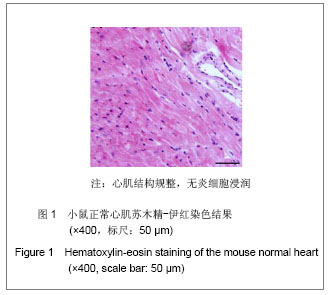
2.4 小鼠-大鼠异种心脏移植模型手术失败原因及供心存活时间 在全部实验过程中,由于手术操作失误导致受体死亡或移植物无功能者共18例,其中练习阶段14例,稳定及定型阶段共4例,出血(10/18)、血管栓塞(4/18)和套管失败(4/18)是主要原因。小鼠-大鼠异种异位心脏移植术后,供心存活时间(40.17±3.76) h。 2.5 小鼠-大鼠异种心脏移植模型供心肉眼大体情况 ①同系移植:术后72 h剖开切口见供心颜色红润,搏动有力,与周围组织无粘连。取下供心见心脏体积无增大,质地柔软,心腔内无血凝块。②异种移植24 h:术后 24 h剖开切口见供心颜色红润,与复跳时基本相同,搏动良好,但较复跳后有所减弱,与周围组织有轻度粘连。取下供心见心脏体积稍增大,质地较韧。③异种移植停跳后:供心停跳时剖开切口见供心呈暗紫色,局部坏死发黑,被周围组织包裹,难以分离。取下供心见心脏体积增大,质地坚硬,心腔及大血管内充满大量血凝块。 2.6 正常心肌、同系心脏移植、异种心脏移植模型供体心肌组织切片苏木精-伊红染色结果比较 正常心肌:心肌纤维排列规整,血管内皮细胞无水肿,血管内无血栓形成,心肌间质无出血,无炎症细胞浸润,见图1。"
| [1] Zhou S, Peng LK, Xie XB, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(44):8283-8287.周松,彭龙开,谢续标,等. 异种器官移植的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(44):8283-8287.[2] Dou KF, Li X, Li JJ, et al. Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi. 2012; 33(3):184-188.窦科峰,李霄,李俊杰,等. 异种器官移植研究的主要问题与对策[J]. 中华器官移植杂志,2012,33(3):184-188.[3] Chu J, Yu YB, Zhang SH, et al. Shandong Yiyao. 2011;51(44): 112-113.储建,禹亚彬,章世海,等. 异种器官移植的研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2011,51(44):112-113.[4] Mendicino M, Liu M, Ghanekar A, et al. Targeted deletion of Fgl-2/fibroleukin in the donor modulates immunologic response and acute vascular rejection in cardiac xenografts. Circulation. 2005;112(2):248-256.[5] Hosiawa KA, Wang H, Devries ME, et al. CD80/CD86 costimulation regulates acute vascular rejection. J Immunol. 2005;175(9):6197-6204.[6] Won JY, Ahn KS, Sorrell AM, et al. Cytolytic assessment of hyperacute rejection and production of nuclear transfer embryos using hCD46-transgenic porcine embryonic germ cells. Zygote. 2009;17(2):101-108.[7] Liu B, Cheng C, Wu Y, et al. Transgenic mice designed to express human alpha-1,2-fucosyltransferase in combination of human DAF and CD59 to avoid xenograft rejection. Sci China C Life Sci. 2008;51(3):199-204.[8] Su S. Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi. 2007;28(4):251-252.苏松. 小鼠器官移植模型的现状和展望[J]. 中华器官移植杂志,2007,28(4):251-252.[9] Tao R, Wang L, Han R, et al. Differential effects of B and T lymphocyte attenuator and programmed death-1 on acceptance of partially versus fully MHC-mismatched cardiac allografts. J Immunol. 2005;175(9):5774-5782.[10] Tomita Y, Zhang QW, Matsuzaki G, et al. Absent mRNA accumulation of Th1 or Th2 cytokines in heart allografts with chimerism-based drug-induced tolerance. Surg Today. 2005; 35(5):364-370.[11] Qi F, Zhu LW, He XH, et al. Tianjin Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2010; 16(4):559-562.戚峰,朱理玮,何向辉,等. 多靶点联合用药抑制小鼠到大鼠异种心脏移植排斥反应[J]. 天津医科大学学报,2010,16(4):559-562.[12] Cooper DK, Teuteberg JJ. Pig heart xenotransplantation as a bridge to allotransplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010; 29(8):838-840.[13] Manji RA, Menkis AH, Cooper DK. Cardiac xenotransplantation technology provides materials for improved bioprosthetic heart valves. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142(1):238-239, 239.[14] Huang XS, Liu X, Chen DZ, et al. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2005;19(7):583-586.黄雪珊,刘璇,陈道中,等. 改良Heron法建立异种异位心脏移植模型[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(7):583-586.[15] Tang H, Yao ZX, Liu SC, et al. Zhongguo Xiandai Yixue Zazhi. 2008;18(1):21-24.唐华,姚榛祥,刘盛春,等. 鼠异种异位心脏移植模型建立与病理特征观察[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2008,18(1):21-24.[16] Wei L, Wang M, Qu X, et al. Differential expression of microRNAs during allograft rejection. Am J Transplant. 2012; 12(5):1113-1123.[17] Chen WW, Yang YR, Xia P, et al. Wenzhou Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2011;41(3):252-254.陈文伟,杨亦荣,夏鹏,等. 小鼠颈部异位心脏移植手术的改良[J]. 温州医学院学报,2011,41(3):252-254.[18] Wang JX, Huang SD, Xu ZY, et al. Tongji Daxue Xuebao. 2008; 29(1):106-108.王建雄,黄盛东,徐志云,等. 改良移植技术建立豚鼠至大鼠异位心脏移植模型[J]. 同济大学学报: 医学版, 2008,29(1):106-108.[19] Zhang SL, Sun ZQ. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(31):5883-5886.张松林,孙宗全. 应用Tail-cuff技术改良小鼠颈部异位心脏移植模型[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(31): 5883-5886.[20] Postrach J, Bauer A, Schmoeckel M, et al. Heart xenotransplantation in primate models. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;885:155-168.[21] Choi HJ, Kim MK, Lee HJ, et al. Effect of alphaGal on corneal xenotransplantation in a mouse model. Xenotransplantation. 2011;18(3):176-182.[22] Hawthorne WJ, Simond DM, Stokes R, et al. Pre-clinical model of composite foetal pig pancreas fragment/renal xenotransplantation to treat renal failure and diabetes. Xenotransplantation. 2011;18(6):390-399.[23] Luca G, Calvitti M, Mancuso F, et al. Reversal of experimental Laron Syndrome by xenotransplantation of microencapsulated porcine Sertoli cells. J Control Release. 2012.[24] Li C, Luo L, Lu J, et al. A modified splint tubing technique for heterotopic heart transplantation in mouse. Transpl Immunol. 2011;25(1):82-87.[25] Jiang XF, Zhu L, Cui ZM, et al. Zhongguo Puwai Jichu yu Linchuang Zazhi. 2010;17(9):914-916.姜晓峰,朱磊,崔哲铭,等. 一种改良的吻合法小鼠腹腔异位心脏移植模型[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志,2010,17(9):914-916.[26] Yan GF, Zhang J, Zhou Y, et al. Shiyan Dongwu yu Bijiao Yixue. 2008;28(5):341-342.严国锋,张健,周勇,等. 保温措施对小鼠麻醉效果的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学,2008,28(5):341-342.[27] Hansen TN, Haworth RA, Southard JH. Warm and cold ischemia result in different mechanisms of injury to the coronary vasculature during reperfusion of rat hearts. Transplant Proc. 2000;32(1):15-18.[28] Li S, Guan Q, Chen Z, et al. Reduction of cold ischemia-reperfusion injury by graft-expressing clusterin in heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2011;30(7): 819-826.[29] Brenner P, Keller M, Beiras-Fernandez A, et al. Prevention of hyperacute xenograft rejection through direct thrombin inhibition with hirudin. Ann Transplant. 2010;15(4):30-37.[30] Schumacher M, Van Vliet BN, Ferrari P. Kidney transplantation in rats: an appraisal of surgical techniques and outcome. Microsurgery. 2003;23(4):387-394. |
| [1] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [2] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [3] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [4] | Jiang Xin, Qiao Liangwei, Sun Dong, Li Ming, Fang Jun, Qu Qingshan. Expression of long chain non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 in serum of renal transplant patients and its regulation of human glomerular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [5] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [6] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [7] | Liu Yang, Gong Yi, Fan Wei. Anti-hepatoma activity of targeted Pluronic F127/formononetin nanocomposite system in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| [8] | Huang Zhusong, Lin Yu, Chen Xiang, Lan Jinfu, Guan Yong, Gao Xi. Alcohol extract of Morinda officinalis improves lipid metabolism and bone metabolism in ovariectomized obese rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 205-210. |
| [9] | Chen Yutong, Li Chenchen, Liu Yang, Zheng Yaqin, Yang Xihua, An Meiwen. Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model in Wistar rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 237-241. |
| [10] | Mu Yufeng, Wei Lina, Wu Yong, Shao Anliang, Chen Liang, Qu Shuxin, Xu Liming. Development and evaluation of alpha-galactosyl antigen-deficient rabbit model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 281-285. |
| [11] | Zhang Shengmin, Cao Changhong, Liu Chao. Adipose-derived stem cells integrated with concentrated growth factors prevent bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2982-2987. |
| [12] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| [13] | Chen Siyu, Li Yannan, Xie Liying, Liu Siqi, Fan Yurong, Fang Changxing, Zhang Xin, Quan Jiayu, Zuo Lin. Thermosensitive chitosan-collagen composite hydrogel loaded with basic fibroblast growth factor retards ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2472-2478. |
| [14] | Chen Zhenyu, Zhang Xiaoning, Luo Yuxin, Liang Jianwei, Yan Chi. Evaluation of silk fibroin/curcumin composite film for promoting wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2554-2561. |
| [15] | Wang Donghui, Wu Xin, Sun Ningning, Zhang Han, Gao Jianfeng. Electroacupuncture intervention on the expression of synaptic plasticity-related proteins in the hippocampi of mice with radiation-induced brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2205-2210. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||