Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (2): 331-336.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.02.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism underlying interaction between estrogen and runt-related transcription factor 2 in osteoblasts
Wang Hui, Sun Hui-qiang
- Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedicine, Stomatological School of Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2012-04-10Revised:2012-07-17Online:2013-01-08Published:2013-01-08 -
Contact:Sun Hui-qiang, Doctor, Master’s supervisor, Associate professor, Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedicine, Stomatological School of Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China whitedove69@163.com -
About author:Wang Hui, Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedicine, Stomatological School of Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China wanghui-89@hotmail.com -
Supported by:Supported by: the Natural Science Fund of Shandong Province, No. ZR2010HM035*; Shandong Province Medical and Health Technology Development Project, No. 2011WSB19002*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Hui, Sun Hui-qiang. Mechanism underlying interaction between estrogen and runt-related transcription factor 2 in osteoblasts[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(2): 331-336.
share this article
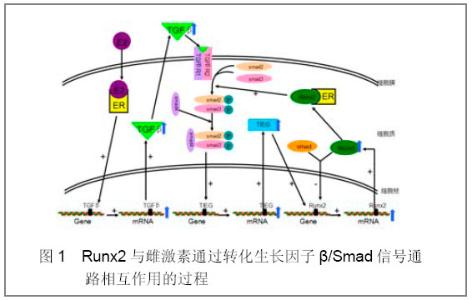
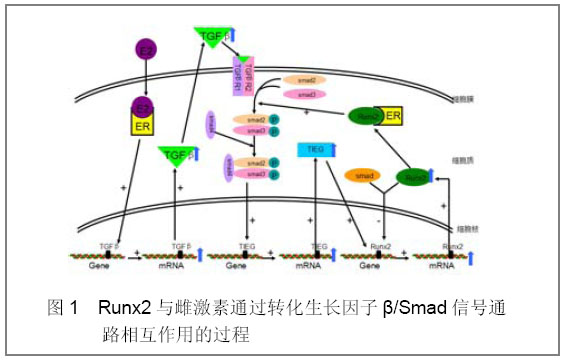
2.1 转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路 雌激素和转化生长因子β是骨骼系统的非常重要的两种调控因子,目前已有许多报道阐明二者之间的信号通路[6-7]。雌激素可通过多种途径影响转化生长因子β信号通路的活性,继而通过转化生长因子β信号通路中的多个组成成分影响Runx2的表达和活性。首先,很多研究在成骨细胞和非成骨细胞[8-9],比如人前列腺基质细胞, 大鼠骨细胞等,证明雌激素可诱导转化生长因子β基因表达而激活转化生长因子β信号通路。 转化生长因子β信号系统主要通过Smads和转化生长因子β诱导早期基因(TIEG)影响Runx2的表达和活性。Smads家族蛋白在将转化生长因子β信号从细胞表面受体传导至细胞核的过程中起到关键性作用,且不同的Smad介导不同的转化生长因子β家族成员的信号转导,如Smad2/3可以与Runx2形成异质二聚体,从而介导雌激素和Runx2之间的作用[9]。转化生长因子β诱导早期基因(TIEG)属于KLF家族,通过其锌指结构与DNA结合从而影响基因的表达。如图1:转化生长因子β与其受体结合后,激活转化生长因子β信号通路,引起Smad2和Smad3结合形成二聚体,此二聚体与Smad4结合形成的复合物进入核内作用于TIEG基因,上调TIEG的表达。在人和鼠成骨细胞中TIEG不但可直接诱导Runx2的表达,而且可与Runx2结合而刺激依赖Runx2的基因的表达[9]。在这个通路中,Runx2与Smad结合形成的异二聚体还可以反过来下调Runx2的表达。Runx2与雌激素受体结合形成的异二聚体可以增强转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路的活性。"
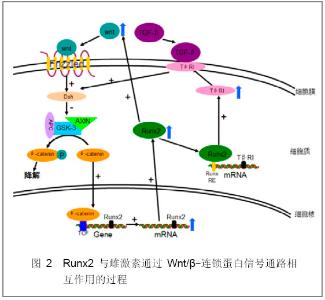
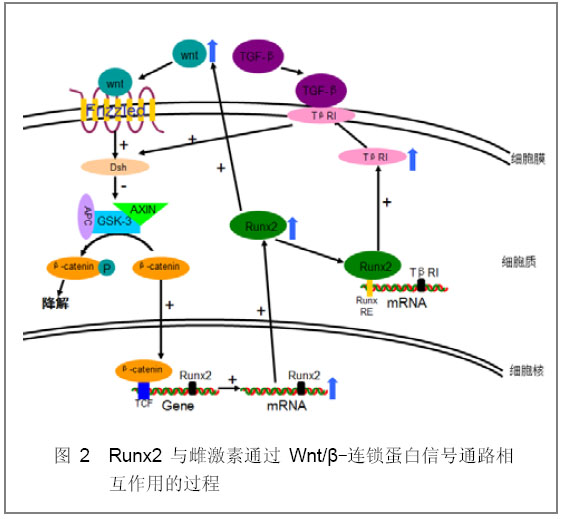
2.2 Wnt/β-连锁蛋白信号通路 Wnt信号通路是骨骼系统发育、成熟、重构的一个重要信号系统,可以引起胞内β-连锁蛋白的积累。Chandar等[10]发现雌激素作用于ROS17/2.8细胞可显著上调由Wnt通路介导的β-连锁蛋白和碱性磷酸酶,而雌激素受体调节剂ICI 182780和三苯氧胺及雌激素受体α敲除可终止上述现象[11]。这说明Wnt/β-连锁蛋白信号通路参与雌激素对成骨细胞的调控。 Gaur 等[12]认为Wnt/β-连锁蛋白信号通路通过激活Runt基因表达从而调控成骨细胞分化和骨骼发育,其理论基于以下实验:①敲除分泌型卷曲相关蛋白1(SFRP1)的大鼠表达激活的Wnt信号通路,其T细胞因子1、Runt2及骨钙素的表达显著增加。②Runx2启动子(-97-93)存在功能性T 细胞因子调控元件。③Runt基因募集β-连锁蛋白和T细胞因子1。④T细胞因子1和经典Wnt蛋白的共表达可以使Runt启动子活性显著提高,并且其mRNA水平显著增加。通过对FABP4-Wnt10b鼠的研究发现Wnt10b可促进间质细胞向成骨细胞转化,抑制其向脂肪细胞转化,其机制之一是Wnt10b可诱导Runx2的表达而抑制PPAR-γ2的表达[13]。也有研究发现Wnts尽管可以增加依赖Runx2基因的表达,但是不能增加核内Runx2的蛋白水平,也不能促进Runx2与DNA的结合[14]。这说明Wnts可能影响Runx2与其他转录因子的相互作用。如图2:Wnt信号通过细胞表面7次跨膜受体Frizzled家族成员激活胞质Dishevelled(Dsh)蛋白,从而抑制由GSK3、Axin、APC和β-连锁蛋白组成的蛋白复合物的活性,使β-连锁蛋白免于磷酸化而不被降解,导致β-连锁蛋白在胞内积聚并易位到核内与转录因子T细胞因子家族成员结合,促进Runx2表达。 Runx2也可通过上调TβRI的表达而作用于转化生长因子β信号通路,继而增强Wnt信号系统的活性。另外,Runx2还可直接调节Wnt的基因表达。在成骨细胞分化早期,前列腺素E2诱导的Runx2的活化可增强依赖Wnt的基因表达,当抑制内源性Runx2表达时Wnt基因的表达也受到显著抑制,如图2[14]。因此,Wnt极有可能是Runx2作用于雌激素介导的生物效应的重要靶点之一。"
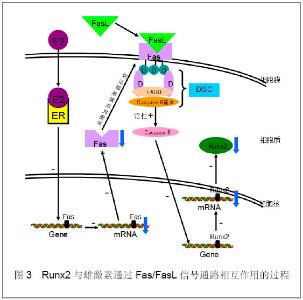
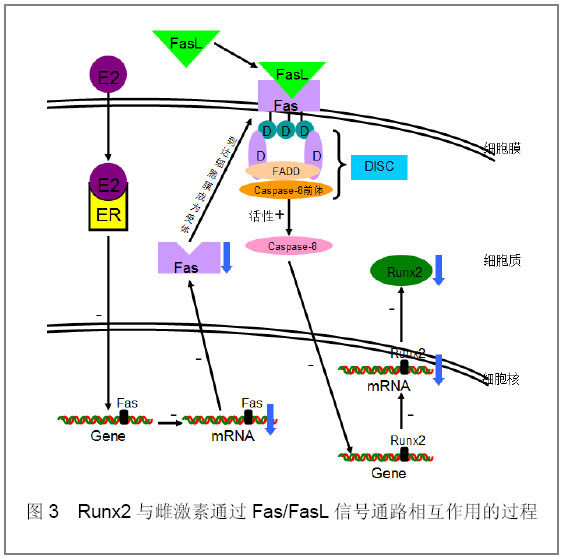
2.3 Fas/FasL信号通路 雌激素通过抑制Fas/FasL信号通路而促进Runx2表达。Kovacic[15]通过实验证明,人和鼠的成骨细胞表达Fas,并且随着成骨细胞的进一步分化Fas表达量增加。该研究同时证明了Fas/FasL能抑制成骨细胞的分化,但是对其凋亡影响甚微,因为FasL能降低成骨细胞的比例但是不能影响总细胞的数目,进一步实验发现FasL可以通过caspase8的激活而减少Runx2基因的表达,而在不表达Fas或者FasL的鼠骨髓细胞中Runx2基因以及依赖Runx的碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、骨桥蛋白等的表达量显著上升[15]。如图3:配体FasL与死亡受体Fas结合后,诱导Fas胞质区内的死亡结构域DD结合Fas结合蛋白FADD,FADD再以其氨基端的死亡效应结构域结合caspase-8前体,形成Fas-FADD- caspase-8前体组成的死亡诱导复合物DISC,DISC激活caspase-8,活化的caspase-8减少Runx2基因的表达。 雌激素可减少Fas的表达并一定程度上降低Fas对成骨细胞分化的抑制作用[16]。Kovacic等[16]还发现与假手术组相比,行卵巢切除术的C57BL/6J鼠成骨细胞的Fas基因表达量明显上升;而敲除Fas基因后,雌激素缺乏不能引起骨质疏松症。Krum等[17]研究FasL基因发现其下游86kb处为细胞类型特异性的激素诱导增强子,可作为雌激素受体α的作用靶点,介导Fas信号系统与雌激素的相互作用。因此,Fas信号通路可能参与雌激素介导的对成骨细胞分化的作用。"
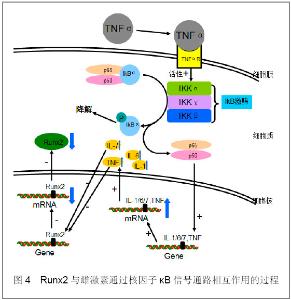
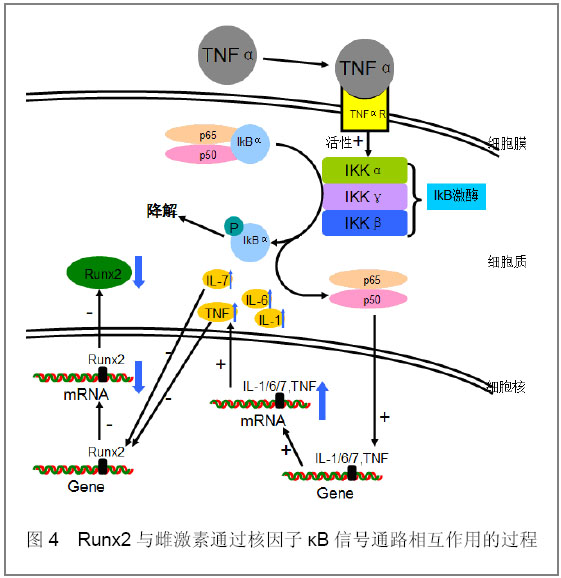
2.4 核因子κB信号通路 雌激素也能通过抑制核因子κB信号通路而促进Runx2表达。在哺乳动物中迄今发现5种核因子kB家族成员:RelA(p65)、RelB、c-Rel、核因子kB1(p50)、核因子kB2(p52)。它们以同源或异源二聚体形式存在,最常见的二聚体是p50-p65异二聚体,也就是常说的核因子kB。在骨骼系统中核因子κB信号通路和雌激素发挥着相反的调节作用。雌激素可以通过抑制核因子κB配体激活因子(RANKL)而防止乙醇诱导的骨质丢失[18]。因卵巢切除导致的骨质减少在Bglap2-IKK-DN鼠(表达无功能IKKγ等位基因产物)中得到明显改善,说明核因子κB的激活破坏了成骨细胞骨形成[19]。核因子κB可促进多种细胞因子的合成,这些细胞因子在成骨细胞分化和骨形成中发挥重要的功能。 绝经期雌激素水平的降低伴随着血清白细胞介素1,白细胞介素6,白细胞介素7和肿瘤坏死因子的升高[19]。如图4:当细胞受到炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子α等刺激时,肿瘤坏死因子α与其受体结合,激活胞浆中IKKs(IkB激酶),使无活性的核因子kB三聚体复合物种的IkB的N端调节区的Ser32/36磷酸化,随后发生泛素化,在蛋白酶体作用下降解,IkB的解离暴露出p50亚基的DNA结合位点,使p50-p65异二聚体从细胞浆易位至细胞核内,与kB序列结合,促进白细胞介素1,白细胞介素6,白细胞介素7和肿瘤坏死因子的基因合成。有研究发现肿瘤坏死因子可通过下调Runx2的表达而抑制细胞分化[20]。白细胞介素6可抑制骨吸收[21]。白细胞介素7不但可抑制骨吸收还可以通过抑制Runx2基因启动子的活性而下调Runx2表达从而抑制骨形成[22]。 Krum[19]假设了雌激素影响核因子κB信号通路的4个机制,包括雌激素受体α与核因子κB结合影响核因子κB的功能;雌激素受体α调节IKK和IκB的活性;雌激素受体α使辅激活蛋白远离核因子κB;雌激素受体α可阻止IκB降解从而抑制核因子κB激活。除此之外,雌激素受体α可直接与肿瘤坏死因子启动子结合而影响肿瘤坏死因子的表达。 2.5 其他 雌激素和Runx2的相互作用还通过许多其他信号通路而实现,如:Runx2增强固醇/类固醇激素代谢相关的酶的基因表达活性而促进雌激素合成; Runx2通过与雌激素受体α基因的F启动子结合剂量依赖性影响雌激素受体α基因的表达;前列腺素 E2通过调控视网膜母细胞瘤结合蛋白1来上调Runx2的表达和活性等等,这些分子机制有待于进一步研究。"
| [1] Rickard DJ, Subramaniam M, Spelsberg TC. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of estrogen action on the skeleton. J Cell Biochem.1999;32(33):123-132.[2] 王凌,李大金. 雌激素受体亚型对成骨细胞的调控作用[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2005, 24(9):715-717[3] Frenkel B, Hong A, Baniwal SK, et al. Regulation of adult bone turnover by sex steroids. J Cell Physiol.2010;224(2): 305-310.[4] Komori T. RUNX2/PEBP2 alpha A . Nippon Rinsho, 1998, 56(6):1430-1434[5] Jüttner KV, Perry MJ. High-dose estrogen induced osteogenesis is decreased in aged RUNX2+/- mice. Bone. 2007;41(1):25-32.[6] Gao Y, Qian WP, Dark K, et al. Estrogen prevents bone loss through transforming growth factor beta signaling in T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2004; 101(47):16618-16623.[7] Janssens K, ten Dijke P, Janssens S, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta1 to the bone. Endocr Rev.2005; 26(6): 743-774.[8] Bord S, Beavan S, Ireland D, et al. Mechanisms by which high-dose estrogen therapy produces anabolic skeletal effects in postmenopausal women: role of locally produced growth factors. Bone.2001;29(3): 216-222.[9] Hawse JR, Subramaniam M, Ingle JN, et al. Estrogen-TGFβ cross-talk in bone and other cell types Role of TIEG, Runx2, and other transcription factors. J Cell Biochem.2008; 103(2): 383-392.[10] Chandar N, Saluja R, Lamar PC, et al. P53 and beta-catenin activity during estrogen treatment of osteoblasts. Cancer Cell Int.2005;5:24.[11] Armstrong VJ, Muzylak M, Sunters A, et al. Wnt beta catenin signaling is a component of osteoblastic bone cell early responses to load-bearing and requires estrogen receptor alpha. J Biol Chem.2007;282(28): 20715-20727.[12] Gaur T, Lengner CJ, Hovhannisyan H, et al. Canonical WNT signaling promotes osteogenesis by directly stimulating Runx2 gene expression. J Biol Chem.2005;280(39): 33132-33140.[13] Bennett CN, Longo KA, Wright WS, et al. Regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2005;102(9): 3324-3329.[14] McCarthy TL, Centrella M. Novel Links among Wnt and TGF-β Signaling and Runx2 . Mol. Endocrinol.2010; 24(3): 587-597.[15] Kovaci? N, Luki? IK, Grcevi? D,et al.The Fas/Fas Ligand System Inhibits Differentiation of Murine Osteoblasts but Has a Limited Role in Osteoblast and Osteoclast Apoptosis. J Immunol.2007;178: 3379-3389.[16] Kovacic N, Grcevic D, Katavic V,et al. Fas receptor is required for estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss in mice. Lab Invest. 2010;90(3): 402-413.[17] Krum SA, Miranda-Carboni GA, Hauschka PV, et al. Estrogen protects bone by inducing Fas ligand in osteoblasts to regulate osteoclast survival. EMBO J.2008;27(3):535-545.[18] [Chen JR,Haley RL,Hidestrand M,et al.Estradiol protects against ethanol-induced bone loss by inhibiting up-regulation of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand in osteoblasts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.2006; T 319(3): 1182-1190.[19] Krum SA,Chang J,Miranda-Carboni G,et al.Novel functions for NFκB: inhibition of bone formation. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(10): 607-611.[20] Gilbert L,He X,Farmer P, et al. Expression of the osteoblast differentiation factor RUNX2 (Runx2/ AML3/Pebp2alpha A) is inhibited by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem.2002; 277(4):2695-2701.[21] Jilka RL, Hangoc G, Girasole G, et al. Increased osteoclast development after estrogen loss: mediation by interleukin-6. Science.1992;257(5066):88-91.[22] Weitzmann MN, Roggia C, Toraldo G, et al. Increased production of IL-7 uncouples bone formation from bone resorption during estrogen deficiency. J Clin Invest.2002; 110(11):1643-1650. |
| [1] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [2] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [3] | Zheng Xiaolong, He Xiaoming, Gong Shuidi, Pang Fengxiang, Yang Fan, He Wei, Liu Shaojun, Wei Qiushi. Bone turnover characteristics in patients with alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 657-661. |
| [4] | Fan Junchao, Chen Yong, Song Junjie. Sevoflurance combined with xenon pretreatment protects against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3660-3665. |
| [5] | Huo Hua, Cheng Yuting, Zhou Qian, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Yang Tongjing, Liao Jian, Hong Wei. Effects of drug coating on implant surface on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3558-3564. |
| [6] | Zhong Yuanming, He Bingkun, Wu Zhuotan, Wu Sixian, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng. An exploration on the mechanism of Shaoyao Gancao Decoction in treating early pain of lumbar disc herniation based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3194-3201. |
| [7] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Sun Changliang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Epigenetic reprogramming and exercise regulation of bone metabolism disorders [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3210-3218. |
| [8] | Chen Xinling, Wang Shenglan. Cell autophagy, pathway, regulation and its multiple correlations with pulmonary hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 311-316. |
| [9] | Huang Zhusong, Lin Yu, Chen Xiang, Lan Jinfu, Guan Yong, Gao Xi. Alcohol extract of Morinda officinalis improves lipid metabolism and bone metabolism in ovariectomized obese rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 205-210. |
| [10] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [11] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [12] | Yan Xiurui, Tao Jin, Liang Xueyun. Mechanism by which exosomes from human fetal placental mesenchymal stem cells protect lung epithelial cells against oxidative stress injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2994-2999. |
| [13] | Su Mingzhu, Ma Yuewen. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy regulates the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells in the hippocampus via Notch1/Hes1 pathway after cerebral ischemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3009-3015. |
| [14] | Zhou Yi, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun, Lai Yu, Liao Jianzhao, Li Shibin. An exploration on mechanism of Shengyu Decoction in treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2687-2696. |
| [15] | Chen Jiayun, Li Anan, Lü Zhaohui, Wu Zixuan, Cai Minjie, Huang Xuyan . Effect of long-term use of proton pump inhibitors on bone mineral density and bone metabolism: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2775-2780. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||