Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (34): 5447-5453.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1966
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and property study of sustained-release osteoinductive gel
- 1Orofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration Laboratory, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2019-06-24Online:2019-12-08Published:2019-12-08 -
Contact:He Yun, MD, Associate professor, Orofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration Laboratory, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Lü Dongmei, Master candidate, Orofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration Laboratory, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 11702231 (to HY); Sichuan Medical Association Program, No. S16079 (to HY); Human Resources and Social Security Department of Sichuan Province, No. 201864 (to HY); National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for Students, No. 201816032054 (to HY); Southwest Medical University Project, No. 2016014 (to HY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lü Dongmei, Luo Yonghua, Wan Xiaolong, Zeng Chunyu, Li Ling, He Yun. Preparation and property study of sustained-release osteoinductive gel[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5447-5453.
share this article
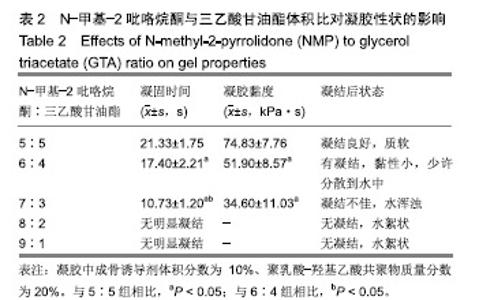
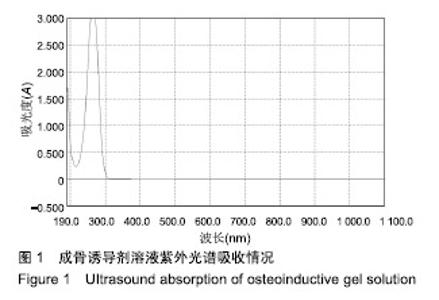
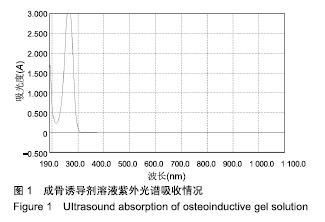
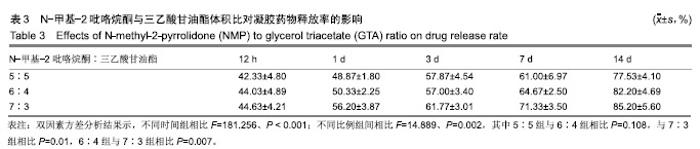
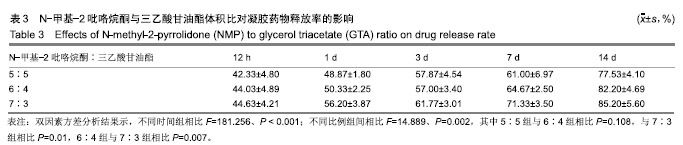
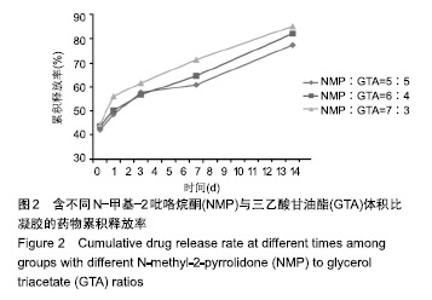
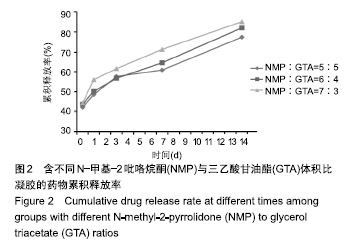
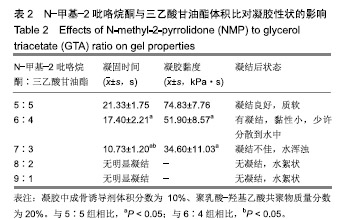
2.2 N-甲基-2吡咯烷酮与三乙酸甘油酯比值对凝胶凝结性能的影响 随着N-甲基-2吡咯烷酮的增多和三乙酸甘油酯的减少,凝胶的流动性增加而遇水凝结所需时间缩短,凝结后硬度和黏度减小,见表2。N-甲基-2吡咯烷酮∶三乙酸甘油酯为7∶3时,遇水凝固时间最短,与5∶5和6∶4组凝胶相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。当N-甲基-2吡咯烷酮∶三乙酸甘油酯达到8∶2和9∶1时,凝胶无明显凝结。从凝胶黏度来看,N-甲基-2吡咯烷酮∶三乙酸甘油酯为 5∶5时最大,与6∶4和7∶3组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。不同N-甲基-2吡咯烷酮与三乙酸甘油酯比例组不同时间下的药物累计释放量不全相同(P < 0.01),5∶5组药物总体释放量最少,药物维持浓度久,在前3 d药物释放速率与6∶4组相似,而两组的总体比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.108);5∶5组、6∶4组与7∶3组相比差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。见表3、图2。"
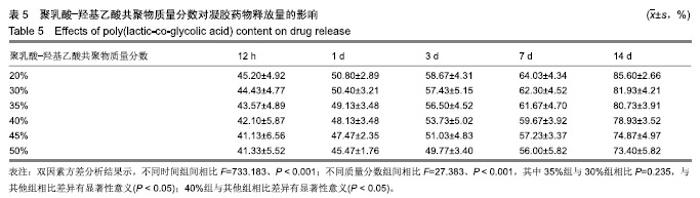
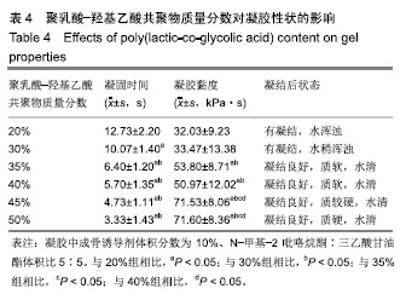
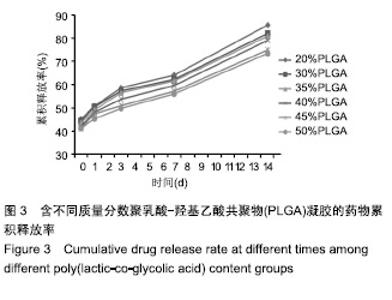
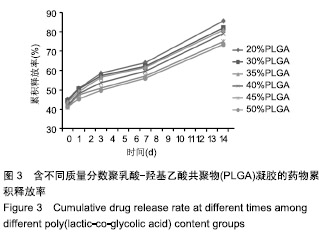
PLGA质量分数由20%增加到50%时,凝胶的凝结时间从(12.73±2.20) s缩短为(3.33±1.43) s,凝胶的黏度则由(32.03±9.23) kPa·s增加到(71.60±8.36) kPa·s。PLGA质量分数为35%和40%时凝胶状态最好。不同PLGA含量的缓释凝胶组间药物累积释放量不全相同(P < 0.001),PLGA越多,相同时间下凝胶的药物累积释放量越少,药物浓度持续时间久,在两两比较中35%组与30%组相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.235),与其余组相比差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);40%组与其余组相比差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);不同组间不同时间药物累计释放量也不全相同(P < 0.001),见表5、图3。"

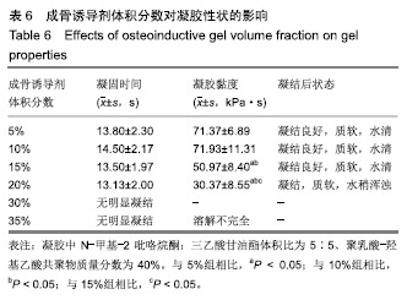
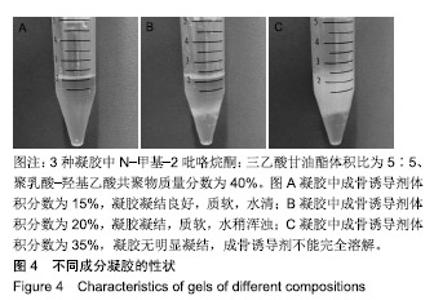
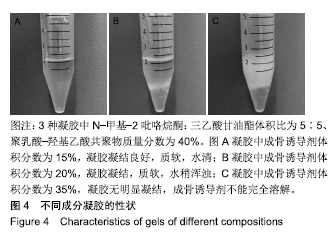
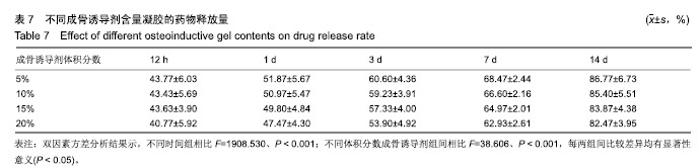
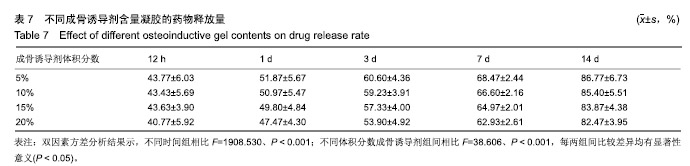
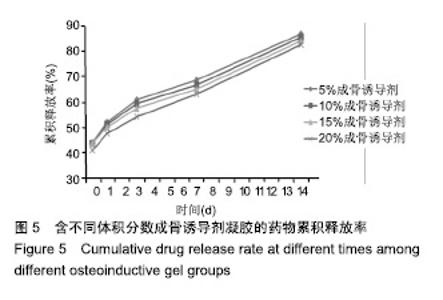
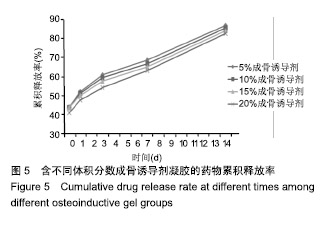
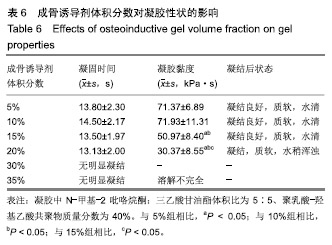
综合以上几点来说,PLGA质量分数为40%时凝结良好,质软,水清,且凝固时间和凝胶黏度合适,药物释放缓慢,释放速率稳定。因此选择N-甲基-2吡咯烷酮∶三乙酸甘油酯体积比为5∶5、PLGA质量分数40%来检测成骨诱导剂体积分数对凝胶状态的影响。 2.4 成骨诱导剂体积分数对凝胶凝结性能的影响 在N-甲基-2吡咯烷酮与三乙酸甘油酯体积比为5∶5、PLGA质量分数为40%时,如果成骨诱导剂体积分数大于20%,凝胶遇水无凝结;如果成骨诱导剂体积分数达到35%,出现了溶解不完全的现象;如果成骨诱导剂体积分数小于20%,各组凝胶凝结时间相似,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);凝胶黏度随成骨诱导剂体积分数的增加而变小,见表6。N-甲基-2吡咯烷酮∶三乙酸甘油酯体积比为5∶5、PLGA质量分数为40%、成骨诱导剂体积分数为15%的凝胶凝固时间适宜,黏度适宜,凝结良好,质软,水清,且凝胶载药含量多,见图4。对不同成骨诱导剂体积分数的缓释凝胶组间药物累积释放量不全相同(P < 0.001),各组药物释放速率均较稳定,而成骨诱导剂越多相同时间下凝胶的药物累积释放量越少,药物浓度持续时间久,在两两比较中各组间差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),不同组间不同时间药物累计释放量不全相同(P < 0.001),见表7、图5。基于以上几点及载药量的考虑,选择15%成骨诱导剂制作缓释药物。"
| [1]Pommer B,Valkova V,Ubaidha Maheen C,et al.Scientific Interests of 21st Century Clinical Oral Implant Research: Topical Trend Analysis.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2016;18(4):850-856.[2]Madan R,Mohan R,Bains VK,et al.Analysis of Socket Preservation Using Polylactide and Polyglycolide (PLA-PGA) Sponge:A Clinical Radiographic, and Histologic Study.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2014;34(15):36-42.[3]Sargolzaie N,Rafiee M,Salari Sedigh H,et al.Comparison of the effect of hemihydrate calcium sulfate granules and Cerabone on dental socket preservation: An animal experiment. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects.2018;12(4):238-244.[4]Gupta A,Rattan V,Rai S,et al.Efficacy of Chitosan in promoting wound healing in extraction socket: A prospective study.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res.2019;9(1):91-95.[5]Arai Y,Aoki K,Shimizu Y,et al.Peptide-induced de novo bone formation after tooth extraction prevents alveolar bone loss in a murine tooth extraction model. Eur J Pharmacol.2016; 782(5):89-97.[6]Chen J,He Y,Shan C,et al.Topical combined application of dexamethasone, vitamin C, and β-sodium glycerophosphate for healing the extraction socket in rabbits.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;44(10): 1317-1323.[7]向思捷,潘剑.拔牙后牙槽嵴保存的研究现状[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2019, 37(1):97-101.[8]孙旭,董福生,任贵云,等.拔牙创不同处理方式对牙槽窝愈合影响的实验研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2017,33(4):557-559.[9]Jaiswal N,Haynesworth SE,Caplan AI,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of purified, culture-expanded human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.J Cell Biochem.1997;64(2):295-312.[10]Kaveh K,Ibrahim R,Bakar ZB,et al.Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Osteogenic Lineage and Bone Tissue Engineering: A Review.J Anim Veter Adv.2011; 10(17):2317-2330.[11]Langenbach F,Handschel J.Effects of dexamethasone, ascorbic acid and β-glycerophosphate on the osteogenic differentiation of stem cells in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther.2013;4(5):117.[12]Wang C,Cao X,Zhang Y,et al.A novel bioactive osteogenesis scaffold delivers ascorbic acid, β-glycerophosphate, and dexamethasone in vivo to promote bone regeneration.Oncotarget. 2017;8(19):31612-31625[13]江敏,李桂华,李晓娟,等.载氨基化碳纳米管壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏凝胶对NGF的缓释性及释药机制研究[J].中国新药杂志, 2019,28(2):190-194.[14]Fiorentini E,Granchi D,Leonardi E,et al. Effects of osteogenic differentiation inducers on in vitro expanded adult mesenchymal stromal cells.Int J Artif Organs.2011;34(10):998-1011.[15]刘迪,黄晓英,何旭敏,等.PLGA及PLGA-PEG-PLGA水凝胶的制备[J].厦门大学学报(自然科学版),2016,55(2):162-167.[16]Mcusic AC,Lamba DA,Reh TA.Guiding the morphogenesis of dissociated newborn mouse retinal cells and hES cell-derived retinal cells by soft lithography-patterned microchannel PLGA scaffolds. Biomaterials.2012; 33(5):1396-1405. [17]Bailey BA,Desai KH,Ochyl LJ,et al.Self-encapsulating Poly (lactic-co- glycolic acid) (PLGA) Microspheres for Intranasal Vaccine Delivery.Mol Pharm.2017;14(9):3228-3237. [18]Feczkó T,Fodor-Kardos A,Sivakumaran M,et al.In vitro IFN-α release from IFN-α- and pegylated IFN-α-loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) and pegylated poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles.Nanomedicine (Lond).2016;11(16): 2029-2034. [19]周全,庞锦英,谭登峰,等.载阿奇霉素CS/PLGA缓释材料的制备与性能研究[J].化学研究与应用,2018,30(9):1511-1515.[20]Makadia HK,Siegel ST.Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug Delivery Carrier.Polymers (Basel). 2011;3(3):1377-1397.[21]严瑞瑄.水溶性高分子[M].2版.北京:化学工业出版社,2010:217.[22]Al-itry R,Lamnawar K,Maazouz A.Rheological,morphological,and interfacial properties of compatibilized PLA/PBAT blends.Rheol Acta. 2014;53(7):501-517.[23]陈占,熊俊超,朱广东.超低分子量超低残单聚N-乙烯基吡咯烷酮的制备研究[J].精细与专用化学品,2017,25(8):41-46.[24]杨楠,王希媛,翁云宣,等.三乙酸甘油酯对PLA/PBAT共混体系性能影响[J].生物工程学报,2016,32(6): 839-847.[25]童俊,曾卓,严庆国,等.三乙酸甘油酯含量及不同辊速比对滤棒物理指标的影响[J].轻工科技,2019,35(2):36-37.[26]Hoda N,Saifi AM,Giraddi GB,et al.Clinical use of the resorbable bioscaffold poly lactic co-glycolic acid (PLGA) in post-extraction socket for maintaining the alveolar height: A prospective study.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res.2016;6(3):173-178.[27]黄文良,叶鹏,莫刚,等.制备缓释骨形态发生蛋白2的丝素蛋白/壳聚糖/纳米羟基磷灰石生物支架[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(22):3488-3493.[28]Steinberg D,Friedman M.Sustained-release drug delivery of antimicrobials in controlling of supragingival oral biofilms.Expert Opin Drug Deliv.2017;14(4):571-581.[29]王桂芳,邱俊,吕宪俊,等.溶剂体系对蒙脱石/烷基铵复合物凝胶粘度的影响[J].化工矿物及加工,2009,15(9):7-9.[30]叶鹏,骆付丽,刘安平,等.缓释左氧氟沙星三维丝素蛋白/壳聚糖/纳米羟基磷灰石复合骨组织工程支架材料的制备与表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(14):2147-2155.[31]Maincent J,Williams RO 3rd. Sustained-release amorphous solid dispersions. Drug Deliv Transl Res.2018;8(6):1714-1725. [32]向虎,费小琛,卢清萍,等.PLGA/TCP 材料的浓度-粘度性能研究[J].材料导报,2004,18(7):93-95. [33]魏欣欣.牙周炎缓释凝胶基质的筛选及研制[D].青岛:青岛大学, 2017. |
| [1] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [2] | Liu Yang, Gong Yi, Fan Wei. Anti-hepatoma activity of targeted Pluronic F127/formononetin nanocomposite system in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| [3] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [4] | Gan Lili, Xiong Na, Liu Yanfei. Hydrogel as drug scaffold in skin wound repair: challenges of clinical application possibilities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3578-3583. |
| [5] | Liu Fang, Shan Zhengming, Tang Yulei, Wu Xiaomin, Tian Weiqun. Effects of hemostasis and promoting wound healing of ozone sustained-release hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3445-3449. |
| [6] | He Fan, Xiong Xiuli, Shan Xianfeng, Zhang Shutong, Hu Jian, Wang Xuejin. Guided bone regeneration in a small animal model of critical size craniofacial bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3226-3231. |
| [7] | Zhang Shengmin, Cao Changhong, Liu Chao. Adipose-derived stem cells integrated with concentrated growth factors prevent bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2982-2987. |
| [8] | Wang Liu, Song Dongzhe, Huang Dingming. Bone morphogenetic protein 9 regulates stem cell differentiation and bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3064-3070. |
| [9] | Gan Zhoujie, Pei Xibo. Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles in tumor therapy: superiority of nanoparticles in accumulation and drug release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2562-2568. |
| [10] | Chen Jufang, Tian Yulou, Hao Xin. Role and potential of adipose-derived stem cells in cranio-maxillofacial bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2087-2096. |
| [11] | Fan Haixia, Tan Qingkun, Wang Hong, Cheng Huanzhi, Liu Xue, Ching-chang Ko, Geng Haixia. Rabbit skull defects repaired by the hydroxyapatite/geltin scaffold combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1495-1499. |
| [12] | Zhang Lixing, Tian Ang, Li Xi, Bai Xizhuang. Drug-release characteristic and biological toxicity of TiO2 nanotube/hydroxyapatite loaded vancomycin coating [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1500-1506. |
| [13] | Zhao Binbin, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu, Li Yongqi, Wang Ning. Comparison of the osteogenic effect of three different bone graft materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1507-1510. |
| [14] | Shi Zhengliang, Zhang Hua, Fan Zhiyong, Ma Wei, Yuan He, Yang Bing. Nerve conduits of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol with brain-derived neurotrophic factor microspheres for peripheral nerve defects in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1555-1559. |
| [15] | Feng Xiaoxia, Hou Weiwei, Jin Xiaoting, Wang Xinhua. Construction of periodontal biomimetic membrane with electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibers and electrosprayed chitosan microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 511-516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||