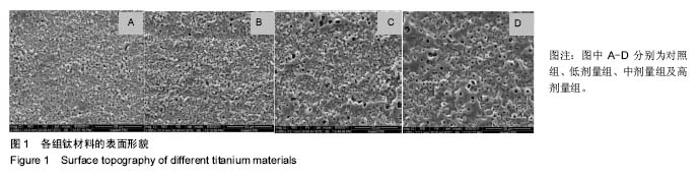
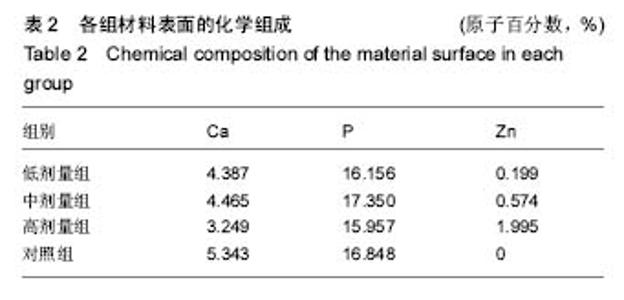
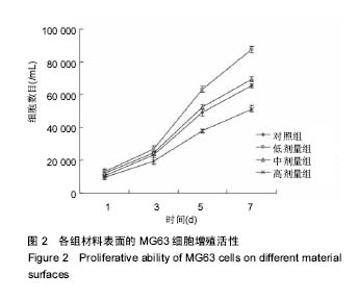
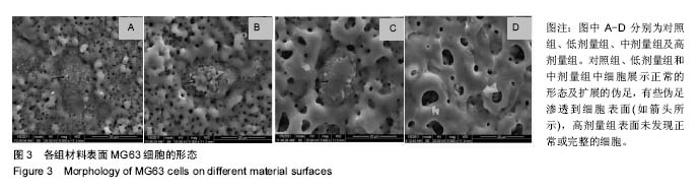
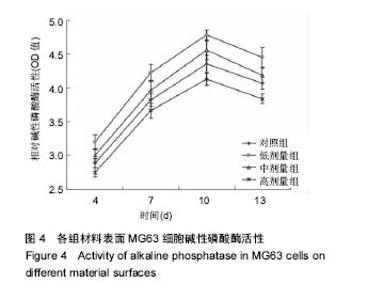
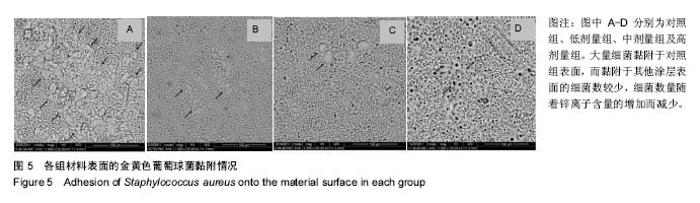
| [1]porous silicon-incorporated TiO2 coating prepared by micro-arc oxidation.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2011;97(2):224-234. [2]Wang W,Wan P,Liu C,et al.Degradation and biological properties of Ca-P contained micro-arc oxidation self-sealing coating on pure magnesium for bone fixation.Regen Biomater. 2015;2(2):107- 118. [3]Duarte LT,Bolfarini C,Biaggio SR.Growth of aluminum-free porous oxide layers on titanium and its alloys Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-7Nb by micro-arc oxidation.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2014; 41:343-348. [4]Yoshinari M,Oda Y,Kato T.Influence of surface modifications to titanium on antibacterial activity in vitro.Biomaterials. 2001; 22(14):2043-2048.[5]Hu H,Zhang W,Qiao Y,et al.Antibacterial activity and increased bone marrow stem cell functions of Zn-incorporated TiO2 coatings on titanium.Acta Biomater.2012;8(2):904-915. [6]Applerot G,Lipovsky A,Dror R,et al.Enhanced antibacterial activity of nanocrystalline ZnO due to increased ROS-mediated cell injury.Adv Funct Mater.2009;19:842-852.[7]Storrie H,Stupp SI.Cellular response to zinc-containing organoapatite: an in vitro study of proliferation, alkaline phosphatase activity and biomineralization.Biomaterials. 2005;26:5492-5499.[8]Tang A,Chappell HF,Dove MT.Zinc incorporation into hydroxylapatite.Biomaterials.2009;30: 2864-2872.[9]Lusvardi G,Zaffe D,Menabue L,et al.In vitro and in vivo behaviour of zinc-doped phosphosilicate glasses.Acta Biomater. 2009;5:419-428.[10]Miao S,Cheng K,Weng W,et al.Fabrication and evaluation of Zn containing ?uoridated hydroxyapatite layer with Zn release ability.Acta Biomater.2008;4:441-446.[11]Zreiqat H,Ramaswamy Y,Wu C.The incorporation of strontium and zinc into a calcium–silicon ceramic for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2010;31:3175-3184.[12]Wu C,Ramaswamy Y,Chang J, et al.The Effect of Zn contents on phase composition, chemical stability and cellular bioactivity in Zn-Ca-Si system ceramics.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;87:346-353.[13]Ramaswamy Y,Wu C,Zhou H,et al.Biological response of human bone cells to zinc-modi?ed Ca–Si-based ceramics. Acta Biomater.2008;4:1487-1497.[14]Tas AC,Bhaduri S,Jalota S.Preparation of Zn-doped b-tricalcium phosphate (β-Ca3(PO4)2) bioceramics. Mater Sci Eng C.2007;27:394-401.[15]Xu J,Ding G,Li J,et al.Zinc-ion implanted and deposited titanium surfaces reduce adhesion of Streptococccus mutans. Appl Surf Sci.2010;256(24):7540-7544.[16]Raghupathi KR,Koodali RT,Manna AC.Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles.Langmuir. 2011;27: 4020-4028.[17]Reddy KM,Feris K,Bell J,et al.Selective toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems.Appl Phys Lett.2007;90:2139021-2139023.[18]Atmaca S,Gul K, Clcek R.The effect of zinc on microbial growth.Tr J Med Sci.1998;28:595-597. |