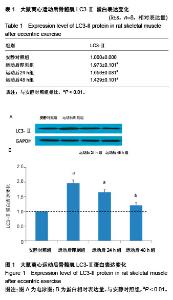
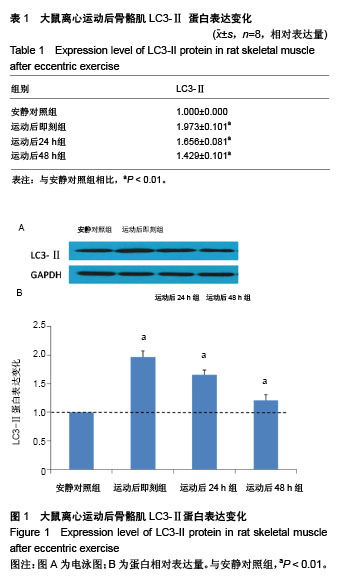
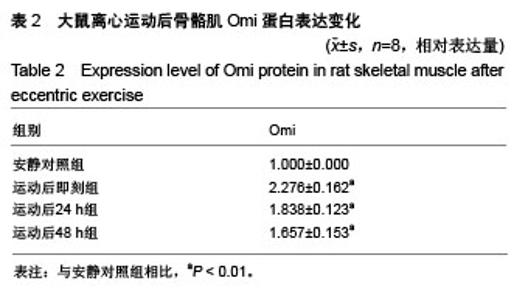
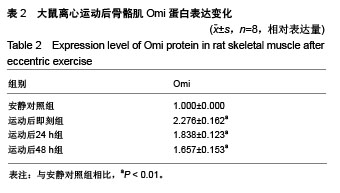
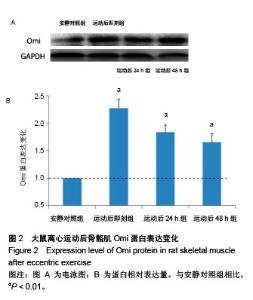
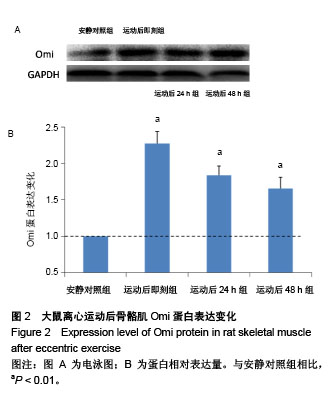
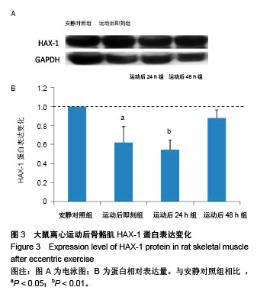
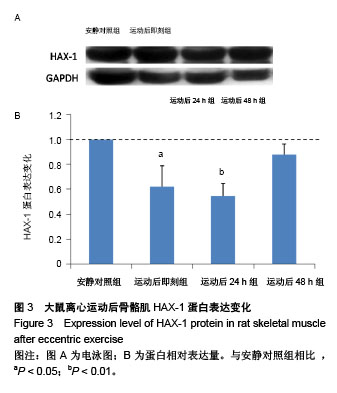
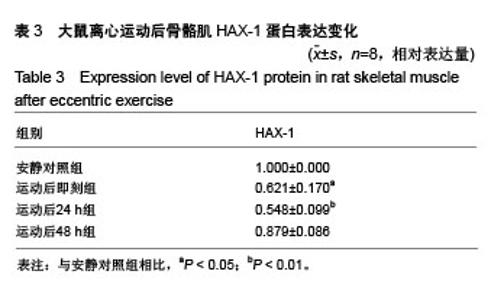
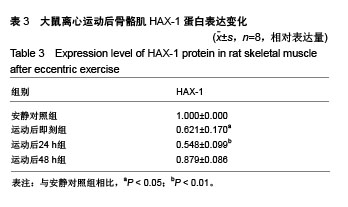
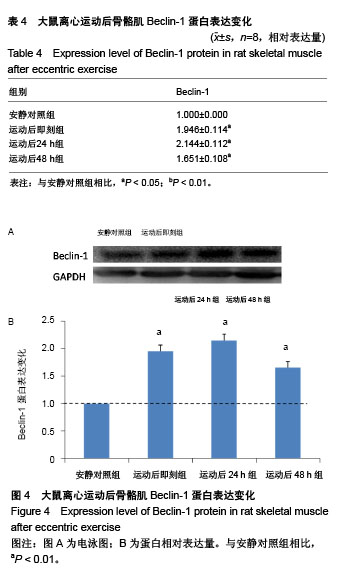
| [1] Silva LA, Silveira PC, Ronsani MM, et al. Taurine sup-plementation decreases oxidative stress in skeletal muscle after eccentric exercise. Cell Biochem Funet.2011; 29(1):43- 49.[2] 卢鼎厚,樊景禹,屈竹青,等.针刺和静力牵张对大负荷运动后骨骼肌收缩结构变化影响的免疫电镜研究[J].体育科学,1992,12(6): 47-51.[3] 李晓楠,樊景禹,卢鼎厚.针刺和静力牵张对大负荷运动后人骨骼肌Z带变化影响的免疫电镜研究[J].体育科学,1992,12( 6): 60-65.[4] Zhou P, Tan YZ, Wang HJ, et al. Cytoprotective effect of autophagy on phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages. Exp Cell Res.2016;348(2):165-176.[5] Shpilka T, Mizushima N, Elazar Z. Ubiquitin-like proteins and autophagy at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 10): 2343-2348.[6] He C, Bassik MC , Moresi V , et al. Exercise-induced BCL2-regulated autophagy is required for muscle glucose homeostasis. Nature.2012;481(7382):511-515.[7] 张欣. 大负荷运动诱导骨骼肌细胞自噬的Omi途径及针刺干预效应[D]. 北京:北京体育大学,2016.[8] Klionsky DJ. Autophagy: from phenomenology to molecular understanding in less than a decade. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(11):931-937. [9] 冯文之,陈扬,俞立. 细胞自噬分子机制的进展[J].生命科学,2015, 27(7):859-866.[10] Gatica D, Chiong M, Lavandero S, et al. Molecular mechanisms of autophagy in the cardiovascular system. Circ Res.2015;116(3):456-467.[11] 钱帅伟,罗艳蕊,漆正堂,等. 细胞自噬的分子学机制及运动训练的调控作用[J]. 体育科学,2012,32(1): 64-70.[12] 赵晓琴,孙君志,王瑞元,等. 离心运动诱导大鼠骨骼肌损伤中丝氨酸蛋白酶Omi的表达升高[J].天津体育学院学报, 2015,30(2): 110-114.[13] 李斌.丝氨酸蛋白酶Omi/HtrA2通过调节细胞自噬参与神经退行性疾病发生[D].合肥:中国科学技术大学,2010.[14] Nakatogawa H, Suzuki K, Kamada Y, et al. Dynamics and diversity in autophagy mechanisms: lessons from yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.2009;10: 458-467.[15] Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, et al. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J.2000;19: 5720-5728.[16] Cilenti L,Ambivero CT,Ward N,et al.Inactivation of Omi/HtrA2 protease leads to the deregulation of mitochondrial Mulan E3 ubiquitin ligase and increased mitophagy.Biochim Biophys Acta.2014;1843(7):1295-1307.[17] Li B, Hu Q, Wang H, Man N,et al.Omi/HtrA2 is a positive regulator of autophagy that facilitates the degradation of mutant proteins involved in neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17(11):1773-1784.[18] Zhou H,Chen J,Lu X, et al. Melatonin protects against rotenone-induced cell injury via inhibition of Omi and Bax-mediated autophagy in Hela cells.J Pineal Res.2012; 52(1): 120-127.[19] Cilenti L, Soundarapandian MM, Ky riazis GA, et al. Regulation of H AX- 1 ant-i apoptotic protein by Omi/H trA2 protease during cell death.J Biol Chem.2004;279(48): 50295-50301.[20] Fadeel B, Grzybowska E. HAX-1: a multifunctional protein with emerging roles in human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta.2009;1790(10):1139-1148.[21] Fava LL, Rainer J, Haschka MD. Beclin 1 is dispensable for chromosome congression and proper outer kinetochore assembly. EMBO Reports.2015;16(10):1233-1236.[22] Chen L,Liu D,Zhang Y.The autophagy molecule Beclin 1 maintains persistent activity of NF-κB and Stat3 in HTLV-1-transformed Tlymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2015;465(4): 739-745.[23] Kang R, Zeh HJ,Lotze MT,et al.The Beclin-1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis.Cell Death Differ.2011; 18(4):571-580.[24] Zhao W, Waggoner JR, Zhang ZG, et al. The anti-apoptotic protein HAX-1 is a regulator of cardiac function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(49):20776-20781. |