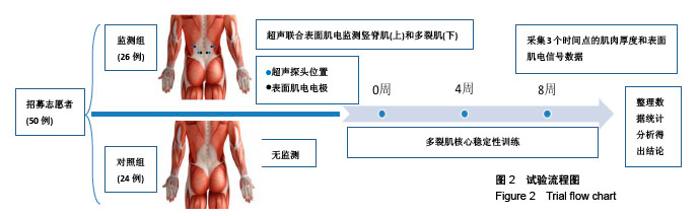
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (36): 5785-5790.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0562
Previous Articles Next Articles
Core stability training targeting multifidus: monitor using ultrasound combined with surface electromyogram versus no monitor
Zheng Yaochao1, Lin Caina1, Ke Songjian1, Luo Haijie2, Liu Cuicui1, Ma Chao1, Wu Shaoling1
- (1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China; 2the Fifth People’s Hospital of Dongguan, Dongguan 523903, Guangdong Province, China)
-
Received:2018-07-11Online:2018-12-28Published:2018-12-28 -
Contact:Wu Shaoling, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zheng Yaochao, Master candidate, Physical therapist, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81771201 and 81671088; the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2016A030311045; the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province, No. 201807010050; the Yat-Sen Clinical Research and Cultivation Project
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zheng Yaochao1, Lin Caina1, Ke Songjian1, Luo Haijie2, Liu Cuicui1, Ma Chao1, Wu Shaoling1. Core stability training targeting multifidus: monitor using ultrasound combined with surface electromyogram versus no monitor[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5785-5790.
share this article
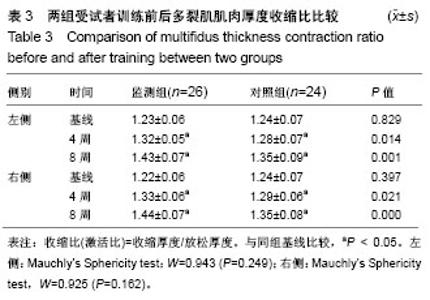
2.3 两组受试者训练前后超声多裂肌厚度收缩比的比较 左侧多裂肌厚度收缩比数据的Mauchly球性检验结果为 P=0.249,满足球形对称性条件,时间与处理的交互作用检验的F=4.892,P=0.009,存在交互作用,故采用独立样本t 检验观察两组左侧厚度收缩比每个时间点的差异。右侧多裂肌厚度收缩比数据的Mauchly球性检验结果为P=0.162,满足球形对称性条件,时间与处理的交互作用检验的F=9.777, P ≤ 0.001,存在交互作用,故采用独立样本t 检验观察两 组左侧厚度收缩比每个时间点的差异。再采用重复测量资料方差分析不同时间点的差异,得到如下结果。 两组受试者入组前多裂肌厚度收缩比比较无显著性意义(P > 0.05);经过8周训练,监测组和对照组双侧多裂肌厚度收缩比均明显增大,分别与训练前比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。在训练4周时,监测组和对照组双侧多裂肌厚度收缩比已出现增大,与同组训练前比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),且监测组双侧多裂肌厚度收缩比分别于对照组比较差异已有显著性意义(P < 0.05);在8周时,监测组与训练前比较肌肉厚度收缩比增大更明显(P < 0.05),且双侧厚度收缩比分别与对照组比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表3。"

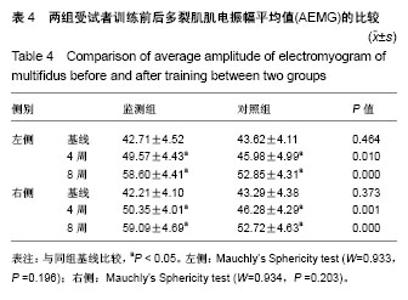
2.4 两组受试者训练前后多裂肌AEMG的比较 左侧多裂肌AEMG的Mauchly球性检验结果为P=0.196,满足球形对称性条件,得到时间与处理的交互作用检验的 F =11.245,P ≤ 0.001,存在交互作用,故采用独立样本t 检验观察两组每个时间点的差异。右侧多裂肌表面肌电数据的Mauchly球性检验结果为P=0.203,满足球形对称性条件,得到时间与处理的交互作用检验的F=17.672,P ≤ 0.001,存在交互作用,故采用独立样本t检验观察两组每个时间点的差异。再采用重复测量方差分析不同时间点的差异,得到如下结果。 两组受试者入组前多裂肌AEMG比较无显著性意义 (P > 0.05);经过8周训练,监测组和对照组双侧多裂肌AEMG均明显增大,分别与训练前比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。在训练4周时,监测组双侧多裂肌AEMG均已出现增大,与训练前比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);在训练8周后,监测组双侧多裂肌AEMG增大更明显(P < 0.05),且分别与训练前比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);且监测组双侧多裂肌AEMG与对照组比较差异也均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表4。"

| [1] Deyo RA, Weinstein JN. Low back pain. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344(5): 363-370.[2] Muzin S, Isaac Z, Walker JR. The role of intradiscal steroids in the treatment of discogenic low back pain. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2008;1(2):103-107. [3] Martin BI, Deyo RA, Mirza SK, et al. Expenditures and health status among adults with back and neck problems. JAMA. 2008;299(6): 656-664. [4] Herbert WJ, Heiss DG, Basso DM. Influence of feedback schedule in motor performance and learning of a lumbar multifidus muscle task using rehabilitative ultrasound imaging: a randomized clinical trial. Phys Ther. 2008;88(2):261-269. [5] Lee NG, Jung JH, You JS, et al. Novel augmented ADIM training using ultrasound imaging and electromyography in adults with core instability. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2011;24(4): 233-240. [6] Ghamkhar L, Emami M, Mohseni-Bandpei MA, et al. Application of rehabilitative ultrasound in the assessment of low back pain: a literature review. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2011;15(4):465-477. [7] Wilson A, Hides J A, Blizzard L, et al. Measuring ultrasound images of abdominal and lumbar multifidus muscles in older adults: a reliability study. Man Ther. 2016;23:114-119. [8] Dar G, Hicks GE. The immediate effect of dry needling on multifidus muscles' function in healthy individuals. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2016;29(2):273-278. [9] de Seze MP, Cazalets JR. Anatomical optimization of skin electrode placement to record electromyographic activity of erector spinae muscles. Surg Radiol Anat. 2008;30(2):137-143. [10] Slipman CW, Shin CH, Patel RK, et al. Etiologies of failed back surgery syndrome. Pain Med. 2002;3(3):200-217. [11] Frymoyer JW. Predicting disability from low back pain. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;(279):101-109.[12] Walker BF. The prevalence of low back pain: a systematic review of the literature from 1966 to 1998. J Spinal Disord. 2000;13(3): 205-217. [13] Hayden JA, van Tulder MW, Tomlinson G. Systematic review: strategies for using exercise therapy to improve outcomes in chronic low back pain. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142(9):776-785. [14] Hayden JA, Cartwright JL, Riley RD, et al. Exercise therapy for chronic low back pain: protocol for an individual participant data meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2012;1:64. [15] Kliziene I, Sipaviciene S, Klizas S, et al. Effects of core stability exercises on multifidus muscles in healthy women and women with chronic low-back pain. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2015; 28(4): 841-847. [16] 朱传芳,黄强民,彭金凤.核心稳定性训练的理论基础与发展近况[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(11):1787-1792. [17] Wan Q, Lin C, Li X, et al. MRI assessment of paraspinal muscles in patients with acute and chronic unilateral low back pain. Br J Radiol. 2015;88(1053):20140546. [18] Wallwork TL, Stanton WR, Freke M, et al. The effect of chronic low back pain on size and contraction of the lumbar multifidus muscle. Man Ther. 2009;14(5):496-500. [19] 罗海杰,柯松坚,林彩娜,等.运动训练对椎间盘退变模型大鼠疼痛及细胞外基质合成的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(20): 3176-3182. [20] Mangum LC, Sutherlin MA, Saliba SA, et al. Reliability of ultrasound imaging measures of transverse abdominis and lumbar multifidus in various positions. PM R. 2016;8(4):340-347. [21] Teyhen DS. Rehabilitative ultrasound imaging for assessment and treatment of musculoskeletal conditions. Man Ther. 2011;16(1): 44-45. [22] Huang QH, Zheng YP, Li R, et al. 3-D measurement of body tissues based on ultrasound images with 3-D spatial information. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2005;31(12):1607-1615. [23] Belavy DL, Armbrecht G, Felsenberg D. Real-time ultrasound measures of lumbar erector spinae and multifidus: reliability and comparison to magnetic resonance imaging. Physiol Meas. 2015; 36(11):2285-2299.[24] Cifrek M, Medved V, Tonkovic S, et al. Surface EMG based muscle fatigue evaluation in biomechanics. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009;24(4):327-340. [25] Kang H, Jung J, Yu J. Comparison of trunk muscle activity during bridging exercises using a sling in patients with low back pain. J Sports Sci Med. 2012;11(3):510-515. [26] Yoshihara K, Nakayama Y, Fujii N, et al. Atrophy of the multifidus muscle in patients with lumbar disk herniation: histochemical and electromyographic study. Orthopedics. 2003;26(5):493-495. [27] Lehman GJ, Hoda W, Oliver S. Trunk muscle activity during bridging exercises on and off a Swiss ball. Chiropr Osteopat. 2005;13:14. [28] Ferreira PH, Ferreira ML, Hodges PW. Changes in recruitment of the abdominal muscles in people with low back pain: ultrasound measurement of muscle activity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29(22): 2560-2566.[29] Mcmeeken JM, Beith ID, Newham DJ, et al. The relationship between EMG and change in thickness of transversus abdominis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2004;19(4):337-342. [30] O'Sullivan PB, Phyty GD, Twomey LT, et al. Evaluation of specific stabilizing exercise in the treatment of chronic low back pain with radiologic diagnosis of spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(24):2959-2967. [31] Brumitt J, Matheson JW, Meira EP. Core stabilization exercise prescription, part 2: a systematic review of motor control and general (global) exercise rehabilitation approaches for patients with low back pain. Sports Health. 2013;5(6):510-513. |
| [1] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Peng Kun, Lin Yimin, Gan Xiaoling, Wu Zhiyong. Development prospect of orthopedic rehabilitation medicine based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 632-637. |
| [4] | Huang Maomao, Hu Yue, Wang Binchuan, Zhang Chi, Xie Yujie, Wang Jianxiong, Wang Li, Xu Fangyuan. Bibliometric and visual analysis of international literature addressing ischemic stroke rehabilitation in recent 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3725-3733. |
| [5] | Chen Xingying, Hao Fei, Gao Yudan, Zhao Wen, Duan Hongmei, Yang Chaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Rehabilitation training combined with neurotrophin 3-chitosan scaffolds enhanced skeletal muscle morphology and functional recovery in rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2514-2520. |
| [6] | Lin Yi, Feng Jierong, Luo Xingwen. Mobilization with movement facilitates early functional recovery after fixed-bearing posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1842-1846. |
| [7] | Sun Kai, Chen Lei, Mai Yao, Hu Hua, Chen Liang, Zhong Jun, Hu Yong, Qiu Bo. Clinical application of enhanced recovery after surgery in the perioperative period of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1647-1651. |
| [8] |
Yin Jiandong, Wang Xinling, Zuo Biao, Li Nongyi.
Relationship of extrusion and elevation of blood-expelling methods during
total knee arthroplasty with postoperative complications |
| [9] | Liu Yu, Zhang Nanxin, Dai Liqun, Ying Wei. Meta-analysis of the effectiveness of cold therapy after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1443-1448. |
| [10] | Ding Meizhu, Hu Peixin, Shen Qian, Zhong Shuxian, Yang Yalan, Li Chun. Remote rehabilitation applied in patients with stable stage of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1306-1312. |
| [11] | Zhu Dongming, Zhang Zhen, Zhang Jie, Yan Lianqi. Risk factors for prosthetic dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: recent progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(36): 5864-5870. |
| [12] | Fan Zhongbao, Shen Jianfen, Wang Jian, Yu Hao, Liu Yanfeng. Comparison of 3Dmax light-weight hernia mesh and Prolene weight mesh for the repair of inguinal hernia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5545-5551. |
| [13] | Cai Danxian, Zeng Qing, He Longlong, Huang Guozhi. Application and mechanism of virtual reality technology in post-stroke rehabilitation of the hemiplegic upper limb [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5228-5235. |
| [14] | Lu Shuqing, Li Xin, Guo Jin, Liu Shiyu, Yang Shunbo, Feng Yuxia, Pang Wei. Advantages in instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization for chronic soft tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4709-4716. |
| [15] |
Wang Dexin, Xu Zhanwu, Pei Guoxian.
Osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on hydroxyapatite/icariin/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3974-3980. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||