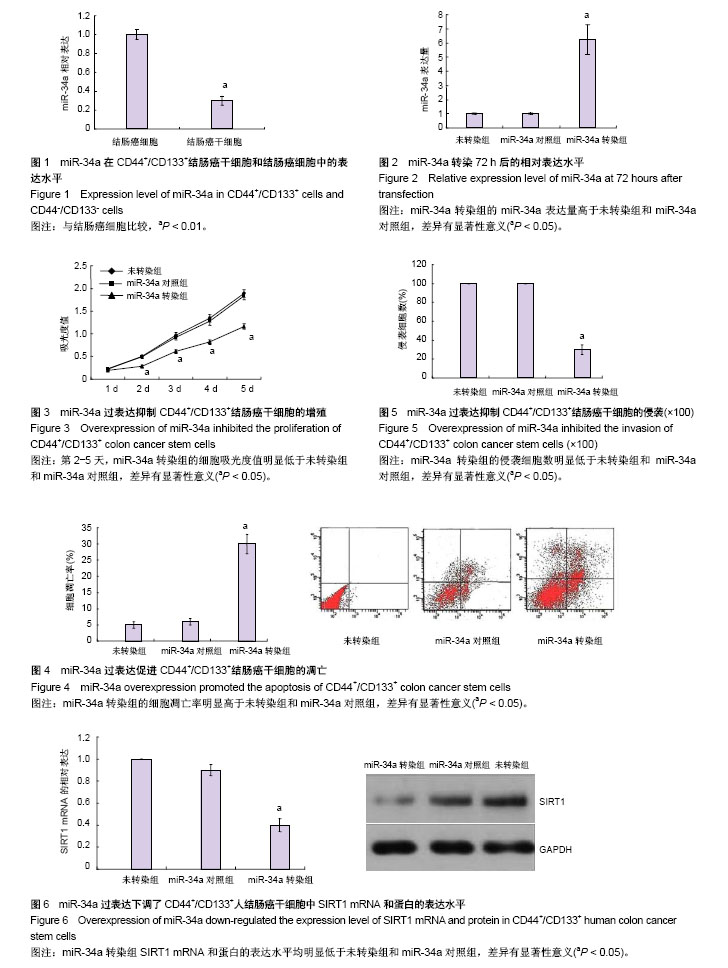
| [1] 陈达民.结直肠癌的流行病学及危险因素[J].国外医学:消化系统疾病分册,1997,17(4):208.[2] 张振书,马强.结肠癌的流行病学[J].胃肠病学, 2001, 6(4):231-232.[3] 张好刚,徐训政,乔鹏飞,等. 微小RNA在结肠癌中的研究进展[J].中国医师进修杂志,2017,40(9):861-864.[4] Ahmed FE. miRNA as markers for the diagnostic screening of colon cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2014;14(4):463-485.[5] 公小迪,姜斌.MicroRNA与肿瘤信号通路交互作用的研究进展[J].现代肿瘤医学,2012,20(3): 634-637.[6] Yang L, Peng F, Qin J, et al. Downregulation of microRNA-196a inhibits human liver cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting FOXO1. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(4):2148-2154.[7] Wang L, Bu P, Ai Y, et al. A long non-coding RNA targets microRNA miR-34a to regulate colon cancer stem cell asymmetric division. Elife. 2016;5(pii): e14620.[8] Jiang H, Ge F, Hu B, et al. rs35301225 polymorphism in miR-34a promotes development of human colon cancer by deregulation of 3'UTR in E2F1 in Chinese population. Cancer Cell Int. 2017;17:39.[9] Li H, Wang R. Blocking SIRT1 inhibits cell proliferation and promotes aging through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Life Sci. 2017;190:84-90.[10] Kojima K, Ohhashi R, Fujita Y, et al. A role for SIRT1 in cell growth and chemoresistance in prostate cancer PC3 and DU145 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;373(3): 423-428.[11] 黄立勇,潘杰,沈徐宁,等.沉默信息调节因子1在结直肠癌组织中的表达及意义[J].肿瘤学杂志, 2016, 43(3) :188-192.[12] 明浩,谢荃沁,宗赟,等.肺腺癌组织SIRT1表达及其临床意义[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2016,23(6):358-363.[13] 李军,许荣华,周晓华,等.上调miRNA-34a表达对人结肠癌细胞体外生长的影响[J].中国普通外科杂志,2016,25(4):524-528.[14] Ghosh A, Sengupta A, Seerapu GPK, et al. A novel SIRT1 inhibitor, 4bb induces apoptosis in HCT116 human colon carcinoma cells partially by activating p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;488(3):562-569.[15] 姜尧.肿瘤干细胞学说在非小细胞肺癌研究中的应用[J].医学综述, 2011,17(1):56-60.[16] Weissman I. Evolution of normal and neoplastic tissue stem cells: progress after Robert Hooke. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015;370(1680):20140364.[17] Hodgkinson N, Kruger CA, Abrahamse H. Targeted photodynamic therapy as potential treatment modality for the eradication of colon cancer and colon cancer stem cells. Tumour Biol. 2017;39(10):1010428317734691.[18] 郭开峰,曾云.无血清悬浮培养法富集结肠癌干细胞[J]. 四川解剖学杂志,2012,20(2):9-11.[19] Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, et al. Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 2003;63(18): 5821-5828.[20] Stotz M, Herzog SA, Pichler M, et al. Cancer Stem Cell Gene Variants in CD44 Predict Outcome in Stage II and Stage III Colon Cancer Patients. Anticancer Res. 2017;37(4):2011-2018.[21] Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, et al. Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface marker CD44. Stem Cells. 2009;27(5):1006-1020.[22] 冯燕君,夏璐,李晓露,等.HT29和HCT116结肠癌细胞无血清培养形成肿瘤干细胞球特性的差异性研究[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2011, 20(10) :892-896.[23] Zhou JY, Chen M, Ma L, et al. Role of CD44(high)/CD133(high) HCT-116 cells in the tumorigenesis of colon cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(7):7657-7666.[24] 柯慧,丁彦青,王爽,等.MicroRNA在人类肿瘤中的角色及其应用[J].临床与病理杂志, 2009, 29(3):225-230.[25] Kim HR, Roe JS, Lee JE, et al. p53 regulates glucose metabolism by miR-34a. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 437(2):225-231.[26] 陈苗,沈帅,于承仟,等.MicroRNA-34a 对多种肿瘤细胞迁移的影响及其作用机制探讨[J].现代肿瘤医学,2017,25(1):135-138.[27] Jiang L, Hermeking H. miR-34a and miR-34b/c Suppress Intestinal Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2017;77(10):2746-2758.[28] Sun H, Tian J, Xian W, et al. miR-34a inhibits proliferation and invasion of bladder cancer cells by targeting orphan nuclear receptor HNF4G. Dis Markers. 2015;2015:879254.[29] Raver-Shapira N, Marciano E, Meiri E, et al. Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to p53-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell. 2007;26(5):731-743.[30] Ribeiro J, Sousa H. MicroRNAs as biomarkers of cervical cancer development: a literature review on miR-125b and miR-34a. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41(3):1525-1531.[31] Ma W, Xiao GG, Mao J, et al. Dysregulation of the miR-34a- SIRT1 axis inhibits breast cancer stemness. Oncotarget. 2015; 6(12):10432-10444.[32] Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M, Lowenstein CJ. miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2008; 105(36):13421-13426.[33] Deng CX. SIRT1, is it a tumor promoter or tumor suppressor. Int J Biol Sci. 2009;5(2):147-152.[34] Kabra N, Li Z, Chen L, et al. SirT1 is an inhibitor of proliferation and tumor formation in colon cancer. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(27): 18210-18217.[35] 王雷,高琳璐.乳腺癌组织中SIRT1的表达观察[J].广州医药,2017, 48(4):17-19,28.[36] Shin SY, Kim TH, Wu H, et al. SIRT1 activation by methylene blue, a repurposed drug, leads to AMPK-mediated inhibition of steatosis and steatohepatitis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;727: 115-124.[37] Ramakrishnan G, Davaakhuu G, Kaplun L, et al. Sirt2 deacetylase is a novel AKT binding partner critical for AKT activation by insulin. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(9):6054-6066.[38] Yang A, Wang X, Yu C, et al. microRNA-494 is a potential prognostic marker and inhibits cellular proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting SIRT1 in epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett. 2017;14(3):3177-3184.[39] Sun LN, Zhi Z, Chen LY, et al. SIRT1 suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis by transcriptional repression of miR-15b-5p. Cancer Lett. 2017;409:104-115.[40] Zhao H, Tang W, Chen X, et al. The NAMPT/E2F2/SIRT1 axis promotes proliferation and inhibits p53-dependent apoptosis in human melanoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017; 493(1):77-84. |