Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (9): 1382-1388.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0468
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of exosome extracting methods from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
Guo Ying1, Wang Xiu-wei2, Niu Yu-hu3, Wang Li1, Zhou Nan4, Li Bai-yi1, Wang Zhen-dong1, Zhang Pin1, Gao Ya-jie1, Niu Bo3
- 1School of Basic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Capital Institute of Pediatrics, Beijing 100020, China; 3Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 4Department of Anatomy, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Revised:2017-10-13Online:2018-03-28Published:2018-04-03 -
Contact:Niu Bo, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Guo Ying, Master candidate, School of Basic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81370312; the Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province, No. 812180; the Scientific Innovation Project for Medical Treatment and Public Health in Sanya City, No. 2014 YW01
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Ying, Wang Xiu-wei, Niu Yu-hu, Wang Li, Zhou Nan, Li Bai-yi, Wang Zhen-dong, Zhang Pin, Gao Ya-jie, Niu Bo. Comparison of exosome extracting methods from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1382-1388.
share this article
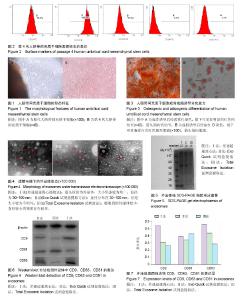
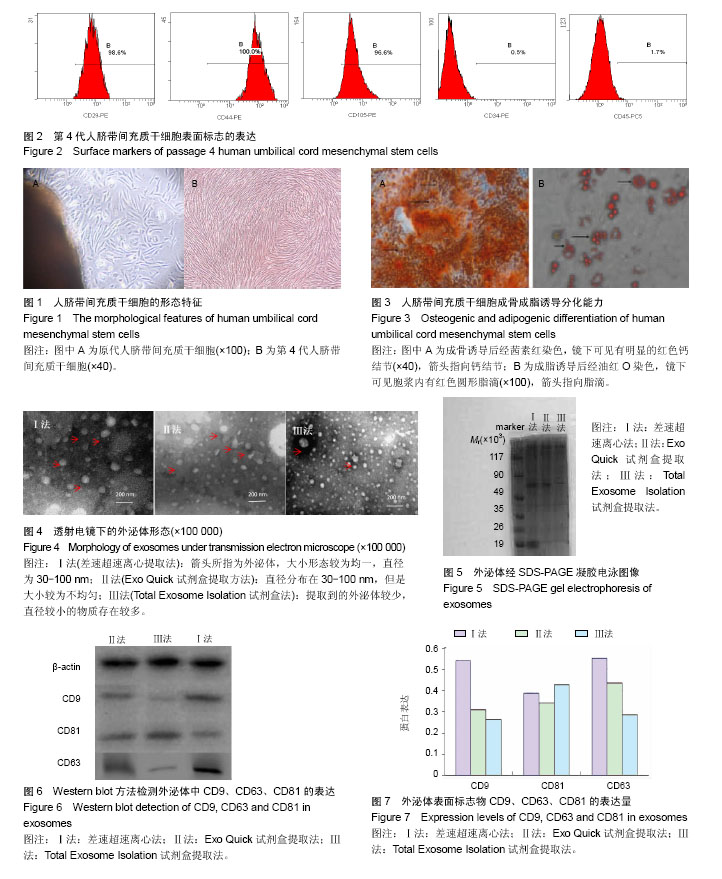
2.1 脐带间充质干细胞的形态 培养7-12 d时,倒置显微镜下可以看到贴壁细胞,呈梭形,较肥大。待细胞融合率达80%,进行第1次传代,传代培养至第4代,细胞形态均匀一致,排列紧密,集落中心呈漩涡状,见图1。 2.2 细胞表面标志的表达 流式细胞仪检测结果显示,细胞高表达CD29、CD44和CD105(> 95%),极低表达CD34与CD45,符合间充质干细胞的特性,见图2。 2.3 人脐带间充质干细胞的成骨成脂分化能力 第4代人脐带间充质干细胞加入成骨诱导培养基后,细胞生长缓慢,培养到第20天经茜素红染色,显微镜下可见有明显的红色钙结节(图3A)。加入成脂诱导培养基后,培养到第15天经油红O染色,镜下可见胞浆内有红色圆形脂滴(图3B)。 2.4 外泌体的形态 透射电镜观察发现经3种方法提取到的外泌体均呈椭圆形囊泡,可见外周分界清楚的膜性结构,可单个分布,也可聚集成群。差速超速离心法获得的外泌体直径多分布于30-100 nm,较为均一,Exo Quick试剂盒法获得的外泌体不够均匀,Isolation试剂盒法获得的外泌体背景污染较严重,可能存在蛋白质污染,见图4。 2.5 外泌体蛋白浓度 绘制标准曲线,根据标准曲线得出的公式y=0.388x+0.029 4(相关系数R2=0.994 7)分别算出相应的蛋白量,经计算得出差速超速离心法所得的外泌体蛋白浓度为2.0-3.0 g/L,Exo Quick试剂盒提取方法获得的外泌体蛋白浓度为1.5-2.5 g/L,Total Exosome Isolation试剂盒法获得的外泌体蛋白浓度为1.0-2.0 g/L。差速超速离心法获得的外泌体蛋白浓度较其他两种方法高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.6 SDS-PAGE电泳及凝胶图像 3种方法所得的外泌体中含有多种蛋白成分,而在上样量以及条件相同的情况下,不同方法得到的外泌体的蛋白表达强度不同,在Mr 35 000-49 000之间及Mr19 000以下较为富集。差速超速离心法和Exo Quick试剂盒提取的外泌体在Mr40 000-49 000的蛋白含量明显高于Total Exosome Isolation试剂盒法。在Mr19 000以下,差速超速离心法提取的外泌体蛋白含量明显高于其他两种方法,见图5。 2.7 Western blot检测外泌体标志蛋白表达 利用Western blot方法检测3种方法提取的外泌体中的CD9、CD63、CD81表达。结果显示3种方法提取的外泌体都可以表达特异性表面标志物CD9、CD63和CD81(图6)。差速超速离心法提取到的外泌体特异性标志物CD9与CD63在表达强度上远高于其他两种方法;其次,Exo Quick试剂盒法和Total Exosome Isolation试剂盒法提取到的外泌体特异性标志物仅在CD81的表达上略高于差速超速离心法(图7),说明差速超速离心法提取到的样本较其他两种纯。 2.8 操作时间比较 差速超速离心法平均耗时(160.0± 8.0) min;Exo Quick试剂盒法平均耗时(40.0±4.5) min;Total Exosome Isolation试剂盒法平均耗时(111.5±5.0) min。传统差速超速离心法和Total Exosome Isolation试剂盒法的操作时间明显多于Exo Quick试剂盒法,差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.05)。"
| [1] Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420.[2] Ho DH, Yi S, Seo H, et al. Increased DJ-1 in urine exosome of Korean males with Parkinson's disease. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:704678.[3] Pironti G, Strachan RT, Abraham D, et al. Circulating Exosomes Induced by Cardiac Pressure Overload Contain Functional Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptors. Circulation. 2015;131(24):2120-2130.[4] Yang J, Wei F, Schafer C, et al. Detection of tumor cell-specific mRNA and protein in exosome-like microvesicles from blood and saliva. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e110641. [5] 张顺华. 猪不同泌乳期乳汁Exosome中microRNA转录组的鉴定和表达谱分析[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2013.[6] Lässer C. Identification and analysis of circulating exosomal microRNA in human body fluids. Methods Mol Biol. 2013; 1024:109-128.[7] Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, et al. Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1820(7):940-948.[8] Simons M, Raposo G. Exosomes--vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21(4): 575-581.[9] Eggenhofer E, Steinmann JF, Renner P, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells together with mycophenolate mofetil inhibit antigen presenting cell and T cell infiltration into allogeneic heart grafts. Transpl Immunol. 2011;24(3):157-163.[10] Tian LL, Yue W, Zhu F, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells play a dual role on tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226(7):1860-1867.[11] Roura S, Bagó JR, Soler-Botija C, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote vascular growth in vivo. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49447.[12] Bagno LL, Werneck-de-Castro JP, Oliveira PF, et al. Adipose-derived stromal cell therapy improves cardiac function after coronary occlusion in rats. Cell Transplant. 2012; 21(9):1985-1996.[13] Meyer GP, Wollert KC, Lotz J, et al. Intracoronary bone marrow cell transfer after myocardial infarction: eighteen months' follow-up data from the randomized, controlled BOOST (BOne marrOw transfer to enhance ST-elevation infarct regeneration) trial. Circulation. 2006;113(10):1287-1294.[14] Wubbolts R, Leckie RS, Veenhuizen PT, et al. Proteomic and biochemical analyses of human B cell-derived exosomes. Potential implications for their function and multivesicular body formation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(13):10963-10972.[15] Théry C, Ostrowski M, Segura E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009; 9(8):581-593.[16] Théry C, Boussac M, Véron P, et al. Proteomic analysis of dendritic cell-derived exosomes: a secreted subcellular compartment distinct from apoptotic vesicles. J Immunol. 2001;166(12):7309-7318.[17] Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214-222.[18] 赵晓琦,程敏.外泌体相关微小RNA的生物学特性及其在多种心血管疾病中的诊断价值[J].临床心血管病杂志,2015,31(9): 924-928.[19] Ciravolo V, Huber V, Ghedini GC, et al. Potential role of HER2-overexpressing exosomes in countering trastuzumab-based therapy. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(2): 658-667.[20] Sheldon H, Heikamp E, Turley H, et al. New mechanism for Notch signaling to endothelium at a distance by Delta-like 4 incorporation into exosomes. Blood. 2010;116(13): 2385-2394.[21] Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, et al. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science. 2008;319(5867):1244-1247.[22] Jansen FH, Krijgsveld J, van Rijswijk A, et al. Exosomal secretion of cytoplasmic prostate cancer xenograft-derived proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009;8(6):1192-1205.[23] Chen TS, Arslan F, Yin Y, et al. Enabling a robust scalable manufacturing process for therapeutic exosomes through oncogenic immortalization of human ESC-derived MSCs. J Transl Med. 2011;9:47.[24] Chang SH, Hla T. Post-transcriptional gene regulation by HuR and microRNAs in angiogenesis. Curr Opin Hematol. 2014; 21(3):235-240.[25] Jakob P, Doerries C, Briand S, et al. Loss of angiomiR-126 and 130a in angiogenic early outgrowth cells from patients with chronic heart failure: role for impaired in vivo neovascularization and cardiac repair capacity. Circulation. 2012;126(25):2962-2975.[26] 胡国文,李青,牛鑫,等. 旋转超滤:一种提取细胞外泌体的新方法[J]. 第二军医大学学报,2014,35(6):598-602.[27] Qiao C, Xu W, Zhu W, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the umbilical cord. Cell Biol Int. 2008;32(1):8-15.[28] 周楠. 脐带间充质干细胞来源Exosomes的制备及其与源细胞体内治疗效果的比较研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2014.[29] Zhang L, Wu X, Luo C, et al. The 786-0 renal cancer cell-derived exosomes promote angiogenesis by downregulating the expression of hepatocyte cell adhesion molecule. Mol Med Rep. 2013;8(1):272-276.[30] Simari RD, Pepine CJ, Traverse JH, et al. Bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction: a perspective from the cardiovascular cell therapy research network. Circ Res. 2014;114(10):1564-1568.[31] Quyyumi AA, Vasquez A, Kereiakes DJ, et al. PreSERVE-AMI: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of Intracoronary Administration of Autologous CD34+ Cells in Patients With Left Ventricular Dysfunction Post STEMI. Circ Res. 2017;120(2):324-331.[32] Bruno S, Grange C, Collino F, et al. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33115. [33] Li T, Yan Y, Wang B, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(6):845-854.[34] Caradec J, Kharmate G, Hosseini-Beheshti E, et al. Reproducibility and efficiency of serum-derived exosome extraction methods. Clin Biochem. 2014;47(13-14): 1286-1292.[35] Diamandis EP. Mass spectrometry as a diagnostic and a cancer biomarker discovery tool: opportunities and potential limitations. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004;3(4):367-378.[36] Yamada T, Inoshima Y, Matsuda T, et al. Comparison of methods for isolating exosomes from bovine milk. J Vet Med Sci. 2012;74(11):1523-1525.[37] Arslan F, Lai RC, Smeets MB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;10(3):301-312.[38] Xu R, Greening DW, Zhu HJ, et al. Extracellular vesicle isolation and characterization: toward clinical application. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(4):1152-1162.[39] Witwer KW, Buzás EI, Bemis LT, et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013;2: 1-25.[40] Tauro BJ, Greening DW, Mathias RA, et al. Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods. 2012;56(2):293-304.[41] Chen TS, Arslan F, Yin Y, et al. Enabling a robust scalable manufacturing process for therapeutic exosomes through oncogenic immortalization of human ESC-derived MSCs. J Transl Med. 2011;9:47.[42] Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;Chapter 3: Unit 3.22.[43] Fong MY, Zhou W, Liu L, et al. Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17(2): 183-194.[44] Escudier B, Dorval T, Chaput N, et al. Vaccination of metastatic melanoma patients with autologous dendritic cell (DC) derived-exosomes: results of thefirst phase I clinical trial. J Transl Med. 2005;3(1):10.[45] Kukielka GL, Hawkins HK, Michael L, et al. Regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in ischemic and reperfused canine myocardium. J Clin Invest. 1993;92(3): 1504-1516.[46] Rieu S, Géminard C, Rabesandratana H, et al. Exosomes released during reticulocyte maturation bind to fibronectin via integrin alpha4beta1. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267(2):583-590.[47] Taylor DD, Zacharias W, Gercel-Taylor C. Exosome isolation for proteomic analyses and RNA profiling. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;728:235-246. |
| [1] | Li Xuan, Sun Yimin, Li Longbiao, Wang Zhenming, Yang Jing, Wang Chenglin, Ye Ling. Manufacturing of nano-modified polycaprolactone microspheres and its biological effects in dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1602-1608. |
| [2] | Liu Xiaogang, Li Tian, Zhang Duo. Effect and mechanism of the effective components of Chinese medicine on promoting the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 121-126. |
| [3] | Zhao Xu, Mao Xin, Li Chuntian, Wang Feng. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 132-137. |
| [4] | Shuai Zhiqin, Chen Jiameng, Liu Taotao, Hu Anling, Li Lisheng, Yu Limei, Xu Shangfu. Research status and problems of stem cells and their derived exosomes for prevention and treatment of vascular restenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 138-144. |
| [5] | Li Zhongkang, Zheng Jiahua, Tian Yanpeng, Huang Xianghua. Latest progress and mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells on premature ovarian failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 145-152. |
| [6] | Wang Shuyun, Xie Junhui, Yu Xuefeng. Effect and mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 153-158. |
| [7] | Lin Miaoyuan, Li Yuwan, Liu Yi, Chen Bei, Zhang Li. Research hotspots and application value of tissue-engineered skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 159-166. |
| [8] | Song Huifang, Tan Jiayin, Kang Yi, Li Bin, Bi Zhifei, Long Nü, Xia Zhongnian, Guo Rui. Hypoxic pretreatment enhances the protective effect of aged human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells conditioned medium against H9C2 oxidative stress damage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 1-6. |
| [9] | Xie Xingqi, Hu Wei, Tu Guanjun. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes combined with chondroitinase ABC for treating spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 20-26. |
| [10] | Zhang Xuelei, Luo Gan, Yu Shenghui, Gu Zuchao, Peng Xu, He Xueling, Liu Yan, Zhang Xiaomei. Acellular nerve scaffold combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich gel for femoral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 27-32. |
| [11] | Zhao Laihe, Xia Bing, Ma Teng, Gao Jianbo, Li Shengyou, Gao Xue, Zheng Yi, Hu Guangwen, Luo Zhuojing, Huang Jinghui. Extracellular matrix of Schwann-like cells induced by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes axonal regeneration after peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 33-39. |
| [12] | Mai Liping, He Guodong, Chen Shaoxian, Zhu Jiening, Hou Xinghua, Zhang Mengzhen, Li Xiaohong. Expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase 3B1 during human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells senescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 40-44. |
| [13] | Yang Tengyun, Li Yanlin, Liu Dejian, Wang Guoliang, Zheng Zhujun. Chondrogenic differentiation of peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells induced by transforming growth factor beta 3: a dose-effect relationship [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 45-51. |
| [14] | Huang Tao, Cheng Zhijian, Jia Zhiqiang, Zhao Xiaoguang, Wang Lei, Zhai Wenjing, Zhou Yongxin. Mechanism by which miR-146a regulates osteogenic differentiation of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 70-75. |
| [15] | Jing Jin, Zhao Shandi, Chen Long, Peng Shuanglin, Tang Hui, Guo Daijin, Zeng Xinyi, Xiao Jingang. Repair of calvarial defects in osteoporotic mice by adipose-derived stem cells combined with biphasic calcium phosphate ceramic scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 90-95. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||