Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Metabolomics applied in Chinese medicine syndromes: a bibliometric analysis
He Jing1, Sun Zhi-ling1, Xie Tong2, Jiao Wen-juan1, Zhang Yong-yi1
- 1College of Nursing, 2Institute of Chinese Medicine for Pediatrics, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2018-02-24Online:2018-06-08Published:2018-06-08 -
Contact:Sun Zhi-ling, M.D., Professor, College of Nursing, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:He Jing, Master candidate, College of Nursing, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81774383; the Research Innovation Project for the Academic Postgraduates in Colleges of Jiangsu Province, No. KYLX16-1164
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Jing1, Sun Zhi-ling1, Xie Tong2, Jiao Wen-juan1, Zhang Yong-yi1. Metabolomics applied in Chinese medicine syndromes: a bibliometric analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0195.
share this article

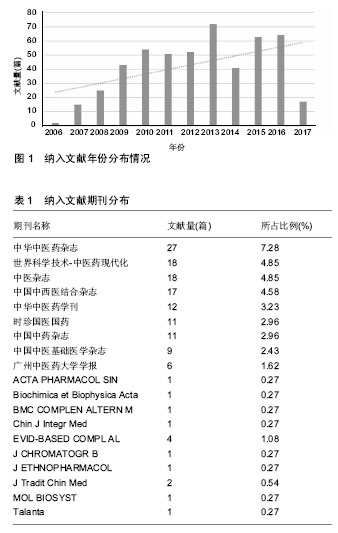
2.1 检索结果 共检索到文献3 012篇。去除重复的文献570篇;通过阅读文献题目及摘要,剔除与主题不相关文献1 880篇;阅读全文,剔除与代谢组学无关文献63篇;最终纳入文献499篇,其中中文文献485篇(97.19%),英文文献14篇(2.81%)。 2.2 纳入文献的基本特征 2.2.1 年份分布 由图1知,2013年发表文献最多,共72篇(14.43%);2006年发表文献最少,共2篇(0.4%)。从趋势图可知,中医证型研究领域应用代谢组学技术的研究不断增加,可预测2017年发文量应高于2016年。 2.2.2 文献类型分布 纳入文献中期刊文献371篇(74.35%),会议论文30篇(6.01%),学位论文98篇(19.64%)。"

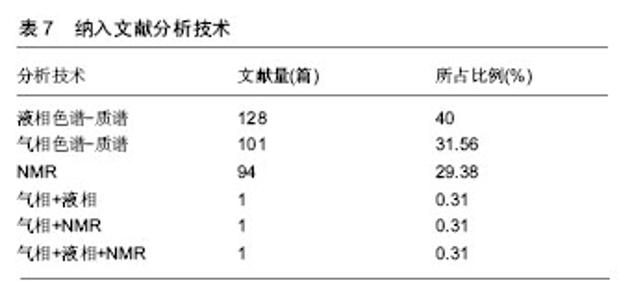
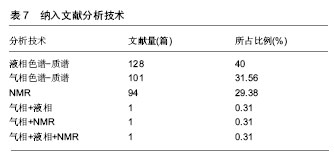
2.2.3 期刊分布 371篇关于代谢组学在中医证型研究领域应用的期刊文献共分布在124种期刊上,其中,发表相关文献1篇的期刊有70种,发表2篇的16种,发表3篇的8种,发表4篇的11种,发表5篇的4种,发表6篇及以上的仅14种。按2016版《北京大学核心期刊目录》筛查,中文核心期刊32种,载文量共168篇,占总文献量的45.28%;SCI期刊10种,载文量共14篇,占总文献量的3.77%(表1为中文核心期刊载文量6篇及以上和SCI期刊分布情况)。由此可见,目前相关文献期刊分布较为分散,集中度不高,而发表在核心期刊和SCI的文献较少,说明发表在高质量水平杂志的文献量有待提高。 2.2.4 第一作者单位 第一作者共分布于145个单位,主要分布在高校(321,64.33%)和医院(125,25.05%),高校中,发文量居首位的是南京中药大学,其次是山东中医药大学;医院中,发文量居首位的是上海中医药大学附属曙光医院,其次是天津中医药大学第二附属医院;发文量前10的单位中,高校占94.44%,医院占5.56%,说明高校在该领域是研究成果的主力军,详见表2,3。 2.2.5 基金资助 统计显示,371篇期刊文献中有312篇(84.10%)基金论文,按基金的级别,将其分为国家级、省级、市级,国家级基金资助217篇(69.55%),其中国家自然科学基金资助163篇(52.24%),可见国家级基金资助远远领先于其他级别基金资助的文献发表量;省级基金资助50篇(16.03%),市级基金资助26篇(8.33%),其中省市级基金资助主要分布在21个地区,排名进入前五的是江苏省(12篇),上海市(12篇),广东省(9篇),北京市(8篇),浙江省(8篇),以上数据反映了国家对代谢组学在中医证型研究领域应用的高度支持,预示这个领域将来的一段时间将是国家的重点资助方向。 2.3 纳入文献内容特征 2.3.1 文献研究类型 499篇纳入文献分为6类:综述、专家论坛、描述性研究:病例对照;实验性研究:多以动物实验为主,以探讨其机制;类实验性研究,主要对疾病的不同证型给予干预措施,以观察其代谢产物的差异性。具体见表4。 2.3.2 研究对象 纳入的文献中,研究对象主要分为临床患者(204,64.35%)和实验动物(113,35.65%),其中使用最多的实验动物是大鼠(95篇),占29.97%,详见表5。 2.3.3 实验内容分析 将本次纳入文献中采用干预措施且具体描述辨证分型的进行分析,有且仅有58篇(11.62%),统计分类得到7类病症系统,涉及23种疾病,39种干预措施,其中免疫系统疾病8篇,消化系统15篇,循环系统12篇,呼吸系统11篇,内分泌系统7篇,神经系统1篇,泌尿系统1篇,其它类3篇,包括原发性痛经(2篇)和恶性肿瘤(1篇),具体内容见表6。 2.4 代谢组学分析 2.4.1 样本 完整的代谢组学分析流程包括样本的制备、样本分析和数据的解析,而样本的制备则又包含了样本的采集和预处理,样本主要包含体液、粪便和组织。统计显示,在中医证型研究领域最常用的样本是血液和尿液,除此之外还有组织、关节液、唾液、粪便。纳入文献中,血液123篇(63.73%),其中血清59篇(30.57%),血浆64篇(32.43%);尿液63篇(32.64%);组织8篇(4.15%),其中滑膜组织2篇(1.04%),胸腺组织2篇(1.04%),肺组织2篇(1.04%),心肌组织1篇(0.52%),脾脏组织1篇(0.52%);关节液1篇(0.52%);唾液2篇(1.04%);粪便1篇(0.52%)。血清样本最多使用于高血压10篇(16.95%),其中肝火亢盛证4篇,痰湿雍盛证3篇,阴虚阳亢证3篇,痰热证1篇;血浆样本最常见于冠心病15篇(23.44%),其中气虚血瘀证3篇,气虚证2篇,"

| [1] Qi Q,Li C,Yong W,et al.Plasma metabonomics study on Chinese medicine syndrome evolution of heart failure rats caused by LAD ligation. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14(1):232-232. [2] Kang H,Zhao Y,Li C,et al.Integrating Clinical Indexes into Four-Diagnostic Information Contributes to the Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Syndrome Diagnosis of Chronic Hepatitis B. Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 23;5:9395[3] 孙安会,袁肇凯,夏世靖,等.中医证候系统生物学研究的现状和展望[J].中华中医药杂志, 2016,31(1):200-204.[4] Lu YY,Chen QL,Guan Y,et al.Study of ZHENG differentiation in hepatitis B-caused cirrhosis: a transcriptional profiling analysis. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:371. [5] 邱文琪,吴芊,宋明,等.宏基因组学与中医证候研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2017,32(9): 4186-4188.[6] 季青,陆奕宇,宋雅楠,等. 基于iTRAQ蛋白组学技术的大肠癌和肝癌术后肝肾阴虚证血浆差异表达蛋白的研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2017, 32(6):2626-2630.[7] Guo Z, Yu S, Guan Y, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Same TCM Syndrome for Different Diseases and Different TCM Syndrome for Same Disease in Chronic Hepatitis B and Liver Cirrhosis.Evid Based Complement Alternat . 2012;2012:120350[8] Klassen A,Faccio AT,Canuto GA,et al.Metabolomics: Definitions and Significance in Systems Biology.[M]//Metabolomics: From Fundamentals to Clinical Applications.Springer International Publishing, 2017.[9] Nielsen J.Systems Biology of Metabolism. Annual Review of Biochemistry.2017;86:245.[10] Paternain L,Campion J.Metabolomics and Transcriptomics of Metabolic Disorders.Current Nutrition Reports.2013;2(4):199-206.[11] 郭慧,崔扬,王秋红,等.基于代谢组学技术的中药复方研究近况[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017,23(1):213-219.[12] Jiang N,Liu HF,Li SD, et al. An integrated metabonomic and proteomic study on Kidney-Yin Deficiency Syndrome patients with diabetes mellitus in China. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015;36(6):689-698.[13] 刘石密,吴凝,万玲,等.代谢综合征痰浊郁阻证患者的血清代谢组学特征[J].中医杂志,2015, 56(23):2043-2048.[14] Lin H,Pi Z,Men L,et al.Uinary metabonomic study of Panax ginseng in deficiency of vital energy rat using ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;184:10-17.[15] 于静波,孙晖,韩越,等.代谢组学助力中医证候动物模型研究[J].中华中医药杂志, 2014,29(7):2259-2262.[16] Wang X, Sun H, Zhang A, et al. Potential role of metabolomics apporoaches in the area of traditional Chinese medicine: As pillars of the bridge between Chinese and Western medicine. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011;55(5):859-868.[17] 王阶,姚魁武,刘咏梅,等. 冠心病血瘀证转录组学研究——病证结合生物标志物研究思路与方法[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017,23(19):1-5.[18] Liu Y, Ai N, Liao J, et al. Transcriptomics: a sword to cut the Gordian knot of traditional Chinese medicine. Biomark Med. 2015;9(11): 1201-1213. [19] Jiang M, Zhang C, Zheng G, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine Zheng in the Era of Evidence-Based Medicine: A Literature Analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:409568.[20] Lu XY, Xu H, Li G, et al.Study on Correspondence between Prescription and Syndrome and the Essence of Phlegm and Blood Stasis Syndrome in Coronary Heart Disease Based on Metabonomics. Chin J Integr Med. 2014;20(1):68-71. [21] Wang X,Xie G,Wang X,et al.Urinary Metabolite Profiling Offers Potential for Differentiation of Liver-Kidney Yin Deficiency and Dampness-Heat Internal Smoldering Syndromes in Posthepatitis B Cirrhosis Patients. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:464969 [22] Lu C,Deng J,Li L,et al. Application of metabolomics on diagnosis and treatment of patients with psoriasis in traditional Chinese medicine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1844(1 Pt B):280-288.[23] 历凯,匡海学,殷越,等.痛泻要方对IBS模型血清内源性物质代谢干预的实验研究[J].中国中药杂志, 2017, 42(5):970-981.[24] Feng X, Yang Z, Chu Y, et al. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic study on efficacy of Qingrehuatan decoction against abundant phlegm-heat syndrome in young adults with essential hypertension. J Tradit Chin Med. 2015;35(1):28-35.[25] 陶嘉磊,汪受传,田曼,等.小儿支气管哮喘发作期证候学标记物的代谢组学研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志, 2017,37(3):319-325. [26] Wei H, Pasman W, Rubingh C, et al. Urine metabolomics combined with the personalized diagnosis guided by Chinese medicine reveals subtypes of pre-diabetes. Molecular Biosystems.2012;8(5):1482.[27] Nan Y, Zhou X, Liu Q, et al. Serum metabolomics strategy for understanding pharmacological effects of ShenQi pill acting on kidney yang deficiency syndrome.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.2016;1026:217-226.[28] Nunes de Paiva MJ, Menezes HC,de Lourdes Cardeal Z.Sampling and analysis of metabolomes in biological fluids.Analyst. 2014;139(15): 3683-3694.[29] 刘琦,赵宏伟,张爱华,等. 基于中医方证代谢组学研究男仕胶囊治疗肾阳虚证的药效物质基础及作用机制[J]. 中国中药杂志,2016,41(15): 2901-2914. [30] 王斯婷,李晓娜,王皎,等.代谢组学及其分析技术[J]. 药物分析杂志, 2010, 30(9):1792-1799.[31] 罗和古,岳广欣,陈家旭.代谢组学技术在中医证候研究中的应用探讨[C]中华中医药学会中医诊断学分会2007'年会,福建:2007. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [3] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [6] | Zheng Xiaolong, He Xiaoming, Gong Shuidi, Pang Fengxiang, Yang Fan, He Wei, Liu Shaojun, Wei Qiushi. Bone turnover characteristics in patients with alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 657-661. |
| [7] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [8] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [9] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [10] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [11] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [12] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [13] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [14] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [15] | Lu Yuyun, Huang Mei, Shi Xinlei, Chen Baoyan. Bibliometric and visualization analysis of breast cancer stem cell literature from 2011 to 2020 based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4001-4008. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||