Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (16): 2607-2612.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0225
Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristics and acute responses of eccentric exercise
Xu Zhi-yong1, Yin Xin2, Huang Qiang-nian3, Xu Sheng-jia3
- 1Jiangsu Vocational Institute of Commerce, Nanjing 211100, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Heath and Exercise Science, Nanjing Sport Institute, Nanjing 210014, Jiangsu Province, China; 3School of Basic Education for Commanding Officers, the PLA University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 211101, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2017-12-25Online:2018-06-08Published:2018-06-08 -
Contact:Xu Sheng-jia, School of Basic Education for Commanding Officers, the PLA University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 211101, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Xu Zhi-yong, Lecturer, Jiangsu Vocational Institute of Commerce, Nanjing 211100, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Advance Research Foundation of the PLA University of Science and Technology, No. KYJYZLXY1602-35
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Zhi-yong1, Yin Xin2, Huang Qiang-nian3, Xu Sheng-jia3. Characteristics and acute responses of eccentric exercise[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(16): 2607-2612.
share this article
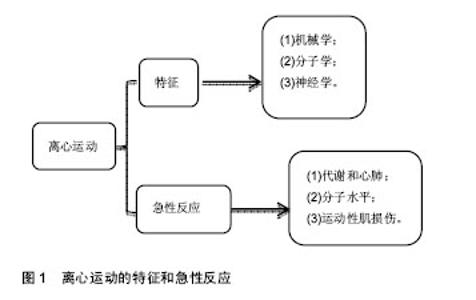
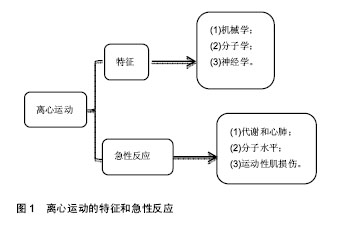
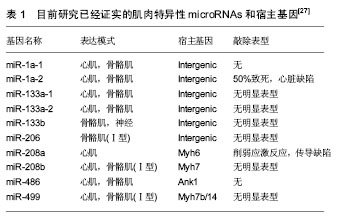
机械学特征:离心训练肌肉收缩的同时涉及到拉伸肌肉的动作;相反,向心训练肌肉收缩的同时肌肉被缩短。离心训练可以产生比肌肉向心训练或者等张训练更大的肌肉力量[1-2]。肌肉离心训练能够产生更大的力量可能是各种特殊性综合的结果,例如横桥移动过程中分子水平上的变化特殊的神经控制方式[3-4]。因此,在肌肉做离心运动的过程中,可能会给肌肉带来一个更高水平的机械学刺激,并且这个可能潜在的作用于离心训练方案后的骨骼肌机械学上的适应。 肌肉离心动作激活策略的特殊性可能主要因为其更大的肌肉输出。大脑皮质激活的更早,并且在肌肉离心动作过程中活动的更加剧烈[5],在一个相同的机械功率输出情况下,肌肉离心训练过程中股四头肌肌电信号的振幅要比等速向心运动和自行车运动要低[6]。因此,每一条肌纤维产生的张力和肌肉周围组织(如细胞外基质)产生的张力可能在离心运动中都比较高,由此导致了离心活动更多的肌肉输出。 分子学特征:肌肉收缩过程中,粗肌丝和细肌丝长度不变,肌纤维长度的变化是通过两者之间重叠程度增加实现的,也就是肌丝滑行学说。这个滑行力来自于两个肌丝重叠部分,肌球蛋白横桥结构,肌球蛋白朝向肌动蛋白上的结合位点重复的相互作用,每一次接触都产生移动的力量[7]。并且每一个横桥上的活动在一个肌节以致整个肌肉都是独立的,不受其他横桥上活动的影响,这样才可能使肌肉产生恒定的张力和连续的缩短,而且横桥激活的数目直接影响了肌张力和缩短的距离。这个过程有效的解释了向心和等长肌肉收缩动作。等长肌肉收缩时,肌肉长度不变,横桥与肌动蛋白的相互作用仍然存在,这时横桥与肌动蛋白自然分离,并被其他新的桥取代来维持横桥网络的形成,这样尽管缺少外部的身体活动,仍然能产生能量。上面是已建立经典的肌肉收缩理论,基于此理论有人进一步提出假设,在离心收缩时,横桥并未完成一次完整的横桥周期[8],它们在肌动蛋白边界变得高度活跃,在迅速接触肌动蛋白结合位点后立即被强行分离,这是因为完整的横桥周期没有完成,较少的ATP是维持力量的一个必要条件[9]。 神经学特征:与向心收缩相比,离心收缩过程中更少的运动单元被募集,并且放电率也更低[10-12]。皮质兴奋性在离心收缩过程中被加强,并且不被离心收缩的负重情况和较低的运动单位募集度影响[5,13]。这个过程的具体机制现在仍然不是很清楚,可能和运动皮质的输出量降低或来自外周神经的促进突触前抑制的增加有关[10]。 总之,现有的肌丝滑行理论很难解释离心收缩过程中产生的更大的肌力以及低能量消耗,结合横桥分离理论,可能有助于理解认识离心运动的诸多特性。相比于向心收缩和等长收缩,不论在最大收缩或次最大收缩情况下,离心收缩显示出独特的神经策略。这些差异可能主要与脊髓抑制的调停有关,需要更加精确的数据来证明。大强度的力量训练被有效用于降低最大离心收缩过程中的反射抑制,从而诱导改善神经肌肉活性和提高肌肉最大离心力量[14]。 2.2.2 离心运动的急性反应 代谢和心肺反应:肌肉离心动作机械学和代谢学的特异性已经在人和动物身上被研究。当进行相同的机械功输出的前提下,急性离心运动后的代谢和心肺反应与向心运动反应情况不同,运动过程中尤其要控制离心运动的训练负荷和强度。 在一个既定的机械功输出前提下,离心运动比向心运动代谢需求更低[15],并且相同的工作效率时,离心运动需要更少的运动单位参与[16]。其次,摄氧量在存在不同,进行速度为4.8 km/h的下坡走(坡度-5°至-15°),氧气消耗(VO2)要比相同速度下进行水平走或者上坡走的VO2要低[17]。并且在增加运动强度提高代谢需求的下坡跑实验中,在相同的、速度的前提下,下坡跑比上坡跑的VO2也要低四五倍[18]。这说明相比于向心运动,离心运动的能量消耗低,这也让离心运动更加适合运用于衰老人群的肌肉质量和力量恢复以及临床康复中[11,19]。尽管离心运动被认为是“节省能量”的,但是离心运动可能会增加运动后的安静状态下能量消耗,并在运动后 72 h仍然能够观察到此现象[20]。Gavin等[21]近期研究表明较低的肌糖原对运动型肌损伤后的代谢和心肺反应有影响,在下坡跑后12 h,较低的肌糖原组脂肪氧化率增加,并且减少了碳水化合物,表明损伤性的运动伴随糖原减少在之后的低强度离心运动后仅12 h便能够增加脂肪利用率。这表明离心运动独特的代谢反应和适应,运动后安静状态能量消耗增加可能和离心运动对肌肉刺激大导致运动后生物适应带来的表型变化有关,需要进一步证据证实以及机制的研究。 如果肌肉离心模式中机械功输出足够大的话(例如:功率自行车运动中肌肉离心活动是肌肉向心活动机械功输出的5倍,能够完成一次离心运动与向心运动相似的VO2。在这种特定的情况下,离心运动的心输出量(Q)和心率(HR)都比向心运动要高。在绝对摄氧量接近或高于1 L/min时,这个特性更加明显,肌肉离心活动的心输出量和心率分别比肌肉向心活动高了17%-27%[17]。这个现象对于运动训练强度和负荷的控制具有重要的影响,此外,一个既定的心率在离心和向心运动中对应不同水平的VO2。在相同心率情况下离心运动中的VO2会比向心运动中的VO2要低,这表明在相同的VO2下运动,离心运动需要比向心运动更高的心率[17]。 根据现有研究,离心运动的这些生理反应在自行车运动中更加明显,提示离心自行车运动可能是一个研究离心运动的理想模型,能够在保证大强度机械刺激的同时带来较低的代谢刺激。因此,需要根据肌肉工作不同类型和模式研究心率,以监控运动强度和训练负荷。 分子水平反应:已有研究表明运动能够激活卫星细胞,在运动性肌损伤后的肌肉修复过程以及随后的肥大适应过程中卫星细胞发挥了至关重要的作用[22]。卫星细胞是骨骼肌中位于肌细胞膜和基膜之间具有增殖分化潜力的肌源性细胞。Hyldahl等[23]研究发现当肌细胞受损后,卫星细胞能够增殖并到达受损肌细胞,参与到肌细胞重建和修复过程中,而且卫星细胞的激活可能与运动方式有关,最大离心力量训练能够诱发卫星细胞在运动后剧烈增殖,而在向心力量训练后却没有发生,这提示运动造成肌损伤过程中离心运动的部分可能是激活卫星细胞的主要因素。目前研究已经很好的证实了离心训练能够增加肌细胞核数量和卫星细胞含量[24]。在最大等速离心运动后24 h,卫星细胞含量从30%增加到150%,卫星细胞含量的大幅增加说明肌肉在受到最大离心运动刺激后需要更多卫星细胞的激活,从而满足肌肉重建和修复的急性需求。卫星细胞的增加还和肌纤维类型有关,在最大离心运动后发现卫星细胞活性在Ⅱ型肌纤维中显著增加,而在Ⅰ型肌纤维中却没有显著变 化[24]。另外有研究表明,卫星细胞激活的信号分子白细胞介素6(IL-6)在离心运动后急性期升高,而白细胞介素6在肌损伤急性免疫反应中发挥作用[25]。肌肉肥大是运动训练中关键的适应性反应,涉及到肌纤维蛋白合成的过程,而相比于最大向心运动,最大等速离心运动能够更多的诱发肌纤维蛋白迅速生成,并在接下来的恢复期形成肌肉肥大[26]。最近研究表明肌肉在生长和修复期间,卫星细胞和骨骼肌中的细胞外基质之间的相互作用在肌肉适应过程中发挥重要的作用,卫星细胞在激活时可通过自我更新或增殖产生肌原性祖细胞(MPCs),后者能够迁移到细胞外基质中,并能通过分泌含有microRNA-206的外泌体(exosome),抑制核糖体结合蛋白1抗体(Rrbp1)从而调节纤维形成细胞胶原表达,肌原性祖细胞在运动后肌肉肥大适应过程中发挥着防止细胞外基质的过度沉积、促进长期肌纤维肥大的重要作用,而microRNA-206在其中发挥重要的负调控作用[22]。目前已知的几种肌肉特异性的microRNAs(myomiRs)可能在离心运动生物适应过程中发挥重要的调控作用,见表1。"
| [1] Westing SH, Cresswell AG, Thorstensson A. Muscle activation during maximal voluntary eccentric and concentric knee extension. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1991;62(2):104-108.[2] Crenshaw AG, Karlsson S, Styf J, et al. Knee extension torque and intramuscular pressure of the vastus lateralis muscle during eccentric and concentric activities. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1995;70(1):13.[3] Brunelli S, Sciorati C, D'Antona G, et al. Nitric oxide release combined with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory activity prevents muscular dystrophy pathology and enhances stem cell therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(1):264.[4] Enoka RM. Eccentric contractions require unique activation strategies by the nervous system. J Appl Physiol. 1996;81(6): 2339-2346.[5] Fang Y, Siemionow V, Sahgal V, et al. Distinct brain activation patterns for human maximal voluntary eccentric and concentric muscle actions. Brain Res. 2004;1023(2):200-212.[6] Mchugh MP, Tyler TF, Greenberg SC, et al. Differences in activation patterns between eccentric and concentric quadriceps contractions. J Sports Sci. 2002;20(2):83-91.[7] Herzog W, Powers K, Johnston K, et al. A new paradigm for muscle contraction. Front Physiol. 2015;6:174.[8] Linari M, Bottinelli R, Pellegrino MA, et al. The mechanism of the force response to stretch in human skinned muscle fibres with different myosin isoforms. J Physiol. 2004;554(2):335-352.[9] Huxley AF. Biological motors: energy storage in myosin molecules. Curr Biol. 1998;8(14):R485.[10] Duchateau J, Enoka RM. Neural control of lengthening contractions. J Exp Biol. 2016;219:197-204. [11] Hoppeler H. Eccentric exercise: physiology and application in sport and rehabilitation. Routledge. 2014.[12] Aagaard P, Simonsen EB, Andersen JL, et al. Neural inhibition during maximal eccentric and concentric quadriceps contraction: effects of resistance training. J Appl Physiol. 2000;89(6): 2249-2257.[13] Sekiguchi H, Nakazawa K, Suzuki S. Differences in recruitment properties of the corticospinal pathway between lengthening and shortening contractions in human soleus muscle. Brain Res. 2003; 977(2):169-179.[14] Nardone A, Romanò C, Schieppati M. Selective recruitment of high-threshold human motor units during voluntary isotonic lengthening of active muscles. J Physiol. 1989;409(1):451. [15] Peñailillo L, Blazevich A, Numazawa H, et al. Metabolic and muscle damage profiles of concentric versus repeated eccentric cycling. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013;45(9):1773-1781.[16] Perrey S, Betik A, Candau R, et al. Comparison of oxygen uptake kinetics during concentric and eccentric cycle exercise. J Appl Physiol. 2001;91(5):2135-2142.[17] Navalta JW. Physiological responses to downhill walking in older and younger individuals. J Exer Physiol. 2004;7(6):45-51. [18] Minetti AE, Moia C. Roi GS, et al. Energy cost of walking and running at extreme uphill and downhill slopes. J Appl Physiol. 2002;93(3):1039-1046.[19] Mitchell WK, Taivassalo T, Narici MV, et al. Eccentric Exercise and the Critically Ill Patient. Front Physiol. 2017;8:120.[20] Hackney KJ, Engels HJ, Gretebeck RJ. Resting energy expenditure and delayed-onset muscle soreness after full-body resistance training with an eccentric concentration. J Strength Cond Res. 2008;22(5):1602.[21] Gavin JP, Myers SD, Willems ME. Cardiorespiratory and metabolic responses after exercise-induced muscle damage: the influence of lowered glycogen. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2016.[22] Fry CS, Kirby TJ, Kosmac K, et al. Myogenic progenitor cells control extracellular matrix production by fibroblasts during skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;20:56-69.[23] Hyldahl RD, Olson T, Welling T, et al. Satellite cell activity is differentially affected by contraction mode in human muscle following a work-matched bout of exercise. Front Physiol. 2014; 5:485.[24] Cermak NM, Snijders T, Mckay BR, et al. Eccentric exercise increases satellite cell content in type II muscle fibers. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013;45(2):230.[25] Willoughby DS, Mcfarlin BC. Interleukin-6 expression after repeated bouts of eccentric exercise. Int J Sports Med. 2003; 24(1):15.[26] Eliasson J, Elfegoun T, Nilsson J, et al. Maximal lengthening contractions increase p70 S6 kinase phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle in the absence of nutritional supply. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006;291(6):E1197.[27] Kirby Tyler J, McCarthy John J. MicroRNAs in skeletal muscle biology and exercise adaptation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;64: 95-105.[28] Fridén J, Lieber RL. Structural and mechanical basis of exercise-induced muscle injury. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1992; 24(5):521.[29] Bonde-Petersen F, Knuttgen HG, Henriksson J. Muscle metabolism during exercise with concentric and eccentric contractions. J Appl Physiol. 1972;33(6):792-795.[30] 董贵俊,吕晨曦,葛新发,等.一次和重复大强度离心运动前后大鼠骨骼肌超微结构变化[J].中国运动医学杂志,2013,32(2):142-148. [31] 刘向东,李阳.一次力竭性离心运动损伤模型大鼠骨骼肌波形蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(18):2880-2885.[32] McHugh MP, Tetro DT. Changes in the relationship between joint angle and torque production associated with the repeated bout effect. J Sports Sci. 2003;21(11):927-932.[33] Murayama M, Nosaka K, Yoneda T, et al. Changes in hardness of the human elbow flexor muscles after eccentric exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 2000;82(5):361.[34] Tee JC, Bosch AN, Lambert MI. Metabolic consequences of exercise-induced muscle damage. Sports Med. 2007;37(10):827.[35] Dartnall TJ, Nordstrom MA, Semmler JG. Adaptations in biceps brachii motor unit activity after repeated bouts of eccentric exercise in elbow flexor muscles. J Neurophysiol. 2011;105(3): 1225-1235.[36] Eston RG, Lemmey AB, Mchugh P, et al. Effect of stride length on symptoms of exercise-induced muscle damage during a repeated bout of downhill running. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2000;10(4): 199-204.[37] Sayers SP, Clarkson PM. Short-term immobilization after eccentric exercise. Part II: creatine kinase and myoglobin. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2003;35(5):762.[38] Telley IA, Stehle R, Ranatunga KW, et al. Dynamic behaviour of half‐sarcomeres during and after stretch in activated rabbit psoas myofibrils: sarcomere asymmetry but no sarcomere popping. J Physiol. 2006;573(1):173-185.[39] Allen DG, Whitehead NP,Yeung EW. Mechanisms of stretch-induced muscle damage in normal and dystrophic muscle: role of ionic changes. J Physiol. 2005;567(3):723-735.[40] Butterfield TA. Eccentric exercise in vivo: strain-induced muscle damage and adaptation in a stable system. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2010;38(38):51-60.[41] Gomez-Cabrera MC, Domenech E, Viña J. Moderate exercise is an antioxidant: upregulation of antioxidant genes by training. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008;44(2):126-131.[42] Proske U, Morgan DL. Muscle damage from eccentric exercise: mechanism, mechanical signs, adaptation and clinical applications. J Physiol. 2001;537(2):333-345.[43] Fridén J, Lieber RL. Segmental muscle fiber lesions after repetitive eccentric contractions. Cell Tissue Res. 1998;293(1): 165-171.[44] Sorichter S, Mair J, Koller A, et al. Creatine kinase, myosin heavy chains and magnetic resonance imaging after eccentric exercise. J Sports Sci. 2001;19(9):687.[45] Brancaccio P, Lippi GN. Biochemical markers of muscular damage. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2010;48(6):757.[46] Chapman DW, Simpson JA, Iscoe S, et al. Changes in serum fast and slow skeletal troponin I concentration following maximal eccentric contractions. J Sci Med Sport. 2013;16(1):82-85.[47] Hyldahl RD, Chen TC, and Nosaka K. Mechanisms and mediators of the skeletal muscle repeated bout effect. Exerc Sport Sci. 2017; 45:24-33.[48] Howatson G, Van SK, Hortobágyi T. Repeated bout effect after maximal eccentric exercise. Int J Sports Med. 2007;28(7): 557-563.[49] Nosaka K, Clarkson PM. Muscle damage following repeated bouts of high force eccentric exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1995;27(9):1263-1269.[50] Starbuck C, Eston RG. Exercise-induced muscle damage and the repeated bout effect: evidence for cross transfer. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(3):1005-1013.[51] Lapier TK, Burton HW, Almon R, et al. Alterations in intramuscular connective tissue after limb casting affect contraction-induced muscle injury. J Appl Physiol. 1995;78(3):1065-1069.[52] Lastayo PC, Ewy GA, Pierotti DD, et al. The positive effects of negative work: increased muscle strength and decreased fall risk in a frail elderly population. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2003; 58(5):M419.[53] Lastayo PC, Pierotti DJ, Pifer J, et al. Eccentric ergometry: increases in locomotor muscle size and strength at low training intensities. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2000;278(5): R1282.[54] Ingham SA, van Someren KA, Howatson G. Effect of a concentric warm-up exercise on eccentrically induced soreness and loss of function of the elbow flexor muscles. J Sports Sci. 2010;28(13): 1377-1382. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Bai Shengchao, Gao Yang, Wang Bo, Li Junping, Wang Ruiyuan. Dynamic changes of mitochondrial function of the skeletal muscle after acupuncture intervention in rats with heavy load exercise-induced injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3648-3653. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||