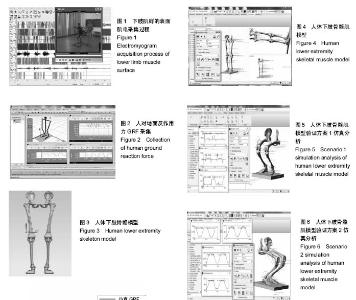
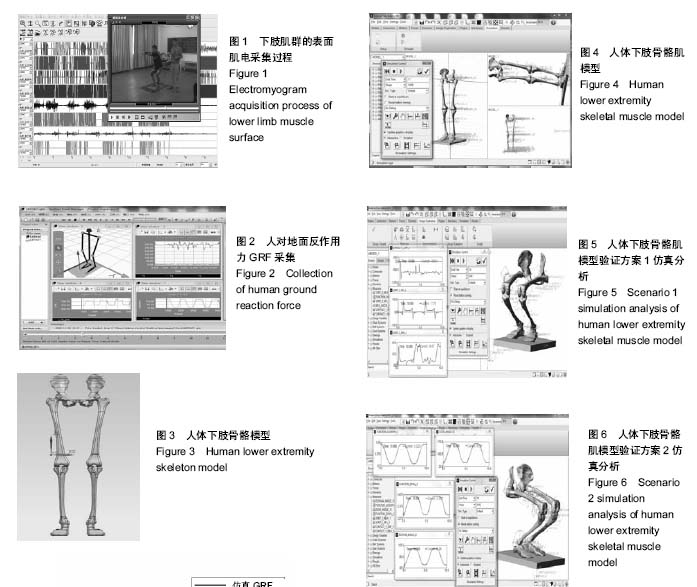
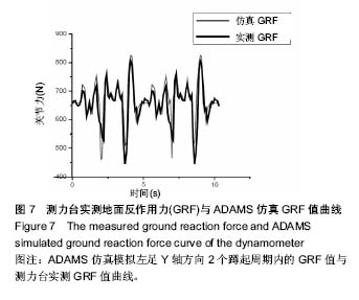
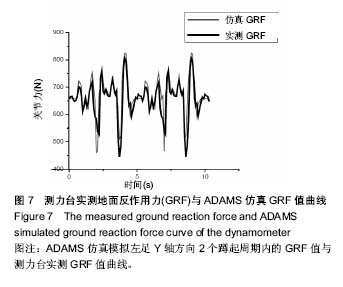
| [1] 郑海华,贺继林,赵喻明,等. 基于ADAMS的移动机器人避障仿真研究[J].计算机仿真,2014, 31(5): 336-341.[2] 朱昌义. 单杠上人体摆动的凯恩动力学模型[J].成都体育学院学报, 2000,26(6):71-74.[3] 郑秀缓,贾书惠,高云峰,等. 现代运动生物力学[M]. 2版.北京:北京国防工业出版社,2007:148-150.[4] 张莹,李志俊. 骨骼肌肉建模及其仿真[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2009, 9(10):1865-1868.[5] 张彦龙,陈民盛. 基于ADAMS人体下肢建模关节力的计算——兼与测力台比较[J].天津体育学院学报, 2015,30(2): 169-174.[6] 张彦龙,陈民盛. 太极拳典型动作与行走、广场舞、慢跑运动的膝关节动力学的仿真比较分析[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2015,38(06): 82-88.[7] 李增刚.ADAMS入门详解与实例[M].北京:北京国防工业出版社, 2012:19-22.[8] 尚鹏,叶铭,王成焘,等. 基于CT&MRI的人体下肢肌肉-骨骼数字化模型[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2004,21(5):756-760.[9] 姜丽,李世明,周博,等.递增负重下人体膝关节控制肌群肌电变化特征的个案研究[J].鲁东大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 29(4): 371-376.[10] Li J, Cheng Q, Liang H, et al. The motion simulation of human lower extremity based on dynamics[C]// Asian-Pacific Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering.2008:151-154.[11] 刘细阳. 人体足底压力分布特征的建模与仿真[J]. 计算机仿真, 2016, 33(06): 321-324.[12] 方奥,郑敏. 基于反求工程的人体下肢骨骼的三维重建[J].制造业自动化, 2014,36(2):57-60.[13] 姜丽.递增负重人体下肢关节力矩与sEMG关系的研究[D].烟台:鲁东大学, 2014.[14] Kadaba MP, Ramakrishnan HK, Wootten ME, et al. Repeatability of kinematic, kinetic and electromyographic data in normal adult gait.Orthop Res.1989;7(6):849-860. [15] 魏高峰,田丰,唐刚,等.基于超级计算人体骨骼肌系统弯腰搬物整体有限元的建模与仿真[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(30):5539-5542.[16] 唐刚,王洪生,张希安,等.基于反向动力学的人体肌肉力预测平台[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(35):6475-6478.[17] 谭景旺,吴雪萍.全身振动训练对老年人下肢功能和慢性疾病影响的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(08):1288-1293.[18] 吕屏,杨鹏飞,李旭.基于VR技术的虚拟博物馆交互设计[J].包装工程, 2017,38(24):137-141.[19] 闫静怡,夏岩石.基于VR技术的图书馆资源重建[J].现代电子技术, 2017,40(24):12-14.[20] 崔仁争,周美芳.VR技术在体育中的应用现况调查研究[J].当代体育科技,2017,7(32):156+158.[21] 李榕玲,张悦.基于VR技术的家居陈列方法研究[J].现代电子技术, 2017,40(22):95-97+100.[22] 何高奇,郁明强,蒋正清,等.基于VR火灾逃生游戏的应急行为评估系统[J].系统仿真学报,2017,29(11):2796-2803+2810.[23] 张伟.基于VR的健美操仿真系统设计关键技术[J].电子设计工程, 2015,23(19):83-84+88.[24] 李涛涛,方雄兵,林锐等.基于Top-down建模机制的三维虚拟人快速建模方法[J].中国舰船研究,2017,12(01):38-44.[25] 林洪,陈一平,贾渠,等.运动平衡能力陆上训练测试器材的研制[J].体育科学,2015,35(11):61-66+96.[26] 吴超宇,钱小吾,余伟,等.直线驱动型并联机器人反向动力学分析与验证[J].农业机械学报,2017,48(12):412-420.[27] 申浩宇,吴洪涛,陈柏.多自由度串联机器人的高效率反向动力学建模方法[J].中国机械工程,2016,27(1):20-24.[28] 刘芳华,吴洪涛,周波,方喜峰.基于旋量与模态分析理论的多柔体系统反向动力学仿真[J].机械科学与技术,2013,32(9):1337-1341.[29] 张争辉. 人体上肢骨肌建模及肌肉力预测方法研究[D].天津大学, 2013.[30] 张竟,韩旭,文桂林.基于ADAMS.LifeMOD的人体头颈部动力学仿真与验证[J].系统仿真学报,2008,20(10):2718-2721 |