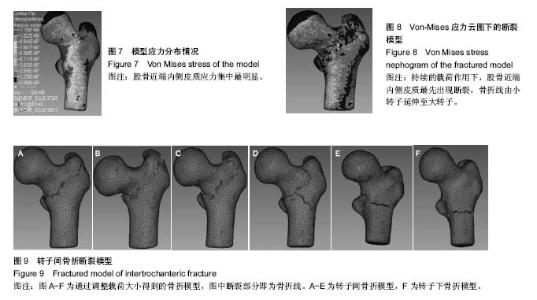
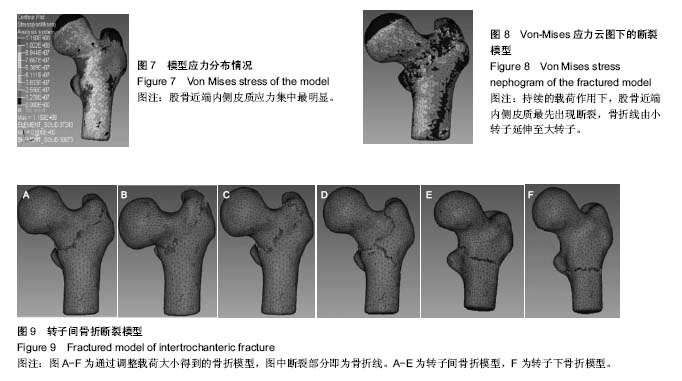
| [1] Hernlund E,Svedbom A,Ivergård M, et al.Osteoporosis in the European Union: Medical Management, Epidemiology and Economic Burden. A Report Prepared in Collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA).Arch Osteoporos. 2013;8:136.[2] Stevens JA, Rudd RA. The impact of decreasing U.S. hip fracture rates on future hip fracture estimates.Osteoporos Int.2013; 24(10):2725-2728.[3] Kannus P,Parkkari J,Sievanen H,et al.Vuori I,Järvinen M: Epidemiology of hip fractures.Bone.1996;18(1):S57-S63.[4] Herrera A,Martínez AA,Ferrández L,Moreno A: Epidemiology of osteoporotic hip fractures in Spain.Int Orthop. 2006;30(1):11-14. [5] Johnell O,Kanis JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures.Osteoporos Int. 2006;17(12):1726-1733.[6] Bessette L,Jean S,Lapointe-Garant MP,et al.Direct medical costs attributable to peripheral fractures in Canadian post-menopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23:1757-1768. [7] Bass E, French DD, Bradham DD, et al. Risk-adjusted mortality rates of elderly veterans with hip fractures.Ann Epidemiol. 2007;17(7) : 514-519.[8] 王凯.三维有限元分析在骨科中的应用[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2013,10(1):31-34.[9] López E, Ibarz E, Herrera A, et al. A mechanical model for predicting the probability of osteoporotic hip fractures based in DXA measurements and finite element simulation. Biomed Eng Online. 2012;11:84. [10] 贺洪辉,侯威.不同内固定方法治疗不稳定型粗隆间骨折的有限元分析[J]. 现代医药卫生,2015,31(24):3700-3703.[11] 吴锋,叶劲,邹仲兵.两种不同方式固定EvansⅢ型股骨粗隆间骨折稳定性的有限元分析[J].中国现代药物应用,2015, 9(17):7-8.[12] 周筑宝,卢楚芬.连续损伤力学的几个基本问题[J].湘潭大学自然科学学报,1989, 7(4):24-33.[13] 刘泉声,魏莱,刘学伟,等.基于Griffith强度理论的岩石裂纹起裂经验预测方法研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2017,36(7):1561-1569.[14] 朱俊.基于有限元方法对骨质疏松的研究[D]. 哈尔滨工业大学硕士论文, 2013.[15] Seref-Ferlengez Z, Kennedy OD, Schaffler MB. Bone microdamage, remodeling and bone fragility: how much damage is too much damage. Bonekey Rep. 2015;4: 644.[16] 戴如春,石泽梅,李瑾.骨微损伤累积与修复[J].药品评价,2015,12(15): 13-15+21.[17] 任学平,杨松涛.基于LS-DYNA和HyperMesh的转炉倾动机构减速器不同步启动仿真[J].机械传动,2015, 39(6):88-92.[18] 钟尖,刘唐志,陈柳晓.基于Hypermesh/Ls-Dyna的油桶拦挡安全性能与适用条件研究[J].武汉理工大学学报,2015, 37(10):51-56.[19] 李鹏飞,杜根发,林梓凌,等.基于LS-DYNA模拟老年股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(44): 6606-6611.[20] Bessho M, Ohnishi I, Okazaki H, et al.Prediction of the strength and fracture location of the femoral neck by CT-based finite-element method: a preliminary study on patients with hip fracture. J Orthop Sci. 2004;9(6):545-550.[21] 陈振沅.股骨转子部骨折六部分骨折分型产生机制的有限元分析[D].遵义医学院,2015.[22] 姜自伟,虎群盛,黄枫,等.PFNA-Ⅱ治疗不稳定型股骨转子间骨折的动态有限元研究[J].山东医药,2016, 56(33):14-17.[23] 冯卫,郝廷,郝增涛,等.三种股骨近端髓内钉固定股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(8):730-733.[24] 王磊,陆钦,王黎明,等.成人股骨粗隆间骨折PFNA内固定的有限元分析[J]. 西南国防医药,2015,25(6):657-659.[25] 林梓凌,李鹏飞,庞智晖,等.骨密度与老年髋部骨折股骨近端三维有限元模型密度的关系[J].中国老年学杂志,2015, 35(11):3069-3070.[26] 彭睿.行人在汽车碰撞事故中下肢骨折的有限元仿真研究[D].湖南大学, 2006.[27] 李平.不同跌倒姿势与髋部应力变化关系的有限元分析[D].广州中医药大学,2014.[28] 付鑫,马信龙,马剑雄,等.应用三维有限元分析正常站立位股骨近端结构生物力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(52): 10241-10246.[29] 汪金平,杨天府,钟凤林,等.股骨生物力学特性的有限元分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(10):931-933.[30] 黄梦全,余斌,林春秀,等.有限元法分析后内侧骨折对近端股骨的力学影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010, 18(4):294-296.[31] Lin PC,Chang SY.Functional recovery among elderly people one year after hip fracture surgery.J Nursres. 2004;12(1):72-82.[32] 李意,李新志.股骨粗隆间骨折内固定手术治疗的研究进展[J].重庆医学, 2013, 42(10):1172-1175.[33] 刘存欢,张建华.股骨转子间骨折治疗的研究进展[J].中医药临床杂志, 2015, 27(11):1627-1630.[34] [Cole RE.Clinical strategies to address patients’ concerns in osteoporosis management with bisphosphonates. Postgrad Med. 2011;123(2):131-144.[35] Hughson J,Newman J,Pendleton RC.Hip fracture management for the hospital-based clinician:a review of the evidence and best practices Hosp Prac. Hosp Pract(1995). 2011;39(1):52-61.[36] 王磊,陆钦,王黎明,等.成人股骨粗隆间骨折PFNA内固定的有限元分析[J]. 西南国防医药,2015, 25(6):657-659.[37] 窦庆寅,张美超.股骨三维有限元模型三种钢板内应力分布曲线分析[J].现代医学,2016, 44(12):1654-1659.[38] Luo Y, Ferdous Z, Leslie WD. Precision study of DXA-based patient-speci?c ?nite element modeling for assessing hip fracture risk. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2013;29(5):615-629. [39] Hambli R, Allaoui S. A robust 3D finite element simulation of human proximal femur progressive fracture under stance load with experimental validation.Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(12):2515-27.[40] 何祥鑫,李鹏飞,林梓凌,等.基于有限元分析法的老年粗隆间骨折建模仿真[J]. 中国医药导报,2017,14(24):88-91+195. [41] Brekelmans WA, Poort HW, Slooff TJ. A new method to analyze the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts.Acta Ortho Scand. 1972;43: 301.[42] 方驰华,周五一,黄立伟,等.虚拟中国人女性一号肝脏图像三维重建和虚拟手术的切割[J].中华外科杂志,2005, 43(11):748-752.[43] 刘文军,钟世镇.虚拟中国人女性一号松质骨图像数据的配准与三维重建[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2004, 22(4):380-383.[44] 张建国,芦俊鹏,阮世捷,等.以头部为例的人体有限元几何重建的方法初步探讨[J].微机计算机信息(管控一体化), 2006,22(22):249-252.[45] 张国栋,廖维靖,陶圣祥,等.股骨有限元分析赋材料属性的方法[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(43):8436-8441.[46] 袁高翔,张伟滨.有限元分析在骨骼肌肉系统模型材料特性研究中的应用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(6):352-355. |