Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (34): 5528-5535.doi: 10.12307/2024.801
Previous Articles Next Articles
Molecular mechanism of naringin in prevention and treatment of osteoporosis
Wang Wenchi1, 2, Wu Ruiqi1, 2, Huang Jierong1, 2, Zhu Lifeng1, 2, Cui Xianqin1, 2, Li Dongzong1, 2, Chen Wenhui3, Lin Chunting2, Cui wei1
- 1Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China;3The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-11-21Accepted:2024-01-05Online:2024-12-08Published:2024-03-14 -
Contact:Cui Wei, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Wenchi, Master candidate, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82360869 (to CWH); Guangxi Key Research & Development Program, No. AB20159026 (to CWH); Self-funded Scientific Research Project of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. GZC2020041(to LCT [project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Wenchi, Wu Ruiqi, Huang Jierong, Zhu Lifeng, Cui Xianqin, Li Dongzong, Chen Wenhui, Lin Chunting, Cui wei. Molecular mechanism of naringin in prevention and treatment of osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5528-5535.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
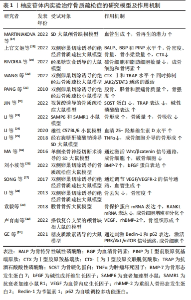
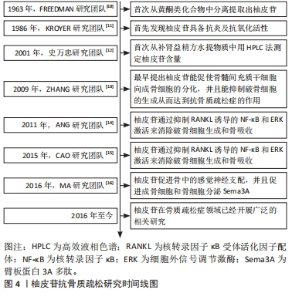
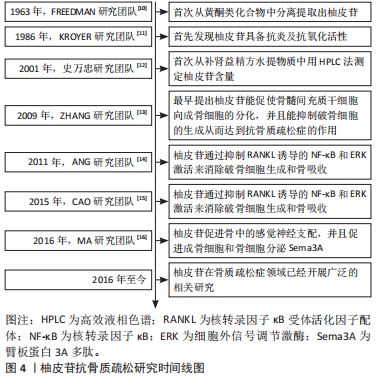
2.2 柚皮苷抗骨质疏松的体内实验研究 MARTINIAKOVA等[17]研究发现在颅骨缺损的雄性SD大鼠中,柚皮苷(100,500,1 000 μmol/L)呈浓度正相关性的增加毛细血管数量和骨再生,经苏木精-伊红染色可以观察到大量的毛细血管和新骨,表明柚皮苷在严重骨缺损模型中具有增强血管生成和骨再生的潜力,从而发挥抗骨质疏松症的作用。此外,上官文姬等[18]在双侧卵巢切除的雌性SD大鼠中,术后第3天开始每日以200 mg/kg柚皮苷灌胃处理,持续3个月,发现双侧卵巢切除大鼠经相同剂量柚皮苷治疗后,骨形成标志物骨特异性碱性磷酸酶、血清骨钙素和Ⅰ型前胶原氨基端原肽(typeⅠprocollagen amino terminal peptide,PINP)水平升高,而Ⅰ型胶原羧基端肽(typeⅠcollagen carboxy terminal peptide,CTX-Ⅰ)水平降低,同时骨密度升高,骨小梁数量显著增加,表明柚皮苷具有抑制双侧卵巢切除大鼠骨质流失的作用,因此可发挥抗骨质疏松症的功效。然而,RIVOIRA等[19]研究发现在经富含果糖饮食诱导的大鼠中,在10 mg/kg柚皮苷作用下不能恢复骨钙素水平,但40,80 mg/kg柚皮苷干预后都得到了正常的循环骨钙素值,抗酒石酸抗性酸性磷酸(tartaric acid resistant acid phosphatase,TRAP)染色显示,柚皮苷抑制了由果糖饮食所致的破骨细胞和脂肪细胞数量的增加以及骨细胞和骨钙素(+)细胞数量的减少,从而达到抗骨质疏松的作用。与此同时,WANG等[20]研究发现在双侧卵巢切除诱导的绝经后骨质疏松大鼠中,每天口服柚皮苷(300 mg/kg)持续5周后,苏木精-伊红染色结果显示绝经后骨质疏松组软骨下小梁骨体积减少,经柚皮苷治疗后受损的小梁骨得以恢复;在另一方面用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测骨钙素、CTX-Ⅰ和TRAP的水平,并测定了大鼠血清中碱性磷酸酶酶活性,结果表明双侧卵巢切除诱导了大鼠骨代谢异常,而柚皮苷[300 mg/(kg·d)]治疗部分恢复了绝经后骨质疏松大鼠降低的骨钙素水平和碱性磷酸酶活性,并增加的CTX-Ⅰ和TRAP水平,总之,柚皮苷改善了绝经后骨质疏松大鼠异常骨代谢,而达到抗骨质疏松的作用,其机制与体内抑制JAK2/STAT3通路的激活有关。另一方面,PANG等[21]研究发现在双侧卵巢切除的雌性小鼠模型中,在柚皮苷治疗[200,400 mg/(kg·d),持续6周]后,双侧卵巢切除小鼠的股骨、胫骨和腰痛骨质量增强,尿钙排泄减少,进而实现抗骨质疏松症作用。JIN等[22]通过研究发现在视黄酸诱导的骨质疏松大鼠中,每天皮下注射柚皮苷(50 mg/kg),持续30 d,通过减弱了骨质疏松大鼠骨硬化蛋白(osteosclerotic protein,SOST)的蛋白表达、抑制了TRAP的表达、增强了碱性磷酸酶的蛋白表达,表明柚皮苷减轻了视黄酸诱导的大鼠骨质疏松症并且抑制骨质疏松股骨和胫骨的骨吸收。此外,LI等[23]研究发现,在雄性无特定病原体衰老加速小鼠(aging accelerated mice,SAMP6)和SPF水平的骨质疏松症和抗衰老加速小鼠R1(anti aging accelerated mice,SAMR1)中,口服柚皮苷500 mg/kg,每日2次,连续4周,结果表明经柚皮苷治疗后骨吸收受到抑制,骨形成和骨质量得到增强,从而证实了柚皮苷具有抗骨质疏松的作用。此外,近年来在另一项新的实验研究中发现,在雄性C57BL/6小鼠中,通过灌胃方式口服含有柚皮苷和淫羊藿苷的中药复方骨舒康(0.38 g/kg),治疗60 d后,老年小鼠血清25-羟基维生素D水平显著升高,表明骨舒康可改善老年小鼠的钙平衡,从而达到抗骨质疏松症作用[24]。在右旋糖酐硫酸钠诱导SD大鼠中,在第2周每日口服柚皮苷(100,200 mg/kg),共5周(每周5次),结果表明柚皮苷干预对地塞米松处理的炎症性肠病大白鼠的骨丢失具有保护作用,并且观察到骨形成指数增加,特别是200 mg/kg剂量时,其保护作用可能是对肿瘤坏死因子α的抑制作用的结果,也可能是通过阻断氧化应激促进成骨细胞介导的骨形成,从而发挥抗骨质疏松症的作用[25]。 MA等[16]研究发现在单侧坐骨神经切断术诱导的雄性SD大鼠中,用柚皮苷(30,100,300 mg/kg)灌胃处理,骨钙素和TRAP的组织学染色所示,柚皮苷呈浓度依赖性的增加了骨形成,但抑制了骨吸收,尤其是300 mg/kg柚皮苷组,而且柚皮苷促进成骨细胞和骨细胞分泌臂板蛋白3A多肽(arm plate protein 3A peptide,Sema3A)。增加Sema3A通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号,可以在局部增强成骨细胞骨的形成,同时抑制破骨细胞生成;柚皮苷直接参与激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,从而诱导成骨细胞分化,柚皮苷促进骨中的感觉神经支配,这可能是由Sema3A介导的。刘小坡等[26]研究表明在双侧卵巢联合股骨中端1/3处横行截骨的绝经后骨质疏松大鼠中,予灌胃柚皮苷处理,连续干预4周,经苏木精-伊红染色显示大鼠股骨组织病变得到明显改善,骨小梁数量明显增加。并且出现较多的成熟小梁状骨;在另一方面大鼠股骨组织BMP-7、碱性成纤维生长因子(basic fibroblast growth factor,bFGF)蛋白相对表达量均高于模型组,促进新骨形成,改善大鼠骨质疏松性骨折。SONG等[27]研究发现在切除双侧卵巢及其包膜和部分输卵管的SD大鼠中,通过鼻胃导管用柚皮苷[40,100,300 mg/(kg·d)]治疗,结果表明柚皮苷具有更高的通过血管生成治疗骨质疏松性骨折的能力,300 mg/(kg·d)效果最为显著,其具体机制可能是通过调控VEGF/VEGFR-2的信号通路促进血管的生成,从而达到治疗骨质疏松的作用。LI等[28]研究发现在双侧卵巢切除 SD大鼠中,分别以60,300和1 500 mg/kg柚皮苷灌胃,结果表明柚皮苷可有效抑制双侧卵巢切除诱导的骨丢失,并增加骨密度、骨体积和小梁厚度,中等剂量(300 mg/kg)为最佳剂量。袁毅等[29]在建立大鼠股骨骨折动物模型中,经柚皮苷灌胃100 mg/(kg·d),2次/d,在此浓度下,柚皮苷能够有效刺激大鼠骨折部位形成大量连续性骨痂,导致骨折线逐渐消失,并显著提高骨折端的骨矿物质含量和骨体积;组织学研究的结果表明,柚皮苷显著促进了成骨细胞的增殖和分化,从而加速了骨折的愈合过程。 此外,柚皮苷还能提高骨折组织中骨保护蛋白mRNA的表达,并抑制RANKL mRNA的表达。其作用机制涉及激活骨保护蛋白/RANKL/RANK信号通路,促进骨折的愈合,进而实现抗骨质疏松症的效果。卢育南等[30]的研究采用柚皮苷、壳聚糖和羟基磷灰石的混合物制作了一种复合支架,用于填充大鼠颅骨缺损,结果显示该复合支架能有效促进骨折新生骨的生成和骨缺损区域的良好修复;同时,该复合支架还增加了成簇的成骨细胞和骨小梁的数量。值得注意的是,柚皮苷-壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石展现出了卓越的组织相容性,其机制为柚皮苷通过激活VEGF和rhBMP-2的生成,加速新生骨组织的形成,这表明柚皮苷-壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石复合支架是一种有效的骨缺损修复工具,通过促进新生骨组织的生成,更好地发挥了抗骨质疏松症作用。GE等[31]研究团队在糖皮质激素诱导的大鼠模型中,柚皮苷可以刺激苄氯素1(benzyl chloride 1,Beclin-1)和自噬调控多功能蛋白p62等自噬相关因子的表达,诱导成骨细胞自噬;此外,随着柚皮苷剂量的增加,成骨细胞的增殖、分化能力增加,并同时检测细胞内p-PI3k,p-AKT及p-mTOR mRNA和蛋白的表达,表明柚皮苷通过激活PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路发挥抗骨质疏松症作用。 通过对上述文献的研究发现,就体内实验而言,对大鼠、小鼠、雄性及雌性等动物进行的研究,涉及颅骨缺损、双侧卵巢切除、果糖饮食、右旋糖酐硫酸钠诱导、单侧坐骨神经切断诱导、视黄酸诱导、搭载复合支架及糖皮质激素诱导等多种造模方法,这些实验结果一致表明柚皮苷具备抗骨质疏松症的作用,详见表1。此外,柚皮苷在治疗双侧卵巢切除和糖尿病等常见的骨质疏松疾病模型中都展现出了预防和治疗的效果,这表明它具备在治疗高转换型和低转换型等多种骨质疏松病例中的应用潜力,其相关机制涉及阻断了果糖饮食引起的破骨细胞和脂肪细胞数量的增加,减少了骨细胞和骨钙素(+)细胞的数量,此过程与体内抑制JAK2/STAT3通路的激活相关,并通过促进成骨细胞和骨细胞分泌Sema3A来实现。Sema3A的增加通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,增强成骨细胞的骨形成,同时抑制破骨细胞的生成,未来深入研究成骨细胞和骨细胞分泌Sema3A的具体相关机制将成为研究的热点问题,对于柚皮苷在治疗骨质疏松方面的临床应用具有重要的意义。"
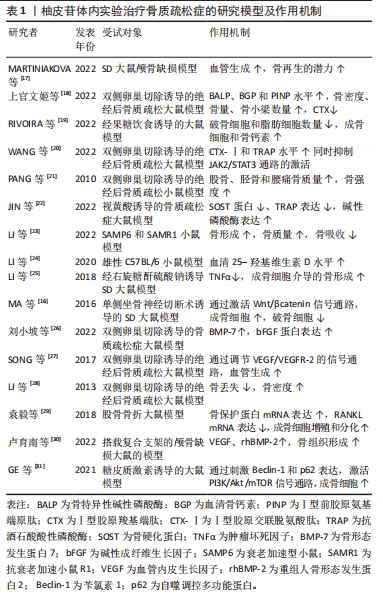
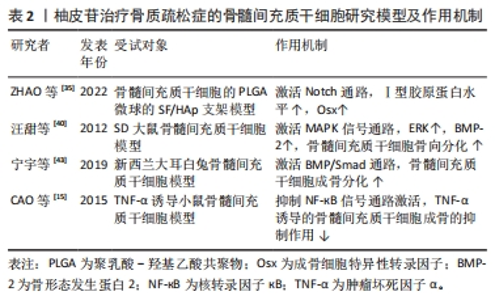
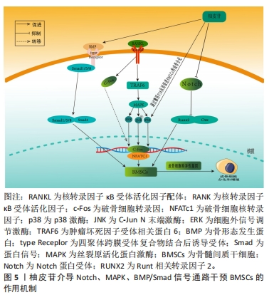
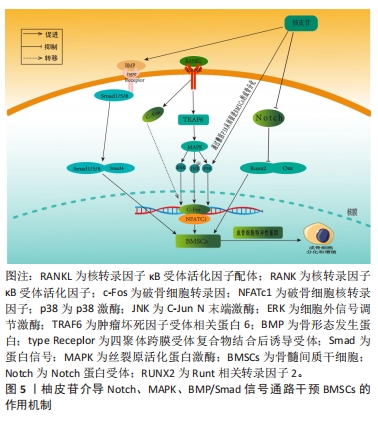
2.3 柚皮苷抗骨质疏松的体外实验研究 2.3.1 柚皮苷对骨髓间充质干细胞的影响 Notch通路能够调节成骨细胞和破骨细胞的功能,从而在骨代谢过程中发挥着重要作用,因此该条通路的信号异常会造成骨质疏松症、骨软化、骨发育系统紊乱等疾病[32-34]。 ZHAO等[35]研究表明在兔骨髓间充质干细胞中,经使用碱性磷酸酶活性、碱性磷酸酶染色和茜素红S染色检测搭载柚皮苷MSN/SF/HAp支架显著增强了成骨作用,其机制为骨髓间充质干细胞中Runt相关转录因子2(Runt related transcription factor 2,Runx2)、成骨细胞特异性转录因子(osteoblast specific transcription factor,Osx)和成骨因子Ⅰ表达水平上升,提升碱性磷酸酶活性,提示柚皮苷可能是通过激活Notch通路促进兔子骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。 MAPK信号通路是一组能够被细胞外刺激物激活的MAPK[36],是将细胞表面所受刺激传导至核内的重要载体蛋白,包括p38MAPK、细胞外信号调节激酶1/2(extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2,ERK1/2)和c-Jun氨基末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase,JNK)等3种激酶,参与调节细胞增殖、凋亡、分化和生存及细胞之间功能同步等一系列生命活动,尤其在细胞的增殖和发育,成骨细胞的分化及骨骼发育等过程中发挥着至关重要的作用[37-38]。在MAPK信号通路中,调控p38可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[39]。汪甜等[40]研究证实SD大鼠的骨髓间充质干细胞中,柚皮苷在10-7 mol/L的浓度下显著增强了骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的能力,这一机制主要是通过激活MAPK信号通路中的JNK、ERK和BMP-2、骨钙素、Runx2和碱性磷酸酶等基因的表达明显上调来实现的,提示柚皮苷通过激活p38通路促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。 相关研究证明,在骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞及胞外基质的过程中,BMP/Smad信号通路发挥了十分重要的作用,当Smads信号被激活后,可以增强成骨细胞的成熟,促使骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨转化[41-42]。在一项相关的研究中,宁宇等[43]应用1,2,4×10-3,1×10-4,10-5,10-6 mol/L柚皮苷培养液干预新西兰大耳白兔骨髓间充质干细胞72 h,发现在1×10-4 mol/L柚皮苷干预的兔骨髓间充质干细胞中BMP2,Smad1,Smad4和Runx2蛋白的表达较模型组显著上升,提示柚皮苷可以通过激活BMP/Smad通路,促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,改善骨代谢水平,从而达到抗骨质疏松症的作用。CAO等[15]在经肿瘤坏死因子α诱导小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中,发现0.001,0.01,0.1 μmol/L浓度的柚皮苷具有扭转由肿瘤坏死因子α触发的间充质干细胞细胞凋亡和提升细胞存活率的能力;在肿瘤坏死因子α处理过程中,通过剂量相关性诱导碱性磷酸酶的染色和活性下降,以及Runx2和Osx mRNA水平的降低,柚皮苷可以完全逆转由肿瘤坏死因子α引起的间充质干细胞的上述变化。值得注意的是,肿瘤坏死因子α处理还导致细胞核p65和总p-IкBα水平的增加,同时总IкBα的表达下降,从而促进NF-кB的激活,因此,柚皮苷能够直接抑制NF-кB的激活,其作用机制通过抑制NF-кB信号通路的激活来挽救肿瘤坏死因子α引起的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨的抑制作用,进而达到抗骨质疏松症的目的,见表2。"

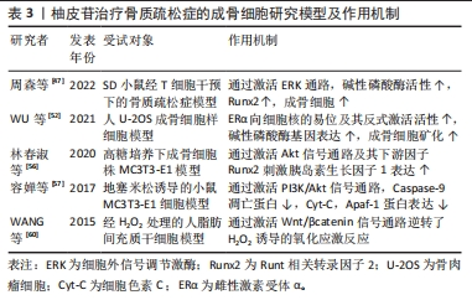
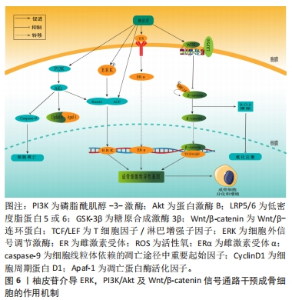
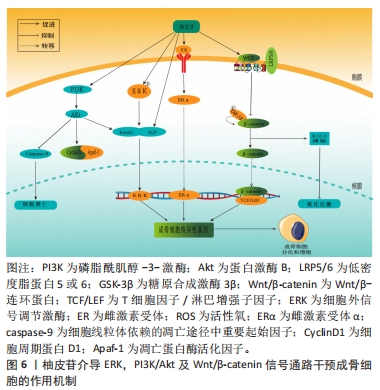
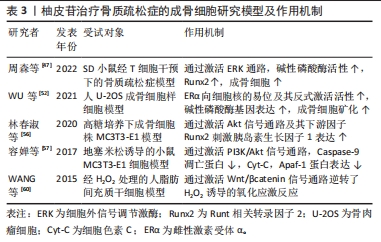
2.3.2 柚皮苷对于成骨细胞的影响 ERK信号通路在成骨细胞的分化中起着至关重要的作用,ERK在成骨分化过程中不断被磷酸化,磷酸化的ERK激活Runx2,Runx2作为成骨分化早期表达的关键转录因子,是成骨细胞表型的主要调节基因,可以通过上调成骨细胞分化标志因子[44-45],碱性磷酸酶促进骨结节的矿化,其在细胞外基质的表达反映了骨的转化水平,能够促进成骨细胞的形成,参与骨的代谢,并启动钙化过程,同时也是ERK信号通路下游重要的靶向蛋白[46]。周森等[47]在SD乳鼠经T细胞干预的成骨细胞中,用柚皮苷(2×10-3,10-4,10-5,10-6,10-7,0 mol/L)孵育24 h,结果表明柚皮苷干预可以激活ERK信号通路,提高成骨基因Ⅰ型胶原、Runx2和碱性磷酸酶的表达水平,提高成骨细胞增殖细胞核抗原蛋白表达,促进成骨细胞增殖及分化,另外研究发现在2×10-7mol/L组成骨细胞增殖分化率最高,从而达到防治骨质疏松症的作用。 雌激素受体是一种属于甾体类激素超家族的核受体,包括雌激素受体α (estrgen receptor α,ERα) 和雌激素受体β (estrogen receptor β,ERβ)两种亚型,二者均在骨和骨髓中广泛表达[48],提示骨组织是雌激素重要的靶器官。并且,骨组织中雌激素受体的表达具有雌激素依赖性,雌激素水平降低后,其受体转录和翻译水平同时受到抑制[49],所以绝经后女性雌激素水平下降的同时,靶器官表达的雌激素受体也随之下降。此外,近年来有研究表明雌激素主要是通过ERα对骨骼产生作用[50-51]。WU等[52]研究表明,在人骨肉瘤细胞(Human osteosarcoma cells,U-2OS)成骨细胞样细胞中,暴露于1,10和100 μmol/L柚皮苷中6,12和24 h,呈浓度依赖性增加成骨细胞的增殖;同时,柚皮苷增加了从ERα向细胞核的易位和反式活化活性,提高骨组织雌激素受体的表达、碱性磷酸酶 mRNA和蛋白的表达及其酶活性,调整ERα/ERβ的比例,随后,对小鼠MC3T3-E1细胞用ERα的特异性抑制剂甲基哌啶吡唑(methylpyridine pyrazole,MPP)预处理,可以减弱柚皮苷诱导的ERα反式激活活性、碱性磷酸酶基因表达,进一步说明柚皮苷可以通过调节ERα依赖性碱性磷酸酶基因的表达来改善成骨细胞矿化和骨愈合,从而达到抗骨质疏松症的效果。 PI3K/Akt作为一种重要的信号通路,能够调控细胞的存活、生长和分化过程,还可与其他信号转导途径以及转录网络相互作用[53]。当受体酪氨酸激酶被激活时,PI3K会使磷脂酰肌醇-二磷酸发生磷酸化反应,从而导致磷脂酰肌醇-三磷酸的积累并激活Akt,调控下游CyclinD1、胰岛素生长因子1、Runx2和Apaf-1等多种蛋白表达,进而调控成骨细胞的增殖分化和凋亡过程,对骨骼生长发育起到关键作用[54-55]。林春淑等[56]研究表明,在高糖培养成骨细胞株MC3T3-E1中,分别将不同浓度柚皮苷溶液(10,1,0.1 μmol/L)+25 mmol/L葡萄糖混合培养,发现柚皮苷在高糖环境下可促进MC3T3-E1细胞增殖,并呈一定的浓度依赖性,以10 μmol/L柚皮苷组效果最显著,机制可能是通过刺激胰岛素生长因子1表达,激活PI3K/Akt信号通路及其下游因子Runx2,提高碱性磷酸酶的表达,从而促进骨的形成,起到治疗骨质疏松症的作用。容婵等[57]研究表明地塞米松诱导的小鼠MC3T3-E1细胞中,柚皮苷(1,10,50 μmol/L)呈浓度依赖性抑制地塞米松诱导的MC3T3-E1细胞凋亡,这种机制可能与下调线粒体凋亡路径中的CyclinD1及Apaf-1的表达以及抑制Caspase-9凋亡蛋白的活性有关,表明柚皮苷通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路来治疗骨质疏松症。 随着氧化应激在骨质疏松症发病中的作用越来越突出,经研究发现,老年性骨质疏松症、绝经性骨质疏松症及继发性骨质疏松症都表现出与氧化应激有关[58-59]。WANG等[60]研究发现在用H2O2处理的人脂肪来源间充质干细胞中,0.1 μmol/L柚皮苷显著增加了人脂肪来源间充质干细胞的活力,逆转了H2O2诱导的氧化应激,同时上调β-catenin蛋白的表达,启动活性氧清除转录程序,促使成骨细胞生成,提示柚皮苷可通过调节Wnt/β-catenin信号通路和抗氧化应激,保护人脂肪来源间充质干细胞免受H2O2诱导成骨分化的抑制,从而达到抗骨质疏松症作用。 通过上述文献研究发现,在体外研究的小鼠、乳鼠的成骨细胞、人U-2OSOB、高糖培养成骨细胞株MC3T3-E1、地塞米松诱导的小鼠MC3T3-E1及H2O2处理的人脂肪来源间充质干细胞等造模方法的实验结果均表明了柚皮苷具有抗骨质疏松的作用,详见表3。在促进成骨细胞增殖及分化方面显示,柚皮苷具有一定的促进成骨细胞增殖与分化作用,可能通过影响ERK,PI3K/Akt,Wnt等相关信号通路来发挥调节骨代谢以及抑制氧化应激等作用,从而预防骨质流失和骨质疏松,表明柚皮苷可能成为未来临床上治疗骨质疏松症的潜在药物相关,具体信号通路见图6。"
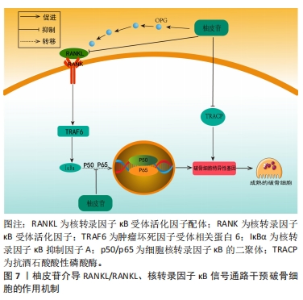
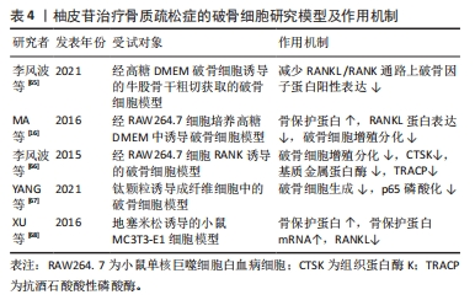
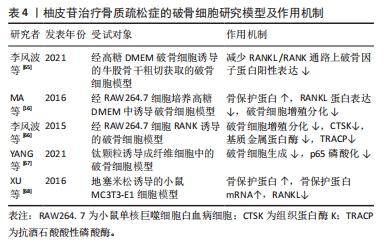
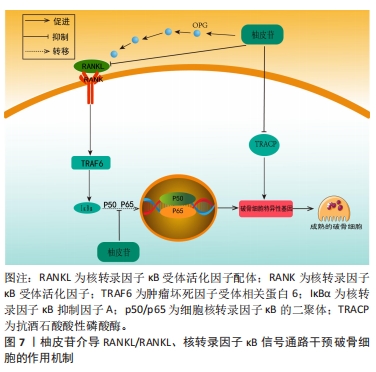
2.3.3 柚皮苷对于破骨细胞的影响 破骨细胞主要受到细胞因子RANKL的调节,RANKL对于维持骨稳态具有关键作用,在骨质疏松病理性骨吸收中发挥核心作用[61]。RANKL和RANK结合后募集肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6激活下游MAPK和核转录因子κB信号通路,活化破骨细胞核转录因子(osteoclast nuclear factor,NFATc1)及NFATc1等转录因子发挥协同作用实现破骨基因表达[62]。MAPK信号通路上调后可激活核转录因子κB信号通路影响骨吸收,此外细胞因子及诱导物刺激核转录因子κB后可以调节氧化应激反应及炎症递质的表达,从而调控骨吸收活动[63]。另一方面,骨保护蛋白是由成骨细胞产生的蛋白,其作用包括降低破骨细胞的活性、增加骨密度。骨保护蛋白能够与RANKL竞争作用于破骨细胞或破骨前体细胞上的RANK受体,从而抑制破骨细胞的分化并减少骨吸收的过程。因此,在破骨细胞分化中,骨保护蛋白和RANKL蛋白表达的比例起着至关重要的调控作用[64]。 李风波等[65]研究表明,在高糖DMEM破骨细胞诱导的牛股骨干粗切获取的皮质骨中,加含柚皮苷0,2,20,200 μg/mL的DMEM培养液,于破骨细胞诱导培养5 d后,实验表明柚皮苷可以显著减少成熟破骨细胞数量,并且与柚皮苷浓度呈正相关,然而在RANKL诱导小鼠单核细胞(RAW264.7)细胞分化的破骨细胞中,20 ng/mL的柚皮苷减少RANKL/RANK通路上破骨因子蛋白阳性表达,使骨重建失衡得到一定程度的恢复,从而进一步体现出其具有抗骨质疏松的作用。与此同时MA等[16]团队将RAW264.7细胞培养在高糖DMEM中,分别加入2,20,200 μg/L柚皮苷培养液连续培养7 d,经TRAP染色,阳性细胞数显著降低,且在20 μg/L与200 μg/L组可提高骨保护蛋白和降低RANKL蛋白表达,抑制破骨细胞活化,进一步说明柚皮苷对破骨细胞的分化和极化有一定的抑制作用。此外,李风波等[66]研究表明,在RAW264.7细胞经RANKL诱导的破骨细胞中,柚皮苷(500,100,50,20,10,1 μg/L)作用48 h后,对抗TRAP阳性细胞计数发现柚皮苷(20 μg/L)可以抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞形成,同时流式细胞术检测证实柚皮苷可以抑制破骨细胞分化过程中胞分泌组织蛋白酶K(cathepsinK,CTSK)和基质金属蛋白酶等破骨特异性因子。在另一项研究中,YANG等[67]在Ti颗粒诱导成纤维细胞中的破骨细胞中,柚皮苷(50,100,150 μmol/L)作用24 h后,柚皮苷以剂量依赖的方式降低Ti颗粒刺激的成纤维细胞产生肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平;而且柚皮苷处理减轻了Ti颗粒诱导的p65磷酸化,尤其是在高剂量处理中,柚皮苷通过MAPK/核转录因子κB信号通路失活降低了Ti颗粒诱导的成纤维细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的产生,这可能表明柚皮苷与核转录因子κB通路在破骨细胞分化成熟过程中具有双向调控功能有关,既能促进破骨细胞的分化,也能抑制破骨的成熟,从而达到抗骨质疏松症的作用。XU等[68]在小鼠MC3T3-E1细胞中的研究发现,以1,10,100 mg/L的柚皮苷处理可提高骨保护蛋白的表达,且这种诱导效果与处理时间和剂量呈相关性;同时,柚皮苷还可以通过处理时间和浓度的相关性抑制骨吸收细胞破骨细胞的生成;此外,柚皮苷还能显著提高培养物中骨保护蛋白 mRNA的表达水平和溶解钙的含量,抑制破骨细胞分泌RANKL,抑制破骨细胞活动,进而抑制骨吸收与骨破坏。 上述研究结果表明,柚皮苷可以抑制RANKL/RANKL激活下游MAPK、核转录因子κB信号通路的作用,见图7。从而对破骨细胞分化成熟具有显著抑制作用,其影响是对RANKL mRNA表达、破骨细胞活性作用均有抑制作用且呈时间和浓度依赖性,另一方面可上调骨保护蛋白 mRNA表达,从而发挥改善骨质疏松症的作用。然而,目前对柚皮苷抑制破骨细胞活性方面的研究大多集中某些相关基因的表达方面,缺乏对表达的相关机制的深入研究,这有待后续进一步探讨,详见表4。"
| [1] LI X, YIN Z, LI X, et al. Efficacy of moxibustion for primary osteoporosis: a trial sequential meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:1268876. [2] GAO Y, PATIL S, JIA J. The development of molecular biology of osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8182. [3] 柯呈辉,何立江,吴文华.双膦酸盐防治骨质疏松性骨折的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(6):870-874. [4] 舒晓春,刘君静,朱丹华,等.不同浓度的骨碎补总黄酮对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2010,26(7): 1261-1264. [5] 邓强,乔小万,李中锋,等.骨碎补活性成分治疗骨骼系统疾病研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2022,24(7):1-5. [6] WANG Y, WU H, CHEN P, et al. Fertility and early embryonic development toxicity assessment of naringin in Sprague-Dawley rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021;123:104938. [7] AN J, YANG H, ZHANG Q, et al. Natural products for treatment of osteoporosis: The effects and mechanisms on promoting osteoblast-mediated bone formation. Life Sci. 2016;147:46-58. [8] ALAM MA, SUBHAN N, RAHMAN MM, et al. Effect of citrus flavonoids, naringin and naringenin, on metabolic syndrome and their mechanisms of action. Adv Nutr. 2014;5(4):404-417. [9] RAJA KUMAR S, MOHD RAMLI ES, Abdul Nasir NA, et al. Preventive effect of naringin on metabolic syndrome and its mechanism of action: a systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:9752826. [10] FREEDMAN L, MERRITT AJ. Citrus flavonoid complex: chemical fractionation and biological activity. Science. 1963;139(3552):344-345. [11] KROYER G. Uber die antioxidative Aktivität von Zitrusfruchtschalen [The antioxidant activity of citrus fruit peels]. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1986;25(1):63-69. [12] 史万忠,徐德生,沈培芝,等.补肾益精方水提物和醇提物化学指标及药效的比较研究[J].中国中药杂志,2001,26(7):28-31. [13] ZHANG P, DAI KR, YAN SG, et al. Effects of naringin on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human bone mesenchymal stem cell. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009;607(1-3):1-5. [14] ANG ES, YANG X, CHEN H, et al. Naringin abrogates osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via the inhibition of RANKL-induced NF-κB and ERK activation. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(17):2755-2762. [15] CAO X, LIN W, LIANG C, et al. Naringin rescued the TNF-α-induced inhibition of osteogenesis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by depressing the activation of NF-кB signaling pathway. Immunol Res. 2015; 62(3):357-367. [16] MA X, LV J, SUN X, et al. Naringin ameliorates bone loss induced by sciatic neurectomy and increases Semaphorin 3A expression in denervated bone. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24562. [17] MARTINIAKOVA M, BABIKOVA M, MONDOCKOVA V, et al. The role of macronutrients, micronutrients and flavonoid polyphenols in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):523. [18] 上官文姬,张跃辉,岳江,等.柚皮苷通过HIF-1α/VEGF信号促进H型血管抗骨质疏松的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(12):1755-1759. [19] RIVOIRA M A, RIGALLI A, CORBALL L, et al. Naringin prevents bone damage in the experimental metabolic syndrome induced by a fructose-rich diet. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2022;47(4):395-404. [20] WANG W, MAO J, CHEN Y, et al. Naringin promotes osteogenesis and ameliorates osteoporosis development by targeting JAK2/STAT3 signalling. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2022;49(1):113-121. [21] PANG WY, WANG XL, MOK SK, et al. Naringin improves bone properties in ovariectomized mice and exerts oestrogen-like activities in rat osteoblast-like (UMR-106) cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159(8):1693-1703. [22] JIN H, JIANG N, XU W, et al. Effect of flavonoids from Rhizoma Drynariae on osteoporosis rats and osteocytes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113379. [23] LI Y, LIU J, ZHOU H, et al. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for discovering the metabolic markers to reveal the potential therapeutic effects of naringin on osteoporosis. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2022;1194:123170. [24] LI XL, XU F, LIN FH, et al. A naringin- and icariin-contained herbal formula, gushukang, ameliorated aged osteoporosis of aged mice with high calcium intake. Am J Chin Med. 2020;48(7):1671-1691. [25] LI C, ZHANG J, LV F, et al. Naringin protects against bone loss in steroid-treated inflammatory bowel disease in a rat model. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2018;650:22-29. [26] 刘小坡,冯云波,曹国龙,等.柚皮苷对老年大鼠骨质疏松性骨折愈合的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2020,36(9):1117-1120. [27] SONG N, ZHAO Z, MA X, et al. Naringin promotes fracture healing through stimulation of angiogenesis by regulating the VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling pathway in osteoporotic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2017;261:11-17. [28] LI N, JIANG Y, WOOLEY PH, et al. Naringin promotes osteoblast differentiation and effectively reverses ovariectomy-associated osteoporosis. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(3):478-485. [29] 袁毅,傅裕,许东,等.柚皮苷联合脉冲电磁场对大鼠股骨骨折愈合的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(6):543-547. [30] 卢育南,张信照,林斌斌,等.柚皮苷-壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石复合支架修复大鼠颅骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(28):4441-4445. [31] GE X, ZHOU G. Protective effects of naringin on glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(6):6330-6341. [32] ZHU Z, WANG Z, MA C, et al. Isopsoralen promotes osteogenic differentiation of human jawbone marrow mesenchymal cells through Notch signaling pathway. Ann Anat. 2023;250:152156. [33] GUO J, TONG CY, SHI JG, et al. Deletion of osteopontin in non-small cell lung cancer cells affects bone metabolism by regulating miR-34c/Notch1 axis: a clue to bone metastasis. Eur J Histochem. 2023;67(3):3631. [34] ZHANG W, BAI J, LI L, et al. EGFL7 secreted by human bone mesenchymal stem cells promotes osteoblast differentiation partly via downregulation of Notch1-Hes1 signaling pathway. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023;19(4):968-982. [35] ZHAO ZH, MA XL, MA JX, et al. Sustained release of naringin from silk-fibroin-nanohydroxyapatite scaffold for the enhancement of bone regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2022;13:100206. [36] XU M, SONG D, XIE X, et al. CGK733 alleviates ovariectomy-induced bone loss through blocking RANKL-mediated Ca2+ oscillations and NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathways. iScience. 2023;26(10):107760. [37] HU R, CHRN L, CHEN X, et al. Aloperine improves osteoporosis in ovariectomized mice by inhibiting RANKL-induced NF-κB, ERK and JNK approaches. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107720. [38] LIU CL, HO TL, FANG SY, et al, Tang CH. Ugonin L inhibits osteoclast formation and promotes osteoclast apoptosis by inhibiting the MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;166:115392. [39] YU X, WU Q, REN Z, et al. Kaempferol attenuates wear particle-induced inflammatory osteolysis via JNK and p38-MAPK signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;318(Pt B):117019. [40] 汪甜,杨丽,张荣华.柚皮苷在促大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞骨向分化过程中对MAPK信号通路的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2012,28(5):769-776. [41] FAN J, ZHANG X, KANG M, et al. Complementary modulation of BMP signaling improves bone healing efficiency. Biomaterials. 2023;302:122335. [42] ZENG L, GU R, LI W, et al. Ataluren prevented bone loss induced by ovariectomy and aging in mice through the BMP-SMAD signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;166:115332. [43] 宁宇,刘想忠,汪伟,等.柚皮苷通过Runx2信号通路促进MSCs成骨分化的实验研究[J].湖北中医药大学学报,2019,21(1):9-14. [44] LI X, LIU C, ZHANG X, et al. Bruceine A: suppressing metastasis via MEK/ERK pathway and invoking mitochondrial apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;168:115784. [45] MA C, MO L, WANG Z, et al. Dihydrotanshinone I attenuates estrogen-deficiency bone loss through RANKL-stimulated NF-κB, ERK and NFATc1 signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;123:110572. [46] ZHANG C, LIU M, WANG X, et al. ALP inhibitors inhibit inflammatory responses and osteoblast differentiation in hVIC via AKT-ERK pathways. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023;29(1):58-65. [47] 周森,孙奇峰,蒋雷,等.失重下柚皮苷作用于T细胞干预的成骨细胞增殖分化研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(8):1099-1103. [48] LIU Y, ZHAO L, HE X, et al. Jintiange proteins promote osteogenesis and inhibit apoptosis of osteoblasts by enhancing autophagy via PI3K/AKT and ER stress pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;311:116399. [49] MA Y, HU J, SONG C, et al. Er-Xian decoction attenuates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by modulating fatty acid metabolism and IGF1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;301:115835. [50] XU X, WANG H, LU X, et al. Sodium p-hydroxybenzoate alleviates osteoporosis through inhibiting bone metabolism and oxidative stress via activating ERα. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2023;36(5):1415-1424. [51] CHEN G, CHEN Y, HONG J, et al. Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside regulates estrogen receptor expression to ameliorate OVX-induced osteoporosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):792. [52] WU GJ, CHEN KY, YANG JD, et al . Naringin improves osteoblast mineralization and bone healing and strength through regulating estrogen receptor alpha-dependent alkaline phosphatase gene expression. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69(44):13020-13033. [53] LI S, CUI Y, LI M, et al. Acteoside derived from cistanche improves glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J Invest Surg. 2023;36(1):2154578. [54] WANG Y, GAoO Y, WANG Y, et al, He H. GDNF promotes the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of jaw bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the Nr4a1/PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Signal. 2023;108:110721. [55] SHANG J, YU Z, XIONG C, et al. Resistin targets TAZ to promote osteogenic differentiation through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. iScience. 2023;26(7): 107025. [56] 林春淑,舒晓春,肖菲娜,等.柚皮苷对高糖作用下MC3T3-E1细胞活力和Akt通路相关因子表达的影响[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版), 2020,10(6):321-327. [57] 容婵,廖莉娅,林道建,等.柚皮苷对地塞米松诱导的小鼠MC3T3-E1细胞凋亡及线粒体凋亡途径的影响[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2017, 16(5):417-420. [58] LIN BH, MA RX, WU JT, et al. Cinnamaldehyde alleviates bone loss by targeting oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in BMSCs and ovariectomized mice. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c03501. [59] FAN JB, YUAN K, ZHU XH,et al. Neuroligin-3 activates Akt-dependent Nrf2 cascade to protect osteoblasts from oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023;208:807-819. [60] WANG L, ZHANG YG, WANG XM, et al. Naringin protects human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced inhibition of osteogenic differentiation. Chem Biol Interact. 2015;242: 255-261. [61] WANG F, YANG G, LI Y, et al. A peptide from wheat germ abolishes the senile osteoporosis by regulating OPG/RANKL/RANK/TRAF6 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2022;104:154304. [62] HASANI S, FATHABADI F, SAEIDI S, et al. The role of NFATc1 in the progression and metastasis of prostate cancer: A review on the molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways. Cell Biol Int. 2023;47(12):1895-1904. [63] XU H, JIA Y, LI J, et al. Niloticin inhibits osteoclastogenesis by blocking RANKL-RANK interaction and suppressing the AKT, MAPK, and NF-κB signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;149:112902. [64] HUANG X, LI Y, LIAO H, et al. Research advances on stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promoting the reconstruction of alveolar bone through RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(4):193. [65] 李风波,孙晓雷,马剑雄,等.柚皮苷对破骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(5):450-454. [66] 李风波,孙晓雷,马剑雄,等.柚皮苷对破骨细胞分化的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2015,40(2):308-312. [67] YANG C, LIU W, SHAN H, et al.Naringin inhibits titanium particles-induced up-regulation of TNF-α and IL-6 via the p38 MAPK pathway in fibroblasts from hip periprosthetic membrane. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(5): 485-494. [68] XU T, WANG L, TAO Y, et al. The function of naringin in inducing secretion of osteoprotegerin and inhibiting formation of osteoclasts. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:8981650. [69] 刘朝晖,马剑雄,马信龙.骨质疏松症的治疗及柚皮苷抗骨质疏松的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(4):615-618,624. |
| [1] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [3] | Guo Sutong, Feng Dehong, Guo Yu, Wang Ling, Ding Yujian, Liu Yi, Qian Zhengying, Li Mingyang. Construction and finite element analysis of normal and osteoporotic hip models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1342-1346. |
| [4] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [5] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [6] | Lin Zeyu, Xu Lin. Research progress in gout-induced bone destruction mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [7] | Qi Xue, Li Jiahui, Zhu Yuanfeng, Yu Lu, Wang Peng. Abnormal modification of alpha-synuclein and its mechanism in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1301-1306. |
| [8] | Huang Haoran, Fan Yinuo, Wei-Yang Wenxiang, Jiang Mengyu, Fang Hanjun, Wang Haibin, Chen Zhenqiu, Liu Yuhao, Zhou Chi. Urolithin A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1149-1154. |
| [9] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Liu Hua, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng, Zeng Hao, Gao Zhengang, Huang Yourong. Effect of Yishen Gushu Formula on bone metabolic markers and clinical efficacyn in patients with osteoporosis of kidney deficiency and blood stasis type [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [10] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [11] | Dai Yuexing, Zheng Liqin, Wu Minhui, Li Zhihong, Li Shaobin, Zheng Desheng, Lin Ziling. Effect of vessel number on computational fluid dynamics in vascular networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1206-1210. |
| [12] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [13] | Liu Jianhong, Liao Shijie, Li Boxiang, Tang Shengping, Wei Zhendi, Ding Xiaofei. Extracellular vesicles carrying non-coding RNA regulate the activation of osteoclasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1076-1082. |
| [14] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [15] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||