Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (34): 5521-5527.doi: 10.12307/2024.831
Previous Articles Next Articles
Possible mechanisms of multi-pathway biological effects of laser therapy for knee osteoarthritis
Lou Xinqi1, Zhong Hao1, Wang Xiyu1, Feng Haoyu2, Li Pengcui3, Wei Xiaochun3, Wang Yanqin1, Wu Xiaogang1, Chen Weiyi1, Xue Yanru2
- 1College of Biomedical Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China; 2Shanxi Bethune Hospital (Tongji Shanxi Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences), Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030032, Shanxi Province, China; 3Shanxi Provincial Key Laboratory for Repair of Bone and Soft Tissue Injury, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-12Accepted:2024-01-22Online:2024-12-08Published:2024-03-14 -
Contact:Xue Yanru, PhD, Lecturer, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital, Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030032, Shanxi Province, China Wu Xiaogang, PhD, Professor, College of Biomedical Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Lou Xinqi, Master, College of Biomedical Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 12272250 and 11972242 (both to WXG); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2020M680913 (to WXG); Shanxi Overseas Returned Scholarship Fund, No. 2022-081 (to WXG); Shanxi Provincial Basic Research Program, No. 202203021212254 (to XYR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lou Xinqi, Zhong Hao, Wang Xiyu, Feng Haoyu, Li Pengcui, Wei Xiaochun, Wang Yanqin, Wu Xiaogang, Chen Weiyi, Xue Yanru. Possible mechanisms of multi-pathway biological effects of laser therapy for knee osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5521-5527.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
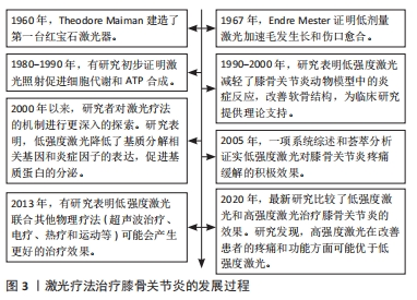
2.1 激光疗法的分类 激光疗法是利用激光的单色性、相干性和高度聚焦的特点,作用于特定的组织或细胞,以达到治疗疾病、缓解症状和促进康复的目的[14]。研究表明,激光疗法涉及的可见红光和近红外光(390-1 600 nm)具有组织穿透能力,对活体组织产生有益的治疗效果[15]。 目前关于激光治疗膝骨关节炎的研究主要分为LLLT和HLLT。LLLT通常是利用波长为600-980 nm、功率≤500 mW的低能量激光改变生物活性,辐照组织的温度升高< 1 ℃,可以穿透浅表组织层,最大穿透能力为2 cm[16]。HLLT是指在短时间内提供较高的能量密度(功率> 500 mW),具有更深的组织穿透力(5-15 cm),从而产生更有效的生物刺激[17]。3种常见激光类型是氦氖激光器、砷化镓激光器和掺钕钇铝石榴石激光器,通常认为氦氖激光和砷化镓是低功率激光,而脉冲掺钕钇铝石榴石激光具有大约3 kW的高峰功率,波长可达1 000 nm,能穿透更深的靶组织[14]。 2.2 激光对膝骨关节炎的影响 激光疗法在膝骨关节炎治疗中的应用可以追溯到20世纪80年代。早期的研究主要集中在LLLT对软骨细胞功能和膝骨关节炎动物模型的影响[18]。随着研究的不断深入,LLLT逐渐应用于临床实践中,一些报告指出LLLT与其他治疗方式联合使用可以产生协同效应,进一步促进组织修复、缓解炎症、减轻疼痛等[19]。近年来,研究人员认为HLLT具有较高的输出功率和更深的组织穿透能力,在治疗膝骨关节炎疾病时能产生更显著的效果[20]。激光疗法治疗膝骨关节炎的发展过程见图3。"
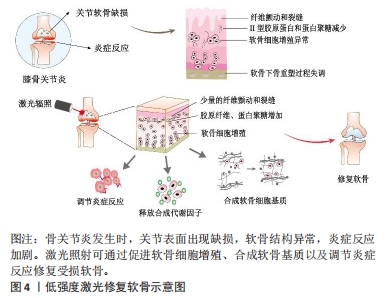
LLLT在膝骨关节炎治疗中已有一定的研究支持,在细胞实验、动物模型以及临床疗效方面均显示出积极作用。相比之下,HLLT在膝骨关节炎治疗中的研究较少,但一些初步的研究结果显示了积极的效果[21]。细胞实验表明LLLT能够促进软骨细胞增殖和细胞外基质的合成[22]。体内实验表明LLLT可以降低促炎症因子的释放,增加蛋白多糖和Ⅱ型胶原的合成,从而改善软骨组织的修复过程[23]。图4展示了LLLT促进软骨修复的过程。在临床试验中,HLLT和LLLT均可以减轻骨关节炎患者的疼痛并改善其功能活动[24]。此外,临床研究中,激光疗法通常作为综合治疗的辅助疗法使用,结合其他治疗方法(如康复训练、物理疗法等)可能会取得更好的疗效[25-28]。然而,由于激光参数和治疗方案的不统一,激光对膝骨关节炎的具体疗效存在差异。当使用适当的激光参数时,激光疗法可以缓解疼痛、抗炎、促进组织修复和改善功能。"
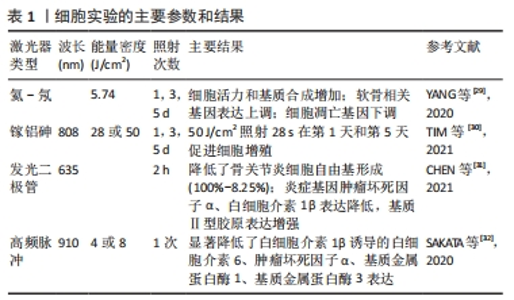
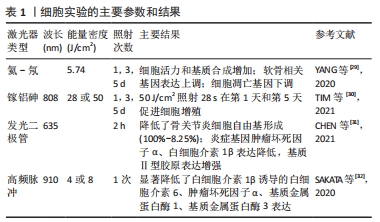
2.2.1 激光对软骨细胞的刺激作用 在体外细胞实验中,通常选用软骨细胞系、原代软骨细胞或骨关节炎软骨细胞,探究激光对软骨细胞增殖、基质合成和炎症反应的影响,以评估其生物学效应和治疗潜力。细胞实验使用的激光参数和主要结果见表1[29-32]。YANG等[29]使用波长为632.8 nm、输出功率为12 mW的激光对兔软骨细胞分别照射1,3,5,8,11,13 min,连续处理1 d或3 d,实验结果表明,与对照组相比,LLLT处理8 min的软骨细胞在1 d和3 d的细胞活力均显著高于对照组(P < 0.01)。qRT-PCR结果显示,能量密度为5.74 J/cm2的LLLT抑制了细胞凋亡基因(半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3、FADD、TNFR1和TRADD)的表达。同时,活/死荧光染色实验表明,LLLT处理5 d的软骨细胞活/死比例显著高于对照组(P < 0.05),这表明LLLT通过阻断细胞凋亡途径抑制了细胞凋亡。TIM等[30]使用波长为808 nm、功率为50 mW的镓-砷化铝激光器评估了不同剂量的LLLT对软骨细胞增殖的影响,结果显示LLLT显著增加软骨细胞增殖,并且在激光干预1 d和3 d时,1.4 J剂量对软骨细胞增殖效果较好。以上研究表明,LLLT能够促进软骨细胞的增殖能力,减少软骨细胞的凋亡,对软骨组织的修复和再生具有重要意义。还有一些实验探究了LLLT对软骨细胞的基质合成和炎症反应的影响。CHEN等[31]将635 nm的红外发光二极管应用于过氧化氢诱导的骨关节炎软骨细胞,结果发现,激光处理2 h可显著降低炎症基因(白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α)表达,增加基质基因Ⅱ型胶原的表达。YANG等[29] 也得到了相似的结论:LLLT降低了白细胞介素1β诱导的基质分解相关基因(基质金属蛋白酶13)的表达,促进了基质蛋白的分泌。总之,LLLT作为一种非侵入性的治疗方法,对软骨细胞具有促进增殖、减少凋亡、调节炎症反应和促进基质合成的积极影响。但仍然存在一些问题需要解决,如LLLT在软骨细胞中的确切作用机制尚不完全清楚,需要更多的研究揭示激光如何被软骨细胞吸收和转化,以及如何调节细胞内的信号通路和生物化学反应。"
目前关于HLLT对软骨细胞的作用效应研究较少。SAKATA等[32]首次评估了高频近红外二极管激光照射对白细胞介素1β诱导的骨关节炎软骨细胞的生物学效应,结果表明,高频近红外二极管激光(910 nm,4或8 J/cm2)照射显著降低了骨关节炎软骨细胞中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和基质降解酶(基质金属蛋白酶1、基质金属蛋白酶3)的表达。与LLLT相比,高频近红外二极管激光具有输出高峰值、低热积累的特点,能够产生高效的生物刺激,这可能是一种新的、有效的、安全的膝骨关节炎治疗方法。 2.2.2 激光对膝骨关节炎动物模型的实验研究 在体内动物实验中,研究人员通常采用切除前交叉韧带或关节腔内注射化学物质建立膝骨关节炎大鼠模型,探究LLLT对软骨组织修复、炎症过程以及缓解疼痛的效果,在每项研究中选用的激光波长、功率、剂量、治疗周期等都有所不同[33-36]。 动物实验使用的激光参数和主要结果见表2。这些体内研究观察到的积极结果进一步证明了LLLT是一种潜在的骨关节炎临床治疗方法。关于HLLT在膝骨关节炎动物模型中的研究相对较少,未来还需要更多的研究进一步验证和探索HLLT在骨关节炎治疗中的潜力。"
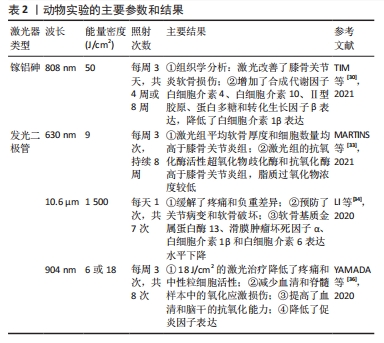
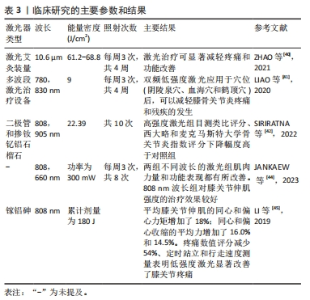
体内实验表明LLLT能够减轻软骨组织降解和炎症反应,对骨关节炎有积极作用。TIM等[30]对膝骨关节炎大鼠进行每周3 d、持续4周或8周的LLLT治疗,组织学分析表明,与对照组相比,4,8周的LLLT组软骨组织出现较轻的退化迹象,国际骨关节炎研究学会评分也显著降低(P < 0.05);免疫组化和qRT-PCR分析进一步证实了以上结果;LLLT治疗组的转化生长因子β、Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白聚糖基因表达增加(P < 0.05)。LORENA等[33]也得到相似的结果,他们对膝骨关节炎大鼠进行每周3次、持续8周的激光干预,结果表明,膝骨关节炎组平均软骨厚度明显减少,软骨细胞数量明显降低,而LLLT组和对照组之间没有显著差异。LI等[34]证明了10.6 μm的激光艾灸可抑制软骨损伤的进程,降低了国际骨关节炎研究学会评分,早期激光艾灸治疗也降低了软骨基质金属蛋白酶13和滑膜肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6的表达水平。一项系统性综述显示,LLLT能够调节炎症过程,对膝骨关节炎治疗显示出积极作用[35]。总之,大多体内实验均表明LLLT减少炎性递质的释放,减轻了炎症反应。LLLT通过抑制软骨降解酶的活性,促进软骨基质成分合成,减缓了软骨退行性病变过程。 体内研究还表明LLLT对膝骨关节炎发展过程中的氧化应激具有一定作用。氧化应激是指活性氧产生与抗氧化防御系统之间的不平衡,可能导致细胞死亡,是膝骨关节炎病理过程中的重要因素之一。YAMADA等[36]发现膝骨关节炎动物模型中超氧化物歧化酶(一种重要的抗氧化酶)表达水平降低,而激光干预后该酶水平升高,氧化标志物丙二醛的水平降低。MARTINS等[33]也发现激光干预有利于增加抗氧化酶活性。这些研究结果表明,LLLT增强了抗氧化酶的活性,调节氧自由基产生,有助于保护软骨组织免受氧化损伤,减缓膝骨关节炎的发展过程。然而,需要进一步研究以深入了解LLLT对膝骨关节炎氧化应激的具体影响,特别是激光对氧化还原平衡、抗氧化系统等的作用机制。 有研究通过动物疼痛行为测试证明了LLLT能够缓解疼痛。LI等[37]采用机械刺激测试和负重差异评价了激光艾灸的镇痛效果,结果表明,激光治疗明显逆转了早期阶段观察到的负重差异,通过激活脊髓腺苷A1受体抑制了痛觉传导,具有持久的镇痛效果。以上结果为LLLT作为一种非药物性疼痛治疗方法提供了科学支持。 目前,也有部分研究将LLLT作为单一治疗方式或与其他治疗方式联合使用以增强治疗效果,常见的联合治疗方式包括药物治疗和康复训练等。ASSIS等[38]比较了LLLT与有氧运动、水上运动训练对大鼠骨关节炎软骨退化过程的影响,他们使用特定波长为808 nm激光设备进行8 周治疗。结果显示,有氧运动和激光联合治疗组软骨退变和细胞异常增殖的现象并不明显;与对照组相比,有氧运动和激光治疗联合组的转化生长因子β表达量明显更高。与ASSIS等[38]的研究不同,SANCHES等[39]探讨了LLLT与硫酸软骨素/硫酸氨基葡萄糖两种药物作为单一或联合疗法对大鼠退行性形态变化的影响,LLLT与药物联合使用的治疗方法对调节炎症过程和基质降解、防止组织变性的积极作用更明显。总之,上述研究表明,LLLT与有氧运动/药物治疗相结合可能会在促进组织愈合和再生方面产生协同效应,这可能与它们各自对膝骨关节炎的疗效有关。有氧运动能够增强肌肉力量、改善关节灵活性,药物治疗可以针对炎症和疼痛进行干预,LLLT与有氧运动/药物治疗联合使用可以共同作用于减缓膝骨关节炎的发展。 2.2.3 激光治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效 LLLT和HLLT在膝骨关节炎临床研究方面均已取得了一些进展,这些研究通常使用目测类比评分或者数字评分量表评估激光疗法对患者疼痛缓解的作用。在膝骨关节炎进程中,患者关节功能,包括关节活动度、力量和平衡等会受到影响。临床研究通常使用健康调查问卷、西大略和麦克马斯特大学骨关节炎指数评分等评估激光疗法对患者的功能改善情况。临床研究表明,激光疗法对患者疼痛缓解和功能改善均显示出一定的潜力,但激光的治疗参数、照射时间和频次等可能对治疗效果产生影响[40-45]。临床研究使用的激光参数以及主要结果见表3。"
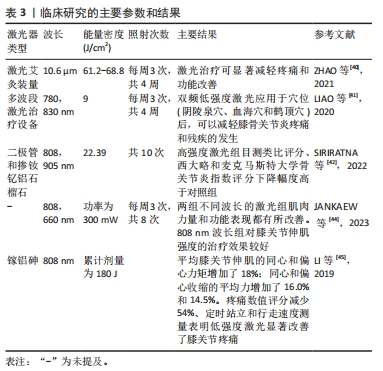

临床研究表明LLLT和HLLT均可以减轻患者疼痛,改善身体功能。ZHAO等[40]对392例患者的膝关节穴位进行了为期4周的激光针灸,结果显示,治疗第4周时,激光组患者的疼痛评分显著降低了36%(P < 0.01)。LIAO等[41]使用780 nm红光和830 nm近红外光联合波长照射患者的阴陵泉穴(SP9)、血海穴(SP10)和鹤顶穴(EX-LE2),与治疗前相比,患者在活动和静息状态下的目测类比评分均明显下降(P < 0.000 1),疼痛压力阈值从治疗前的(11.71±1.86) kg显著增加到(21.23±1.82) kg(治疗4周后)。SIRIRATNA等[42]的研究结果也表明,与对照组相比,能量密度为22.39 J/cm2的HLLT治疗组目测类比评分和骨关节炎指数疼痛评分显著下降。一项系统综述表明,0.51-120 J/cm2的HLLT均能有效减轻膝骨关节炎患者的疼痛并改善其功能[11]。这些结果说明LLLT和HLLT对于膝骨关节炎疼痛管理和康复过程具有潜在的益处,并且在临床实践中逐渐受到关注。 最近,有研究表明LLLT对膝骨关节炎患者的肌肉功能改善有积极作用,但HLLT对肌力的改善作用还需进一步验证[43]。JANKAEW等[44]比较了波长为808 nm和660 nm的LLLT对膝骨关节炎患者肌肉力量的治疗作用,患者膝关节处接受平均功率为300 mW、不同波长的激光治疗。结果表明,与对照组相比,两个不同波长的激光组膝关节伸肌力量和屈肌力量均显著改善(P < 0.001)。波长为808 nm的LLLT组在膝关节伸肌力量方面的效果更显著。LI等[45]通过等动测力计评估了LLLT对膝骨关节炎患者肌力的改善效果。结果显示,激光干预后,膝关节伸肌的峰值扭矩、同心收缩力和偏心收缩力有所增加(P < 0.05)。这些结果表明LLLT增强了患者的肌肉力量,改善周围肌肉的功能,有助于提高关节的稳定性,促进恢复患者日常生活活动,对于患者的临床康复和功能恢复具有重要意义。 大量临床研究表明LLLT与运动治疗方式联合使用比单独运动或单独LLLT更有效地降低膝骨关节炎患者的疼痛,改善功能[46-47]。KHOLVADIA等[48]的研究结果表明,运动+LLLT组患者的西大略和麦克马斯特大学骨关节炎指数功能量表评分提高了24分;与单独LLLT组和单独运动组相比,两者联合的治疗方式在短期和长期疗效方面均显示出更好的效果。STAUSHOLM等[49]探究了LLLT联合力量训练对膝骨关节炎患者的短期和长期疗效,结果表明,LLLT联合力量训练组和单独训练组患者的疼痛均有显著减轻,但在随访期间,LLLT联合力量训练组的患者效果更明显。以上结果表明,LLLT与体育锻炼结合使用是一种膝骨关节炎治疗的可行方式。 一些随机临床研究证明HLLT在减轻关节疼痛和改善功能疗效方面可能比LLLT或其他物理疗法更明显。在AHMAD等[50]的研究中,34例轻度膝骨关节炎患者分别接受了LLLT和HLLT治疗,并且在激光治疗期间,所有患者进行每周1次的康复锻炼,结果表明,与LLLT+康复锻炼相比,HLLT+康复锻炼可显著改善疼痛、身体功能和膝关节功能。一项系统综述表明,与其他可用的物理治疗方式(电刺激+超声治疗、冲击波疗法、热疗+电刺激)相比,HLLT最大程度缓解了膝骨关节炎患者的疼痛,其次是LLLT [51]。这一发现可能是因为传统的LLLT功率较低,光束难以到达关节和滑囊等深层组织,相比之下,HLLT具有更高的功率和更深层的组织渗透能力,能够产生更显著的生物效应,在减轻关节疼痛和改善功能方面表现出更强的治疗效果。 综上所述,激光疗法在膝骨关节炎治疗中显示出一定的潜力,具体表现为减轻患者疼痛、改善身体功能、增强肌肉力量。但目前关于激光治疗膝骨关节炎临床研究报告的结果相互矛盾。一项系统综述指出LLLT并不是治疗膝骨关节炎的唯一有效方式[8]。这些结果的差异可能与激光参数和治疗方法有关,不同研究可能采用不同的治疗参数、照射时间和频次等,会对治疗效果产生直接影响;另一方面,不同研究中样本量大小、研究对象的选择标准存在差异,可能导致结果的不同。因此,激光疗法仍需要对大量研究进行综合分析以筛选有效的激光参数和治疗方案。 2.3 激光疗法的潜在机制 目前激光辐照对细胞转化过程尚未进行详细研究,用于膝骨关节炎的潜在机制仍不明确。关于激光对细胞作用机制的一种假说是低强度激光照射细胞时,光能被细胞吸收能够激活多条信号通路,引发一系列光生物效应[52]。低强度激光功率常为5-500 mW,使用小功率激光照射后照射部位的温度几乎不会升高[16]。因此,LLLT对细胞产生的刺激可能依赖于光生物效应。也有学者认为脉冲大功率激光照射可能会使局部温度升高,改变细胞周围环境,通过细胞-基质之间的相互作用来调节细胞的合成代谢[53]。这种物理效应可能不同于光生物学效应,主要是通过产生热量引起一系列的热力学效应影响细胞的功能和生理过程。激光对细胞的作用机制仍然是一个活跃的研究领域,其在医学和生物科学领域的应用前景还需持续扩展和深化研究。 2.3.1 激光照射具有光生物效应 早期研究表明,激光可能会影响线粒体功能,促进细胞的代谢活动[54]。这一过程主要包括光子被线粒体中的细胞色素C氧化酶吸收,导致呼吸链的电子传递加快,使得ATP合成加快,提高细胞的能量代谢[55]。最近的一项研究表明,波长为980 nm、功率0.1 W的激光会诱发氧化应激,并大幅抑制ATP的产生;而0.8 W的激光可提高线粒体细胞色素氧化酶的活性,增加ATP的产生[56]。WANG等[57]得到相似的结论,他们发现660 nm和810 nm的激光能提高线粒体膜电位,增加ATP合成,促进脂肪来源干细胞增殖。值得注意的是,ATP不仅能够提供细胞代谢所需的能量,而且可以作为信号分子通过P2Y/P2X受体输出到细胞外,参与多种信号通路[58]。研究表明,随着ATP浓度的增加,P2X受体被激活,导致钙内流增加,调节细胞的生长、分化、凋亡等生理过程[59]。P2X受体在炎症过程中也起着关键作用。在炎症微环境下,细胞可释放大量ATP激活P2X受体,参与诱导了白细胞介素1β的释放[60]。许多学者已经证实激光照射会导致细胞内Ca2+增加,能减少炎症因子白细胞介素1β的释放,但这一现象是否与ATP/P2Y/P2X信号通道有关尚未得到解释,这可能为探究激光的作用机制提供了新的方向。 激光可能调节细胞内的多种信号通路,如磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphoinositide 3-kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,Akt)、Wnt/β-catenin、核因子κB,这些信号通路在细胞增殖、代谢和抗炎等方面起着重要作用。PI3K/AKT信号通路是软骨细胞增殖和凋亡的重要因子,抑制PI3K/Akt/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白( mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路可促进软骨细胞的自噬,减缓膝骨关节炎症状[61]。有研究指出Wnt/β-catenin信号通路参与调节软骨细胞的基质合成,促进软骨细胞的增殖和分化,维持软骨组织的稳态和修复受损组织[62]。核因子κB信号通路在调节炎症反应和细胞凋亡过程中发挥着重要作用,核因子κB的过度活化可能导致炎症反应的加剧 [63]。JERE等[64]发现660 nm 的激光激活了成纤维细胞中PI3K/Akt以及下游mTOR和糖原合成酶激酶3β信号通道,增加了细胞迁移、增殖和存活率。KIM等[65]证明激光照射可能通过Wnt/β-catenin和ERK信号通路诱导了口腔源干细胞增殖和迁移,抑制细胞凋亡。以上研究说明,激光疗法可以通过PI3K/Akt、Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进细胞增殖。LI等[66]评估了810 nm激光抗炎作用的潜在机制,结果表明,LLLT减少了巨噬细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和核因子κB的表达,这说明激光可能通过核因子κB信号通路对炎症过程产生积极作用。以上结果在成骨细胞、成纤维细胞和干细胞等其他类型细胞中得到证实,但激光能否激活软骨细胞中的PI3K/AKT、Wnt/β-catenin和核因子κB信号通路来调节细胞的生理生化过程,仍需要进一步验证。 2.3.2 激光照射能够产生热力学效应 软骨主要是由软骨细胞和细胞外基质组成。蛋白多糖、糖胺聚糖、糖蛋白和特异性胶原构成了细胞外基质,使软骨组织具有抗拉强度和刚度,能够抵抗外界载荷。软骨细胞与蛋白多糖和各种膜蛋白相互连接固定在细胞外基质上,细胞与基质的相互作用提供了软骨细胞特有的微环境[67]。 基于软骨细胞及其微环境的相互作用,研究人员认为脉冲激光加热过程改变了细胞周围的力学环境,影响细胞的黏附、迁移和信号传导等过程[68]。ALEXANDROVSKAYA等[69]比较了激光的热力学效应和光生物效应对软骨细胞合成代谢的影响,实验证明对软骨细胞进行红外冲击时,可以局部实现高达20 MPa的流体静力刺激,类似于生理状态下软骨细胞内的循环液体压力,导致Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和蛋白聚糖的积累显著增加。 此外,脉冲激光加热可在细胞外基质中引入气泡,诱导水分子运动,这可能是其对软骨细胞产生影响的另一个因素。SOBOL等[70]认为激光对软骨的影响归因于孔隙和气泡的形成,激光照射在细胞附近产生大量微孔,加速液体流动,使软骨组织得到适当营养,促进了细胞代谢。"

| [1] HAWKER GA. Osteoarthritis is a serious disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019; 37(Suppl 120):3-6. [2] CUI A, LI H, WANG D, et al. Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. E Clin Med. 2020; 29-30:100587. [3] REN Y, HU J, TAN J, et al. Incidence and risk factors of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis among the Chinese population: analysis from a nationwide longitudinal study. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1491. [4] LV Z, YANG YX, LI J, et al. Molecular Classification of Knee Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:725568. [5] KAN HS, CHAN PK, CHIU KY, et al. Non-surgical treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Hong Kong Med J. 2019;25(2):127-133. [6] MAGNI A, AGOSTONI P, BONEZZI C, et al. Management of Osteoarthritis: Expert Opinion on NSAIDs. Pain Ther. 2021;10(2):783-808. [7] FLYNN DM. Chronic musculoskeletal pain: nonpharmacologic, noninvasive treatments. Am Fam Physician. 2020;102(8):465-477. [8] GANJEH S, REZAEIAN ZS, MOSTAMAND J. Low Level Laser Therapy in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Narrative Review. Adv Ther. 2020;37(8):3433-3449. [9] HUANG YY, CHEN ACH, HAMBLIN MR. Low level laser and light therapy. Handbook of Biomedical Optics. 2016:771-814. [10] CHOW R, LIEBERT A, TILLEY S, et al. Guidelines versus evidence: what we can learn from the Australian guideline for low-level laser therapy in knee osteoarthritis? A narrative review. Lasers Med Sci. 2020;36(2):249-258. [11] WYSZYŃSKA J, BAL-BOCHEŃSKA M. Efficacy of High-Intensity Laser Therapy in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis: A First Systematic Review. Photomed Laser Surg. 2018;36(7):343-353. [12] COLLINS NJ, HART HF, MILLS KAG. Osteoarthritis year in review 2018: rehabilitation and outcomes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(3):378-391. [13] GEENEN R, OVERMAN CL, CHRISTENSEN R, et al. EULAR recommendations for the health professional’s approach to pain management in inflammatory arthritis and osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(6):797-807. [14] ROMANOS GE. Laser Fundamental Principles. Adv Laser Sur in Dent. 2021: 3-11. [15] MUSSTTAF RA, JENKINS DFL, JHA AN. Assessing the impact of low level laser therapy (LLLT) on biological systems: a review. Int J Radiat Biol. 2019; 95(2):120-143. [16] MESTER A. Laser Biostimulation. Photomed Laser Surg. 2013;31(6):237-239. [17] WHITE PF, ZAFEREO J, ELVIR-LAZO OL, et al. Treatment of drug-resistant fibromyalgia symptoms using high-intensity laser therapy: a case-based review. Rheumatol Int. 2017;38(3):517-523. [18] HAWKINS D, ABRAHAMSE H. How Long After Laser Irradiation Should Cellular Responses be Measured to Determine the Laser Effect? J Laser Appl. 2007;19(2):74-83. [19] AVCI P, GUPTA A, SADASIVAM M, et al. Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) in skin: stimulating, healing, restoring. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013;32(1): 41-52. [20] OHSHIRO T. A new effect-based classification of laser applications in surgery and medicine. Laser Therapy. 1996;8(4):233-239. [21] SONG HJ, SEO HJ, KIM D. Effectiveness of high-intensity laser therapy in the management of patients with knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2020;33(6):875-884. [22] DA SILVA SERGIO LP, DE SOUZA DA FONSECA A, MENCALHA AL, et al. Photobiomodulation on extracellular matrix. Laser Physics. 2023;33(3): 033001. [23] OLIVEIRA S, ANDRADE R, HINCKEL BB, et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Effects of Light Therapy on Cartilage Regeneration for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Cartilage. 2021;13(2_suppl):1700S-1719S. [24] CHEN JL, HSU CC, CHEN WCC, et al. Intra-Articular Laser Therapy May Be a Feasible Option in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis in Elderly Patients. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:1-8. [25] PAOLILLO FR, PAOLILLO AR, JOÃO JP, et al. Ultrasound plus low-level laser therapy for knee osteoarthritis rehabilitation: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatol Int. 2018;38(5):785-793. [26] DE MATOS BRUNELLI BRAGHIN R, LIBARDI EC, JUNQUEIRA C, et al. The effect of low-level laser therapy and physical exercise on pain, stiffness, function, and spatiotemporal gait variables in subjects with bilateral knee osteoarthritis: a blind randomized clinical trial. Disabil Rehabil. 2018;41(26): 3165-3172. [27] AHMAD MA, HAMID MS, YUSOF A. Effects of low-level and high-intensity laser therapy as adjunctive to rehabilitation exercise on pain, stiffness and function in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Physiotherapy. 2022;114:85-95. [28] MOSTAFA MSEM, HAMADA HA, KADRY AM, et al. Effect of High-Power Laser Therapy Versus Shock Wave Therapy on Pain and Function in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2022;40(3):198-204. [29] YANG X, LIU TC, LIU S, et al. Promoted Viability and Differentiated Phenotype of Cultured Chondrocytes With Low Level Laser Irradiation Potentiate Efficacious Cells for Therapeutics. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:468. [30] TIM CR, MARTIGNAGO CCS, ASSIS L, et al. Effects of photobiomodulation therapy in chondrocyte response by in vitro experiments and experimental model of osteoarthritis in the knee of rats. Lasers Med Sci. 2021;37(3): 1677-1686. [31] CHEN IC, SU CY, FANG CH, et al. Preventative treatment of red light-emitting diode protected osteoarthritis-like chondrocytes from oxidative stress-induced inflammation and promoted matrix gene expression. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2021;127:23-31. [32] SAKATA S, KUNIMATSU R, TSUKA Y, et al. High-Frequency Near-Infrared Diode Laser Irradiation Attenuates IL-1β-Induced Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines and Matrix Metalloproteinases in Human Primary Chondrocytes. J Clin Med. 2020;9(3):881. [33] MARTINS LPO, SANTOS FFD, COSTA TED, et al. Photobiomodulation Therapy (Light-Emitting Diode 630 nm) Favored the Oxidative Stress and the Preservation of Articular Cartilage in an Induced Knee Osteoarthritis Model. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2021;39(4):272-279. [34] LI Y, WU F, WEI J, et al. The Effects of Laser Moxibustion on Knee Osteoarthritis Pain in Rats. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2020; 38(1):43-50. [35] NAMBI G. Does low level laser therapy has effects on inflammatory biomarkers IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and MMP-13 in osteoarthritis of rat models—a systemic review and meta-analysis. Lasers Med Sci. 2020;36(3):475-484. [36] YAMADA EF, BOBINSKI F, MARTINS DF, et al. Photobiomodulation therapy in knee osteoarthritis reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in rats. J Biophotonics. 2020;13(1):e201900204. [37] LI Y, WU F, LAO L, et al. Laser irradiation activates spinal adenosine A1 receptor to alleviate osteoarthritis pain in monosodium iodoacetate injected rats. J Integr Neurosci. 2020;19(2):295-302. [38] ASSIS L, TIM C, MAGRI A, et al. Interleukin-10 and collagen type II immunoexpression are modulated by photobiomodulation associated to aerobic and aquatic exercises in an experimental model of osteoarthritis. Lasers Med Sci. 2018;33(9):1875-1882. [39] SANCHES M, ASSIS L, CRINITI C, et al. Chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine sulfate associated to photobiomodulation prevents degenerative morphological changes in an experimental model of osteoarthritis in rats. Lasers Med Sci. 2018;33(3):549-557. [40] ZHAO L, CHENG K, WU F, et al. Effect of laser moxibustion for knee osteoarthritis: a multisite, double-blind randomized controlled trial. J Rheumatol. 2021;48(6):924-932. [41] LIAO FY, LIN CL, LO SF, et al. Efficacy of Acupoints Dual-Frequency Low-Level Laser Therapy on Knee Osteoarthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:6979105. [42] SIRIRATNA P, RATANASUTIRANONT C, MANISSORN T, et al. Short-Term Efficacy of High-Intensity Laser Therapy in Alleviating Pain in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Single-Blind Randomised Controlled Trial. Pain Res Manag. 2022;2022:1319165. [43] EKICI B, ORDAHAN B. Evaluation of the effect of high-intensity laser therapy (HILT) on function, muscle strength, range of motion, pain level, and femoral cartilage thickness in knee osteoarthritis: randomized controlled study. Lasers Med Sci. 2023;38(1):218. [44] JANKAEW A, YOU YL, YANG TH, et al. The effects of low-level laser therapy on muscle strength and functional outcomes in individuals with knee osteoarthritis: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1):165. [45] LI CF, CHEN YJ, LIN TY, et al. Immediate responses of multi‐focal low level laser therapy on quadriceps in knee osteoarthritis patients. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019;35(11):702-707. [46] STAUSHOLM MB, NATERSTAD IF, COUPPÉ C, et al. Effectiveness of Low-Level Laser Therapy Associated with Strength Training in Knee Osteoarthritis: Protocol for a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Methods Protoc. 2021;4(1):19. [47] ROBBINS SR, ALFREDO PP, JUNIOR WS, et al. Low-level laser therapy and static stretching exercises for patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomised controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2022;36(2):204-213. [48] KHOLVADIA A, CONSTANTINOU D, GRADIDGE PJ. Exploring the efficacy of low-level laser therapy and exercise for knee osteoarthritis. S Afr J Sports Med. 2019;31(1):v31i1a6058. [49] STAUSHOLM MB, NATERSTAD IF, JOENSEN J, et al. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy on pain and disability in knee osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo-controlled trials. BMJ Open. 2019;9(10):e031142. [50] AHMAD MA, MOGANAN M, HAMID MSA, et al. Comparison Between Low-Level and High-Intensity Laser Therapy as An Adjunctive Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial. Life (Basel). 2023;13(7):1519. [51] WU M, LUAN L, PRANATA A, et al. Is high intensity laser therapy more effective than other physical therapy modalities for treating knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:956188. [52] MIGLIARIO M, SABBATINI M, MORTELLARO C, et al. Near infrared low‐level laser therapy and cell proliferation: The emerging role of redox sensitive signal transduction pathways. J Biophotonics. 2018;11(11):e201800025. [53] MONICI M, CIALDAI F, FUSI F, et al. Effects of pulsed Nd: YAG laser at molecular and cellular level. A study on the basis of Hilterapia. Energy Health. 2008;3:27-33. [54] DOMPE C, MONCRIEFF L, MATYS J, et al. Photobiomodulation—Underlying Mechanism and Clinical Applications. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):1724. [55] HAMBLIN MR, CARROLL JD, ARANY P, et al. Photo-excitation of electrons in cytochrome c oxidase as a theory of the mechanism of the increase of ATP production in mitochondria by laser therapy. Mech Low Light Ther. 2014;8932:26-31. [56] AMAROLI A, PASQUALE C, ZEKIY A, et al. Photobiomodulation and Oxidative Stress: 980 nm Diode Laser Light Regulates Mitochondrial Activity and Reactive Oxygen Species Production. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021:6626286. [57] WANG Y, HUANG YY, WANG Y, et al. Red (660 nm) or near-infrared (810 nm) photobiomodulation stimulates, while blue (415 nm), green (540 nm) light inhibits proliferation in human adipose-derived stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7781. [58] LAZAROWSKI ER, BOUCHER RC, HARDEN TK. Mechanisms of release of nucleotides and integration of their action as P2X-and P2Y-receptor activating molecules. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;64(4):785-795. [59] ROKIC M, CASTRO P, LEIVA-SALCEDO E, et al. Opposing Roles of Calcium and Intracellular ATP on Gating of the Purinergic P2X2 Receptor Channel. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1161. [60] DE LA ROSA G, GóMEZ AI, BAÑOS MC, et al. Signaling Through Purinergic Receptor P2Y2 Enhances Macrophage IL-1β Production. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(13):4686. [61] XUE JF, SHI ZM, ZOU J, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89: 1252-1261. [62] CHEN H, TAN XN, HU S, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Chondrocyte Proliferation and Differentiation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:664168. [63] LU C, LI Y, HU S, et al. Scoparone prevents IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes through the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;106:1169-1174. [64] JERE SW, HOURELD NN. Regulatory Processes of the Canonical Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway and Photobiomodulation in Diabetic Wound Repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(8):4210. [65] KIM JE, WOO YJ, SOHN KM, et al. Wnt/β‐catenin and ERK pathway activation: A possible mechanism of photobiomodulation therapy with light‐emitting diodes that regulate the proliferation of human outer root sheath cells. Lasers Surg Med. 2017;49(10):940-947. [66] LI K, LIANG Z, ZHANG J, et al. Attenuation of the inflammatory response and polarization of macrophages by photobiomodulation. Lasers Med Sci. 2020;35(7):1509-1518. [67] ESCHWEILER J, HORN N, RATH B, et al. The Biomechanics of Cartilage—An Overview. Life (Basel). 2021;11(4):302. [68] THOMSEN S. Pathologic Analysis of Photothermal and Photomechanical Effects of Laser–Tissue Interactions. Photochem Photobiol. 1991;53(6): 825-835. [69] ALEXANDROVSKAYA YM, BAUM OI, SHEKHTER AB, et al. Mechanisms of laser activation of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis healing. Laser Physics Letters. 2018;15(8):085601. [70] SOBOL E, BAUM O, SHEKHTER A, et al. Laser-induced micropore formation and modification of cartilage structure in osteoarthritis healing. J Biomed Opt. 2017;22(9):91515. |
| [1] | Li Yongjie, Fu Shenyu, Xia Yuan, Zhang Dakuan, Liu Hongju. Correlation of knee extensor muscle strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters with peak knee flexion/adduction moment in female patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [2] | Du Changling, Shi Hui, Zhang Shoutao, Meng Tao, Liu Dong, Li Jian, Cao Heng, Xu Chuang. Efficacy and safety of different applications of tranexamic acid in high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [3] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [4] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [5] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [6] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [7] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| [8] | Qiao Hujun, Wang Guoxiang. Evaluation of rat osteoarthritis chondrocyte models induced by interleukin-1beta [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 516-521. |
| [9] | Ding Yukun, Zhu Cuiling, Zhang Xiaodong. Effect of time-restricted diet on infrapatellar fat pad in high-fat diet-induced obese rats and relevant mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5425-5431. |
| [10] | Zhu Zhiheng, Ding Jiaying, Ge Yangshuo, Huang Chunmeng, Shen Jun, Wang Xuezong, Zheng Yuxin, Ding Daofang. Celecoxib inhibits thrombin-induced chondrocyte degeneration in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5446-5451. |
| [11] | Jia Xiaofei, Ran Li, Ma Xiaoshuang, Hei Xiaoyan, Liu Jiani, Yang Nan, Ma Haibin, Chang Jingpeng. Regulation of chondrocyte autophagy by acupotomy to promote chondrocyte homeostasis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5452-5457. |
| [12] | Jia Ruiying, Mei Jie, He Qiang, Li Dan, Sun Xin, Qian Weiqing, Liu Zhen. Catalpol from Rehmannia glutinosa regulates senescence in ATDC5 chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5467-5472. |
| [13] | Huang Keqi, Li Jiagen, Chen Shangtong, Rong Xiangbin. Mechanisms of long non-coding RNA in osteoarthritis and traditional Chinese medicine intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5571-5576. |
| [14] | Yu Guangwen, Xie Junjie, Liang Jiajian, Liu Wengang, Wu Huai, Li Hui, Hong Kunhao, Li Anan, Guo Haopeng. Role and significance of deep learning in intelligent segmentation and measurement analysis of knee osteoarthritis MRI images [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5382-5387. |
| [15] | Ren Weiliang, Jiao Yongwei, Zhang Jian, Yang Liying, Yang Qi. Modulatory effect of resveratrol on oxidative stress and inflammatory factors in the joint fluid of rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5154-5158. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||