Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (27): 4312-4318.doi: 10.12307/2024.571
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression of immune-related genes in rheumatoid arthritis and a two-sample Mendelian randomization study of immune cells
Fan Yidong1, Qin Gang2, He Kaiyi2, Gong Yufang3, Li Weicai1, Wu Guangtao1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530222, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3The People’s Hospital of Guigang, Guigang 537199, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-10-08Accepted:2023-11-25Online:2024-09-28Published:2024-01-26 -
Contact:Qin Gang, MD, Chief physician, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Fan Yidong, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530222, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 81860793 and 82360939 (both to QG); Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2020GXNSFAA297140 (to QG); Postgraduate Education Innovation Program of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine in 2022, No. YCSY2022028 (to FYD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fan Yidong, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Gong Yufang, Li Weicai, Wu Guangtao. Expression of immune-related genes in rheumatoid arthritis and a two-sample Mendelian randomization study of immune cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4312-4318.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

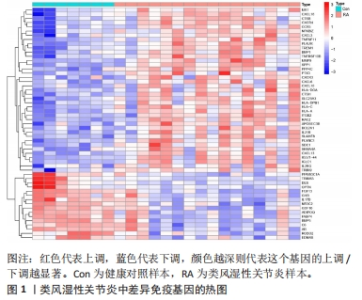
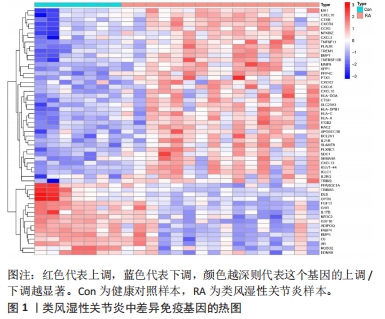
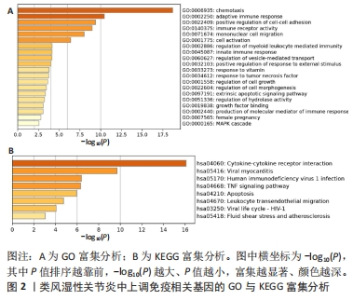
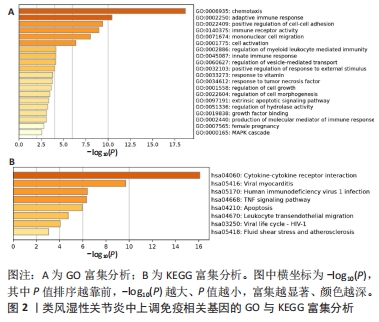
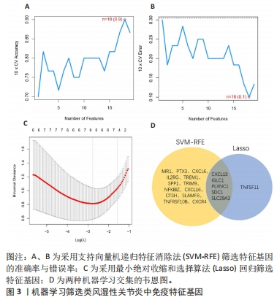
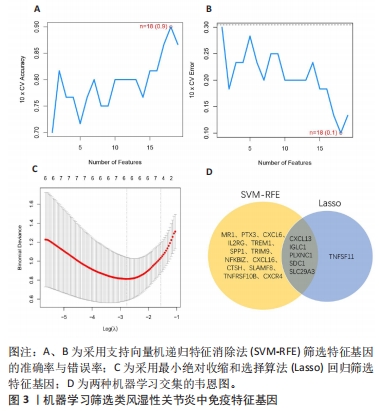
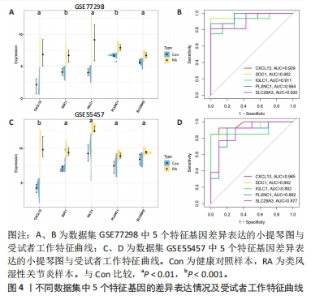
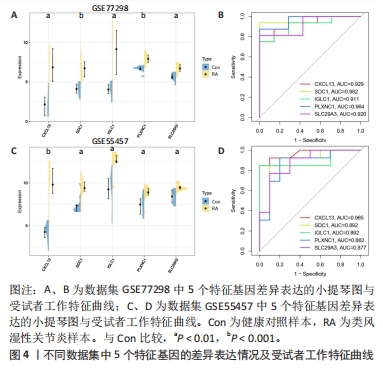
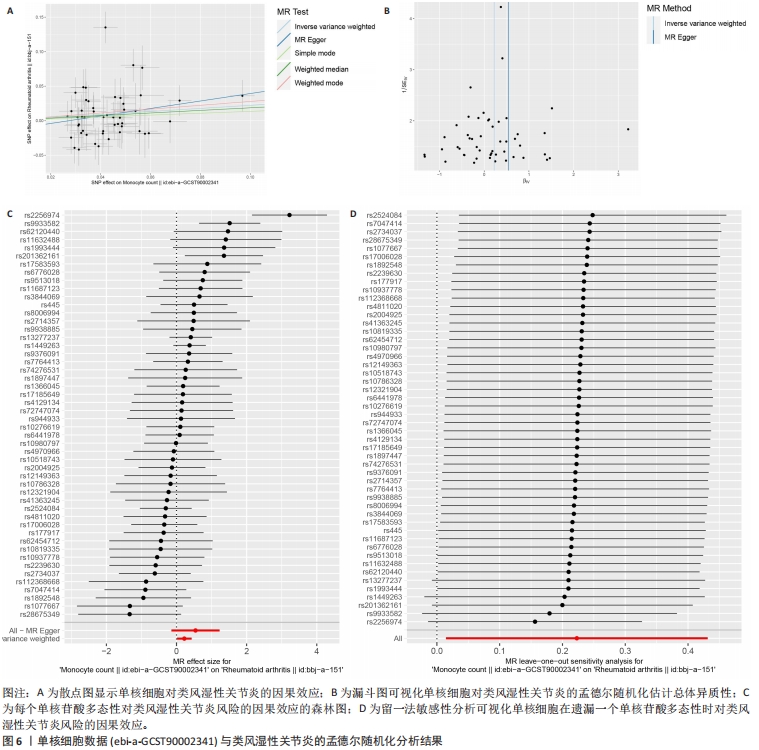
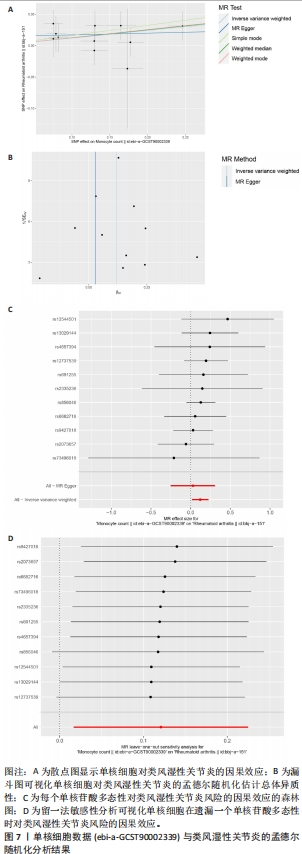
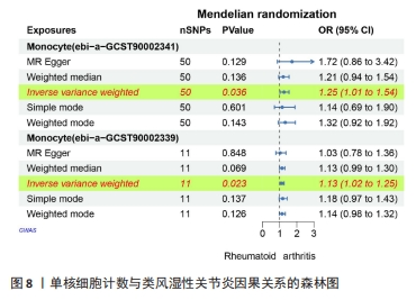
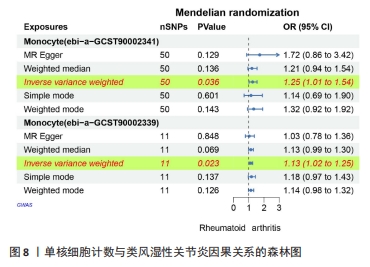
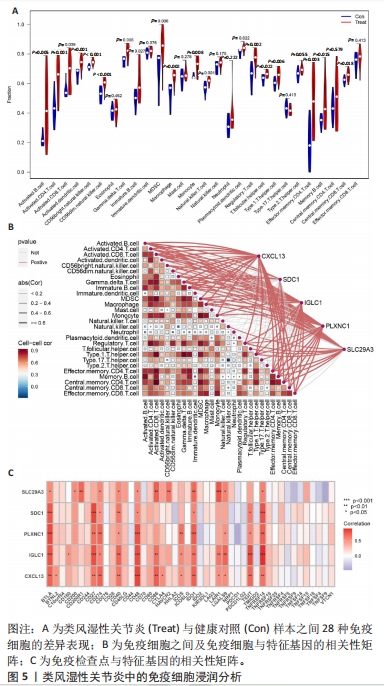
2.5 类风湿性关节炎中的免疫学特征改变 根据免疫细胞浸润及其与免疫特征基因的相关性评估类风湿性关节炎的免疫学特征。与健康对照样本相比,28种免疫细胞中单核细胞、自然杀伤细胞、活化B细胞等19种免疫细胞在类风湿性关节炎样本里表现出更高的浸润水平,见图5A。免疫细胞之间的相关性显示他们大多为正相关关系,其中单核细胞与巨噬细胞、肥大细胞等免疫细胞之间有较强相关性,而中性粒细胞、自然杀伤细胞与其他免疫细胞的相关性较弱。记忆B细胞、不成熟B细胞及活化CD8T细胞等免疫细胞与特征基因呈正相关性,未发现负调控关系,见图5B。在免疫检查点中,BTLA、CD48和TIGIT等免疫检查点与特征基因显示出较强正相关关系,见图5C。"
| [1] WU R, LONG L, ZHOU Q, et al. Identification of hub genes in rheumatoid arthritis through an integrated bioinformatics approach. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):1-9. [2] LIN YJ, ANZAGHE M, SCHÜLKE S. Update on the pathomechanism, diagnosis, and treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis. Cells. 2020;9(4):880. [3] SMOLEN JS. Insights into the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a paradigm in medicine. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102425. [4] REN C, LI M, DU W, et al. Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis reveals hub genes and inflammation state of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6943103. [5] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenic roles of diverse immune cells. Int J Mol. 2022;23(2):905. [6] NEWMAN AM, ALIZADEH AA. High-throughput genomic profiling of tumor-infiltrating leukocytes. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016;41:77-84. [7] ZUO S, WEI M, WANG S, et al. Pan-cancer analysis of immune cell infiltration identifies a prognostic immune-cell characteristic score (ICCS) in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1218. [8] BOEHM FJ, ZHOU X. Statistical methods for Mendelian randomization in genome-wide association studies: A review. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022;20:2338-2351. [9] LAMINA C. Mendelian Randomization: Principles and its usage in Lp (a) research. Atherosclerosis. 2022;349:36-41. [10] XU J, ZHANG S, TIAN Y, et al. Genetic causal association between iron status and osteoarthritis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization. Nutrients. 2022;14(18):3683. [11] BROEREN MGA, DE VRIES M, BENNINK MB, et al. Disease-regulated gene therapy with anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 under the control of the CXCL10 promoter for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Gene Ther. 2016;27(3):244-254. [12] NAKAO H, IMAOKA M, HIDA M, et al. Determination of individual factors associated with hallux valgus using SVM-RFE. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):534. [13] LI Y, LU F, YIN Y. Applying logistic LASSO regression for the diagnosis of atypical Crohn’s disease. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):11340. [14] WOETZEL D, HUBER R, KUPFER P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16:1-22. [15] ZENG Y, CAO S, CHEN M. Integrated analysis and exploration of potential shared gene signatures between carotid atherosclerosis and periodontitis. BMC Med Genomics. 2022;15(1):1-15. [16] HU FF, LIU CJ, LIU LL, et al. Expression profile of immune checkpoint genes and their roles in predicting immunotherapy response. Brief Bioinform. 2021;22(3):bbaa176. [17] ROSZKOWSKI L, CIECHOMSKA M. Tuning monocytes and macrophages for personalized therapy and diagnostic challenge in rheumatoid arthritis. Cells. 2021;10(8):1860. [18] HENRY A, GORDILLO-MARAÑÓN M, FINAN C, et al. Therapeutic targets for heart failure identified using proteomics and Mendelian randomization. Circulation. 2022;145(16):1205-1217. [19] LIN L, LUO P, YANG M, et al. Causal relationship between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis: A two-sample Mendelian randomized study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1011246. [20] SHU MJ, LI JR, ZHU YC, et al. Migraine and ischemic stroke: a Mendelian randomization study. Neurol Ther. 2022;11(1):237-246. [21] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32: 377-389. [22] GUDERUD K, SUNDE LH, FLÅM ST, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis patients, both newly diagnosed and methotrexate treated, show more DNA methylation differences in CD4+ memory than in CD4+ naïve T cells. Front Immunol. 2020;11:194. [23] KONDO N, KURODA T, KOBAYASHI D. Cytokine networks in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(20):10922. [24] PAN Z, ZHU T, LIU Y, et al. Role of the CXCL13/CXCR5 axis in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2022;13:850998. [25] GREISEN SR, SCHELDE KK, RASMUSSEN TK, et al. CXCL13 predicts disease activity in early rheumatoid arthritis and could be an indicator of the therapeutic ‘window of opportunity’. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(5):1-9. [26] VAN RAEMDONCK K, UMAR S, PALASIEWICZ K, et al. Interleukin‐34 Reprograms Glycolytic and Osteoclastic Rheumatoid Arthritis Macrophages via Syndecan 1 and Macrophage Colony‐Stimulating Factor Receptor. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(11):2003-2014. [27] ALZOUBI O, MEYER A, GONZALEZ TP, et al. Significance of IL-34 and SDC-1 in the pathogenesis of RA cells and preclinical models. Clin Immunol. 2023;251:109635. [28] NI Z, HUANG C, ZHAO H, et al. PLXNC1: A novel potential immune-related target for stomach adenocarcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:662707. [29] COMEAU MR, JOHNSON R, DUBOSE RF, et al. A poxvirus-encoded semaphorin induces cytokine production from monocytes and binds to a novel cellular semaphorin receptor, VESPR. Immunity. 1998;8(4):473-482. [30] WALZER T, GALIBERT L, COMEAU MR, et al. Plexin C1 engagement on mouse dendritic cells by viral semaphorin A39R induces actin cytoskeleton rearrangement and inhibits integrin-mediated adhesion and chemokine-induced migration. J Immunol. 2005;174(1):51-59. [31] NOAVAR S, BEHROOZI S, TATARCHEH T, et al. A novel homozygous frame-shift mutation in the SLC29A3 gene: a new case report and review of literature. BMC Med Gene. 2019;20(1):1-7. [32] ALANSARI S, ALSALEEM A, ALZAID T, et al. The SLC29A3 variant, neutrophilic dermatosis, and hyperferritinemia imitate systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis in a Saudi child: a case report. J Rheum Dis. 2023;30(2):133-137. [33] STEINZ MM, EZDOGLIAN A, KHODADUST F, et al. Folate receptor beta for macrophage imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 819163. [34] YANG S, ZHAO M, JIA S. Macrophage: Key player in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1080310. [35] NING Z, LIU K, XIONG H. Roles of BTLA in immunity and immune disorders. Front Immunol. 2021;12:654960. [36] YANG B, HUANG Z, FENG W, et al. The Expression of BTLA Was Increased and the Expression of HVEM and LIGHT Were Decreased in the T Cells of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [corrected]. PLoS One. 2016;11(5): e0155345. [37] KAPELLOS TS, BONAGURO L, GEMÜND I, et al. Human monocyte subsets and phenotypes in major chronic inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2035. [38] PRAJZLEROVÁ K, KRYŠTŮFKOVÁ O, KOMARC M, et al. The dysregulation of monocyte subpopulations in individuals at risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2021;60(4):1823-1831. [39] TSUKAMOTO M, SETA N, YOSHIMOTO K, et al. CD14brightCD16+ intermediate monocytes are induced by interleukin-10 and positively correlate with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):1-10. [40] ZHAO J, GUO S, SCHRODI SJ, et al. Molecular and cellular heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and clinical implications. Front Immunol. 2021;12:790122. [41] YANG M, WAN X, ZHENG H, et al. No evidence of a genetic causal relationship between ankylosing spondylitis and gut microbiota: A two-sample mendelian randomization study. Nutrients. 2023;15(4):1057. |
| [1] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [2] | Chen Jixin, Yu Weijie, Guo Tianci, Zhou Qinxin, Niu Puyu, Ye Yuntian, Liu Aifeng. Sleep characteristics and risk of osteoarthritis: a two-sample and multivariate Mendelian randomization study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5203-5209. |
| [3] | Lu Xiaoling, Liu Bin, Xu Bin. Bioinformatics identification and validation of genes related to fatty acid metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5116-5121. |
| [4] | Xu Wenfei, Ming Chunyu, Duan Kan, Yuan Changshen, Guo Jinrong, Hu Qi, Zeng Chao, Mei Qijie. Identification of ferroptosis signature genes in osteoarthritis based on WGCNA and machine learning and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4909-4914. |
| [5] | Li Shudong, Liang Xuezhen, Luo Di, Li Jiacheng, Yan Bozhao, Li Gang. Identification of biomarkers associated with ferroptosis and pyroptosis for the potential diagnosis of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4511-4515. |
| [6] | Chen Tianxin, Dong Tingting, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between blood metabolites and sarcopenia-related traits: a Mendelian randomization study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4288-4292. |
| [7] | Zhan Qunzhang, Zhang Yuling, Han Yuxin, Lyu Jiazhen, Zheng Xiaoxia, Qu Chongzheng. Association between obesity and osteoporosis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4319-4324. |
| [8] | Chai Jinlian, Li Shudong, Li Wei, Du Haitao, Dong Limin, Liang Xuezhen, Wang Ping. Gut microbiota and drug-associated osteonecrosis: a two‑sample Mendelian randomization study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4325-4331. |
| [9] | Ma Weiwei, Xiong Yong, Chen Honggu, Huang Wenzhuo, Huang Xin, Zhou Xiaohong. Relationship between statin drugs and bone density: a drug target-mediated Mendelian randomization study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4340-4345. |
| [10] | Wu Ruiqi, Zhang Xuan, Zhou Yi, Meng Lin, Li Hongyu. Two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis of the relationship between statins and the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4106-4112. |
| [11] | Xu Chenghan, Zhuo Hanjie, Chai Xubin, Huang Yong, Zhang Bowen, Chen Qin, Hao Yupeng, Li Lin, Zhou Yingjie. Meta-analysis of the incidence and related factors for cervical spine instability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3922-3929. |
| [12] | Peng Zhihua, Pan Junxi, Feng Qinghui, Tian Tianzhao, Zhang Sheng, Li An, Cai Yingfeng. The causal relationship between blood lipids and muscle atrophy based on Mendelian randomization analysis of two samples [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3699-3703. |
| [13] | Wu Ruiqi, Zhou Yi, Xia Tian, Zhang Chi, Yang Qipei, Zhang Xuan, Zhang Yazhong, Cui Wei. Mendelian randomization study on the association between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis and bone mineral density [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3715-3721. |
| [14] | Xu Wenfei, Ming Chunyu, Mei Qijie, Yuan Changshen, Guo Jinrong, Zeng Chao, Duan Kan. Experimental validation of machine learning identification of KDELR3 as a signature gene for osteoarthritis hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3431-3437. |
| [15] | Xie Yue, Zhai Weifeng, Guo Ji, Jia Yongwei. Integrative analyses of pyroptosis-related genes associated with intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3438-3444. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||